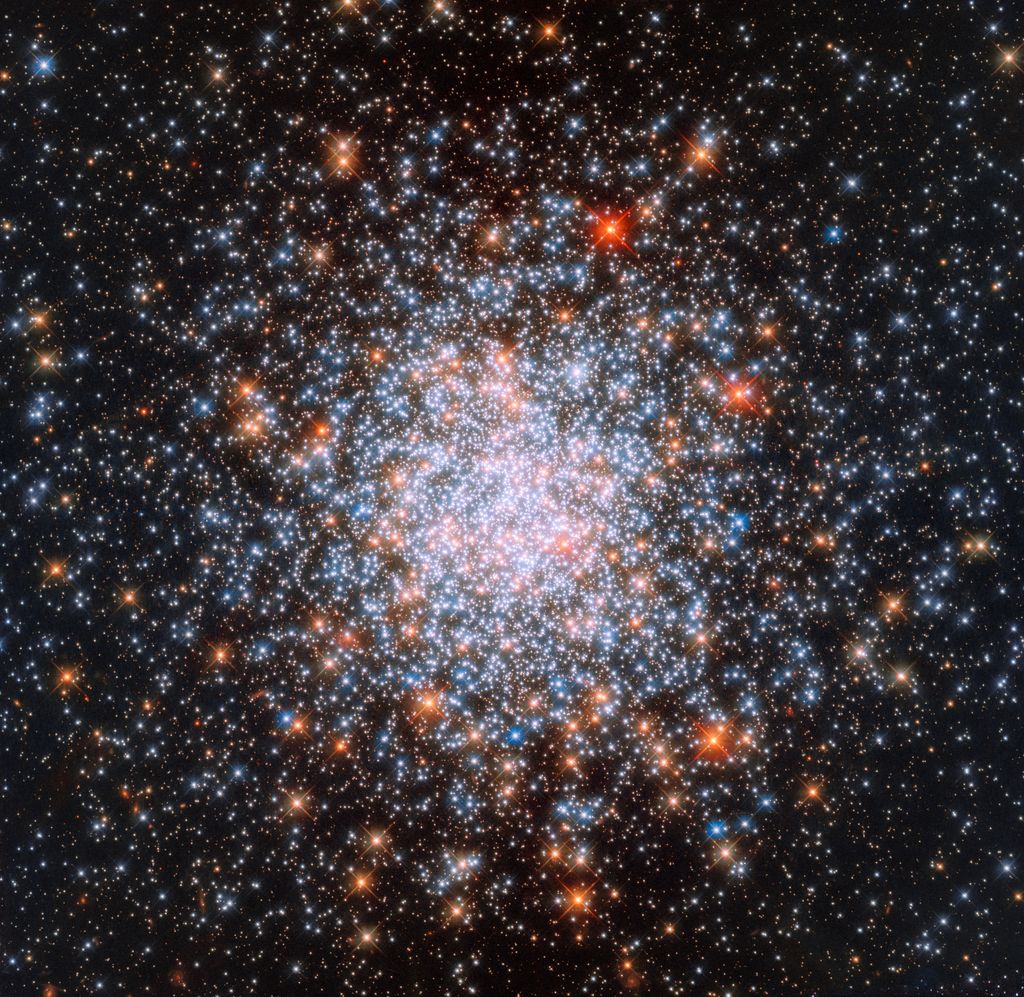
Star clusters are not rare. They’re one of the most common arrangements of stars in the Universe. But star cluster NGC 1866, as seen in this image from Hubble, is different than its brethren. Most clusters are populated by stars the same age, BUT NGC 1866 is like an all-ages club.
Continue reading “Some of the Stars in this Cluster are Almost as Old as the Universe Itself While Others Formed in a Second Generation. It Looks Young and Old at the Same Time”
Some of the Stars in this Cluster are Almost as Old as the Universe Itself While Others Formed in a Second Generation. It Looks Young and Old at the Same Time