Of all the unanswered questions in modern science, perhaps the most talked about is whether we are alone in the Universe. A new paper looks at another way we might be able to detect advanced civilisations and at its centre is the need for energy! The more advanced a civilisation becomes, the greater their need for energy and one of the most efficient ways, according to current theories, is to harness the energy from an actively feeding black hole. The paper suggests a civilisation feeding matter into a black hole could harvest energy from it, more excitingly perhaps, the process could be detectable within 17,000 light years!
New Technique for Spotting Dyson Rings Unveiled.

Dyson spheres and rings have always held a special fascination for me. The concept is simple, build a great big structure either as a sphere or ring to harness the energy from a star. Dyson rings are far more simple and feasible to construct and in a recent paper, a team of scientists explore how we might detect them by analysing the light from distant stars. The team suggests they might be able to detect Dyson rings around pulsars using their new technique.
Continue reading “New Technique for Spotting Dyson Rings Unveiled.”Do Planets Have the Raw Ingredients for Life? The Answer is in their Stars
Finding planets that already have, or have the ingredients for intelligent life is a real challenge. It is exciting that new telescopes and spacecraft are in development that will start to identify candidate planets. Undertaking these observations will take significant amounts of telescope time so we need to find some way to prioritise which ones to look at first. A new paper has been published that suggests we can study the host stars first for the necessary raw elements giving a more efficient way to hunt for similar worlds to Earth.
Continue reading “Do Planets Have the Raw Ingredients for Life? The Answer is in their Stars”That’s No Planet. Detecting Transiting Megastructures
One of the easiest ways to find exoplanets is using the transit method. It relies upon monitoring the brightness of a star which will then dim as a planet passes in front of it. It is of course possible that other objects could pass between us and a star; perhaps binary planets, tidally distorted planets, exocomets and, ready for it…. alien megastructures! A transit simulator has been created by a team of researchers and it can predict the brightness change from different transiting objects, even Dyson Swarms in construction.
Continue reading “That’s No Planet. Detecting Transiting Megastructures”There’s Another, More Boring Explanation for those Dyson Sphere Candidate Stars
Dyson Spheres have been a tantalising digression in the hunt for alien intelligence. Just recently seven stars have been identified as potential candidates with most of their radiation given off in the infrared wavelengths. Potentially this is the signature of heat from a matrix of spacecraft around the star but alas, a new paper has another slightly less exciting explanation; dust obscured galaxies.
Continue reading “There’s Another, More Boring Explanation for those Dyson Sphere Candidate Stars”Do Stars Move? Tracking Their Movements Across the Sky
The night sky, is the night sky, is the night sky. The constellations you learned as a child are the same constellations that you see today. Ancient people recognized these same constellations. Oh sure, they might not have had the same name for it, but essentially, we see what they saw.
But when you see animations of galaxies, especially as they come together and collide, you see the stars buzzing around like angry bees. We know that the stars can have motions, and yet, we don’t see them moving?
How fast are they moving, and will we ever be able to tell?
Stars, of course, do move. It’s just that the distances are so great that it’s very difficult to tell. But astronomers have been studying their position for thousands of years. Tracking the position and movements of the stars is known as astrometry.
We trace the history of astrometry back to 190 BC, when the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus first created a catalog of the 850 brightest stars in the sky and their position. His student Ptolemy followed up with his own observations of the night sky, creating his important document: the Almagest.
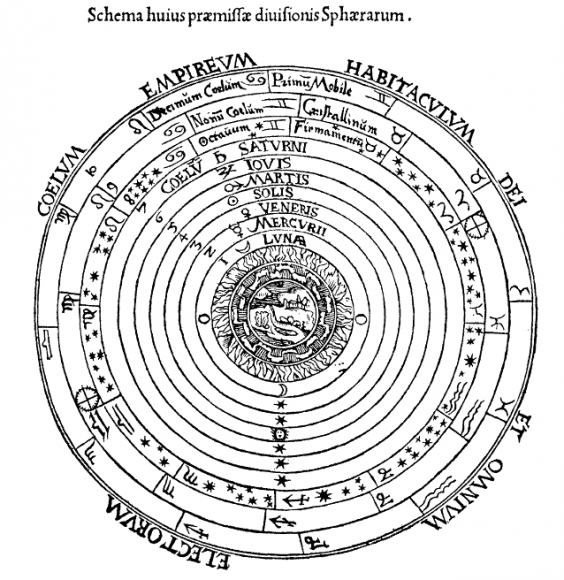
In the Almagest, Ptolemy laid out his theory for an Earth-centric Universe, with the Moon, Sun, planets and stars in concentric crystal spheres that rotated around the planet. He was wrong about the Universe, of course, but his charts and tables were incredibly accurate, measuring the brightness and location of more than 1,000 stars.
A thousand years later, the Arabic astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi completed an even more detailed measurement of the sky using an astrolabe.

One of the most famous astronomers in history was the Danish Tycho Brahe. He was renowned for his ability to measure the position of stars, and built incredibly precise instruments for the time to do the job. He measured the positions of stars to within 15 to 35 arcseconds of accuracy. Just for comparison, a human hair, held 10 meters away is an arcsecond wide.
Also, I’m required to inform you that Brahe had a fake nose. He lost his in a duel, but had a brass replacement made.
In 1807, Friedrich Bessel was the first astronomer to measure the distance to a nearby star 61 Cygni. He used the technique of parallax, by measuring the angle to the star when the Earth was on one side of the Sun, and then measuring it again 6 months later when the Earth was on the other side.

Over the course of this period, this relatively closer star moves slightly back and forth against the more distant background of the galaxy.
And over the next two centuries, other astronomers further refined this technique, getting better and better at figuring out the distance and motions of stars.
But to really track the positions and motions of stars, we needed to go to space. In 1989, the European Space Agency launched their Hipparcos mission, named after the Greek astronomer we talked about earlier. Its job was to measure the position and motion of the nearby stars in the Milky Way. Over the course of its mission, Hipparcos accurately measured 118,000 stars, and provided rough calculations for another 2 million stars.
That was useful, and astronomers have relied on it ever since, but something better has arrived, and its name is Gaia.

Launched in December 2013, the European Space Agency’s Gaia in is in the process of mapping out a billion stars in the Milky Way. That’s billion, with a B, and accounts for about 1% of the stars in the galaxy. The spacecraft will track the motion of 150 million stars, telling us where everything is going over time. It will be a mind bending accomplishment. Hipparchus would be proud.
With the most precise measurements, taken year after year, the motions of the stars can indeed be calculated. Although they’re not enough to see with the unaided eye, over thousands and tens of thousands of years, the positions of the stars change dramatically in the sky.
The familiar stars in the Big Dipper, for example, look how they do today. But if you go forward or backward in time, the positions of the stars look very different, and eventually completely unrecognizable.
When a star is moving sideways across the sky, astronomers call this “proper motion”. The speed a star moves is typically about 0.1 arc second per year. This is almost imperceptible, but over the course of 2000 years, for example, a typical star would have moved across the sky by about half a degree, or the width of the Moon in the sky.

The star with the fastest proper motion that we know of is Barnard’s star, zipping through the sky at 10.25 arcseconds a year. In that same 2000 year period, it would have moved 5.5 degrees, or about 11 times the width of your hand. Very fast.
When a star is moving toward or away from us, astronomers call that radial velocity. They measure this by calculating the doppler shift. The light from stars moving towards us is shifted towards the blue side of the spectrum, while stars moving away from us are red-shifted.
Between the proper motion and redshift, you can get a precise calculation for the exact path a star is moving in the sky.
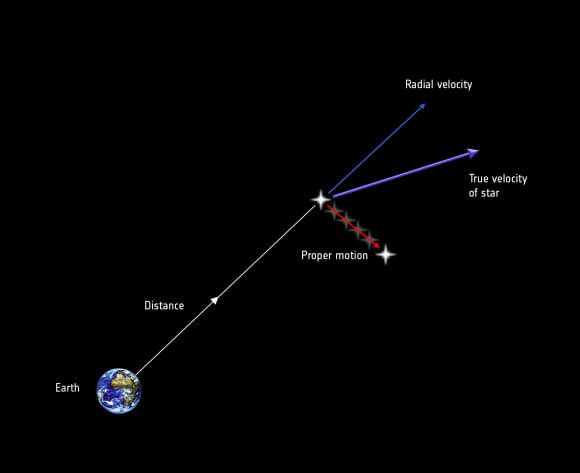
We know, for example, that the dwarf star Hipparcos 85605 is moving rapidly towards us. It’s 16 light-years away right now, but in the next few hundred thousand years, it’s going to get as close as .13 light-years away, or about 8,200 times the distance from the Earth to the Sun. This won’t cause us any direct effect, but the gravitational interaction from the star could kick a bunch of comets out of the Oort cloud and send them down towards the inner Solar System.
The motions of the stars is fairly gentle, jostling through gravitational interactions as they orbit around the center of the Milky Way. But there are other, more catastrophic events that can make stars move much more quickly through space.
When a binary pair of stars gets too close to the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way, one can be consumed by the black hole. The other now has the velocity, without the added mass of its companion. This gives it a high-velocity kick. About once every 100,000 years, a star is kicked right out of the Milky Way from the galactic center.
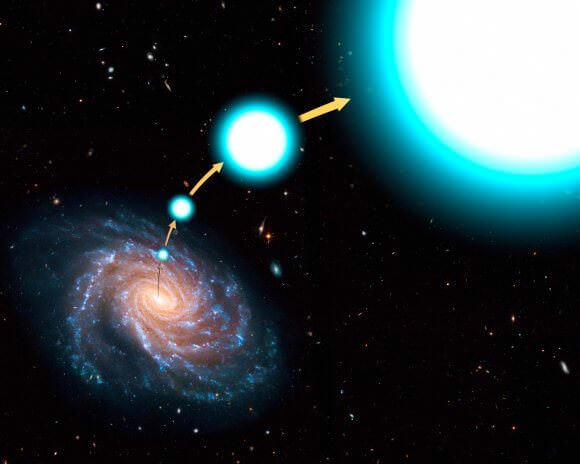
Another situation can happen where a smaller star is orbiting around a supermassive companion. Over time, the massive star bloats up as supergiant and then detonates as a supernova. Like a stone released from a sling, the smaller star is no longer held in place by gravity, and it hurtles out into space at incredible speeds.
Astronomers have detected these hypervelocity stars moving at 1.1 million kilometers per hour relative to the center of the Milky Way.
All of the methods of stellar motion that I talked about so far are natural. But can you imagine a future civilization that becomes so powerful it could move the stars themselves?
In 1987, the Russian astrophysicist Leonid Shkadov presented a technique that could move a star over vast lengths of time. By building a huge mirror and positioning it on one side of a star, the star itself could act like a thruster.
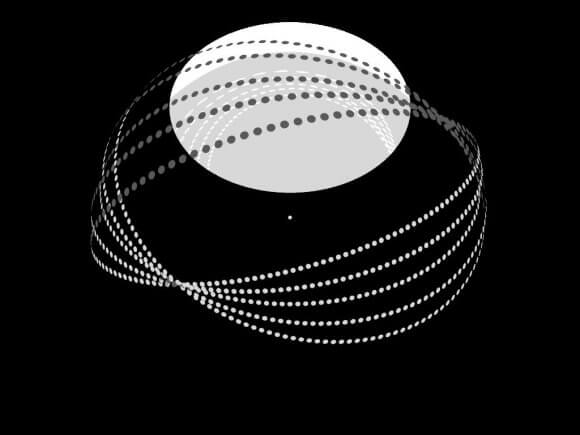
Photons from the star would reflect off the mirror, imparting momentum like a solar sail. The mirror itself would be massive enough that its gravity would attract the star, but the light pressure from the star would keep it from falling in. This would create a slow but steady pressure on the other side of the star, accelerating it in whatever direction the civilization wanted.
Over the course of a few billion years, a star could be relocated pretty much anywhere a civilization wanted within its host galaxy.
This would be a true Type III Civilization. A vast empire with such power and capability that they can rearrange the stars in their entire galaxy into a configuration that they find more useful. Maybe they arrange all the stars into a vast sphere, or some kind of geometric object, to minimize transit and communication times. Or maybe it makes more sense to push them all into a clean flat disk.
Amazingly, astronomers have actually gone looking for galaxies like this. In theory, a galaxy under control by a Type III Civilization should be obvious by the wavelength of light they give off. But so far, none have turned up. It’s all normal, natural galaxies as far as we can see in all directions.
For our short lifetimes, it appears as if the sky is frozen. The stars remain in their exact positions forever, but if you could speed up time, you’d see that everything is in motion, all the time, with stars moving back and forth, like airplanes across the sky. You just need to be patient to see it.
What Are Fast Radio Bursts?
You might think you’re reading an educational website, where I explain fascinating concepts in space and astronomy, but that’s not really what’s going on here.
What’s actually happening is that you’re tagging along as I learn more and more about new and cool things happening in the Universe. I dig into them like a badger hiding a cow carcass, and we all get to enjoy the cache of knowledge I uncover.
Okay, that analogy got a little weird. Anyway, my point is. Squirrel!
Fast radio bursts are the new cosmic whatzits confusing and baffling astronomers, and now we get to take a front seat and watch them move through all stages of process of discovery.
Stage 1: A strange new anomaly is discovered that doesn’t fit any current model of the cosmos. For example, strange Boyajian’s Star. You know, that star that probably doesn’t have an alien megastructure orbiting around it, but astronomers can’t rule that out just yet?
Stage 2: Astronomers struggle to find other examples of this thing. They pitch ideas for new missions and scientific instruments. No idea is too crazy, until it’s proven to be too crazy. Examples include dark matter, dark energy, and that idea that we’re living in a
Stage 3: Astronomers develop a model for the thing, find evidence that matches their predictions, and vast majority of the astronomical community comes to a consensus on what this thing is. Like quasars and gamma ray bursts. YouTuber’s make their videos. Textbooks are updated. Balance is restored.
Today we’re going to talk about Fast Radio Bursts. They just moved from Stage 1 to Stage 2. Let’s dig in.
Fast radio bursts, or FRBs, or “Furbys” were first detected in 2007 by the astronomer Duncan Lorimer from West Virginia University.
He was looking through an archive of pulsar observations. Pulsars, of course, are newly formed neutron stars, the remnants left over from supernova explosions. They spin rapidly, blasting out twin beams of radiation. Some can spin hundreds of times a second, so precisely you could set your watch to them.

In this data, Lorimer made a “that’s funny” observation, when he noticed one blast of radio waves that squealed for 5 milliseconds and then it was gone. It didn’t match any other observation or prediction of what should be out there, so astronomers set out to find more of them.
Over the last 10 years, astronomers have found about 25 more examples of Fast Radio Bursts. Each one only lasts a few milliseconds, and then fades away forever. A one time event that can appear anywhere in the sky and only last for a couple milliseconds and never repeats is not an astronomer’s favorite target of study.
Actually, one FRB has been found to repeat, maybe.
The question, of course, is “what are they?”. And the answer, right now is, “astronomers have no idea.”
In fact, until very recently, astronomers weren’t ever certain they were coming from space at all. We’re surrounded by radio signals all the time, so a terrestrial source of fast radio bursts seems totally logical.
About a week ago, astronomers from Australia announced that FRBs are definitely coming from outside the Earth. They used the Molonglo Observatory Synthesis Telescope (or MOST) in Canberra to gather data on a large patch of sky.
Then they sifted through 1,000 terabytes of data and found just 3 fast radio bursts. Three.
Since MOST is farsighted and can’t perceive any radio signals closer than 10,000 km away, the signals had to be coming outside planet Earth. They were “extraterrestrial” in origin.
Right now, fast radio bursts are infuriating to astronomers. They don’t seem to match up with any other events we can see. They’re not the afterglow of a supernova, or tied in some way to gamma ray bursts.
In order to really figure out what’s going on, astronomers need new tools, and there’s a perfect instrument coming. Astronomers are building a new telescope called the Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment (or CHIME), which is under construction near the town of Penticton in my own British Columbia.
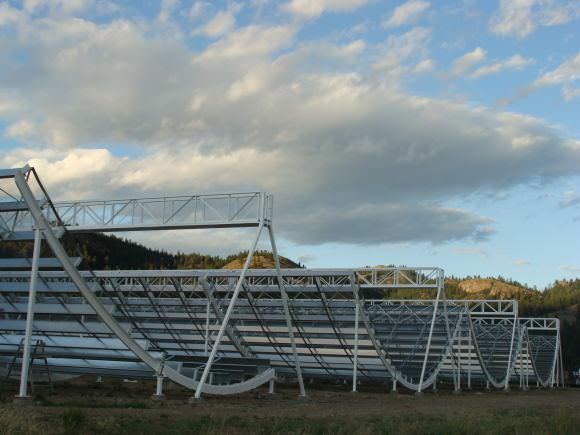

It looks like a bunch of snowboard halfpipes, and its job will be to search for hydrogen emission from distant galaxies. It’ll help us understand how the Universe was expanding between 7 and 11 billion years ago, and create a 3-dimensional map of the early cosmos.
In addition to this, it’s going to be able to detect hundreds of fast radio bursts, maybe even a dozen a day, finally giving astronomers vast pools of signals to study.
What are they? Astronomers have no idea. Seriously, if you’ve got a good suggestion, they’d be glad to hear it.
In these kinds of situations, astronomers generally assume they’re caused by exploding stars in some way. Young stars or old stars, or maybe stars colliding. But so far, none of the theoretical models match the observations.

Another idea is black holes, of course. Specifically, supermassive black holes at the hearts of distant galaxies. From time to time, a random star, planet, or blob of gas falls into the black hole. This matter piles upon the black hole’s event horizon, heats up, screams for a moment, and disappears without a trace. Not a full on quasar that shines for thousands of years, but a quick snack.
The next idea comes with the only repeating fast radio burst that’s ever been found. Astronomers looked through the data archive of the Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico and found a signal that had repeated at least 10 times in a year, sometimes less than a minute apart.
Since the quick blast of radiation is repeating, this rules out a one-time collision between exotic objects like neutron stars. Instead, there could be a new class of magnetars (which are already a new class of neutron stars), that can release these occasional shrieks of radio.
Or maybe this repeating object is totally different from the single events that have been discovered so far.
Here’s my favorite idea. And honestly, the one that’s the least realistic. What I’m about to say is almost certainly not what’s going on. And yet, it can’t be ruled out, and that’s good enough for my fertile imagination.
Avi Loeb and Manasvi Lingam at Harvard University said the following about FRBs:
“Fast radio bursts are exceedingly bright given their short duration and origin at distances, and we haven’t identified a possible natural source with any confidence. An artificial origin is worth contemplating and checking.”
Artificial origin. So. Aliens. Nice.
Loeb and Lingam calculated how difficult it would be to send a signal that strong, that far across the Universe. They found that you’d need to build a solar array with twice the surface area of Earth to power the radio wave transmitter.
And what would you do with a transmission of radio or microwaves that strong? You’d use it to power a spacecraft, of course. What we’re seeing here on Earth is just the momentary flash as a propulsion beam sweeps past the Solar System like a lighthouse.
But in reality, this huge solar array would be firing out a constant beam of radiation that would propel a massive starship to tremendous speeds. Like the Breakthrough Starshot spacecraft, but for million tonne spaceships.
In other words, we could be witnessing alien transportation systems, pushing spacecraft with beams of energy to other worlds.
And I know that’s probably not what’s happening. It’s not aliens. It’s never aliens. But in my mind, that’s what I’m imagining.
So, kick back and enjoy the ride. Join us as we watch astronomers struggle to understand what fast radio bursts are. As they invalidate theories, and slowly unlock one of the most thrilling mysteries in modern astronomy. And as soon as they figure it out, I’ll let you know all about it.
What do you think? Which explanation for fast radio bursts seems the most logical to you? I’d love to hear your thoughts and wild speculation in the comments.
Do I Believe in UFOs?
Whenever I do a new livestream on Instagram (hint hint, @universetoday on Instagram), it’s generally with an audience that doesn’t have a lot of experience with my work here on Universe Today or YouTube.
They’re enthusiastic about space, but they haven’t been exposed to a lot of the modern ideas about astrobiology and the search for extraterrestrials. They have, however, seen a lot of TV and movies.
Continue reading “Do I Believe in UFOs?”What Are Multiple Star Systems?
When we do finally learn the full truth about our place in the galaxy, and we’re invited to join the Galactic Federation of Planets, I’m sure we’ll always be seen as a quaint backwater world orbiting a boring single star.
The terrifying tentacle monsters from the nightmare tentacle world will gurgle horrifying, but clearly condescending comments about how we’ve only got a single star in the Solar System.
The beings of pure energy will remark how only truly enlightened civilizations can come from systems with at least 6 stars, insulting not only humanity, but also the horrifying tentacle monsters, leading to another galaxy spanning conflict.
Yes, we’ll always be making up for our stellar deficit in the eyes of aliens, or whatever those creepy blobs use for eyes.
What we lack in sophistication, however, we make up in volume. In our Milky Way, fully 2/3rds of star systems only have a single star. The last 1/3rd is made up of multiple star systems.

We’re taking binary stars, triple star systems, even exotic 7 star systems. When you mix and match different types of stars in various Odd Couple stellar apartments, the results get interesting.
Consider our own Solar System, where the Sun and planets formed together out a cloud of gas and dust. Gravity collected material into the center of the Solar System, becoming the Sun, while the rest of the disk spun up faster and faster. Eventually our star ignited its fusion furnace, blasting out the rest of the stellar nebula.
But different stellar nebulae can lead to the formation of multiple stars instead. What you get depends on the mass of the cloud, and how fast it’s rotating.
Check out this amazing photograph of a multiple star system forming right now.
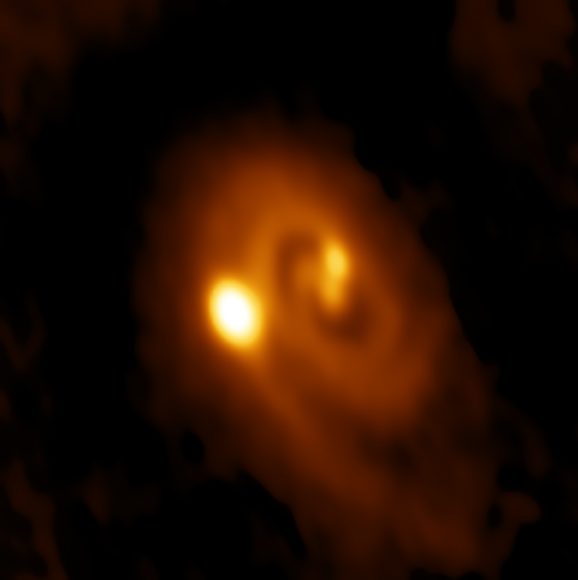

In this image, you can see three stars forming together, two at the center, about 60 astronomical units away from each other (60 times the distance from the Earth to the Sun), and then a third orbiting 183 AU away.
It’s estimated these stars are only 10,000 to 20,000 years old. This is one of the most amazing astronomy pictures I ever seen.
When you have two stars, that’s a binary system. If the stars are similar in mass to each other, then they orbit a common point of mass, known as the barycenter. If the stars are different masses, then it can appear that one star is orbiting the other, like a planet going around a star.
When you look up in the sky, many of the single stars you see are actually binary stars, and can be resolved with a pair of binoculars or a small telescope. For example, in a good telescope, Alpha Centauri can be resolved into two equally bright stars, with the much dimmer Proxima Centauri hanging out nearby.

You have to be careful, though, sometimes stars just happen to be beside each other in the sky, but they’re not actually orbiting one another – this is known as an optical binary. It’s a trap.
Astronomers find that you can then get binary stars with a third companion orbiting around them. As long as the third star is far enough away, the whole system can be stable. This is a triple star system.
You can get two sets of binary stars orbiting each other, for a quadruple star system.
In fact, you can build up these combinations of stars up. For example, the star system Nu Scorpii has 7 stars in a single system. All happily orbiting one another for eons.
If stars remained unchanging forever, then this would be the end of our story. However, as we’ve discussed in other articles, stars change over time, bloating up as red giants, detonating as supernovae and turning into bizarre objects, like white dwarfs, neutron stars and even black holes. And when these occur in multiple star systems, well, watch the sparks fly.
There are a nearly infinite combinations you can have here: main sequence, red giant, white dwarf, neutron star, and even black holes. I don’t have time to go through all the combinations, but here are some highlights.

For starters, binary stars can get so close they actually touch each other. This is known as a contact binary, where the two stars actually share material back and forth. But it gets even stranger.
When a main sequence star like our Sun runs out of hydrogen fuel in its core, it expands as a red giant, before cooling and becoming a white dwarf.
When a red giant is in a binary system, the distance and evolution of its stellar companion makes all the difference.
If the two stars are close enough, the red giant can pass material over to the other star. And if the red giant is large enough, it can actually engulf its companion. Imagine our Sun, orbiting within the atmosphere of a red giant star. Needless to say, that’s not healthy for any planets.
An even stranger contact binary happens when a red giant consumes a binary neutron star. This is known as a Thorne-Zytkow object. The neutron star spirals inward through the atmosphere of the red giant. When it reaches the core, it either becomes a black hole, gobbling up the red giant from within, or an even more massive neutron star. This is exceedingly rare, and only one candidate object has ever been observed.

When a binary pair is a white dwarf, the dead remnant of a star like our Sun, then material can transfer to the surface of the white dwarf, causing novae explosions. And if enough material is transferred, the white dwarf explodes as a Type 1A supernova.
If you’re a star that was unlucky enough to be born beside a very massive star, you can actually kicked off into space when it explodes as a supernova. In fact, there are rogue stars which such a kick, they’re on an escape trajectory from the entire galaxy, never to return.
If you have two neutron stars in a binary pair, they release energy in the form of gravitational waves, which causes them to lose momentum and spiral inward. Eventually they collide, becoming a black hole, and detonating with so much energy we can see the explosions billions of light-years away – a short-period gamma ray burst.
The combinations are endless.

It’s amazing to think what the night sky would look like if we were born into a multiple star system. Sometimes there would be several stars in the sky, other times just one. And rarely, there would be an actual night.
How would life be different in a multiple star system? Let me know your thoughts in the comments.
In our next episode, we try to untangle this bizarre paradox. If the Universe is infinite, how did it start out as a singularity? That doesn’t make any sense.
We glossed over it in this episode, but one of the most interesting effects of multiple star systems are novae, explosions of stolen material on the surface of a white dwarf star. Learn more about it in this video.
What If We Do Find Aliens?
Time to talk about my favorite topic: aliens.
We’ve covered the Fermi Paradox many times over several articles on Universe Today. This is the idea that the Universe is huge, and old, and the ingredients of life are everywhere. Life could and should have have appeared many times across the galaxy, but it’s really strange that we haven’t found any evidence for them yet.
Continue reading “What If We Do Find Aliens?”








