Kyoto University and one of Japan's largest construction companies are collaborating on a study for a "Lunagrass" rotating lunar base!
Continue reading

A "NASA/JPL ambassador" created a map that shows where the objects shown in the James Webb's first images are within (or in relation to) the Milky Way.
Continue reading

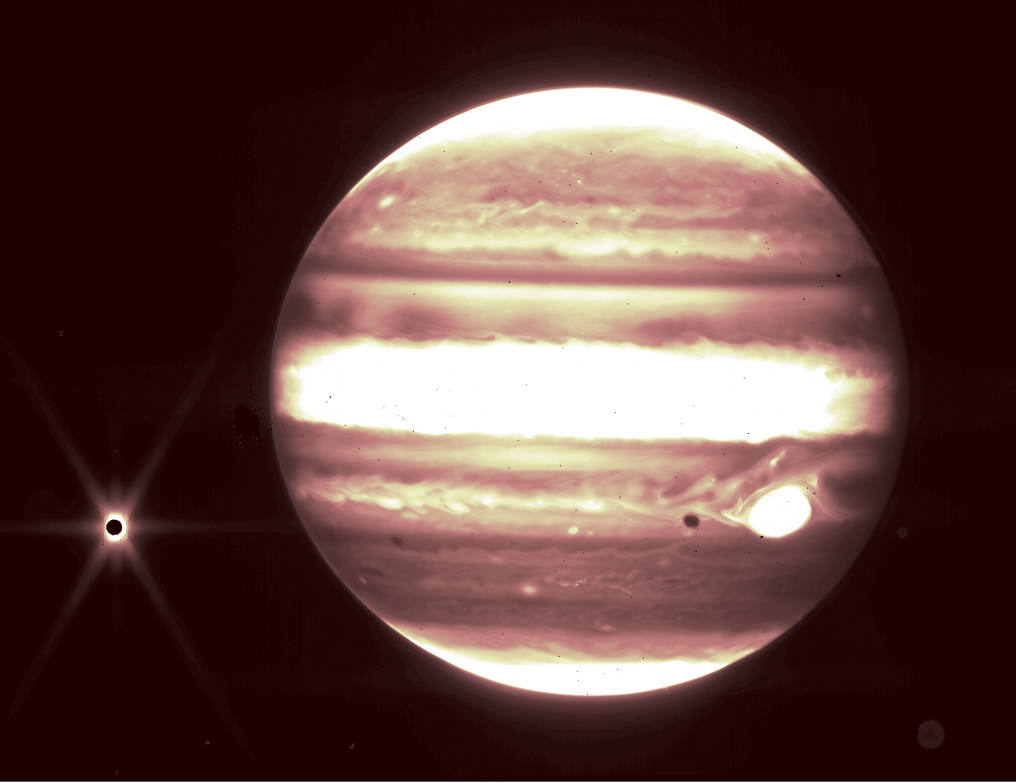
The first images of the James Webb Space Telescope are here!
Continue reading

NASA has just released the first image taken by the James Webb Space Telescope!
Continue reading

A team of Chinese scientists have proposed a mission that would explore Neptune and its largest moon Triton using a nuclear-powered spacecraft.
Continue reading

A new study shows that astronauts do not recover all of their bone strength when they return to Earth, meaning that extended stays in space will cause your bones to age unnaturally!
Continue reading

New research shows that distant quasars were born in the cold dark of turbulent gas.
Continue reading

A team of Canadian engineers have built a gun that will help space agencies test materials that could provide shielding against space debris!
Continue reading

A new study by a team of Canadian researchers shows that our Solar System will not experience a close and disruptive stellar flyby for a very long time!
Continue reading

SpaceX has released new images that show the Starship and Superheavy prototypes with all their engines!
Continue reading

The first images taken by James Webb will be released in a little more than a week! According to NASA, they are so moving that you may cry when you see them!
Continue reading

A new study shows how the study of tidal heating in exomoons could greatly expand the search for life in the Universe.
Continue reading

A galactic nova flared briefly into naked eye visibility for a day, before vanishing from sight.
Continue reading