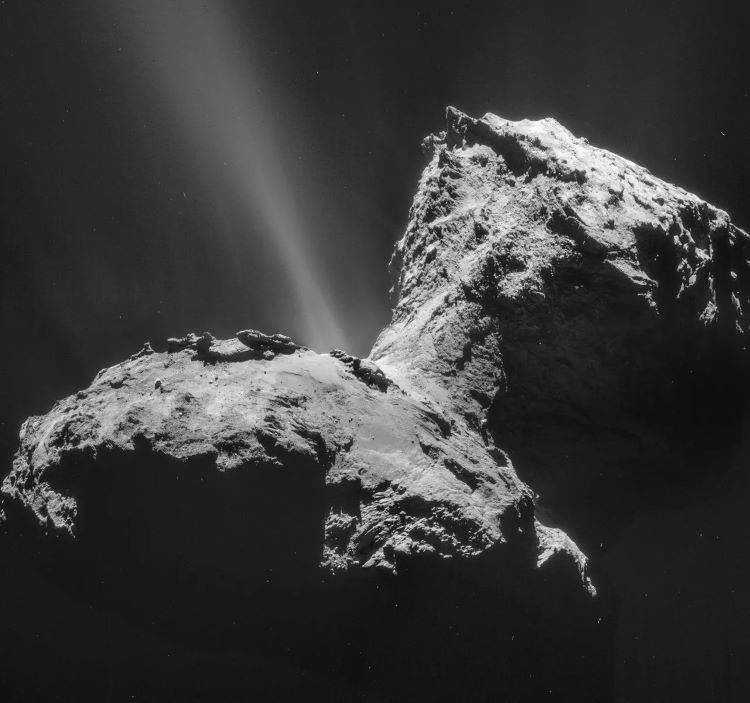
Universe Today has explored the importance of studying impact craters, planetary surfaces, exoplanets, astrobiology, and solar physics, and what this myriad of scientific disciplines can teach scientists and the public regarding the search for life beyond Earth. Here, we will explore some of the most awe-inspiring spectacles within our solar system known as comets, including why researchers study comets, the benefits and challenges, what comets can teach us about finding life beyond Earth, and how upcoming students can pursue studying comets. So, why is it so important to study comets?
Continue reading “Comets: Why study them? What can they teach us about finding life beyond Earth?”Comets: Why study them? What can they teach us about finding life beyond Earth?