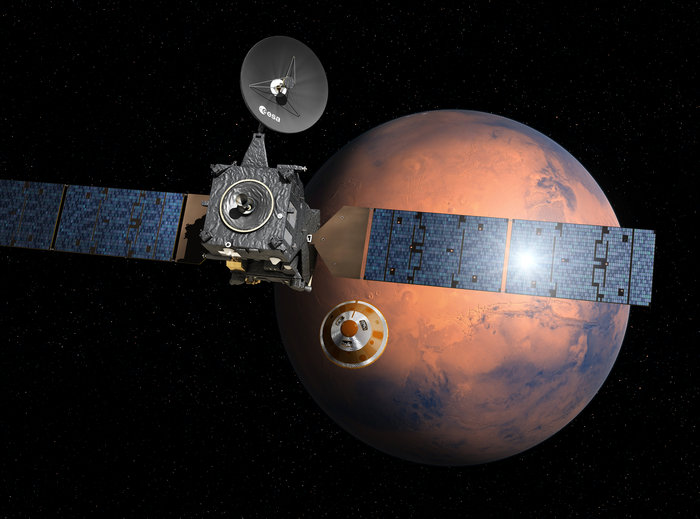
In March of 2016, the European Space Agency (ESA) launched the ExoMars (Exobiology on Mars) mission into space. A joint project between the ESA and Roscosmos, this two-part mission consisted of the Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) and the Schiaparelli lander, both of which arrived in orbit around Mars in October of 2016. While Schiaparelli crashed while attempting to land, the TGO has gone on to accomplish some impressive feats.
For example, in March of 2017, the orbiter commenced a series of aerobraking maneuvers, where it started to lower its orbit to enter Mars’ thin atmosphere and slow itself down. According to Armelle Hubault, the Spacecraft Operations Engineer on the TGO flight control team, the ExoMars mission has made tremendous progress and is well on its way to establishing its final orbit around the Red Planet.
TGO’s mission has been to study the surface of Mars, characterize the distribution of water and chemicals beneath the surface, study the planet’s geological evolution, identify future landing sites, and to search for possible biosignatures of past Martian life. Once it has established its final orbit around Mars – 400 km (248.5 mi) from the surface – the TGO will be ideally positioned to conduct these studies.
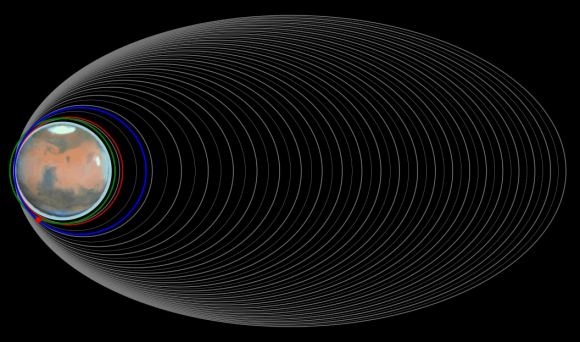
The ESA also released a graphic (shown above) demonstrating the successive orbits the TGO has made since it began aerobraking – and will continue to make until March of 2018. Whereas the red dot indicates the orbiter (and the blue line its current orbit), the grey lines show successive reductions in the TGO’s orbital period. The bold lines denote a reduction of 1 hour while the thin lines denote a reduction of 30 minutes.
Essentially, a single aerobraking maneuver consist of the orbiter passing into Mars’ upper atmosphere and relying on its solar arrays to generate tiny amounts of drag. Over time, this process slows the craft down and gradually lowers its orbit around Mars. As Armelle Hubault recently posted on the ESA’s rocket science blog:
“We started on the biggest orbit with an apocentre (the furthest distance from Mars during each orbit) of 33 200 km and an orbit of 24 hr in March 2017, but had to pause last summer due to Mars being in conjunction. We recommenced aerobraking in August 2017, and are on track to finish up in the final science orbit in mid-March 2018. As of today, 30 Jan 2018, we have slowed ExoMars TGO by 781.5 m/s. For comparison, this speed is more than twice as fast as the speed of a typical long-haul jet aircraft.”
Earlier this week, the orbiter passed through the point where it made its closest approach to the surface in its orbit (the pericenter passage, represented by the red line). During this approach, the craft dipped well into Mars’ uppermost atmosphere, which dragged the aircraft and slowed it down further. In its current elliptical orbit, it reaches a maximum distance of 2700 km (1677 mi) from Mars (it’s apocenter).

Despite being a decades-old practice, aerobraking remains a significant technical challenge for mission teams. Every time a spacecraft passes through a planet’s atmosphere, its flight controllers need to make sure that its orientation is just right in order to slow down and ensure that the craft remains stable. If their calculations are off by even a little, the spacecraft could begin to spin out of control and veer off course. As Hubault explained:
“We have to adjust our pericentre height regularly, because on the one hand, the martian atmosphere varies in density (so sometimes we brake more and sometimes we brake less) and on the other hand, martian gravity is not the same everywhere (so sometimes the planet pulls us down and sometimes we drift out a bit). We try to stay at about 110 km altitude for optimum braking effect. To keep the spacecraft on track, we upload a new set of commands every day – so for us, for flight dynamics and for the ground station teams, it’s a very demanding time!”
The next step for the flight control team is to use the spacecraft’s thrusters to maneuver the spacecraft into its final orbit (represented by the green line on the diagram). At this point, the spacecraft will be in its final science and operation data relay orbit, where it will be in a roughly circular orbit about 400 km (248.5 mi) from the surface of Mars. As Hubault wrote, the process of bringing the TGO into its final orbit remains a challenging one.
“The main challenge at the moment is that, since we never know in advance how much the spacecraft is going to be slowed during each pericentre passage, we also never know exactly when it is going to reestablish contact with our ground stations after pointing back to Earth,” she said. “We are working with a 20-min ‘window’ for acquisition of signal (AOS), when the ground station first catches TGO’s signal during any given station visibility, whereas normally for interplanetary missions we have a firm AOS time programmed in advance.”

With the spacecraft’s orbital period now shortened to less than 3 hours, the flight control team has to go through this exercise 8 times a day now. Once the TGO has reached its final orbit (by March of 2018), the orbiter will remain there until 2022, serving as a telecommunications relay satellite for future missions. One of its tasks will be to relay data from the ESA’s ExoMars 2020 mission, which will consist of a European rover and a Russian surface platform being deployed the surface of Mars in the Spring of 2021.
Along with NASA’s Mars 2020 rover, this rover/lander pair will be the latest in a long line of robotic missions looking to unlock the secrets of Mars past. In addition, these missions will conduct crucial investigations that will pave the way for eventual sample return missions to Earth, not to mention crewed to the surface!
Further Reading: ESA