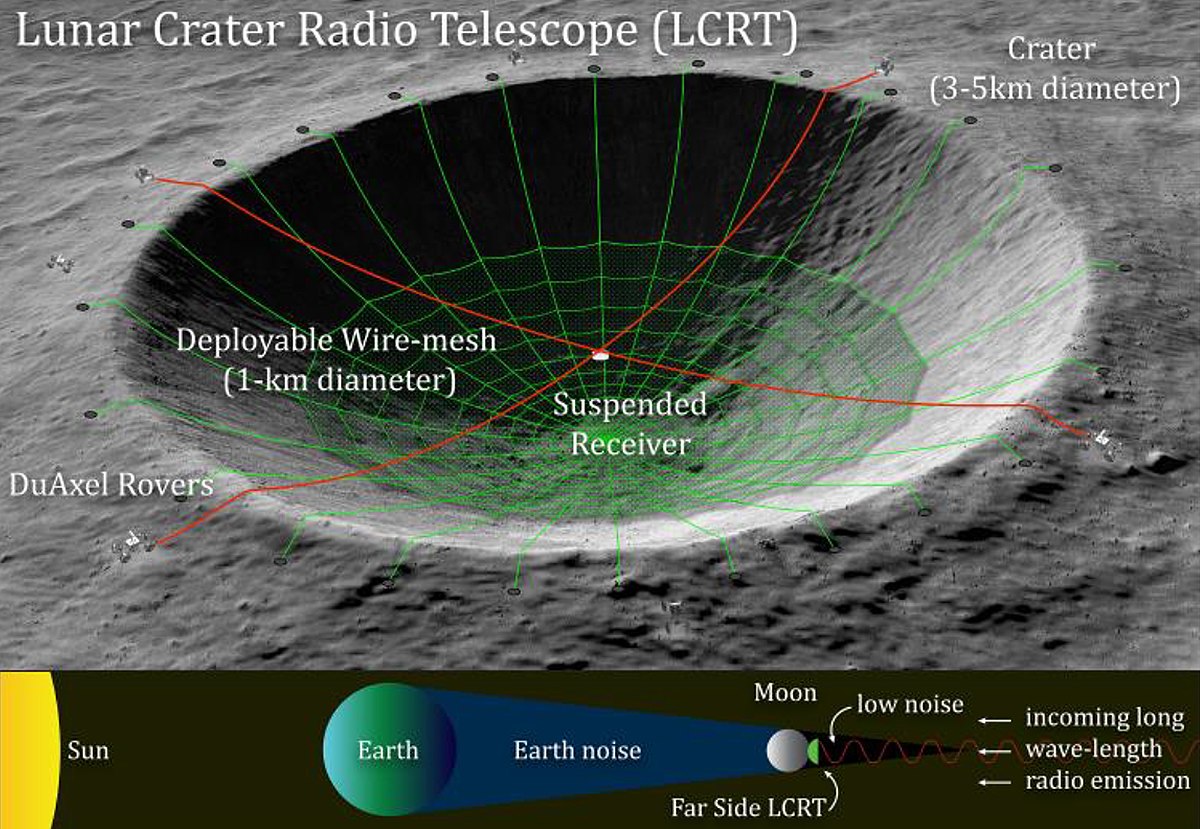
For decades, astronomers have said that one of the most optimal places to build large telescopes is on the surface of the Moon. The Moon has several advantages over Earth- and space-based telescopes that make it worth considering as a future home for giant observatories. A new paper lists all the advantages, including how telescopes on the lunar surface wouldn’t be blocked by an atmosphere or impacted by wind, and how the low gravity would allow gigantic structures to be built that could be upgraded over time by astronauts.
“Progress on the big questions in astronomy, such as life on certain exoplanets or dark matter, will ultimately require high angular resolution, a large collecting area and access to the full optical spectrum,” write French astronomers Jean Schneider, Pierre Kervella, and Antoine Labeyrie. “All astronomy will benefit from the advantages provided by the localization on the Moon.”
And even though it might be decades before we have a permanent presence on the Moon, the astronomers suggest we should start with small telescopes now.
Continue reading “What Kinds of Astronomy Could Be Done With a Telescope on the Moon?”