
Breaking up isn’t hard to do if you’re a comet. They’re fragile creatures subject to splitting, cracking and vaporizing when heated by the Sun and yanked on by its powerful gravitational pull.
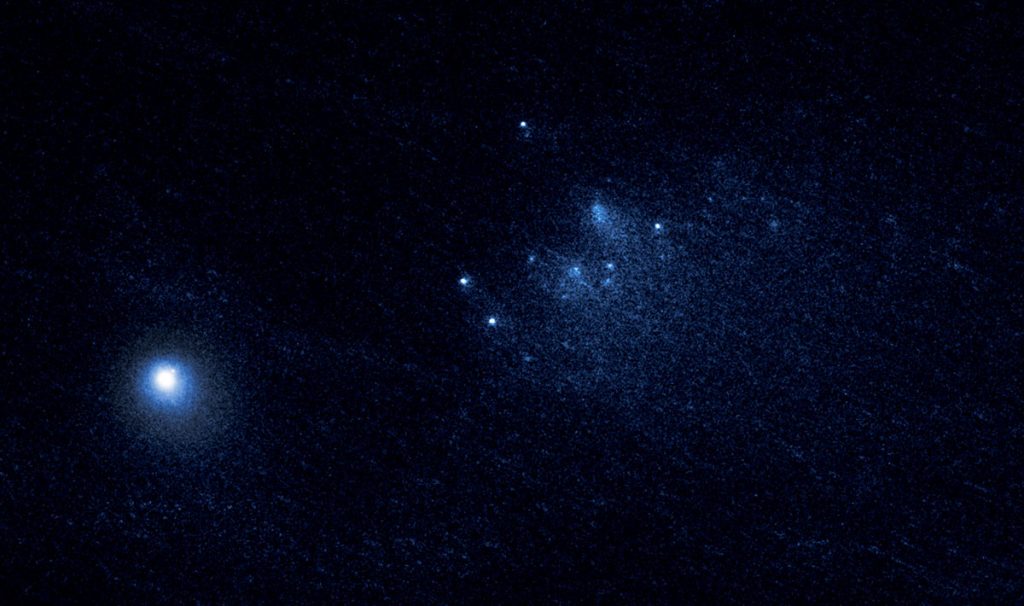
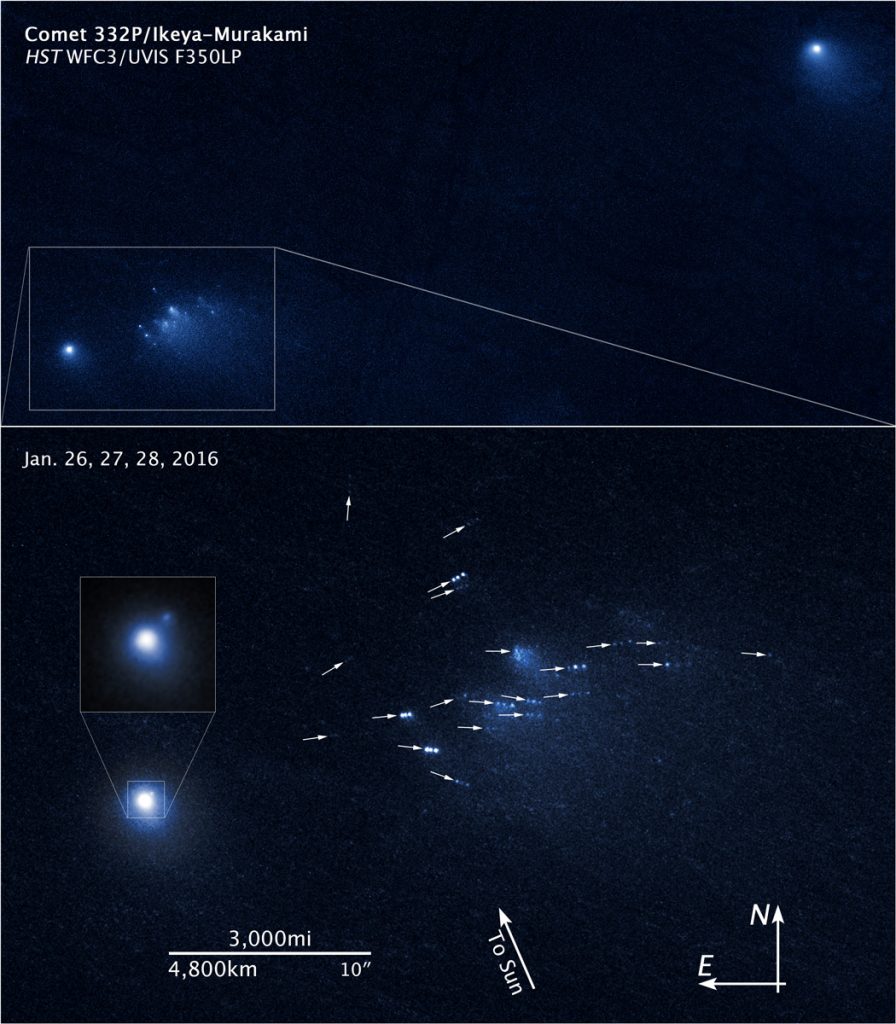
Recently, the Hubble Space Telescope captured one of the sharpest, most detailed observations of a comet breaking apart, which occurred 67 million miles from Earth. In a series of images taken over a three-day span in January 2016, Hubble revealed 25 building-size blocks made of a mixture of ice and dust that are drifting away from the main nucleus of the periodic comet 332P/Ikeya-Murakami at a leisurely pace, about the walking speed of an adult.

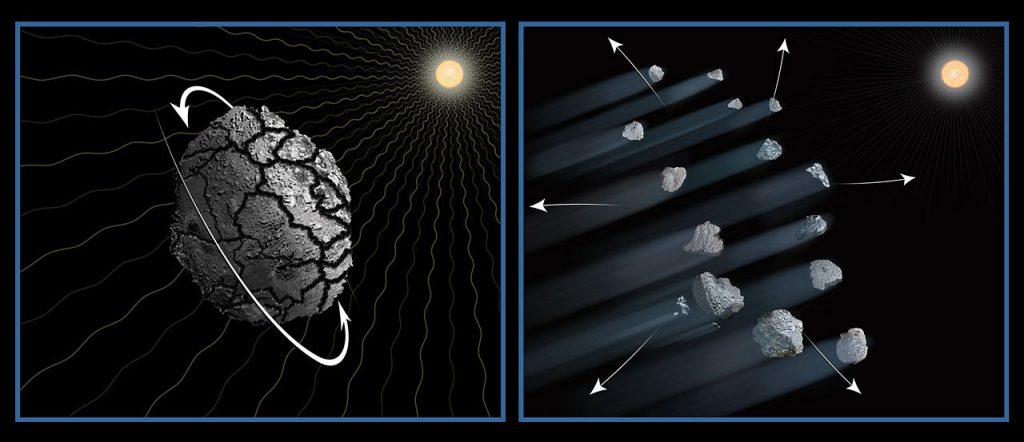
The observations suggest that the comet may be spinning so fast that material is ejected from its surface. The resulting debris is now scattered along a 3,000-mile-long trail, larger than the width of the continental U.S. Much the same happens with small asteroids, when sunlight absorbed unequally across an asteroid’s surface spins up its rotation rate, either causing it to fall apart or fling hunks of itself into space.
Being made of loosely bound frothy ice, comets may be even more volatile compared to the dense rocky composition of many asteroids. The research team suggests that sunlight heated up the comet, causing jets of gas and dust to erupt from its surface. We see this all the time in comets in dramatic images taken by the Rosetta spacecraft of Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Because the nucleus is so small, these jets act like rocket engines, spinning up the comet’s rotation. The faster spin rate loosened chunks of material, which are drifting off into space.

“We know that comets sometimes disintegrate, but we don’t know much about why or how they come apart,” explained lead researcher David Jewitt of the University of California at Los Angeles. “The trouble is that it happens quickly and without warning, and so we don’t have much chance to get useful data. With Hubble’s fantastic resolution, not only do we see really tiny, faint bits of the comet, but we can watch them change from day to day. And that has allowed us to make the best measurements ever obtained on such an object.”
In the animation you can see the comet splinters brighten and fade as icy patches on their surfaces rotate in and out of sunlight. Their shapes even change! Being made of ice and crumbly as a peanut butter cookie, they continue to break apart to spawn a host of smaller cometary bits. The icy relics comprise about 4% of the parent comet and range in size from roughly 65 feet wide to 200 feet wide (20-60 meters). They are moving away from each other at a few miles per hour.

Comet 332P was slightly beyond the orbit of Mars when Hubble spotted the breakup. The surviving bright nucleus completes a rotation every 2-4 hours, about four times as fast as Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko (a.k.a. “Rosetta’s Comet”). Standing on its surface you’d see the sun rise and set in about an hour, akin to how frequently astronauts aboard the International Space Station see sunsets and sunrises orbiting at over 17,000 mph.
Don’t jump for joy though. Since the comet’s just 1,600 feet (488 meters) across, its gravitational powers are too meek to allow visitors the freedom of hopping about lest they find themselves hovering helplessly in space above the icy nucleus.
Comet 332P was discovered in November 2010, after it surged in brightness and was spotted by two Japanese amateur astronomers, Kaoru Ikeya and Shigeki Murakami. Based on the Hubble data, the team calculated that the comet probably began shedding material between October and December 2015. From the rapid changes seen in the shards over the three days captured in the animation, they probably won’t be around for long.
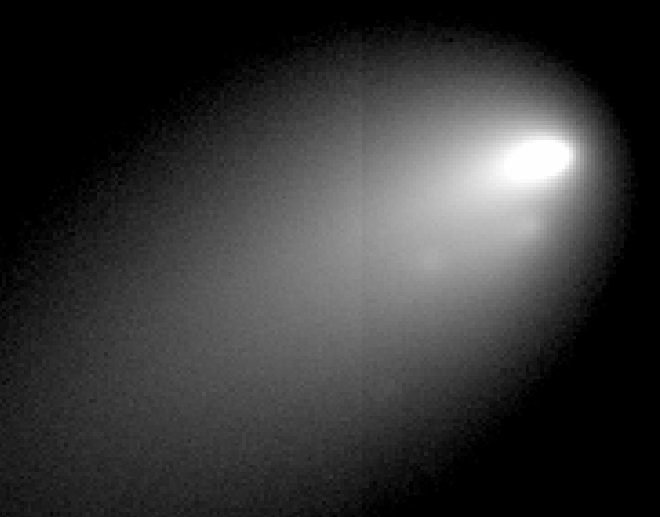
Spectacular breakup of Comet 73P in 2006
More changes may be in the works. Hubble’s sharp vision also spied a chunk of material close to the comet, which may be the first salvo of another outburst. The remnant from still another flare-up, which may have occurred in 2012, is also visible. The fragment may be as large as Comet 332P, suggesting the comet split in two.
“In the past, astronomers thought that comets die when they are warmed by sunlight, causing their ices to simply vaporize away,” Jewitt said. “Either nothing would be left over or there would be a dead hulk of material where an active comet used to be. But it’s starting to look like fragmentation may be more important. In Comet 332P we may be seeing a comet fragmenting itself into oblivion.”
During its closest approach to the Sun on November 28, 2013, Comet ISON’s nucleus broke apart and soon vaporized away, leaving little more than a ghostly head and fading tail.
Astronomers using the Hubble and other telescopes have seen breakups before, most notably in April 2006 when 73P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 3, which crumbled into more than 60 pieces. Unlike 332P, the comet wasn’t observed long enough to track the evolution of the fragments, but the images are spectacular!
The researchers estimate that Comet 332P contains enough mass to endure another 25 outbursts. “If the comet has an episode every six years, the equivalent of one orbit around the sun, then it will be gone in 150 years,” Jewitt said. “It’s the blink of an eye, astronomically speaking. The trip to the inner Solar System has doomed it.”

332P/Ikeya-Murakami hails from the Kuiper Belt, a vast swarm of icy asteroids and comets beyond Neptune. Leftover building blocks from early Solar System and stuck in a deep freeze in the Kuiper Belt, you’d think they’d be left alone to live their solitary, chilly lives but no. After nearly 4.5 billion years in this icy deep freeze, chaotic gravitational perturbations from Neptune kicked Comet 332P out of the Kuiper Belt.
As the comet traveled across the solar system, it was deflected by the planets, like a ball bouncing around in a pinball machine, until Jupiter’s gravity set its current orbit. Jewitt estimates that a comet from the Kuiper Belt gets tossed into the inner solar system every 40 to 100 years.
I wish I could tell you to grab your scope for a look, but 332P is currently fainter than 15th magnitude and located in Libra low in the southwestern sky at nightfall. Hopefully, we’ll see more images in the coming weeks and months as Jewitt and the team continue to follow the evolution of its icy scraps.

