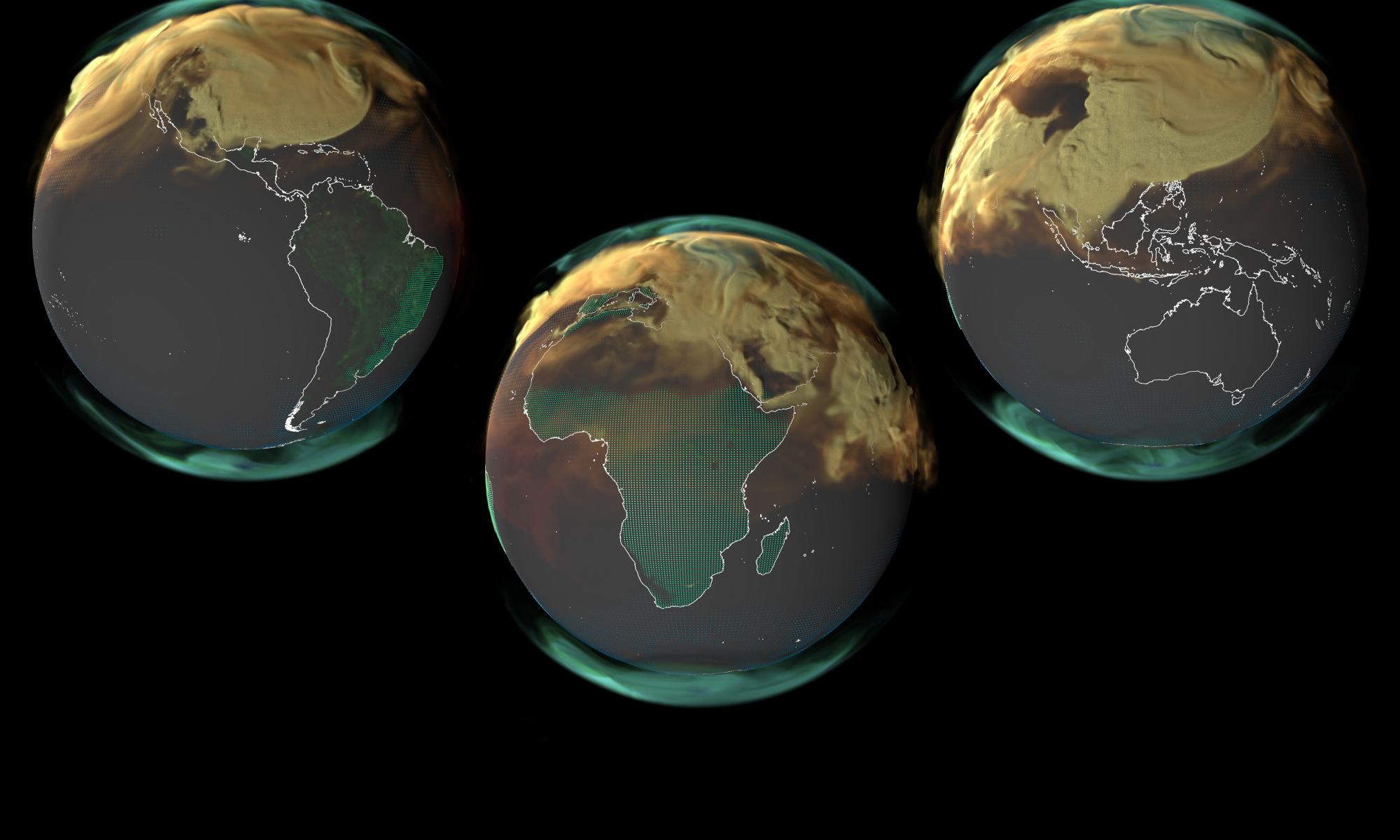
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Sixth Assessment Report (AR6), human activities have significantly impacted the planet. As global greenhouse gas emissions (mainly carbon dioxide) have continued to increase, so too have global temperatures – with severe ecological consequences. Between 2011 and 2020, global surface temperatures rose by an estimated 1.07 °C (2.01 °F) above the average in 1850–1900. At this rate, temperatures could further increase by 1.5 to 2 °C (2.7 to 3.6 °F) in the coming decades, depending on whether we can achieve net zero by 2050.
Unfortunately, the data for the past year is not encouraging. According to the 2023 Global Carbon Budget (GCB), an annual assessment of Earth’s carbon cycle, emissions in 2023 continued to rise by 1.1 percent compared to the previous year. This placed the total fossil fuel emissions from anthropogenic sources at 36.8 billion metric tons (over 40 US tons) of carbon dioxide, with an additional 4.1 billion metric tons (4.5 US tons) added by deforestation, extreme wildfires, and other sources. This trend indicates we are moving away from our goals and that things will get worse before they get better!
Continue reading “Satellite Measurements Show That Global Carbon Emissions are Still Rising”