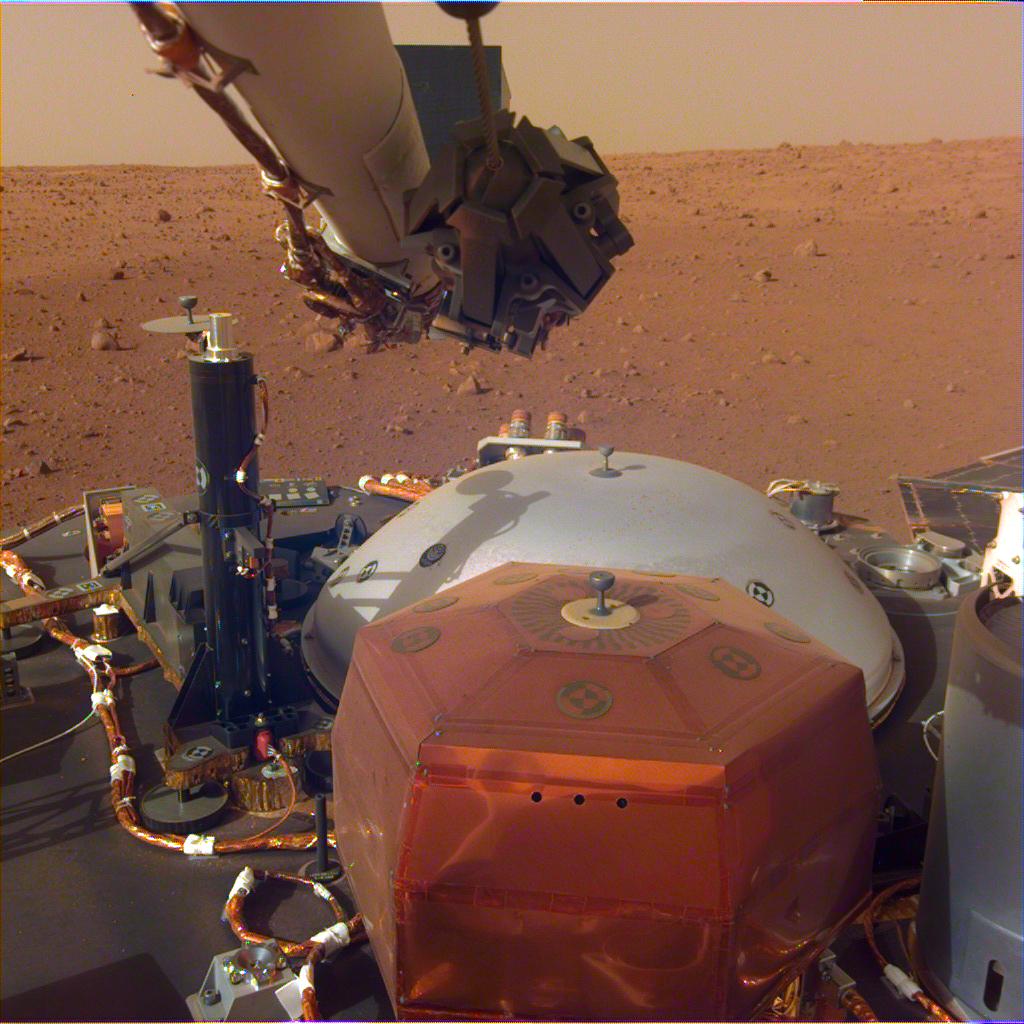
Some new images sent home by the InSight Lander show the robotic arm and the craft’s instruments waiting on deck, on the surface of Mars. The lander is still having its systems tested, and isn’t quite ready to get to work. It’ll use its arm to deploy its science instruments, including a drill that will penetrate up to 5 meters (16 ft.) deep into the Martian surface.
Continue reading “InSight’s Robot Arm is Ready to go to Work”