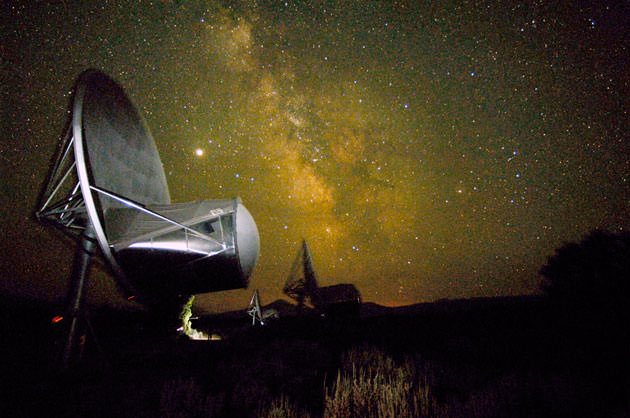
During a hearing last week before the U.S. House Science and Technology Committee SETI scientists Seth Shostak and Dan Werthimer asserted that solid evidence for extraterrestrial life in our galaxy — or, at the very least, solid evidence for a definitive lack of it — will come within the next two decades. It’s a bold claim for scientists to make on public record, but one that Shostak has made many times before (and he’s not particularly off-schedule either.) And with SETI’s Allen Telescope Array (ATA) continually scanning the sky for any signals that appear intentional, exoplanets being discovered en masse, and new technology on deck that can further investigate a select few of their (hopefully) Earth-like atmospheres, the chances that alien life — if it’s out there — will be found are getting better and better each year.
Would you put your bet on E.T. being out there? Actually, you can.
Thanks to the internet and the apparently incorrigible human need to compete you can actually place a wager on when alien life will be discovered, via an Irish online betting site.

Typically focused on the results of international sporting matches, PaddyPower.com has also included the announcement of extraterrestrial life in its novelty bet section, hinging on “the sitting President of the USA making a statement confirming without doubt the existence of alternative life beings from another planet.” The odds of such an announcement being made in the years 2015-2018 are currently listed at 100 to one. After that they drop significantly… probably because by then the JWST will be in operation and we will “have the technology.” Stranieri.com also has offered a chance for Italian players of chance to bet on the sitting president discussing life from other planets, with betting open until 2025 for long-term gamblers!
Of course, whether you personally would place a wager on such things is purely personal preference, and neither I nor Universe Today condones or supports gambling, for aliens or otherwise. (And the legalities of doing so and any and all results thereof are the sole responsibility of the reader.) But it is interesting that we now live in a time when wagering on the discovery of alien life sits just a click away from the results of the Kentucky Derby, French Open, or World Cup.
Now if you really want to support the science that will make such a discovery possible — maybe even within our own Solar System — you can “stand up for space” and write your representatives to tell them you want NASA’s planetary science budget to be funded, and rather than gamble your money you can make a donation to support SETI’s ongoing mission here (or even help out yourself via SETI@home.)
And even if all else fails, you could end up with a free coffee courtesy of Dr. Shostak…
Learn more about SETI and how the ATA works here, and read Dan Werthimer’s May 21 statement to the House Committee here.
Source/ht: FloridaToday Space and The Independent
“Two possibilities exist: either we are alone in the Universe or we are not. Both are equally terrifying.”
– Arthur C. Clarke