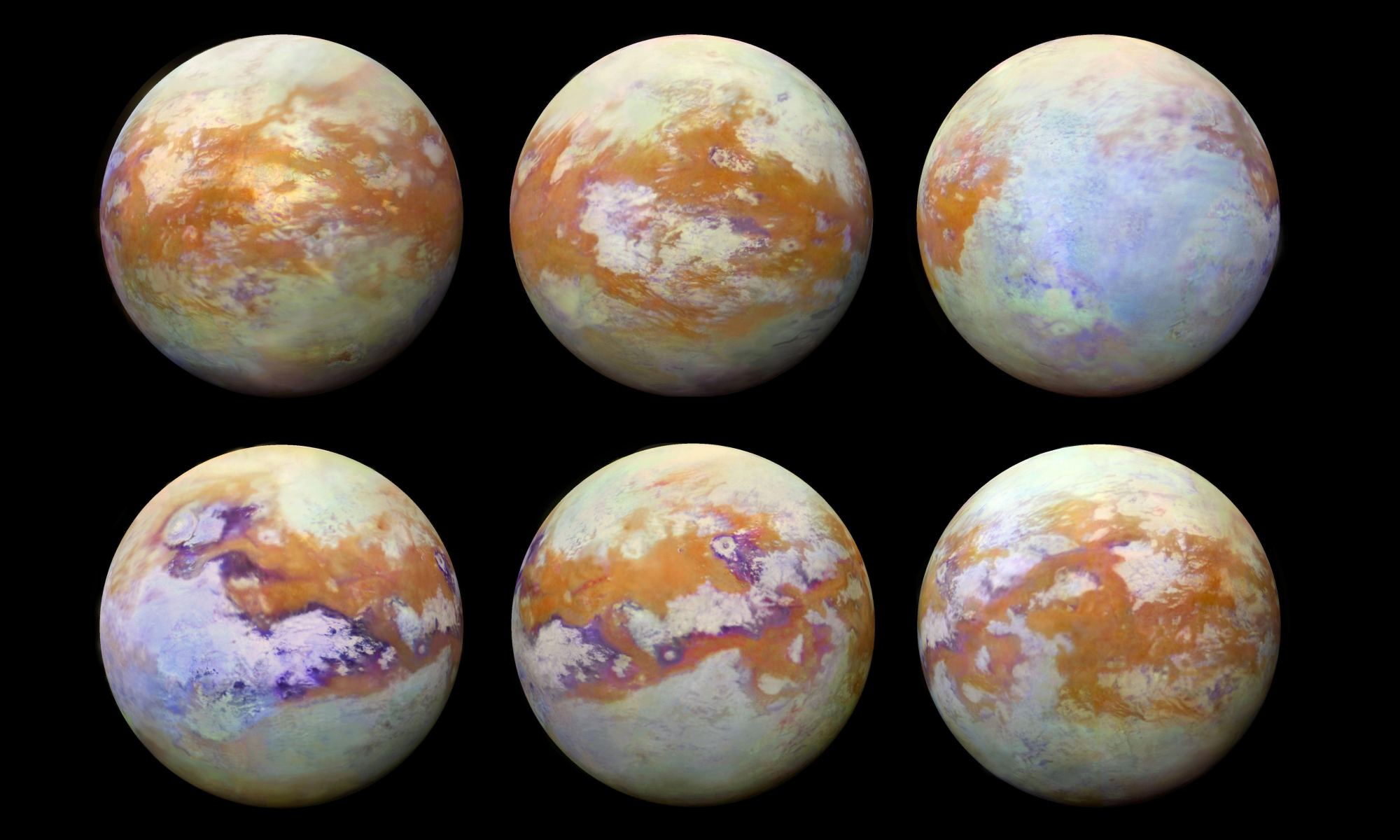
Saturn’s moon Titan is a very strange place. It’s surrounded by a dense, opaque atmosphere, the only moon in the solar system with an atmosphere to speak of. It has lakes of liquid methane on its surface, maybe some cryovolcanoes, and some scientists speculate that it could support a form of life. Very weird life.
But we still don’t know a lot about it, because we haven’t really seen much of the surface. Until now.
Continue reading “Titan’s Thick Clouds Obscure our View, but Cassini Took these Images in Infrared, Showing the Moon’s Surface Features”