Our Sun’s days are numbered. In about 5 billion years the Sun will expand into a red giant, casting off its outer layers before settling down to become a white dwarf. It’s the inevitable fate of most sunlike stars, and the process is well understood. But as a recent study shows, there are still a few things we have to learn about dying Suns.
Continue reading “Dying Star Puffs out six Smoke Rings”Astronomers See Carbon-Rich Nebulae Where Planets are Forming
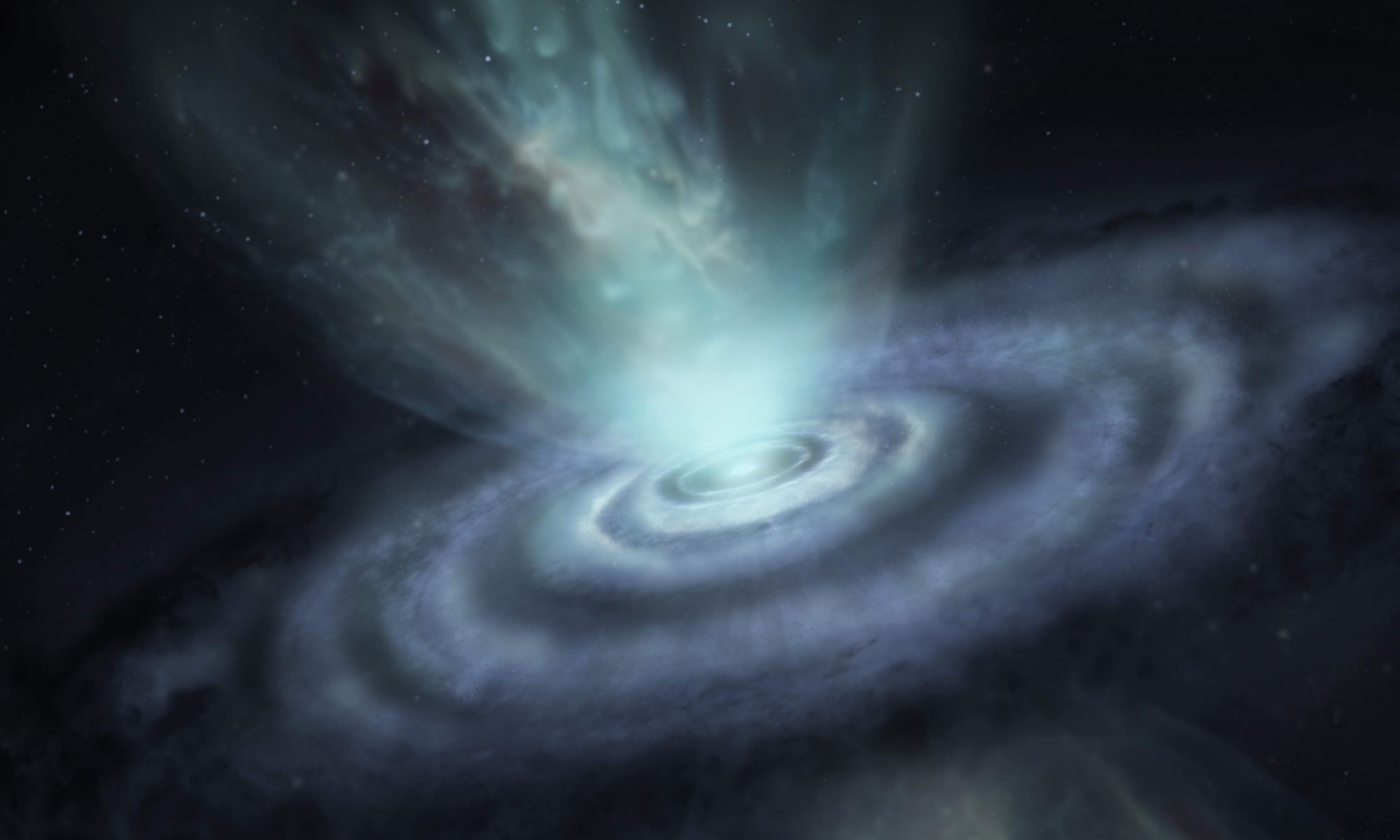
Understanding the birth of a planet is a challenging puzzle. We know that planets form inside clouds of gas and dust that surround new stars, known as protoplanetary disks. But grasping exactly how that process works – connecting the dots between a dust cloud and a finished planet – is not easy. An international team of astronomers is attempting to unlock some of those secrets, and have recently completed the most extensive chemical composition mapping of several protoplanetary discs around five young stars. Their research allows them to begin to piece together the chemical makeup of future exoplanets, offering a glimpse into the formation of new alien worlds.
Continue reading “Astronomers See Carbon-Rich Nebulae Where Planets are Forming”ALMA’s new Receivers Will let it see Longer Wavelengths, Peering Closer to the Beginning of the Universe
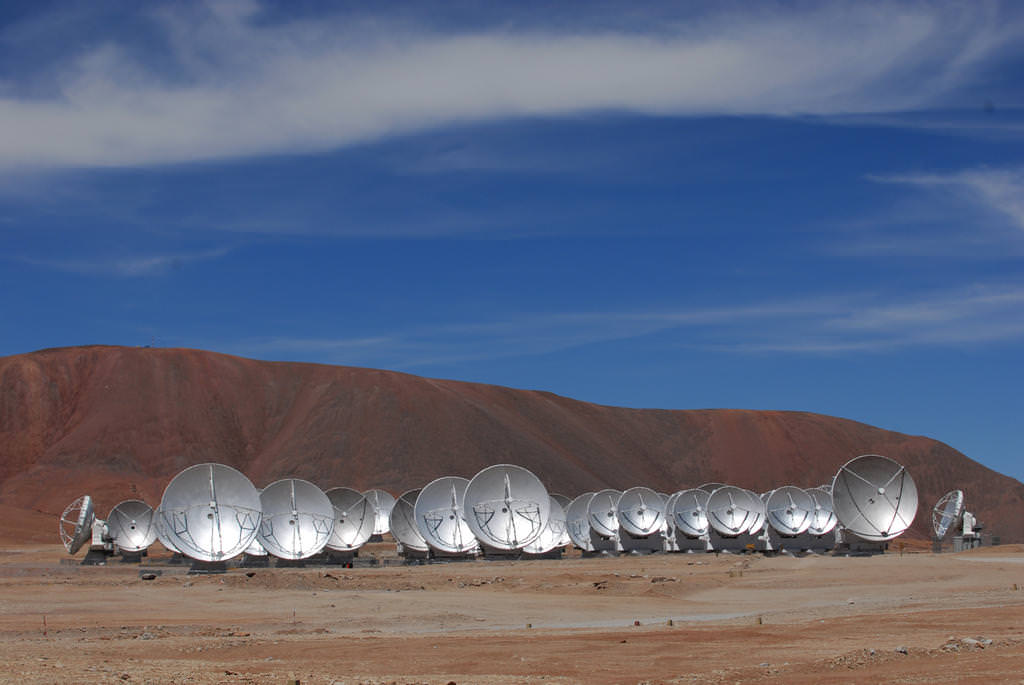

The ALMA telescope is getting a new set of receivers, enabling it to detect wavelengths down to 8.5 mm. These wavelengths are crucial for observations of the transformative epoch of reionization, when the first stars to appear in the universe unleashed a fury of radiation.
Continue reading “ALMA’s new Receivers Will let it see Longer Wavelengths, Peering Closer to the Beginning of the Universe”The Galactic Beauty of Star Formation
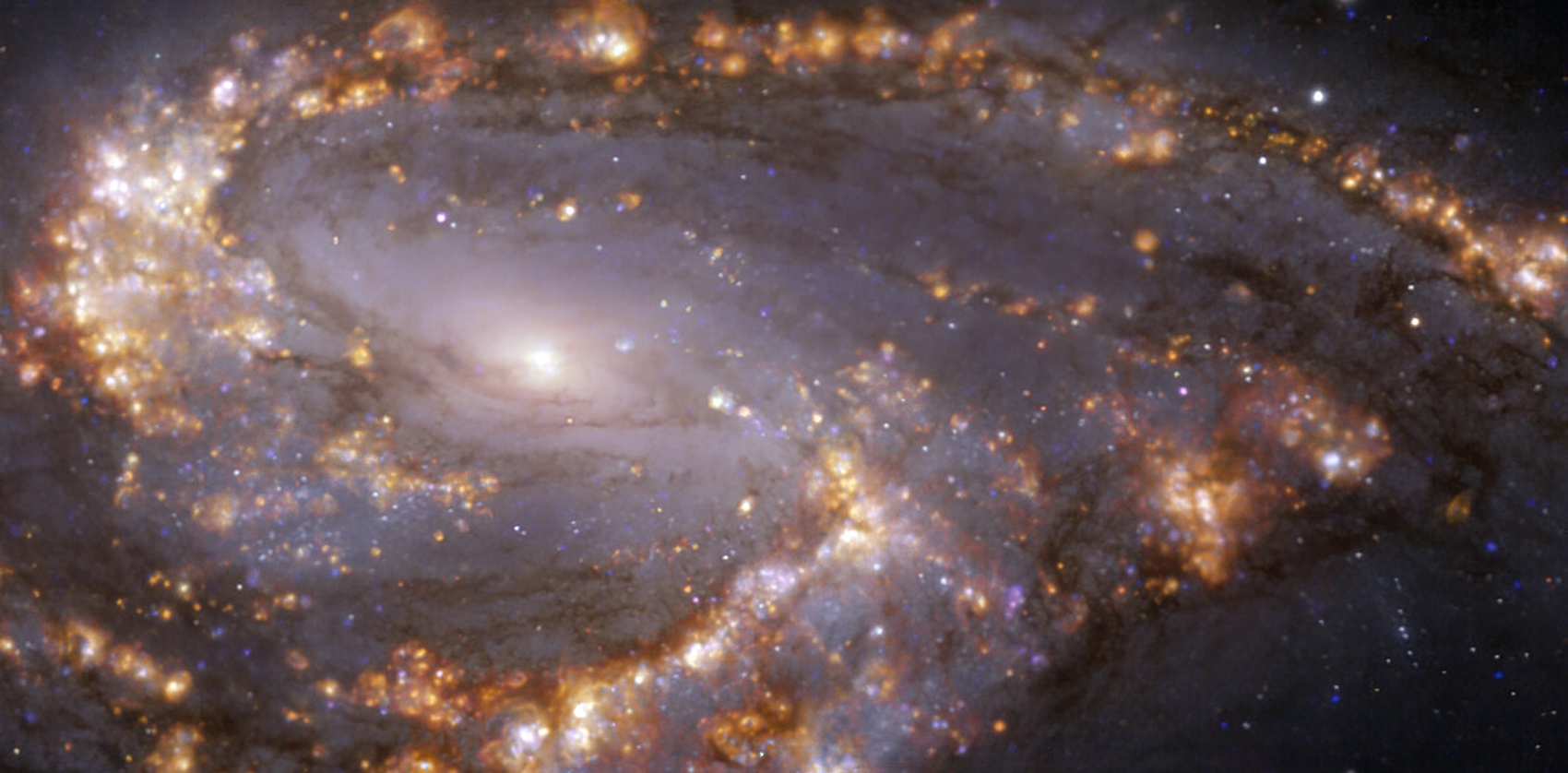

I’d never seen galaxy images like this before. Nobody had! These images highlight star forming regions in nearby(ish) galaxies. There are still a number of unanswered questions surrounding how star formation actually occurs. To answer those questions, we are observing galaxies that are actively forming stars within giant clouds of gas. Until recently, we didn’t have the resolution needed to clearly image the individual gas clouds themselves. But images released by a project called PHANGS (Physics at High Angular resolution in Nearby GalaxieS) in a collaboration between the European Southern Observatory Very Large Telescope and the Atacama Large millimeter/submillmeter Array (ALMA) have provided never before seen detail of star forming clouds in other galaxies.

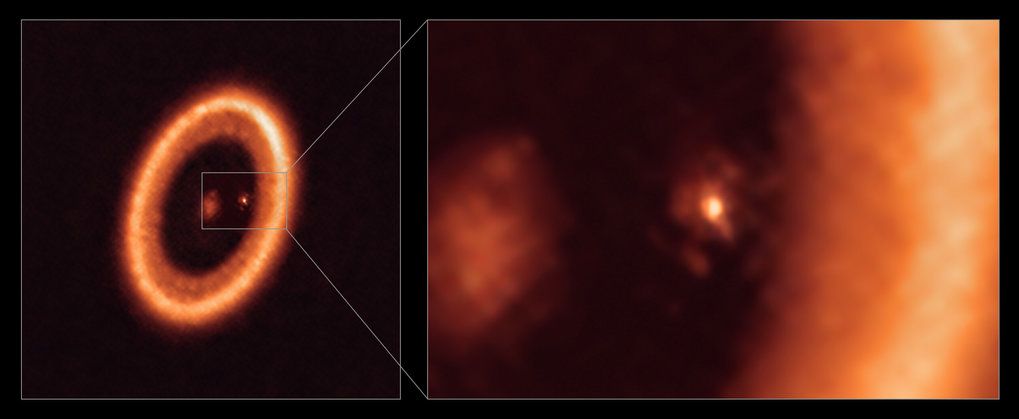
Incredible! Astronomers see a Moon-Forming Disk Around a Newly Forming Planet
Planetary formation is a complicated, multilayered process. Even with the influx of data on exoplanets, there are still only two known planets that are not yet fully formed. Known as PDS 70b and PDS 70c, the two planets, which were originally found by the Very Large Telescope, are some of the best objects we have to flesh out our planetary formation models. And now, one of them has been confirmed to have a moon-forming disk around it.
Continue reading “Incredible! Astronomers see a Moon-Forming Disk Around a Newly Forming Planet”Astronomers Think They’ve Found the Neutron Star Remnant Left Behind from Supernova 1987A
It was the brightest supernova in nearly 400 years when it lit the skies of the southern hemisphere in February 1987. Supernova 1987A – the explosion of a blue supergiant star in the nearby mini-galaxy known as the Large Magellanic Cloud – amazed the astronomical community. It offered them an unprecedented opportunity to observe an exploding star in real-time with modern instruments and telescopes. But something was missing. After the supernova faded, astronomers expected to find a neutron star (a hyper-dense, collapsed stellar core, made largely of neutrons) left-over at the heart of the explosion. They saw nothing.
Continue reading “Astronomers Think They’ve Found the Neutron Star Remnant Left Behind from Supernova 1987A”What Looked Like Phosphine On Venus Might Actually Just Be Sulfur Dioxide
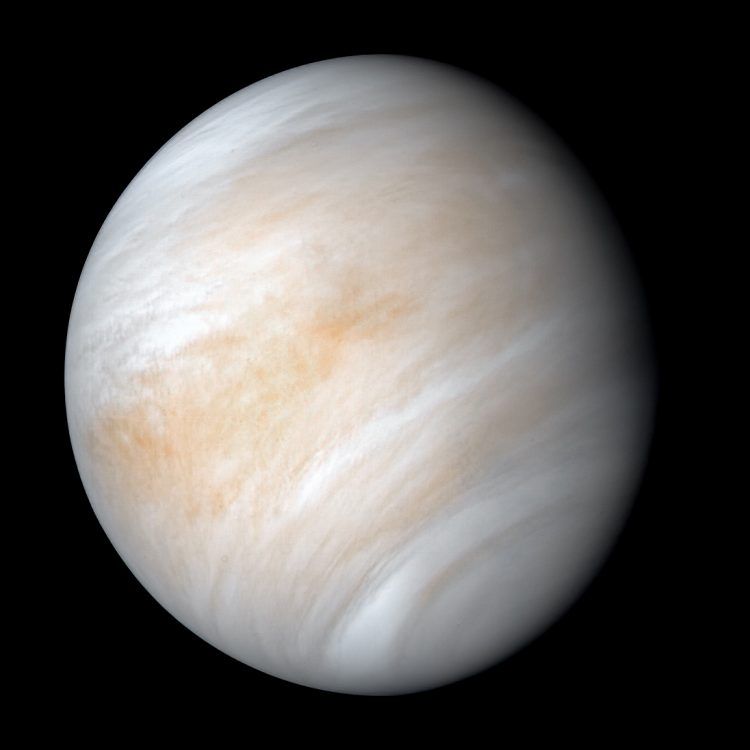
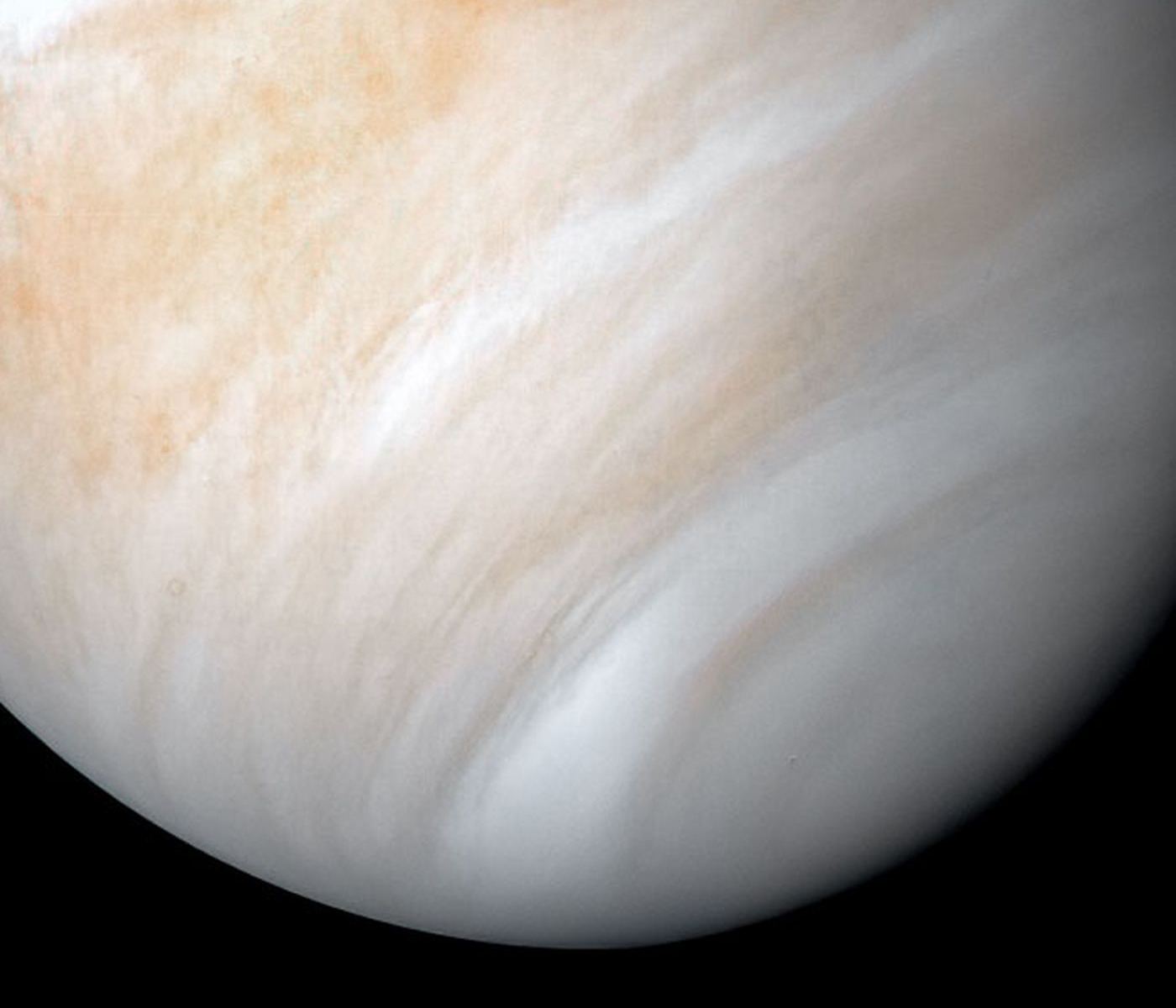
There’s nothing like a good old fashioned science fight. When the discovery being challenged is one of the most public and intriguing of the last year, it’s bound to be even more interesting. A team of scientists, led by Andrew Lincowski and Victoria Meadows at the University of Washington (UW), and involving members from a variety of NASA labs and other universities, has challenged the discovery of phosphine in the atmosphere of Venus that was first announced last year. Their explanation is much simpler: it was most likely sulfur dioxide, one of the most abundant materials already known to be in Venus’ atmosphere.
Continue reading “What Looked Like Phosphine On Venus Might Actually Just Be Sulfur Dioxide”Astronomers are now Finding Planetary Disks Around the Smallest, Least Massive Stars
Astronomers have been watching planetary systems form around sun-like stars for decades. And now, new observations with the ALMA telescope reveal the same process playing out around the smallest, but most common, stars in galaxy.
Continue reading “Astronomers are now Finding Planetary Disks Around the Smallest, Least Massive Stars”Scientists Have Re-Analyzed Their Data and Still See a Signal of Phosphine at Venus. Just Less of it
In September, an international team announced that based on data obtained by the Atacama Millimeter-submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile and the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope (JCMT) in Hawaii, they had discovered phosphine gas (PH3) in the atmosphere of Venus. The news was met with its fair share of skepticism and controversy since phosphine is considered a possible indication of life (aka. a biosignature).
Shortly thereafter, a series of papers were published that questioned the observations and conclusions, with one team going as far as to say there was “no phosphine” in Venus’ atmosphere at all. Luckily, after re-analyzing the ALMA data, the team responsible for the original discovery concluded that there is indeed phosphine in the cloud tops of Venus – just not as much as they initially thought.
Continue reading “Scientists Have Re-Analyzed Their Data and Still See a Signal of Phosphine at Venus. Just Less of it”Titan’s Atmosphere Has All the Ingredients For Life. But Not Life as We Know It
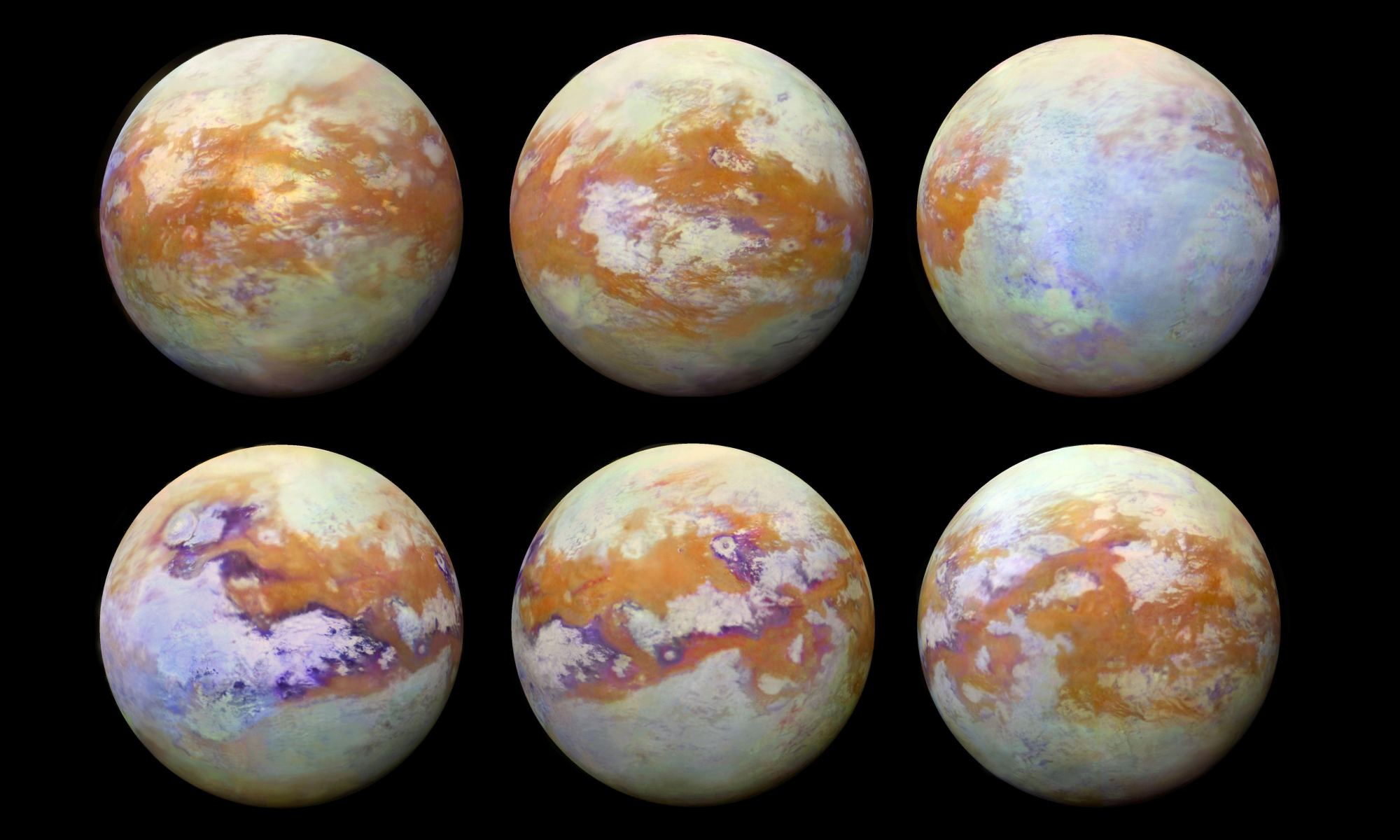
Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), a team of scientists has identified a mysterious molecule in Titan’s atmosphere. It’s called cyclopropenylidene (C3H2), a simple carbon-based compound that has never been seen in an atmosphere before. According to the team’s study published in The Astronomical Journal, this molecule could be a precursor to more complex compounds that could indicate possible life on Titan.
Similarly, Dr. Catherine Neish of the University of Western Ontario’s Institute for Earth and Space Exploration (Western Space) and her colleagues in the European Space Agency (ESA) found that Titan has other chemicals that could be the ingredients for exotic life forms. In their study, which appeared in Astronomy & Astrophysics, they present Cassini mission data that revealed the composition of impact craters on Titan’s surface.
Continue reading “Titan’s Atmosphere Has All the Ingredients For Life. But Not Life as We Know It”