Nothing is immortal. Everything has a finite existence, including the stars themselves. How a star dies depends on several factors, most importantly their mass. For the Sun, this means that in several billion years it will swell to a red giant as it churns through the last of its nuclear fuel. The core that remains will then collapse to become a white dwarf. Of course, the Sun is home to several planets, including Earth. What of their fate? What of ours? According to a recent study, the Sun’s death might consume Earth in the end.
Continue reading “Astronomers Can See the Impact Site Where an Asteroid Crashed Into a White Dwarf”Curiosity Rover is Climbing Through Dramatic Striped Terrain on Mars
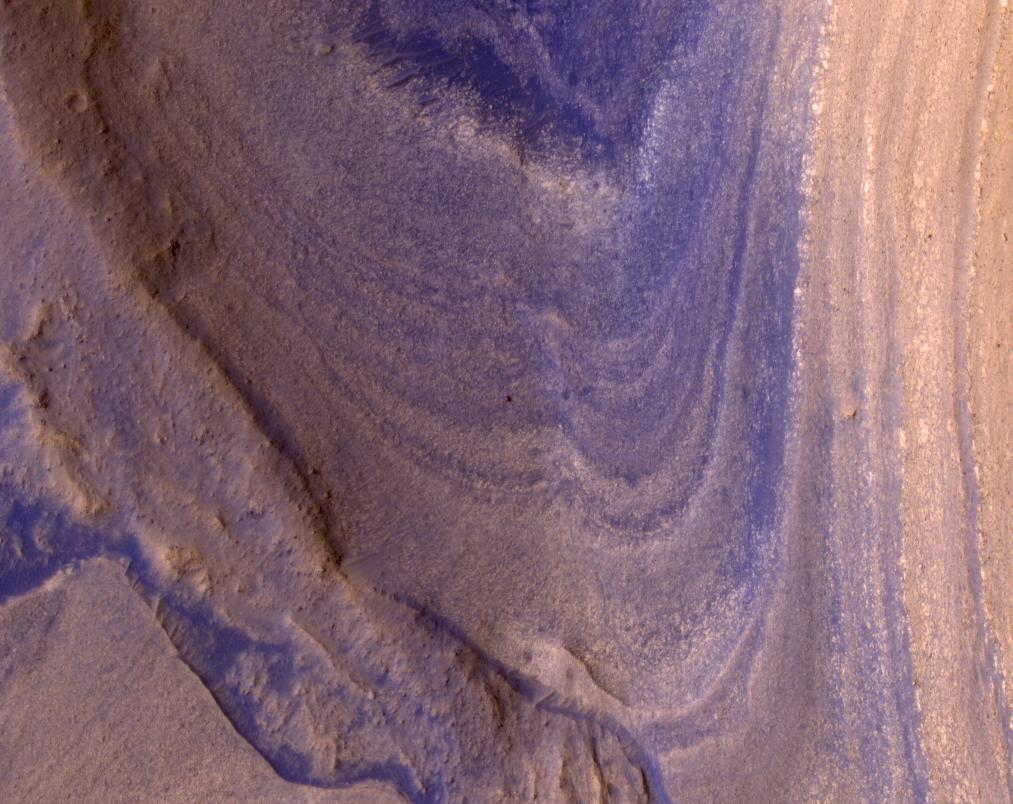

Just about every day we here on Earth get a breathtaking picture of Mars’s terrain sent back by a rover. But, the view from space can be pretty amazing, too. The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) just sent back a thought-provoking picture of Curiosity as it makes its way up a steep ridge on Mount Sharp.
Continue reading “Curiosity Rover is Climbing Through Dramatic Striped Terrain on Mars”A Giant Gamma-Ray Bubble is a Source of Extreme Cosmic Rays
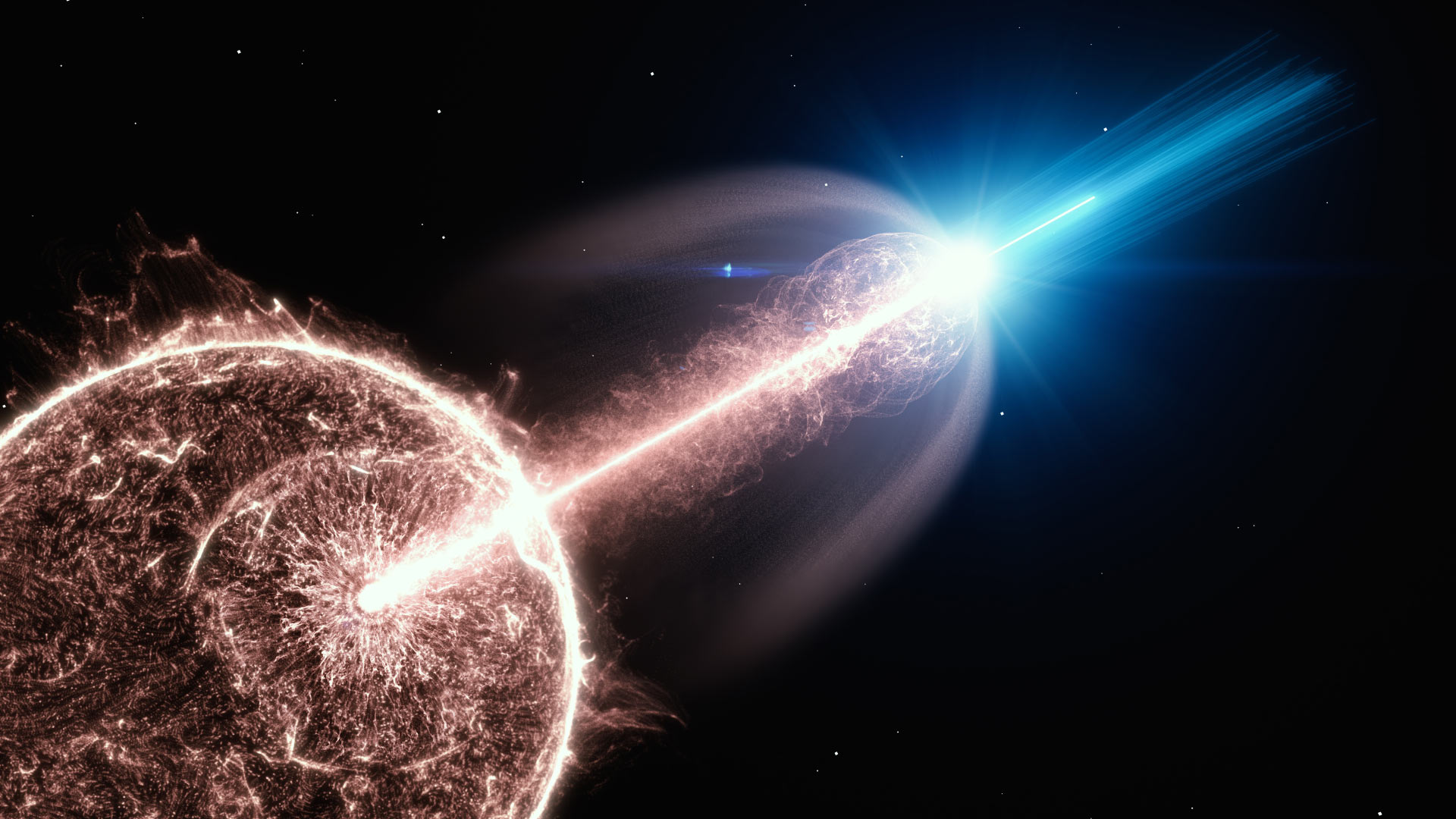

Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are one of the most powerful phenomena in the Universe and something that astronomers have been studying furiously to learn more about their origins. In recent years, astronomers have set new records for the most powerful GRB ever observed – this includes GRB 190114C, observed by the Hubble Space Telescope in 2019, and GRB 221009A, detected by the Gemini South telescope in 2022. The same is true for high-energy cosmic rays that originate from within the Milky Way, whose origins are still not fully understood.
In a recent study, members of China’s Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory (LHAASO) Collaboration discovered a massive gamma-ray burst (designated GRB 221009A) in the Cygnus star-forming region that was more powerful than 10 peta-electronvolts (PeV, 1PeV=1015eV), over ten times the average. In addition to being the brightest GRB studied to date, the team was able to precisely measure the energy spectrum of the burst, making this the first time astronomers have traced cosmic rays with this energy level back to their source.
Continue reading “A Giant Gamma-Ray Bubble is a Source of Extreme Cosmic Rays”New Study Addresses how Lunar Missions will Kick up Moondust.
Before the end of this decade, NASA plans to return astronauts to the Moon for the first time since the Apollo Era. But this time, through the Artemis Program, it won’t be a “footprints and flags” affair. With other space agencies and commercial partners, the long-term aim is to create the infrastructure that will allow for a “sustained program of lunar exploration and development.” If all goes according to plan, multiple space agencies will have established bases around the South Pole-Aitken Basin, which will pave the way for lunar industries and tourism.
For humans to live, work, and conduct various activities on the Moon, strategies are needed to deal with all the hazards – not the least of which is lunar regolith (or “moondust”). As the Apollo astronauts learned, moondust is jagged, sticks to everything, and can cause significant wear on astronaut suits, equipment, vehicles, and health. In a new study by a team of Texas A&M engineers, the regolith motion was found to be significantly altered due to inter-particle collisions. Given the many spacecraft and landers that will be delivering crews and cargo to the Moon in the near future, this is one hazard that merits close attention!
Continue reading “New Study Addresses how Lunar Missions will Kick up Moondust.”How Warm Are the Oceans on the Icy Moons? The Ice Thickness Provides a Clue.

Scientists are discovering that more and more Solar System objects have warm oceans under icy shells. The moons Enceladus and Europa are the two most well-known, and others like Ganymede and Callisto probably have them too. Even the dwarf planet Ceres might have an ocean. But can any of them support life? That partly depends on the water temperature, which strongly influences the chemistry.
We’re likely to visit Europa in the coming years and find out for ourselves how warm its ocean is. Others on the list we may never visit. But we may not have to.
Continue reading “How Warm Are the Oceans on the Icy Moons? The Ice Thickness Provides a Clue.”NASA Tests the New Starship Docking System
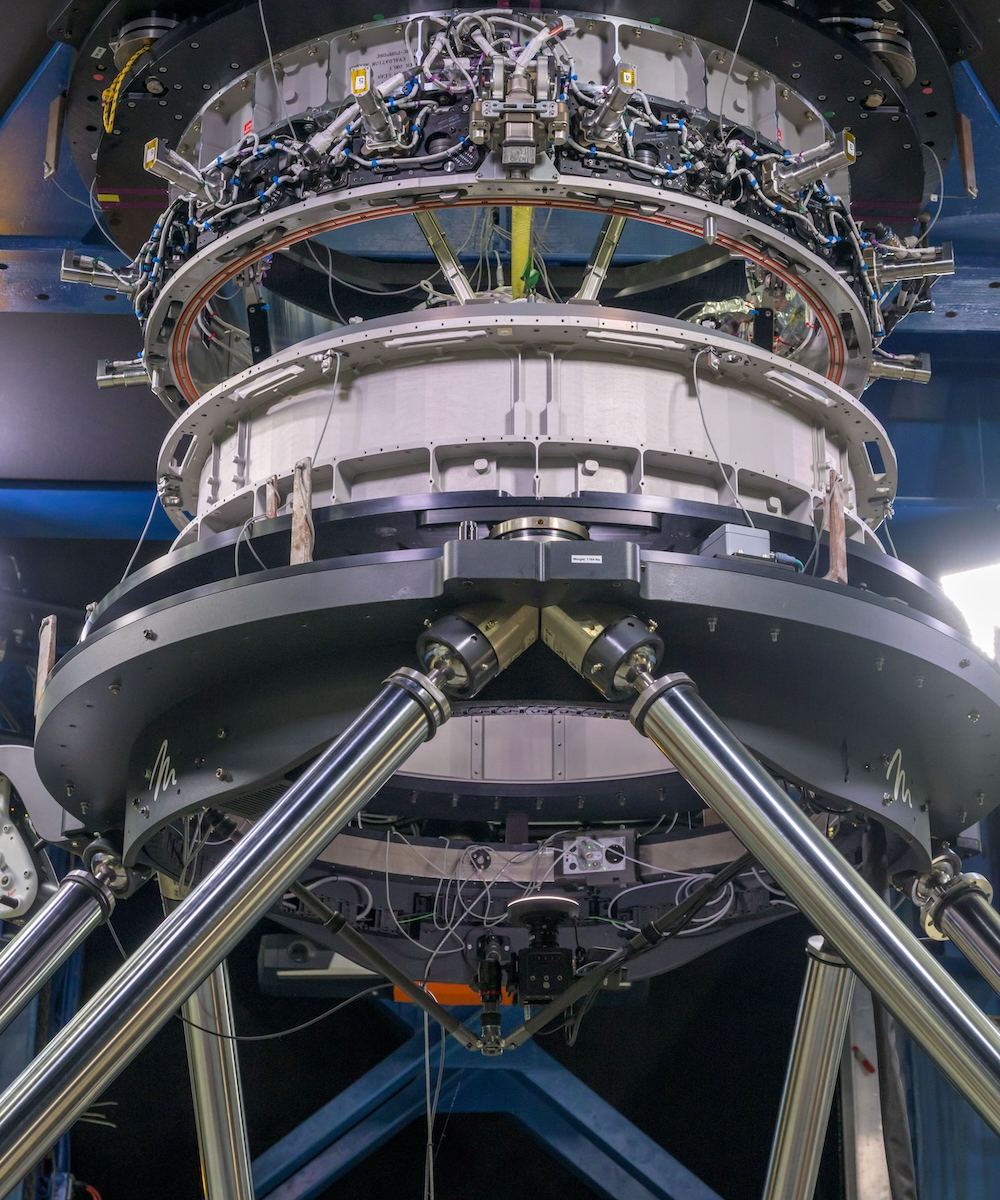

The Apollo Program delivered 12 American astronauts to the surface of the Moon. But that program ended in 1972, and since then, no human beings have visited. But Artemis will change that. And instead of just visiting the Moon, Artemis’ aim is to establish a longer-term presence on the Moon. That requires more complexity than Apollo did. Astronauts will need to transfer between vehicles.
All of that activity requires a reliable spacecraft docking system.
Continue reading “NASA Tests the New Starship Docking System”China Has Built a Huge Space Simulation Chamber
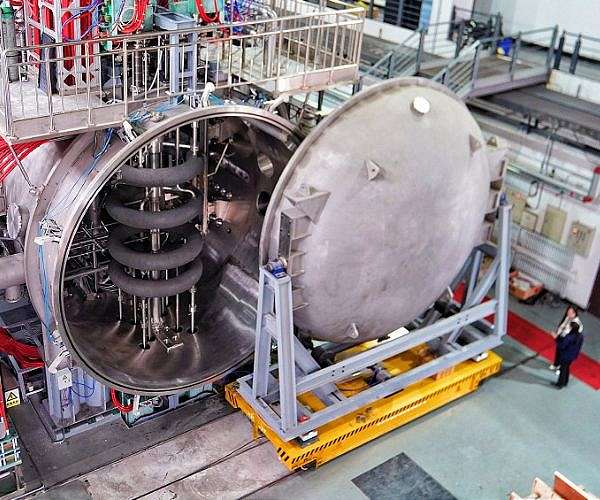
Well it certainly caught my attention when I saw the headlines “China’s first Space Environment Simulator” sounds like something right out of an adventure holiday. Whilst you can’t buy tickets to ‘have a go’ it’s actually for China to test spacecraft before launching them into the harsh environments of space. It allows researchers to simulate nine environmental factors; vacuum, high and low temperature, charged particles, electromagnetic radiation, space dust, plasma, weak magnetic field, neutral gasses and microgravity – and it even looks futuristic too!
Continue reading “China Has Built a Huge Space Simulation Chamber”The International Space Station’s Air Leaks are Increasing. No Danger to the Crew
Only the other week I had to fix my leaky tap. That was a nightmare. I cannot begin to imagine how you deal with a leaky spacecraft! In August 2020 Russia announced that their Zvezda module had an air leak. An attempt was make to fix it but in November 2021 another leak was found. Earlier this week, Russia announced the segment is continuing to leak but the crew are in no danger.
Continue reading “The International Space Station’s Air Leaks are Increasing. No Danger to the Crew”Planetary Atmospheres: Why study them? What can they teach us about finding life beyond Earth?

Universe Today has surveyed the importance of studying impact craters, planetary surfaces, exoplanets, astrobiology, solar physics, and comets, and what these fantastic scientific fields can teach researchers and space fans regarding the search for life beyond Earth. Here, we will discuss how planetary atmospheres play a key role in better understanding our solar system and beyond, including why researchers study planetary atmospheres, the benefits and challenges, what planetary atmospheres can teach us about finding life beyond Earth, and how upcoming students can pursue studying planetary atmospheres. So, why is it so important to study planetary atmospheres?
Continue reading “Planetary Atmospheres: Why study them? What can they teach us about finding life beyond Earth?”How Startups on Earth Could Blaze a Trail for Cities on Mars
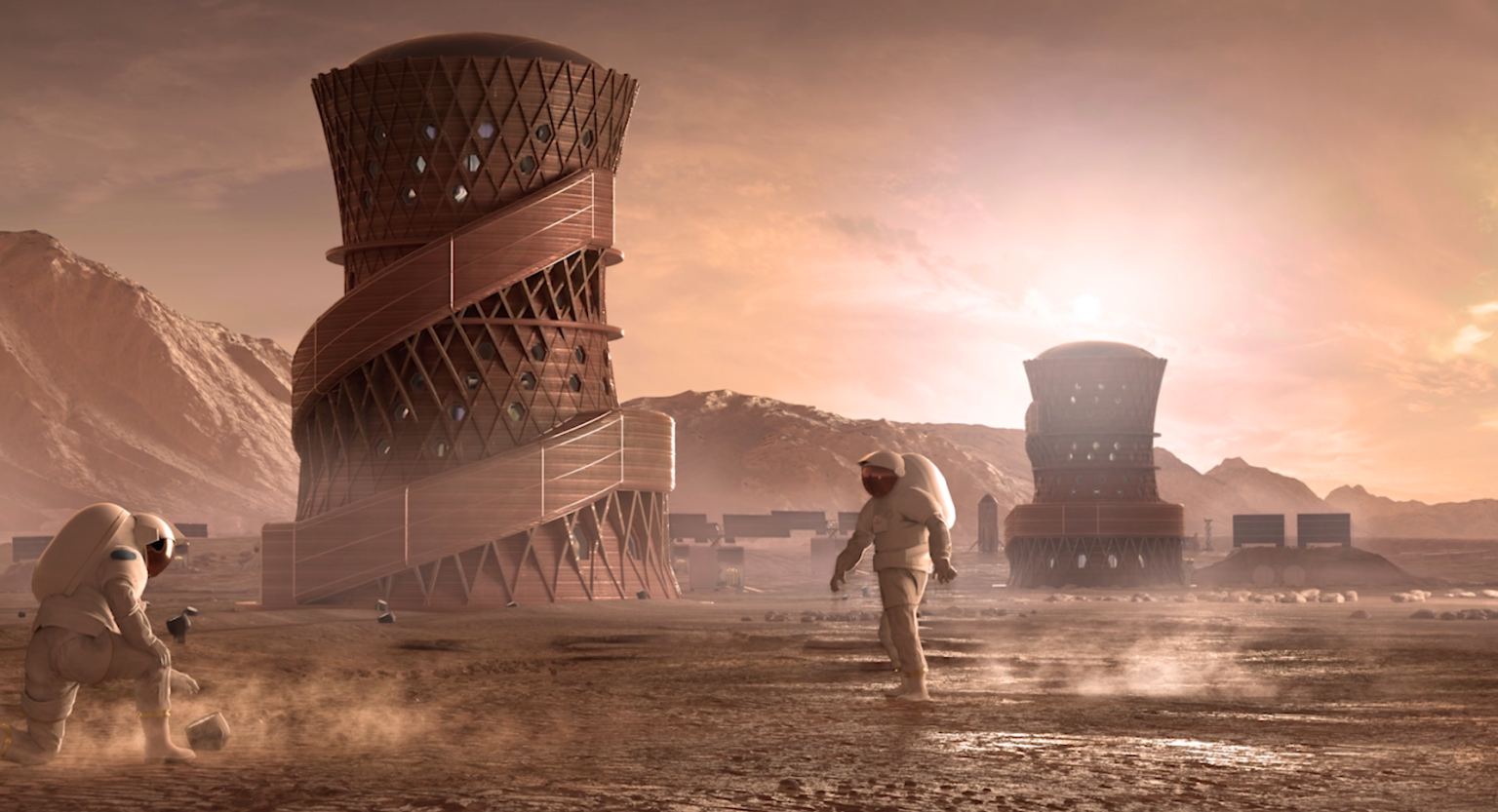

If future explorers manage to set up communities on Mars, how will they pay their way? What’s likely to be the Red Planet’s primary export? Will it be Martian deuterium, sent back to Earth for fusion fuel? Raw materials harvested by Mars-based asteroid miners, as depicted in the “For All Mankind” TV series? Or will future Martians be totally dependent on earthly subsidies?
In a new book titled “The New World on Mars,” Robert Zubrin — the president of the Mars Society and a tireless advocate for space settlement — says Mars’ most valuable product will be inventions.



