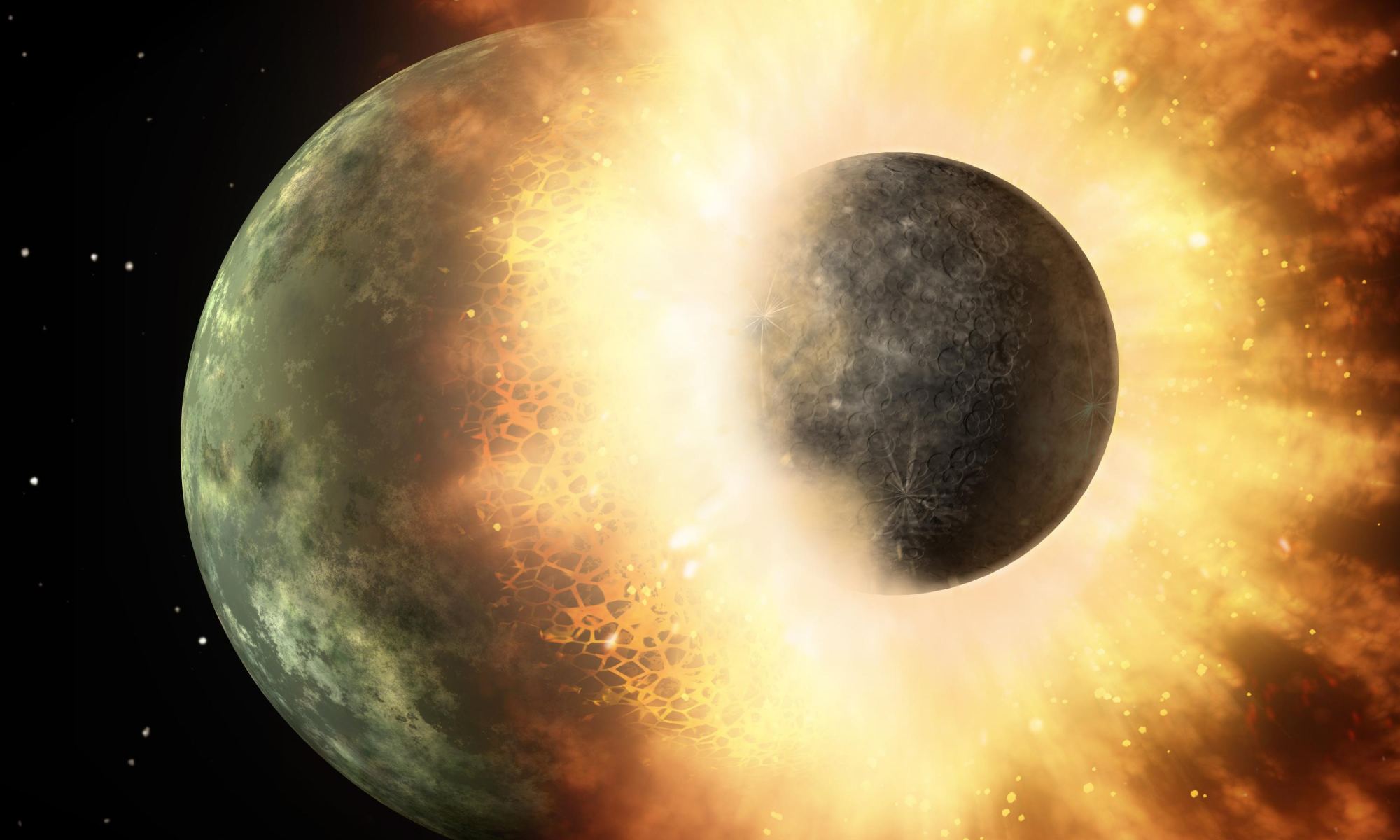
Astronomers are pretty sure they know where the Moon came from. In the early Solar System, a Mars-sized object dubbed Theia smashed into Earth. This cataclysmic collision knocked a huge mass of material into orbit, which coalesced and cooled into the Moon. But establishing exactly when this occurred is a difficult task. At the 55th annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (LPSC 55) last month in The Woodlands, Texas, researchers proposed a new timeline of events that moves the giant impact earlier than previous predictions, at just 50 million years after the formation of the Solar System.
Continue reading “What's the Earliest the Moon Could Have Formed?”What's the Earliest the Moon Could Have Formed?