Voyagers 1 and 2 were, to put it simply, incredible. They were true explorers and unveiled many mysteries of the outer Solar System, revealing the outer planets in all their glory. Communication with Voyager 1 has until recently been possible, slow but possible. More recently however, it has been sending home garbled data rendering communication to all intents impossible although messages can still be sent. Engineers at NASA have narrowed the problem down to an onboard computer, the Flight Data System (FDS). A dump of the entire memory of the FDS has now been received so that engineers can attempt to troubleshoot and fix the issue.
Continue reading “NASA is Fixing its Link to Voyager 1”The Cosmic Neutrino Background Would Tell Us Plenty About the Universe
Readers of Universe Today are probably already familiar with the concept of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). Its serendipitous discovery by a pair of radio astronomers at Bell Labs is the stuff of astronomical legend. Over the past decades, it has offered plenty of insights into the Big Bang and the origins of our universe. But there is another, less well-known background signal that could be just as revolutionary – or at least we think there is. The Cosmic Neutrino Background (CvB) has been posited for years but has yet to be found, primarily because neutrinos are notoriously difficult to detect. Now, a paper from Professor Douglas Scott of the University of British Columbia, developed as part of a summer school on neutrinos held by the International School of AstroParticle Physics in the Italian town of Varenna, discusses what we could potentially learn if we do manage to detect the CvB eventually.
Continue reading “The Cosmic Neutrino Background Would Tell Us Plenty About the Universe”Mars Was Hiding Another Giant Volcano
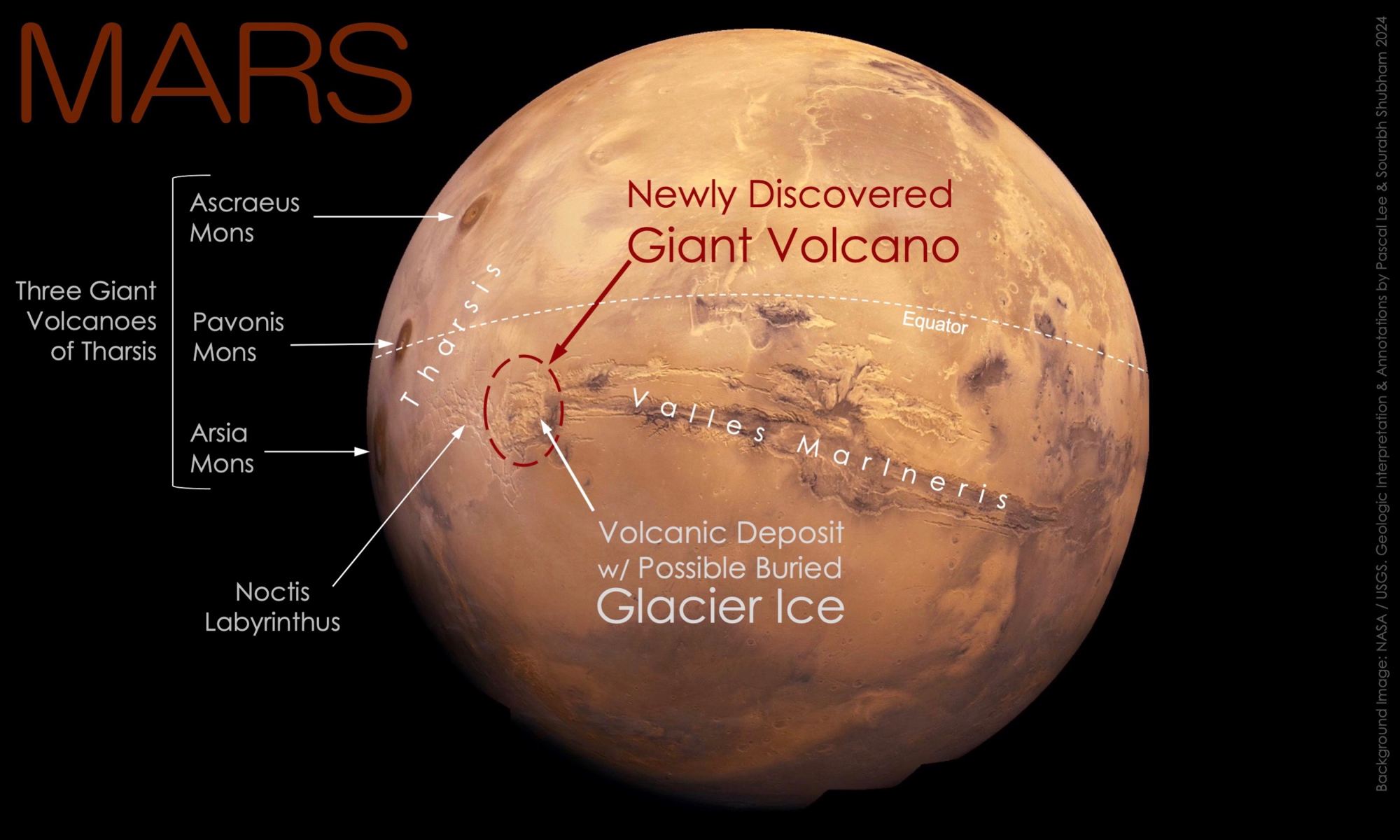
Olympus Mons is well known for being the largest volcano in the Solar System. It’s joined on Mars by three other shield volcanoes; Ascraeus, Pavonis and Arsia but a recent discovery has revealed a fifth. Provisionally called Noctis volcano, this previously unknown Martian feature reaches 9,022 metres high and 450 kilometres across. Its presence has eluded planetary scientists because it has been heavily eroded and is on the boundary of the fractured maze-like terrain of Noctis Labyrinthus.
Continue reading “Mars Was Hiding Another Giant Volcano”It's Time for Jupiter's Annual Checkup by Hubble
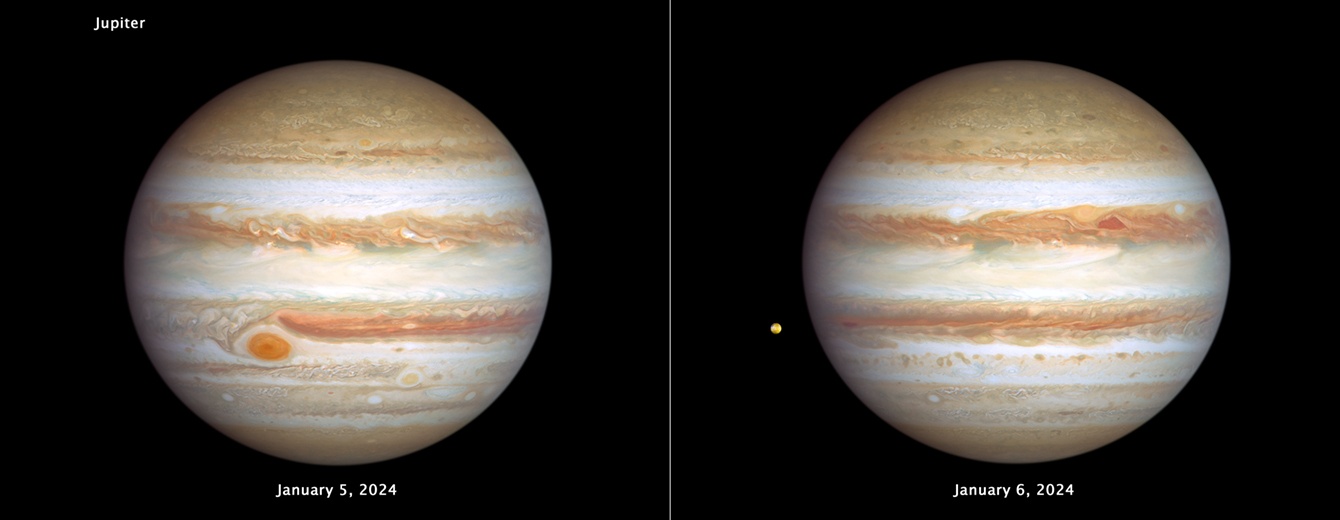
Each year, the Hubble Space Telescope focuses on the giant planets in our Solar System when they’re near the closest point to Earth, which means they’ll be large and bright in the sky. Jupiter had its photos taken on January 5-6th, 2024, showing off both sides of the planet. Hubble was looking for storm activity and changes in Jupiter’s atmosphere.
Continue reading “It's Time for Jupiter's Annual Checkup by Hubble”This is a 1.3 Gigapixel Image of a Supernova Remnant
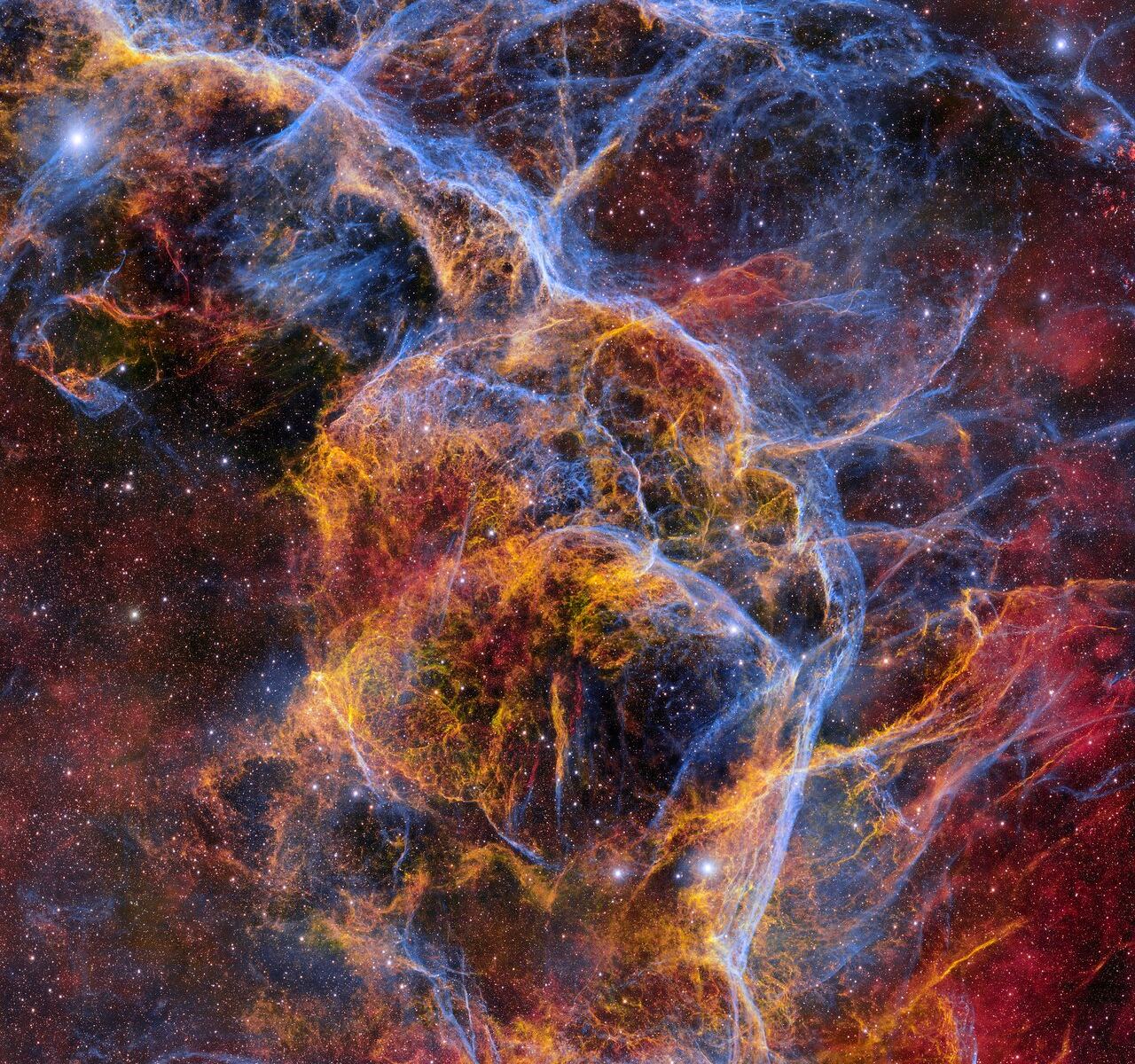

Stars more massive than the Sun blow themselves to pieces at the end of their life. Usually leaving behind either a black hole, neutron star or pulsar they also scatter heavy elements across their host galaxy. One such star went supernova nearly 11,000 years ago creating the Vela Supernova Remnant. The resultant expanding cloud of debris covers almost 100 light years and would be twenty times the diameter of the full Moon. Astronomers have recently imaged the remnant with a 570 megapixel Dark Energy Camera (DECam) creating a stunning 1.3 gigapixel image.
Continue reading “This is a 1.3 Gigapixel Image of a Supernova Remnant”Nancy Grace Roman will Map the Far Side of the Milky Way
The Galaxy is a collection of stars, planets, gas clouds and to the dismay of astronomers, dust clouds. The dust blocks starlight from penetrating so it’s very difficult to learn about the far side of the Galaxy. Thankfully the upcoming Nancy Grace Roman telescope has infrared capability so it can see through the dust. A systematic survey of the far side of the Milky Way is planned to see what’s there and could discover billions of objects in just a month.
Continue reading “Nancy Grace Roman will Map the Far Side of the Milky Way”Another Hycean Planet Found? TOI-270 d

Hycean planets may be able to host life even though they’re outside what scientists consider the regular habitable zone. Their thick atmospheres can trap enough heat to keep the oceans warm even though they’re not close to their stars.
Astronomers have found another one of these potential hycean worlds named TOI-270 d.
Continue reading “Another Hycean Planet Found? TOI-270 d”Starship Reaches Orbit on SpaceX’s Third Test but Breaks Up on Re-Entry
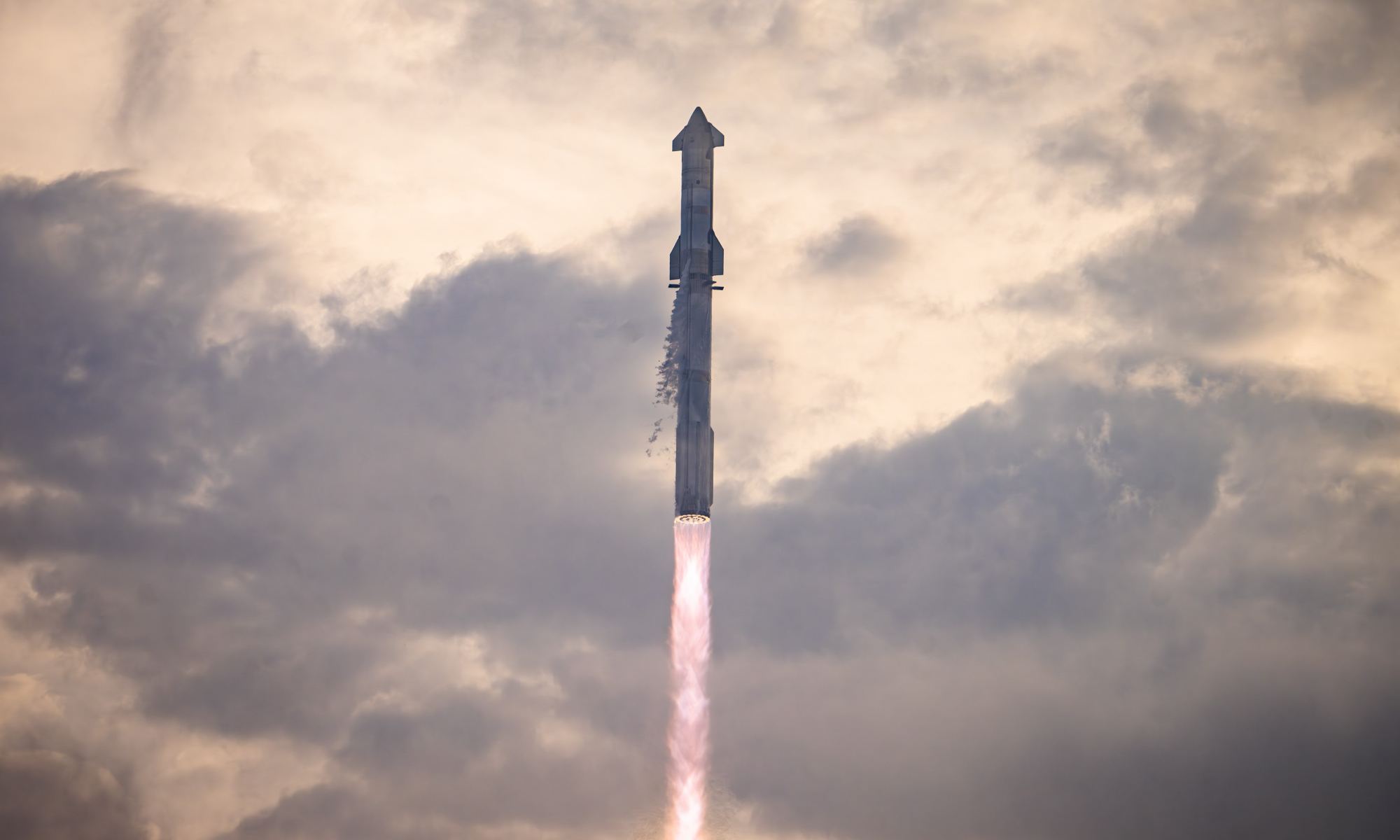
After falling short in its first two attempts, SpaceX got its Starship super-rocket to an orbital altitude today during the launch system’s third integrated flight test. Now it just has to work on the landing.
Today’s test marked a major milestone in SpaceX’s effort to develop Starship as the equivalent of a gigantic Swiss Army knife for spaceflight, with potential applications ranging from the deployment of hundreds of Starlink broadband satellites at a time to crewed odysseys to the moon, Mars and beyond.
Continue reading “Starship Reaches Orbit on SpaceX’s Third Test but Breaks Up on Re-Entry”NASA and Boeing Release New Rendering of their X-66 Sustainable Experimental Airliner
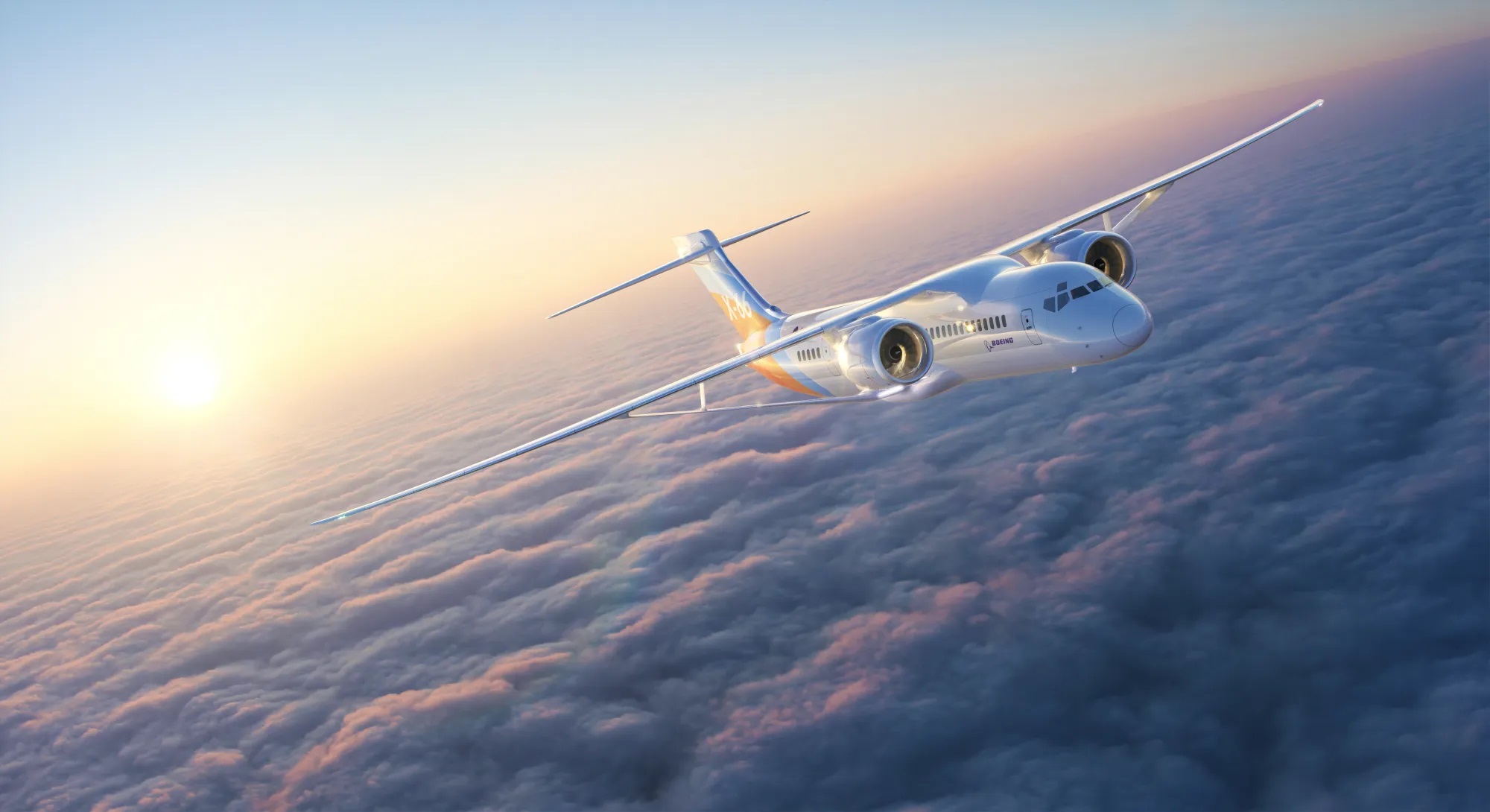

Climate change is arguably the single greatest threat facing the world today. According to the Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) by the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), average global temperatures are set to increase between 1.5 and 2 °C (2.7 to 3.6 °F) by mid-century. To restrict global temperatures to an increase of 1.5 C and avoid the worst-case scenarios, the nations of the world need to achieve net zero emissions by then. Otherwise, things will get a lot worse before they get better, assuming they ever do.
This means transitioning to cleaner methods in terms of energy, transportation, and aviation. To meet our climate commitments, the aviation industry is developing technology to significantly reduce air travel’s carbon footprint. To help meet this goal, NASA and Boeing have come together to create the X-66 Sustainable Experimental Airliner, the first experimental plane specifically focused on helping the U.S. achieve net-zero aviation. Last week, NASA released a new rendering of the concept, giving the public an updated look at the future of air travel.
Continue reading “NASA and Boeing Release New Rendering of their X-66 Sustainable Experimental Airliner”Webb Sees a Star-Forming Region Blowing Vast Bubbles
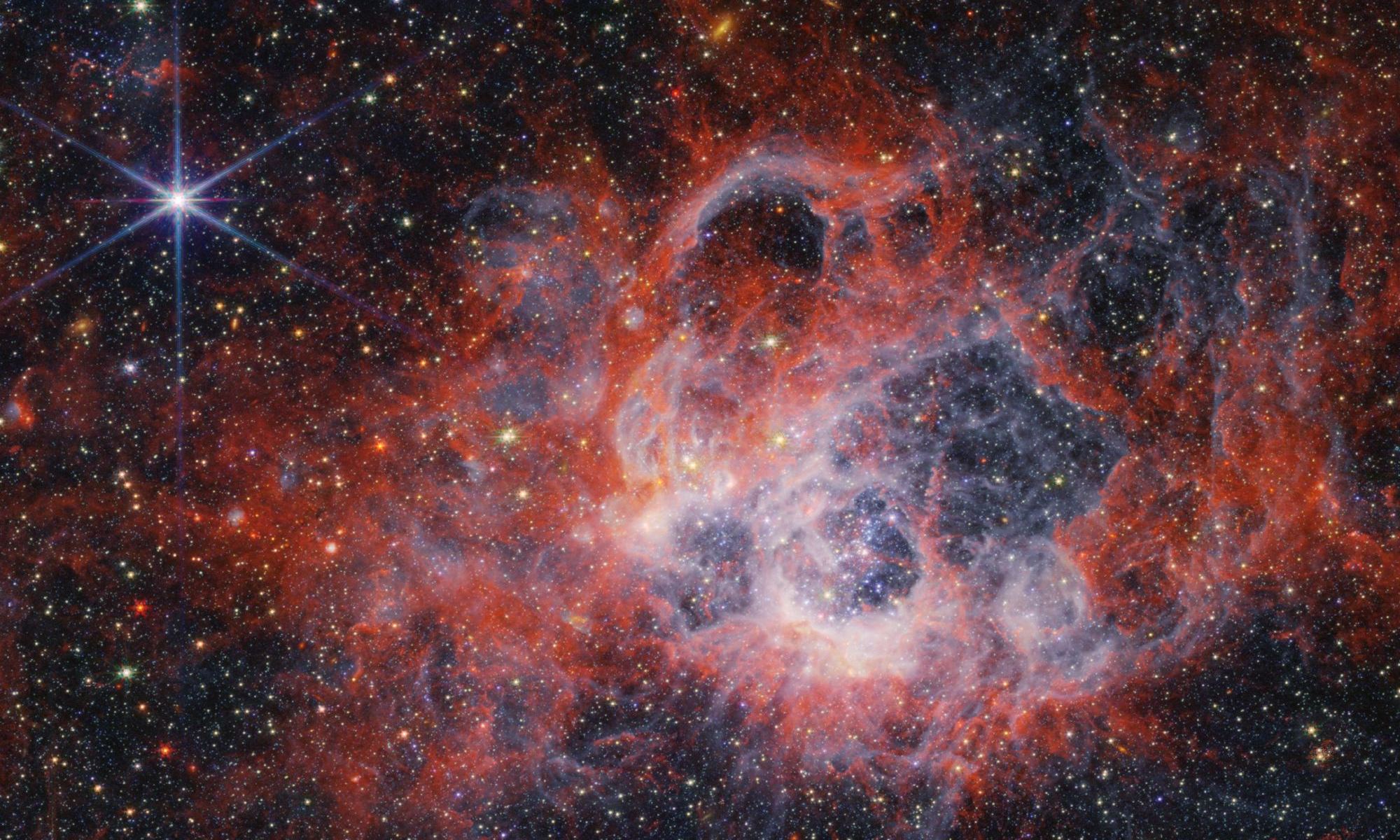

Star birth is a messy and chaotic event. Some of the process remains well hidden behind clouds of gas and dust that make up star-forming regions. However, part of it happens in wavelengths of light we can detect, such as visible light and infrared. It’s an intricate process that the Webb telescope (JWST) can study in detail.
Continue reading “Webb Sees a Star-Forming Region Blowing Vast Bubbles”