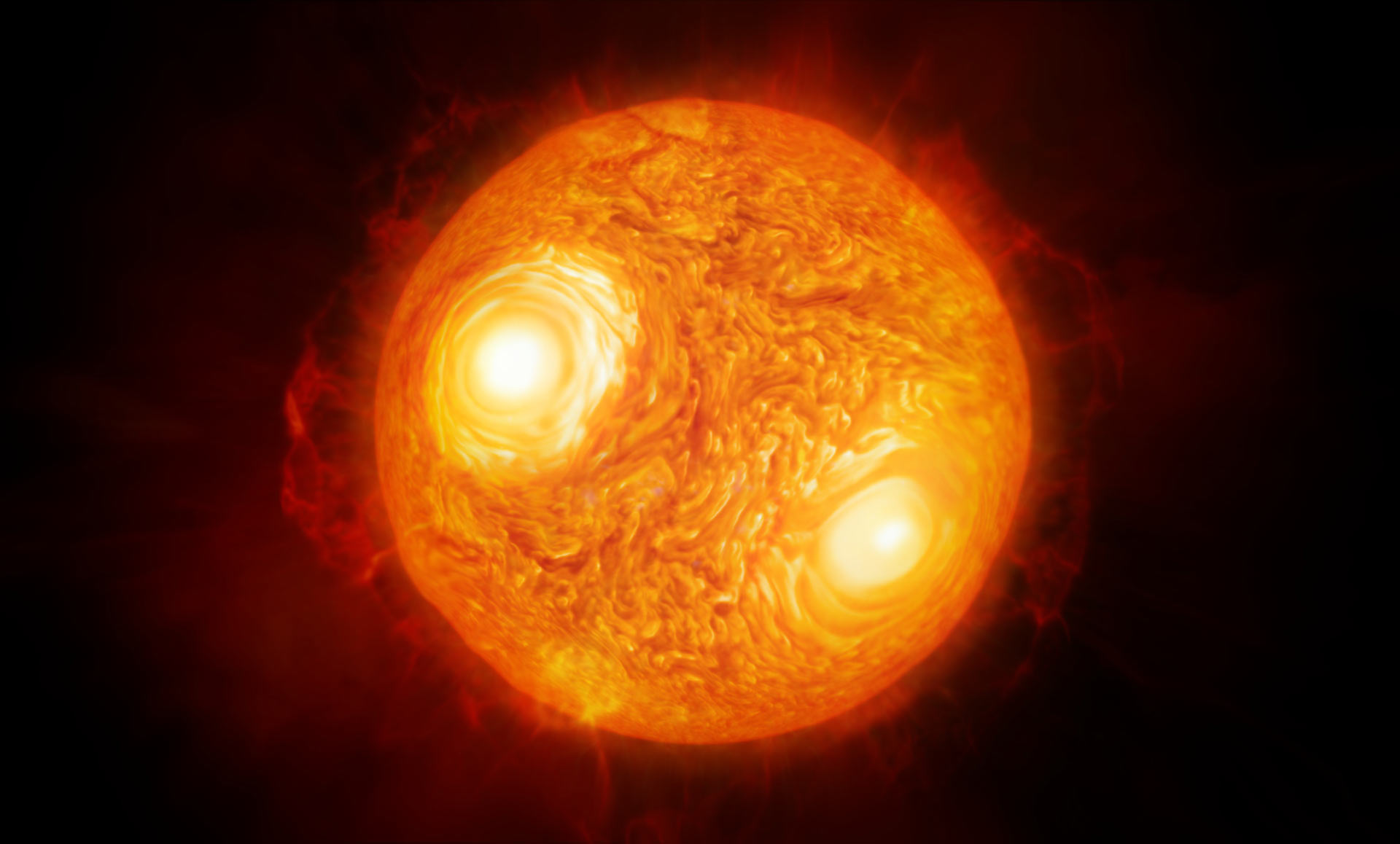
Stars don’t usually evolve fast enough for humans to notice them change within one lifetime. Even a hundred lifetimes won’t do – astronomical processes are just too slow. But not always. There are some phases of stellar evolution that happen quickly, and when they do, they can be tracked. A new paper posted to ArXiv last week uses astronomical observations found in ancient Roman texts, medieval astronomical logs, and manuscripts from China’s Han Dynasty to trace the recent evolution of several bright stars, including red supergiant Antares, and Betelgeuse: one of the most dynamic stars in our sky. With observations from across the historical record, the paper suggests that Betelgeuse may have just recently passed through the ‘Hertzsprung gap,’ the transitional phase between a main sequence star and its current classification as a red supergiant.
Continue reading “Betelgeuse and Antares Have Been Observed for Over 2,000 Years. Astronomers can use This to Figure out how old They are”Antares is a supergiant star that would fill the Solar System beyond Mars, but its atmosphere is 12 times bigger than that

Antares, the angry red eye of the constellation Taurus the bull, is a red supergiant star near the end of its life. And astronomers with the VLA and ALMA have realized that it’s much, much bigger than we ever imagined.
Continue reading “Antares is a supergiant star that would fill the Solar System beyond Mars, but its atmosphere is 12 times bigger than that”Antares Rocket Blasts Off from Virginia Bound for Space Station with Cygnus Cargo Ship and Tons of Vital Science Supplies
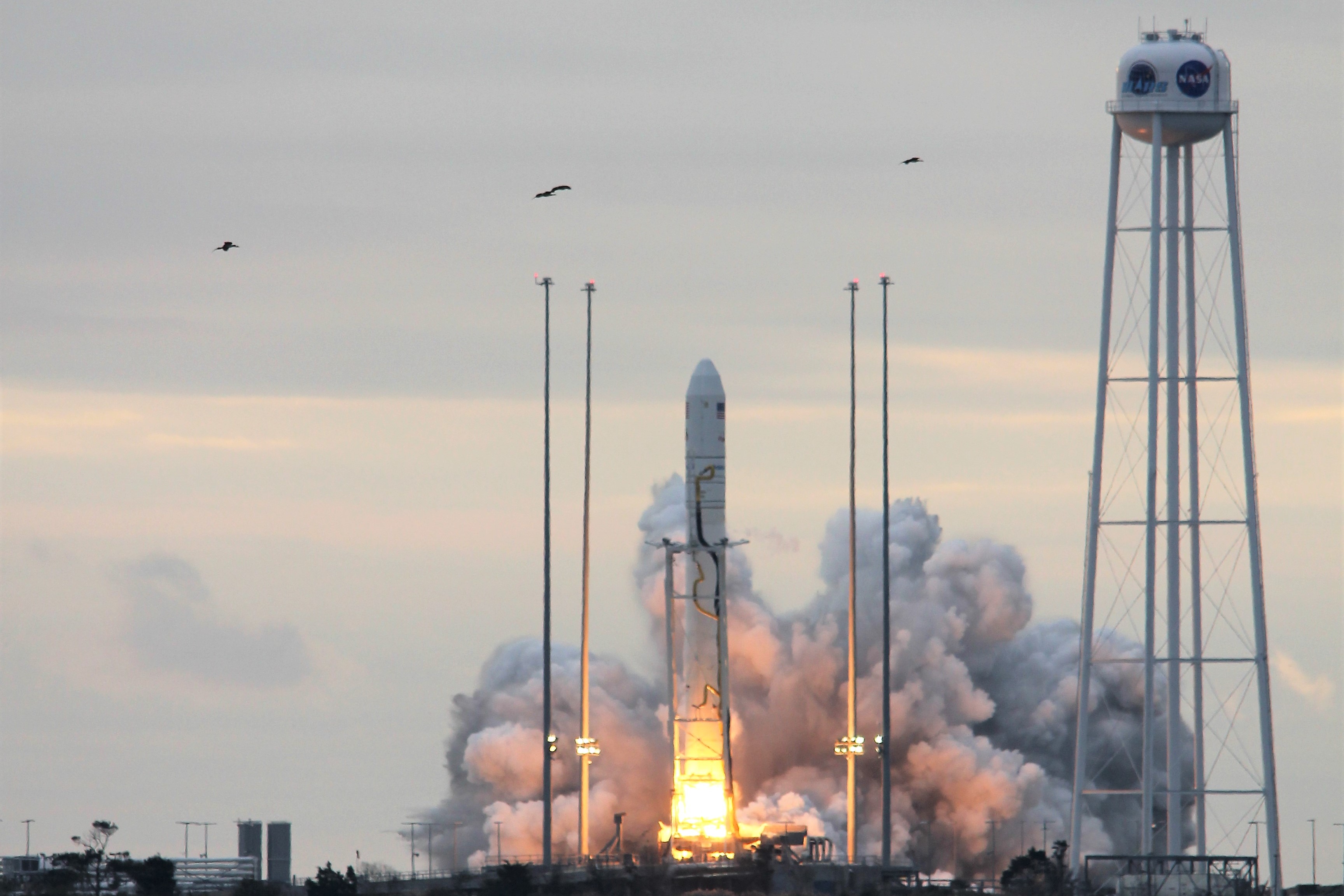


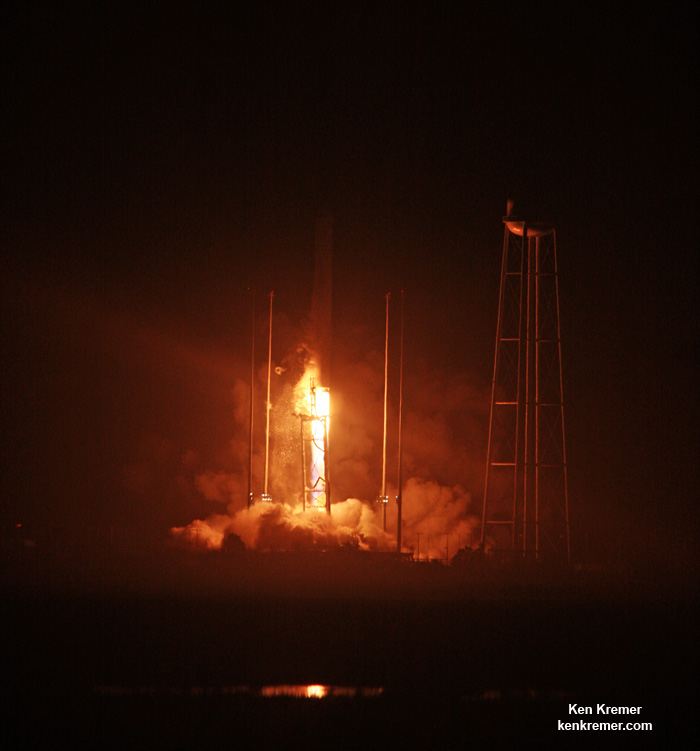
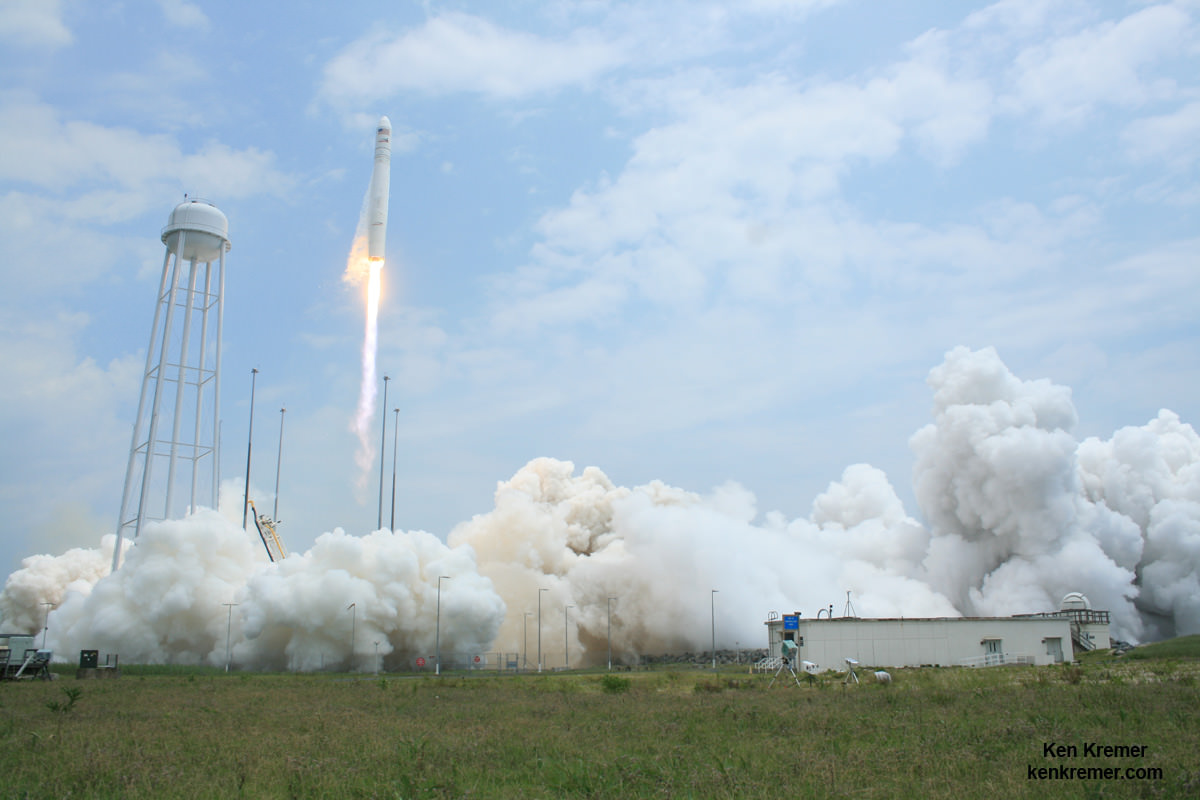
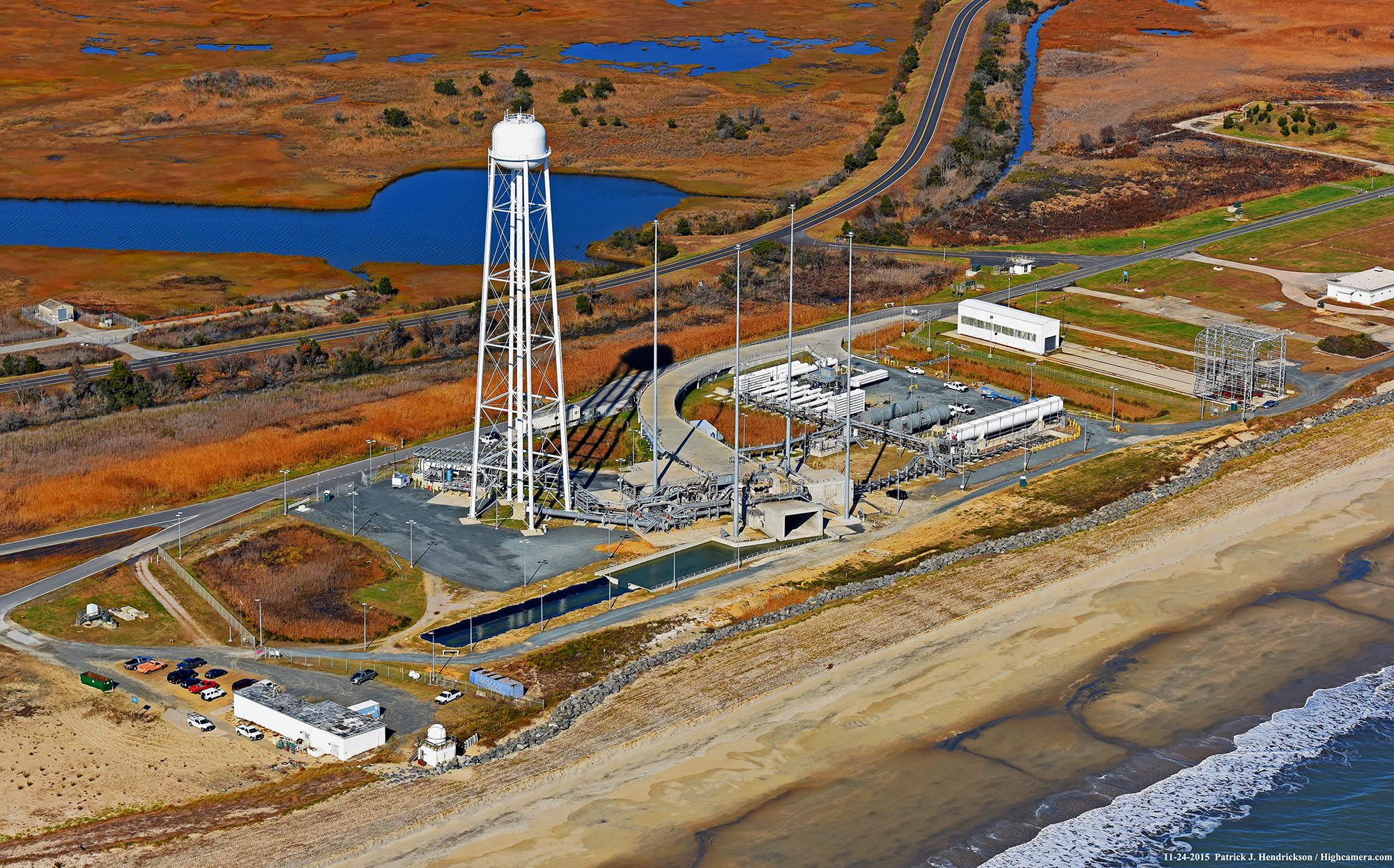
NASA WALLOPS FLIGHT FACILITY, VA – An Orbital ATK Antares rocket successfully blasted off this morning, Sunday, Nov. 12, from the eastern shore of Virginia on a NASA contracted mission bound for the International Space Station (ISS) carrying a Cygnus cargo ship loaded with nearly 4 tons of vital science and supplies.
The two stage Antares rocket launched flawlessly shortly sunrise Sunday at 7:19 a.m. EST, Nov. 12 on an upgraded version of the Antares rocket from Pad-0A at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia carrying the Cygnus resupply spacecraft named in honor of Gene Cernan, the last man to walk on the Moon.
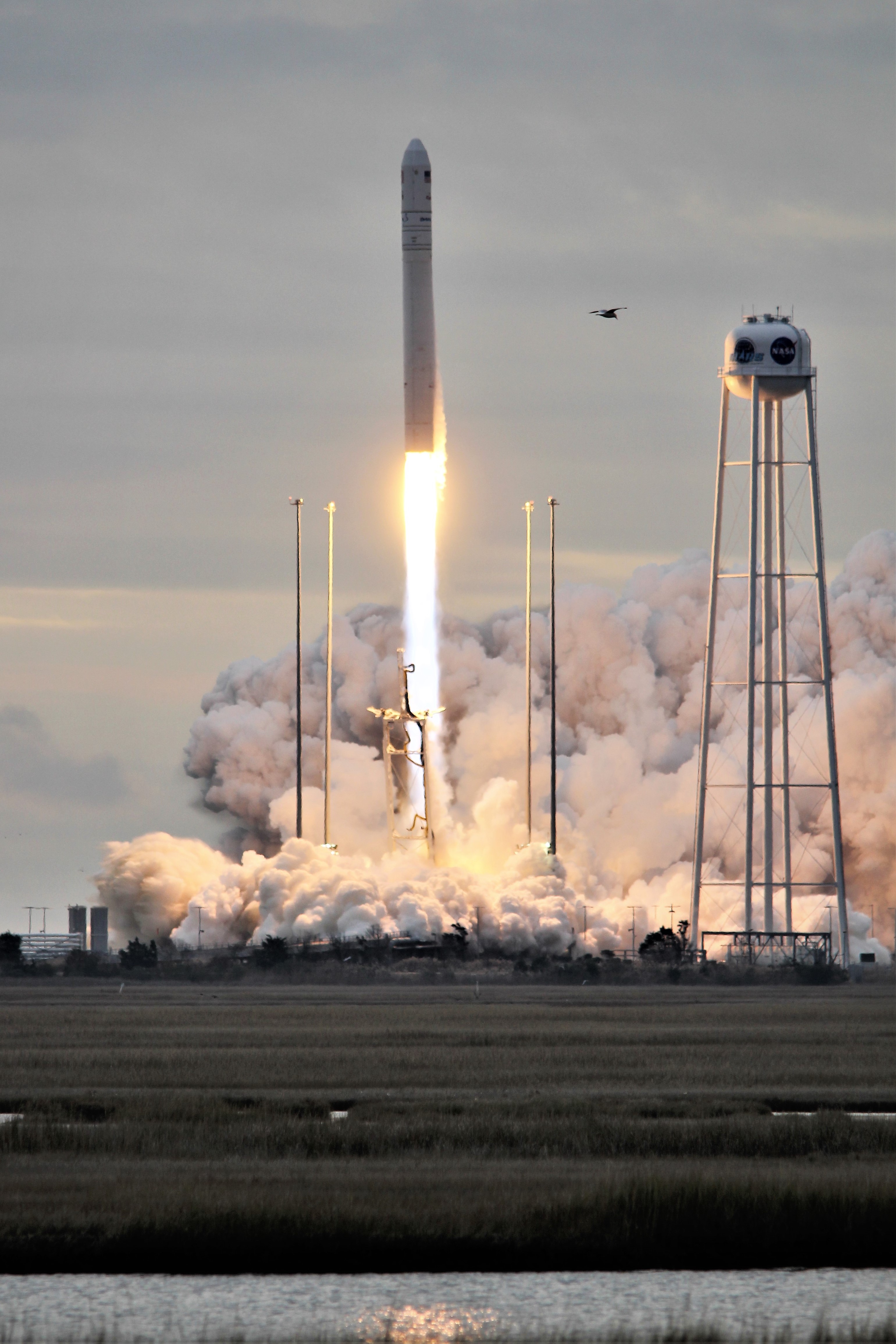

The launch came a day late due to a last moment scrub on the originally planned Veteran’s Day liftoff, Saturday, Nov. 11, when a reckless pilot flew below radar into restricted airspace just 5 miles away from the launch pad – forcing a sudden and unexpected halt to the countdown under absolutely perfect weather conditions.
Finally the rocket roared off the pad Sunday under cloudy skies – to the delight of a spectators, with a brilliant flash of light. Slowly at first and then accelerating almost straight up before arcing over just slightly in a southeasterly direction and soon disappearing into the thick clouds. In fact it was so load that local residents told me their windows and houses shook and rattled.
Saturday’s sudden scrub disappointed tens of thousands of spectators who had gathered around the East coast launch region and beyond for a rare chance to see the launch of a powerful rocket on a critical cargo delivery mission for NASA conducted the benefit of the six person crew serving on the station to advance science for all of humanity.
The pilot may have intentionally flown the plane low enough to avoid detection so he could take photos for profit.
As a result of this extremely serious violation of flight rules which raises significant safety and base security issues the FAA and NASA are now undertaking an intense review of rules after the repeated serious incursions by planes and boats into exclusion zones during launches, and what penalties and fines should be applied.

The Cygnus spacecraft dubbed OA-8 is Orbital ATK’s eighth contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA to the International Space Station under the unmanned Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) program to stock the station with supplies on a continuing and reliable basis.
“Today’s successful launch of the OA-8 Cygnus on our Antares launch vehicle once again demonstrates the reliability of Orbital ATK’s hardware along with our commitment to deliver critical cargo to astronauts on the International Space Station,” said Frank Culbertson, President of Orbital ATK’s Space Systems Group.
“Soon, Cygnus will rendezvous with the space station to deliver valuable scientific experiments, hardware and crew supplies to the orbiting platform. On this mission, Cygnus will again display its flexibility as an in-orbit science platform by supporting experiments to be performed inside the cargo module while attached to the space station. We are proud to dedicate this mission to Apollo astronaut Gene Cernan and his family and look forward to celebrating the OA-8 contributions to science in his name.”
After a two day orbital chase the S.S. Gene Cernan will arrive in the vicinity of the space station early Tuesday, Nov. 14. Cygnus will be grappled by Expedition 53 astronaut Paolo Nespoli of ESA (European Space Agency) of Italy at approximately 4:50 a.m. EST on November 14 using the space station’s robotic arm. He will be assisted by NASA astronaut Randy Bresnik.
NASA TV will provide live coverage of the rendezvous and grappling.
Cygnus will remain at the space station until Dec. 4, when the spacecraft will depart the station and deploy several CubeSats before its fiery re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere as it disposes of several tons of trash.
The 14 story tall commercial Antares rocket launched for only the second time in the upgraded 230 configuration – powered by a pair of the new Russian-built RD-181 first stage engines.
The rocket performed flawlessly said Kurt Eberly, Orbital ATK deputy program manager for Antares, during the post launch briefing at NASA Wallops.
There was only a slight over performance of the Castor XL solid fueled second stage, which was all to the good – as occurred during the first launch of the upgraded Antares a year ago in October 2016 on the OA-5 resupply mission.
Indeed the overperformance of the second stage may allow Orbital ATK to load the Cygnus with an even heavier cargo load than previously foreseen.
On this flight,the Cygnus OA-8 spacecraft is jam packed with its heaviest cargo load to date!
Altogether over 7,400 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware launched to the orbital laboratory and its crew of six for investigations that will occur during Expeditions 53 and 54.
The S.S. Gene Cernan manifest includes equipment and samples for dozens of scientific investigations including those that will study communication and navigation, microbiology, animal biology and plant biology. The ISS science program supports over 300 ongoing research investigations.
Cernan was commander of the Apollo 17, NASA’s last lunar landing mission and passed away in January at age 82. He set records for both lunar surface extravehicular activities and the longest time in lunar orbit on Apollo 10 and Apollo 17.
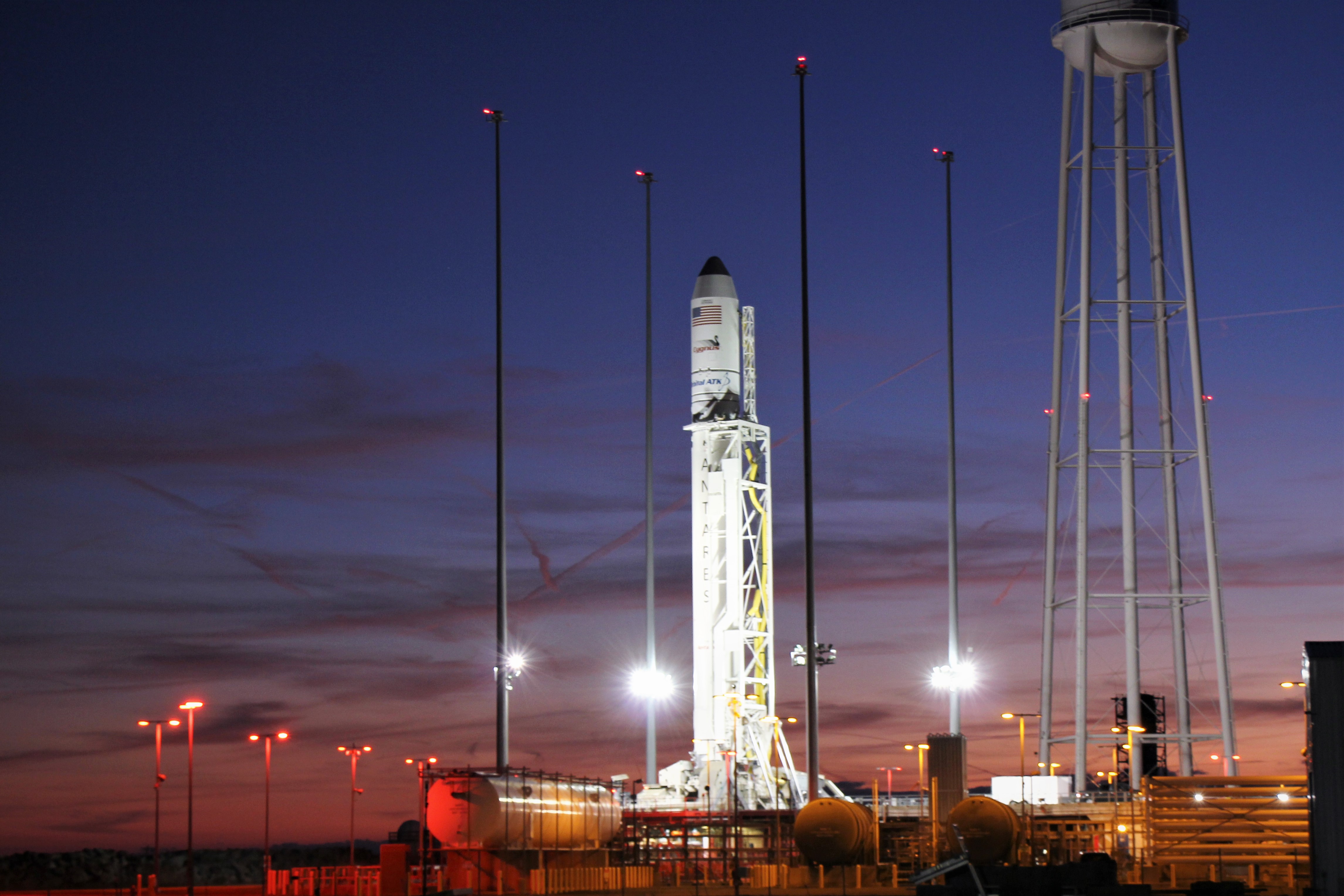

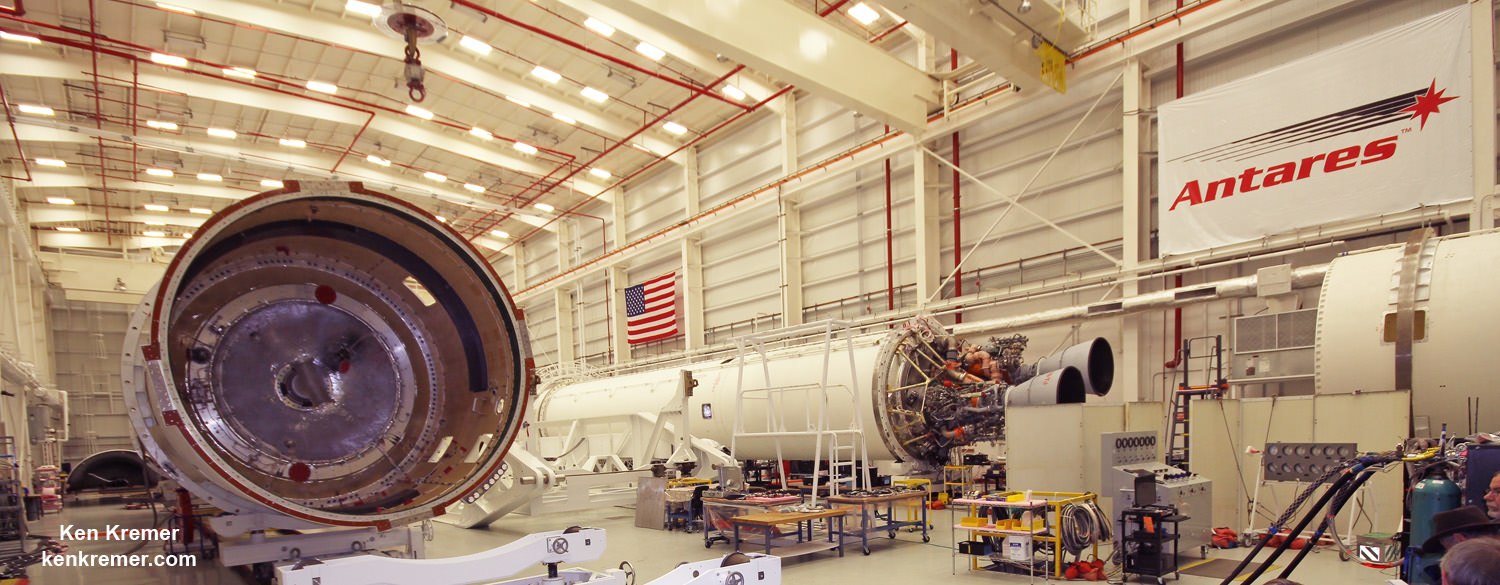
The 139-foot-tall (42.5-meter) Antares rocket had been rolled out to the launch pad around 1 a.m. EST Thursday morning, Nov. 9, and erected as planned into the vertical position, Kurt Eberly, Orbital ATK deputy program manager for Antares, told Universe Today.
The Cygnus OA-8 spacecraft is Orbital ATK’s eighth contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA to the International Space Station under the unmanned Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) program to stock the station with supplies on a continuing basis.
Under the Commercial Resupply Services-1 (CRS-1) contract with NASA, Orbital ATK will deliver approximately 66,000 pounds (30,000 kilograms) of cargo to the space station. OA-8 is the eighth of these missions.
Beginning in 2019, the company will carry out a minimum of six cargo missions under NASA’s CRS-2 contract using a more advanced version of Cygnus.

Watch for Ken’s continuing Antares/Cygnus mission and launch reporting from on site at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, VA during the launch campaign.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
Orbital ATK Antares Rocket Set for Breakfast Blastoff from Virginia to Space Station with S.S. Gene Cernan Cargo Freighter Nov. 11: Watch Live


NASA WALLOPS FLIGHT FACILITY, VA – The Orbital ATK Antares rocket is all set for a breakfast time blastoff from the commonwealth of Virginia to the International Space Station for NASA with a Cygnus cargo freighter named in honor of Gene Cernan, the last man to walk on the Moon.
The Antares launch is targeted for 7:37 a.m. EST on Saturday, Nov. 11, 2017 carrying the S.S. Gene Cernan resupply vessel that’s loaded with nearly four tons of science and supplies for the six person crew serving on the station.
Antares liftoff with the Cygnus spaceship also known as OA-8 will take place from launch Pad-0A at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility located along the eastern shore of Virginia.

The rocket was integrated with the Cygnus OA-8 supply ship this week and rolled out to the launch pad starting around 1 a.m. EST this morning Thursday, Nov. 9.
The Cygnus OA-8 spacecraft is Orbital ATK’s eighth contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA to the International Space Station under the unmanned Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) program to stock the station with supplies on a continuing basis.
The upgraded Antares rocket was erected into the vertical position and is now poised for liftoff early Saturday morning.
Tens of millions of spectators could potentially witness the launch with their own eyeballs since NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility is located within a short driving distance of the most heavily populated area of the United States along the eastern seaboard.
Since Saturdays weather forecast is quite favorable at this time this could be your chance to watch an exciting launch on a critical mission for NASA with your family or friends.
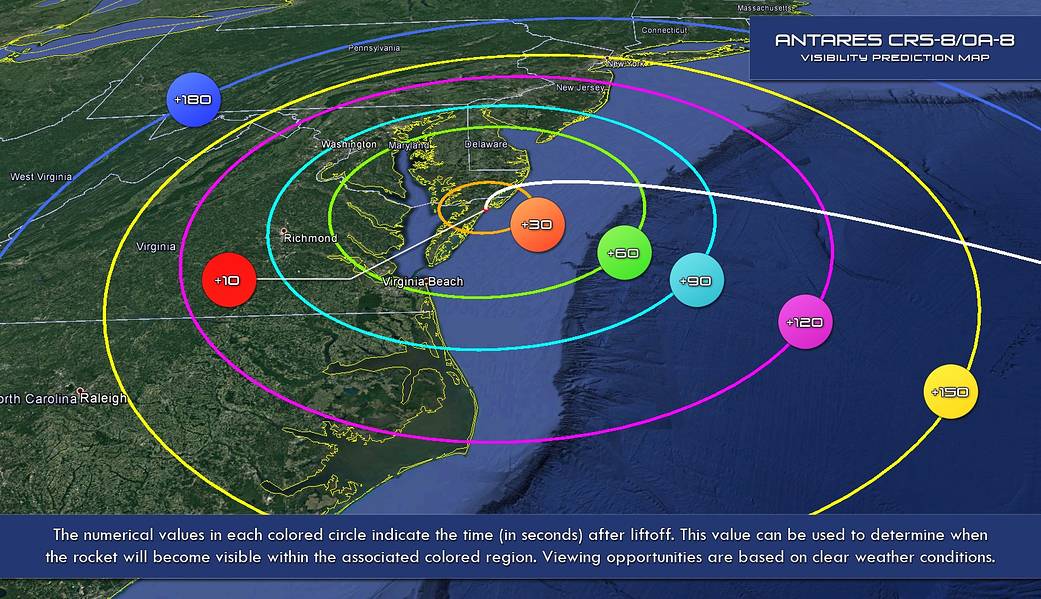
See detailed visibility map below.
But be aware that temperatures will be rather chilly, setting record or near record lows in the 20s throughout the Northeast and Atlantic coast states.
If you are wondering whether to watch, consider that Antares launches are infrequent.
The last Antares launch from Wallops took place a year ago on 23 October 2016 for the OA-5 cargo resupply mission to the ISS for NASA.
If you can’t watch the launch in person, you can always follow along via NASA’s live coverage.
Live launch coverage will begin at 7 a.m. Saturday on NASA Television and the agency’s website: www.nasa.gov
The launch window opens at 7:37 a.m. EST.
The windows runs for five minutes extending to 7:42 a.m. EST.

The 14 story tall commercial Antares rocket will launch for only second first time in the upgraded 230 configuration – powered by a pair of the new Russian-built RD-181 first stage engines.
The Cygnus spacecraft will deliver over 7,400 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew of six for investigations that will occur during Expeditions 53 and 54.
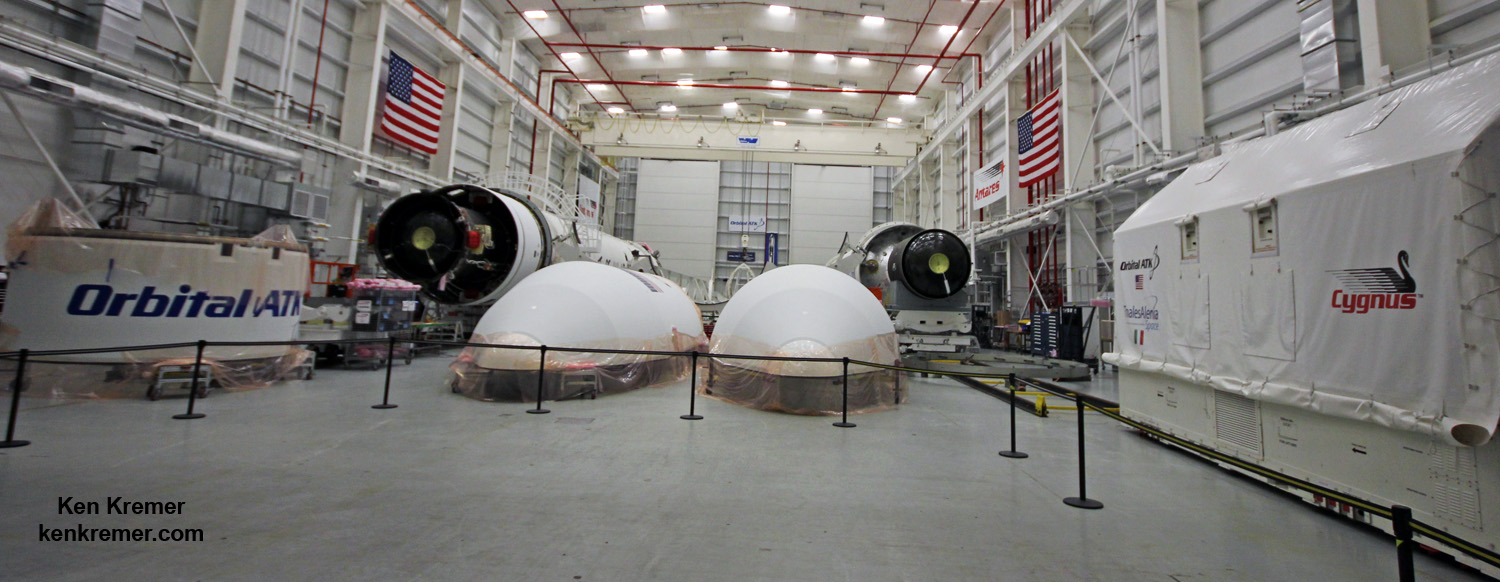

The S.S. Gene Cernan manifest includes equipment and samples for dozens of scientific investigations including those that will study communication and navigation, microbiology, animal biology and plant biology. The ISS science program supports over 250 ongoing research investigations.
Among the science: “Cygnus will carry several CubeSats that will conduct a variety of missions, from technology demonstrations of laser communication and increased data downlink rates to an investigation to study spaceflight effects on bacterial antibiotic resistance. Other experiments will advance biological monitoring aboard the station and look at various elements of plant growth in microgravity that may help inform plant cultivation strategies for future long-term space missions. The spacecraft will also transport a virtual reality camera to record a National Geographic educational special on Earth as a natural life-support system.”
“Orbital ATK is proud to name the OA-8 Cygnus Cargo Delivery Spacecraft after former astronaut Eugene “Gene” Cernan,” said Orbital ATK.
“As the last human to step foot on the moon, Cernan set records for both lunar surface extravehicular activities and longest time in lunar orbit, paving the way for future human space exploration. He died in January 2017.”
The last Cygnus was named the S.S. John Glenn, first American to orbit Earth, and launched atop a ULA Atlas V in March 2017.
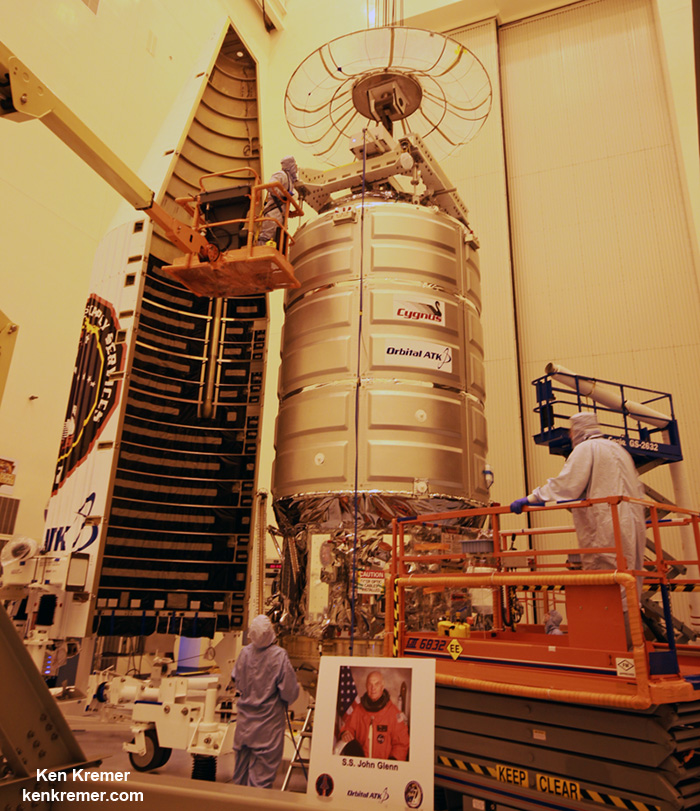
After a two day orbital chase Cygnus will reach the stations vicinity on Monday, Nov. 13.
“Expedition 53 Flight Engineers Paolo Nespoli of ESA (European Space Agency) and Randy Bresnik of NASA will use the space station’s robotic arm to capture Cygnus at about 5:40 a.m. NASA TV coverage of rendezvous and capture will begin at 4:15 a.m.,” said NASA.
“After Canadarm2 captures Cygnus, ground commands will be sent to guide the station’s robotic arm as it rotates and attaches the spacecraft to the bottom of the station’s Unity module. Coverage of installation will begin at 7 a.m.”
“Cygnus will remain at the space station until Dec. 4, when the spacecraft will depart the station and deploy several CubeSats before its fiery reentry into Earth’s atmosphere as it disposes of several tons of trash.”
Under the Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract with NASA, Orbital ATK will deliver approximately 28,700 kilograms of cargo to the space station. OA-8 is the eighth of these missions.

Watch for Ken’s continuing Antares/Cygnus mission and launch reporting from on site at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, VA during the launch campaign.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.


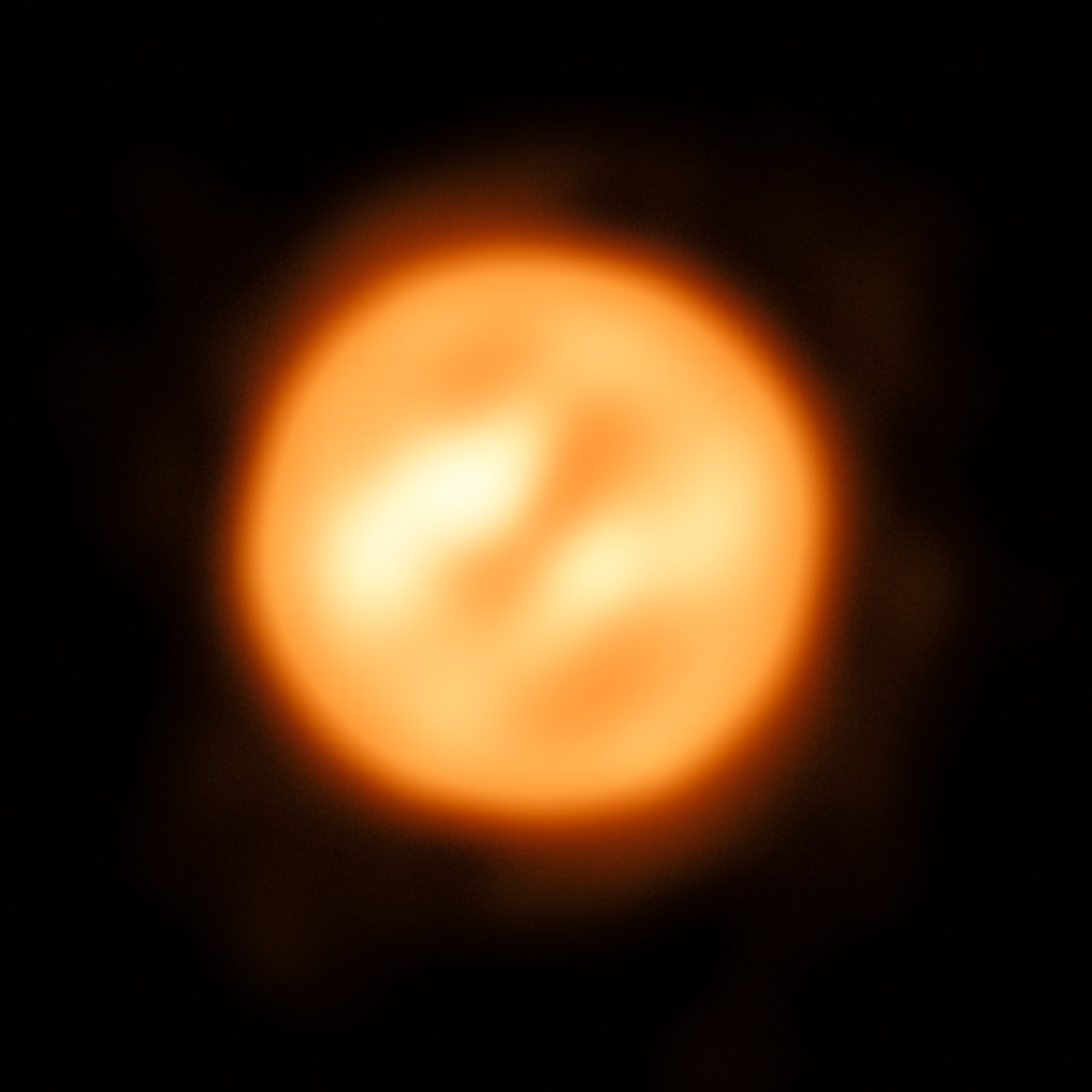
New Study of Antares Creates the Best Map Ever of a Distant Star

When stars exhaust their supply of hydrogen fuel, they exit the main sequence phase of their evolution and enter into what is known as the Red Giant Branch (RGB) phase. This is characterized by the stars expanding significantly and becoming tens of thousands of times larger than our Sun. They also become dimmer and cooler, which lends them a reddish-orange appearance (hence the name).
Recently, a team of astronomers used the ESO’s Very Large Telescope Interferometer (VLTI) to map one such star, the red supergiant Antares. In so doing, they were able to create the most detailed map of a star other than our Sun. The images they took also revealed some unexpected things about this supergiant star, all of which could help astronomers to better understand the dynamics and evolution of red giant stars.
The study which details their work, titled “Vigorous Atmospheric Motions in the Red Supergiant Supernova Progenitor Antares“, recently appeared in the journal Nature. As indicated in the study, the team – which was led by Keiichi Ohnaka, an associate professor at the UCN Institute of Astronomy in Chile = relied on the VLTI at the ESO’s Paranal Observatory in Chile to map Antares’s surface and measure the motions of its surface material.

The purpose of their study was to chart how stars that have entered their RGB phase begin to change. The VLTI is uniquely suited to this task, since it is capable of combining light from four different telescopes – the 8.2-metre Unit Telescopes, or the smaller Auxiliary Telescopes – to create one virtual telescope that has the resolution of a telescope lens measuring 200 meters across.
This allows the VLTI to resolve fine details far beyond what can be seen with a single telescope. As Prof. Ohnaka explained in a recent ESO press statement:
“How stars like Antares lose mass so quickly in the final phase of their evolution has been a problem for over half a century. The VLTI is the only facility that can directly measure the gas motions in the extended atmosphere of Antares — a crucial step towards clarifying this problem. The next challenge is to identify what’s driving the turbulent motions.”
For their study, the team relied on three of the VLTI Auxiliary Telescopes and an instrument called the Astronomical Multi-BEam combineR (AMBER). This near-infrared spectro-interferometric instrument combines three telescopic beams coherently, allowing astronomers to measure the visibilities and closure phases of stars. Using these instruments, the team obtained images of Antares’ surface over a small range of infrared wavelengths.
From these, the team was able to calculate the difference between the speed of atmospheric gas at different locations on Antares’ surface, as well as its average speed over the entire surface. This resulted in a two-dimensional velocity map of Antares, which is the first such map created of another star other than the Sun. As noted, it is also the most-detailed map of any star beyond our Solar System to date.
The study also made some interesting discoveries of what takes place on Antares’ surface and in its atmosphere. For example, they found evidence for high-speed upwellings of gas that reached distances of up to 1.7 Solar radii into space – much farther than previously thought. This, they claimed, could not be explained by convection alone, the process whereby cold material moves downwards and hot material upwards in a circular pattern.
This process occurs on Earth in the atmosphere and with ocean currents, but it is also responsible for moving pockets of hotter and colder gas around within stars. The fact that convection cannot explain the behavior of Antares extended atmosphere would therefore suggests that some new and unidentified process common to red giant stars must be responsible.
These results therefor offer new opportunities for research into stellar evolution, which is made possible thanks to next-generation instruments like the VTLI. As Ohnaka concluded:
“In the future, this observing technique can be applied to different types of stars to study their surfaces and atmospheres in unprecedented detail. This has been limited to just the Sun up to now. Our work brings stellar astrophysics to a new dimension and opens an entirely new window to observe stars.”
NASA Targets ‘Return to Flight’ of Upgraded Antares for mid-October for Station Resupply


NASA is targeting mid-October for the ‘Return to Flight’ launch of the upgraded Orbital ATK Antares rocket on a cargo mission to resupply the International Space Station (ISS) for the first time in nearly two years.
The 14 story tall commercial Antares rocket will launch for the first time in the upgraded 230 configuration powered by new Russian-built first stage engines.
In light of the grounding of the SpaceX Falcon 9 and Dragon cargo flights following the catastrophic Sept.1 launch pad disaster,and the catastrophic Antares launch failure in Oct. 2014, this Orbital ATK mission becomes more critical than ever to keep the space station stocked and fully operational for the resident crews with a reliable American supply train.
NASA and Orbital ATK announced that the re-engined Antares will launch during a five-day launch window that opens no earlier than October 9-13, 2016 on the OA-5 Cygnus cargo mission from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility on Virginia’s picturesque Eastern shore.
“A more specific date will be identified upon completion of final operational milestones and technical reviews,” according to statements from NASA and Orbital ATK.
If Antares launches on Oct. 9, liftoff is set 10:47 p.m. EDT and becomes progressively earlier on succeeding days. The launch time moves up to 9:13 p.m. EDT on Oct. 13.
If the launch takes place during this window, it will mark the first truly nighttime launch for Antares from Virgina.
“The arrival and berthing of Cygnus to the International Space Station will be determined by the exact launch date and in coordination with other space station activities,” says NASA.
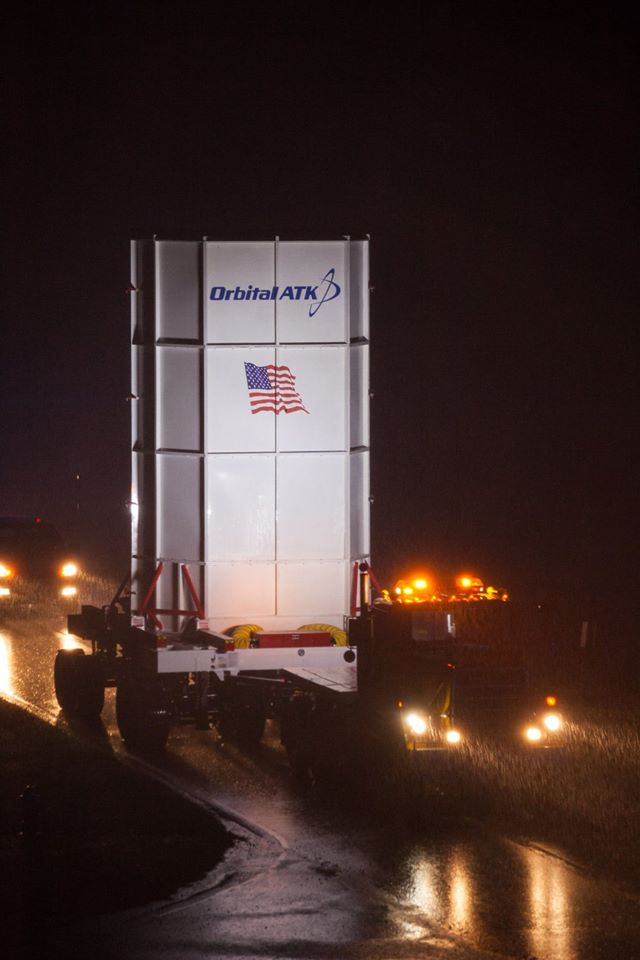

The Cygnus cargo spacecraft was moved this week from the NASA Wallops payload processing facility to the spacecraft fueling facility on Wallops Island.
The next step is to integrate Cygnus onto the Orbital ATK Antares 230 rocket inside the HIF (Horizontal Integration Facility) in anticipation of the launch slated for no earlier than Oct. 9 at 10:47 p.m. EDT.
The Antares 230 medium-class commercial launch vehicle rocket has been upgraded with new first stage Russian-built RD-181 engines fueled by LOX/kerosene – that had to be fully validated before launching NASA’s precious cargo to the International Space Station (ISS).
For the OA-5 mission, the Cygnus advanced maneuvering spacecraft will be loaded with approximately 2,400 kg (5,290 lbs.) of supplies and science experiments for the International Space Station (ISS).
Under the Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract with NASA, Orbital ATK will deliver approximately 28,700 kilograms of cargo to the space station. OA-5 is the sixth of these missions.
Orbital ATK’s Antares commercial rocket had to be overhauled with completely new first stage engines following the catastrophic launch failure nearly two years ago on October 28, 2018 just seconds after blastoff that doomed the Orb-3 resupply mission to the space station.
The goal of the Antares ‘Return to Flight’ mission is to launch Orbital ATK’s Cygnus cargo freighter on the OA-5 resupply mission for NASA to the ISS and restore the Antares rocket to flight status.
To that end the aerospace firm completed a successful 30 second long test firing of the re-engined first stage on May 31 at Virginia Space’s Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Launch Pad 0A – as I reported here earlier.
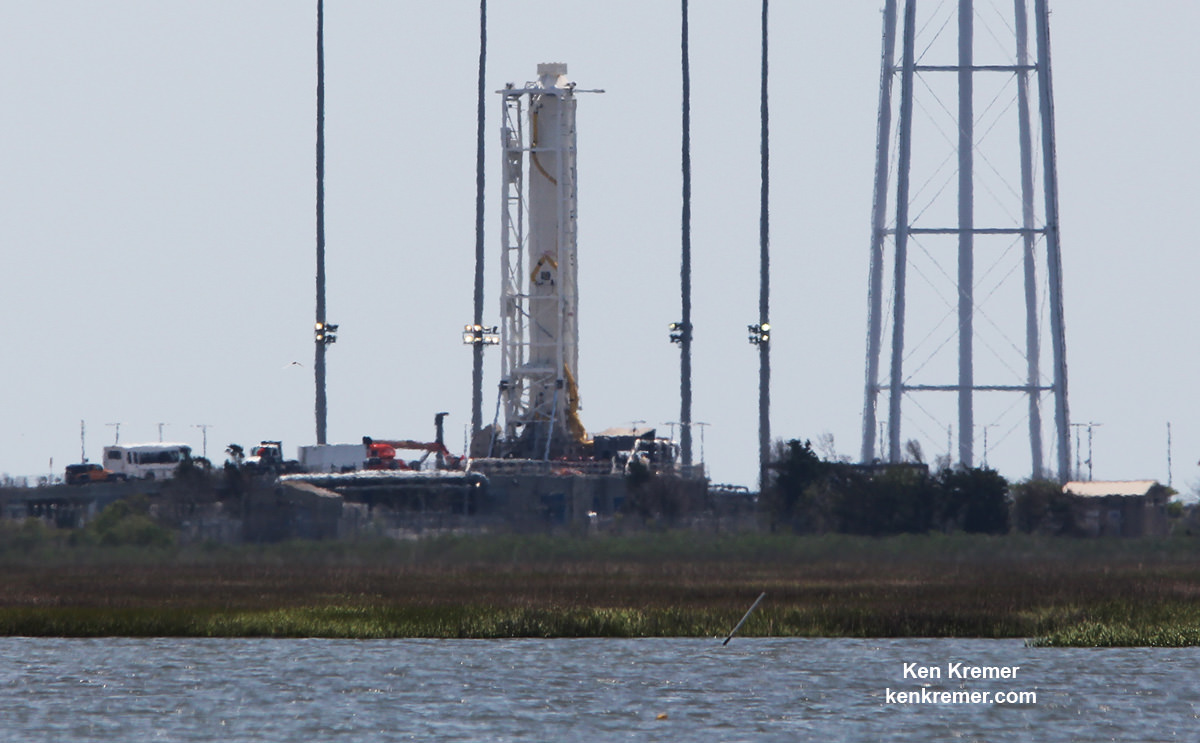

Teams from Orbital ATK and NASA have been scrutinizing the data in great detail ever since then to ensure the rocket is really ready before committing to the high stakes launch.
“Orbital ATK completed a stage test at the end of May and final data review has confirmed the test was successful, clearing the way for the Antares return to flight,” said the company.
“Simultaneously, the company has been conducting final integration and check out of the flight vehicle that will launch the OA-5 mission to ensure that all technical, quality and safety standards are met or exceeded.”
The projected launch date has been delayed several times since the May 31 hot fire test to deal with ‘vibration’ issues detected during the test.
Antares launches had immediately ground to a halt following the devastating launch failure 23 months ago which destroyed the rocket and its critical payload of space station science and supplies for NASA in a huge fireball just seconds after blastoff – as witnessed by this author.
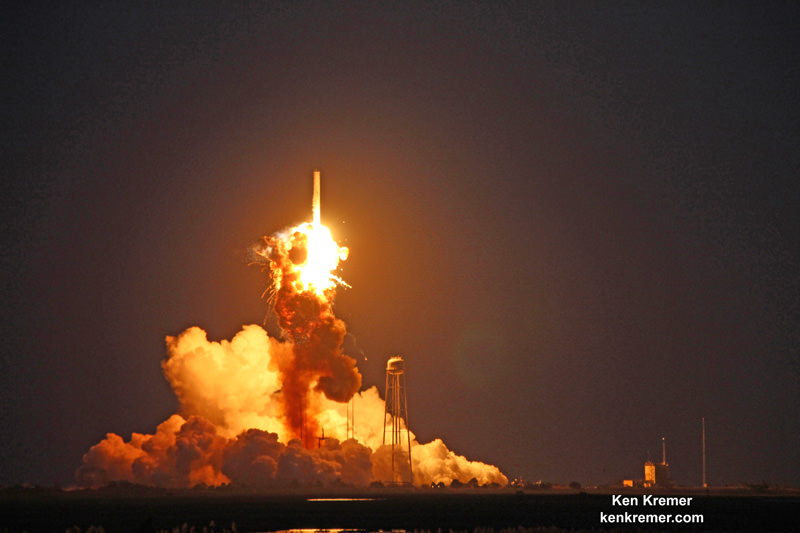

As a direct consequence of the catastrophic launch disaster, Orbital ATK managers decided to outfit the Antares medium-class rocket with new first stage RD-181 engines built in Russia.
The launch mishap was traced to a failure in the AJ26 first stage engine turbopump and caused Antares launches to immediately grind to a halt.
Top Orbital ATK management soon decided to ditch the AJ26s, which were 40 year old refurbished engines, originally built during the Soviet era for their moon rocket and originally known as the NK-33.
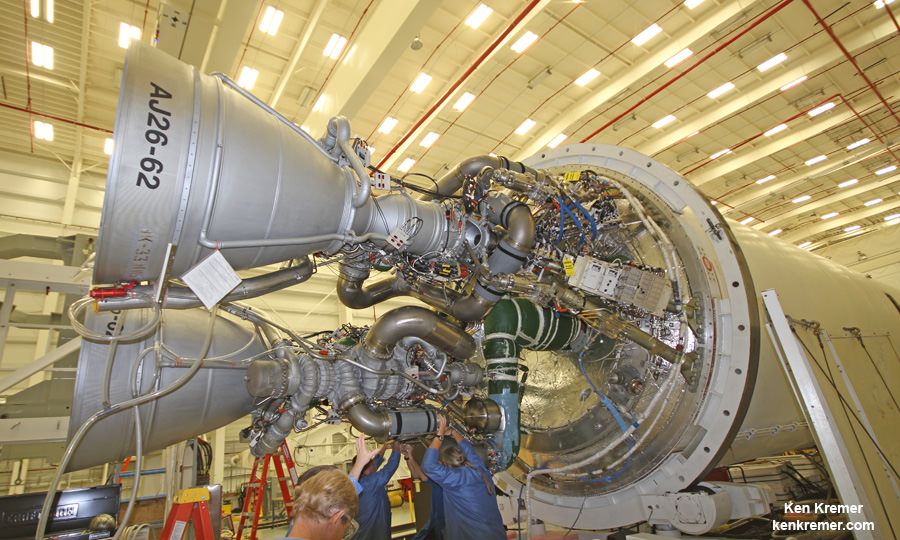

The RD-181 replaces the previously used AJ26 engines which failed moments after liftoff during the last launch on Oct. 28, 2014 resulting in a catastrophic loss of the rocket and Cygnus cargo freighter.
The RD-181 flight engines are built by Energomash in Russia and had to be successfully tested via the static hot fire test to ensure their readiness.

Watch for Ken’s continuing Antares/Cygnus mission and launch reporting. He will be reporting from on site at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, VA during the launch campaign.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.


5 Days, 2 Spectacular Conjunctions


Conjunctions of bright planets make for jewelry in the sky. This week, get ready for some celestial shimmer. If you’ve been following the hither and thither of Mars and Saturn near Antares this summer, you know these planets have been constantly on the move, creating all kinds of cool alignments in the southern sky.
On Tuesday night (August 23) the hopscotching duo will fall in line atop Antares in the southwestern sky at nightfall. Mars will sit just 1.5° above the star and Saturn 4° above Mars. Viewed from the Americas and Europe, the line will appear slightly bent. To catch them perfectly lined up, you’ll have to be in central Asia on the following evening, but the view should be pleasing no matter where you live.
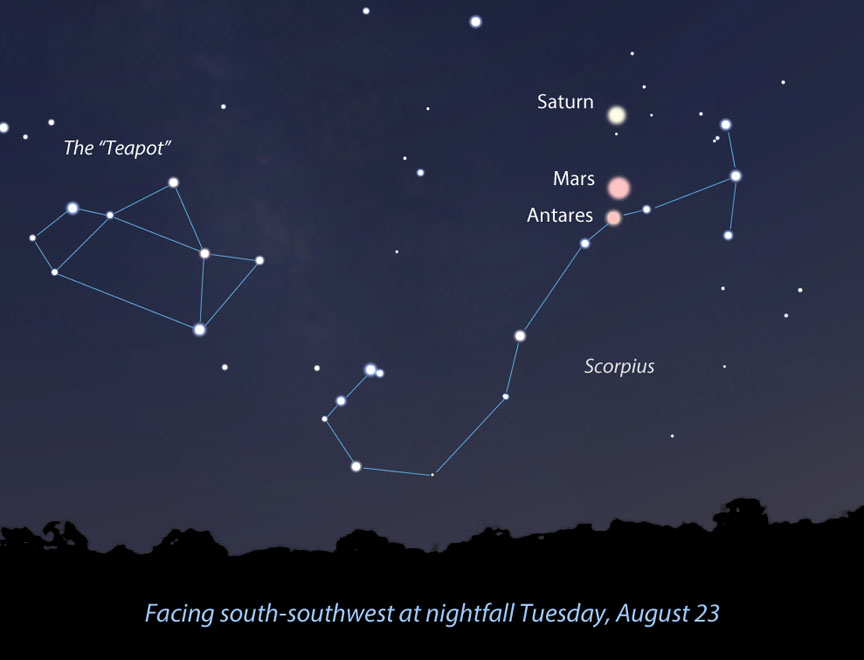
Nice as it is, the Mars-Saturn-Antares lineup is only the warm-up for the big event: the closest conjunction of the two brightest planets this year. On Saturday evening, August 27, Venus and Jupiter will approach within a hair’s breadth of each other as viewed with the naked eye — only 0.1° will separate the two gems. That’s one-fifth of a full moon’s width! While Mars and Saturn will be a snap to spot low in the southwestern sky during their conjunction, Venus and Jupiter snuggle near the western horizon at dusk.

To make sure you see them, find a place in advance of the date with a wide open view to the west. I also suggest bringing a pair of binoculars. It’s so much easier to find an object in bright twilight with help from the glass. You can start looking about 25 minutes after sunset; Venus will catch your eye first. Once you’ve found it, look a smidge to its lower right for Jupiter. If you’re using binoculars, lower them to see how remarkably close the two planets appear using nothing but your eyeballs. Perhaps they’ll remind you of a bright double star in a telescope or even the twin suns of Tatooine in Star Wars.
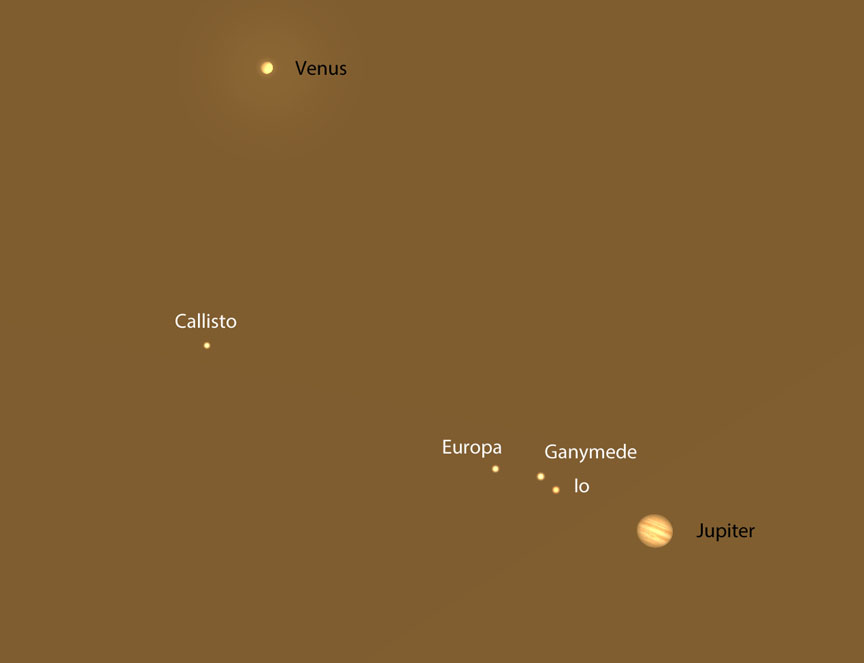
Have a small telescope? Take it along — Jupiter and Venus are so close together that they easily fit in the same high magnification field of view. Jupiter’s four brightest moons will be on display, and Venus will look just like a miniature version of the waxing gibbous moon. Rarely do the sky’s two brightest planets nearly fuse, making this a not-to-miss event.

If cloudy weather’s in the forecast that night, you can still spot them relatively close together the night before and night after, when they’ll be about 1° or two full moon diameters apart. I get pretty jazzed when bright objects approach closely in the sky, and I’m betting you do, too.
I also don’t mind being taken in by illusion once in a while. During a conjunction, planets only appear close together because we view them along the same line of sight. Their real distances add a dose of reality.
On Saturday evening Venus will be 143 million miles (230 million km) away vs. 592 million miles (953 million km) for Jupiter. In spite of appearing to almost touch, Jupiter is more than four times farther than the goddess planet.

That distance translates to the chill realm of the giant gaseous planets where sunlight is weak and ice is common. Try stretching your imagination that evening to sense as best you can the vast gulf between the two worlds.
You might also try taking a picture of them with your mobile phone. I suggest this because the sky will be light enough to get a hand-held photo of the scene. Photos or not, don’t miss what the planets have in store for earthlings this week.
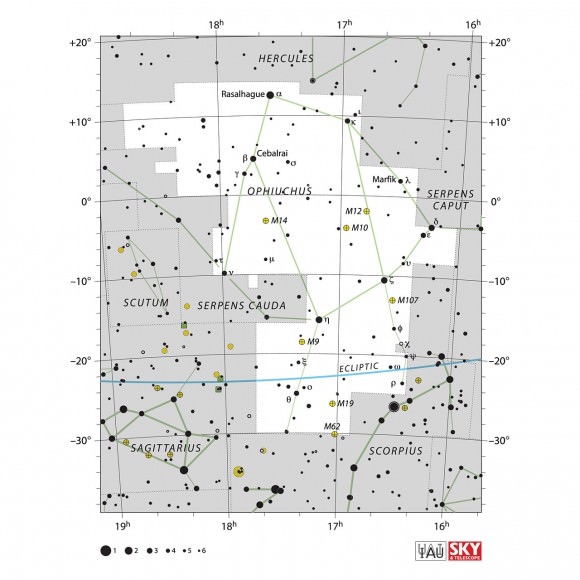
Messier 19 (M19) – The NGC 6273 Globular Cluster
Welcome back to Messier Monday! In our ongoing tribute to the great Tammy Plotner, we take a look at the Messier 19 globular star cluster. Enjoy!
In the 18th century, while searching the night sky for comets, French astronomer Charles Messier began noticing a series of “nebulous objects” in the night sky. Hoping to ensure that other astronomers did not make the same mistake, he began compiling a list of these objects,. Known to posterity as the Messier Catalog, this list has come to be one of the most important milestones in the research of Deep Sky objects.
One of these objects is Messier 19, a globular star cluster located in the constellation Ophiuchus. Of all the known globular clusters, M19 appears to be one of the most oblate (i.e. flattest) in the night sky. Discovered by William Herschel, this cluster is relatively difficult to spot with the naked eye, and appears as a fuzzy point of light with the help of magnification.
Description:
Speeding away from us at a rate of 146 kilometers per second, this gravitationally bound ball of stars measuring 140 light years in diameter, is one of the Messier globular clusters that has the distinction of being closest to the center of the Milky Way. At a little more than 5000 light-years from the intense gravitation of our own galactic core, it has played havoc on M19’s round shape.
In essence, Milky Way’s gravity has caused M19 to become one of the most oblate of all globular clusters, with twice as many stars along the major axis as along the minor. And, although it is 28,000 light-years from Earth, it’s actually on the opposite side of the galactic core. For all of its rich, dense mass, four RR Lyrae variable stars have been found in M19.
Is Messier 19 unique? It has some stellar branch properties that are difficult to pinpoint. And even its age (though estimated at around 11.9 billion years old) is indeterminate. Says F. Meissner and A. Weiss in their 2006 study, “Global fitting of globular cluster age indicators“:
“The determination of globular cluster (GC) ages rests on the fact that colour-magnitude diagrams (CMDs) of single-age single composition stellar populations exhibit specific time-dependent features. Most importantly, this is the location of the turn-off (TO), which – together with the cluster’s distance – serves as the most straightforward and widely used age indicator. However, there are other parts of the CMD that change their colour or brightness with age, too. Since the sensitivity to time is different for the various parts of the cluster CMD, it is possible to use either the various indicators independently, or the differences in colour and brightness between pairs of them; these latter methods have the advantage of being independent of distance.”
What’s occurring is a horizontal branch gap – an not-quite explainable difference in the way the stars inside M19 are aging. However, science is looking for the answer. As G. Busso et al. explained in their 2008 paper titled “The Peculiar Horizontal Branch Morphology of the Galactic Globular Clusters NGC 6388 and NGC 6441“:
“I show that a possible solution of the puzzle is to assume that a small fraction of the stellar population in the two clusters is strongly helium enriched. The presence of two distinct stellar populations characterized by two different initial He contents can help in explaining the brightness difference between the red portion of the HB and the blue component.”

Is helium the answer? Quite probably so. M. Salaris Astrophysics Research Institute and an international team of researchers explained in their 2004 study “The initial helium abundance of the Galactic globular cluster system“:
“Based on a recently updated set of stellar evolution models, we performed an accurate statistical analysis in order to assess whether GGCs show a statistically significant spread in their initial He abundances, and whether there is a correlation with the cluster metallicity. As in previous works on the subject, we do not find any significant dependence of the He abundance on the cluster metallicity; this provides an important constraint for models of Galaxy formation and evolution. Apart from GGCs with the bluest Horizontal Branch morphology, the observed spread in the individual helium abundances is statistically compatible with the individual errors. This means that either there is no intrinsic abundance spread among the GGCs, or that this is masked by the errors. In the latter case we have estimated a firm upper limit of 0.019 to the possible intrinsic spread. In case of the GGCs with the bluest Horizontal Branch morphology we detect a significant spread towards higher abundances inconsistent with the individual errors; this can be fully explained by additional effects not accounted for in our theoretical calibrations, which do not affect the abundances estimated for the clusters with redder Horizontal Branch morphology.”
History of Observation:
M19 was one of Charles Messier’s original discoveries, which he first observed on June 5th, 1764. In his notes, he wrote:
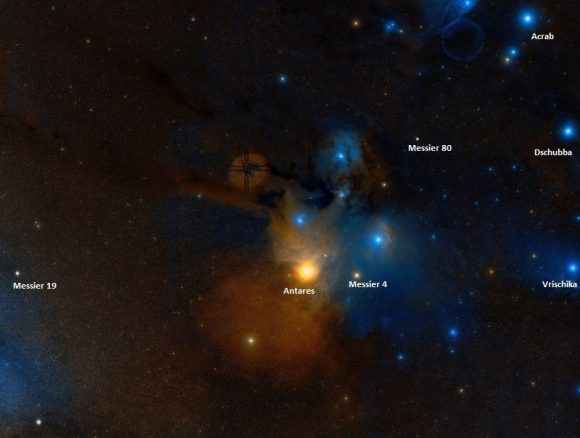
“I have discovered a nebula, situated on the parallel of Antares, between Scorpius and the right foot of Ophiuchus: that nebula is round & doesn’t contain any star; I have examined it with a Gregorian telescope which magnified 104 times, it is about 3 minutes of arc in diameter: one sees it very well with an ordinary refractor of 3 feet and a half. I have observed its passage of the Medirian, and compared it with that of the star Antares; I have determined the right ascension of that nebula of 252d 1′ 45″, and its declination of 25d 54′ 46″ south. The known star closest to that nebula is the 28th of the constellation Ophiuchus, after the catalog of Flamsteed, of sixth magnitude.”

While Charles didn’t resolve it, we must give him due credit for discovery, for its size wouldn’t make it a particularly easy object given his optics. Later, in 1784, William Herschel would become the first to open up its true identity:
“When the 19th of the Connoiss. is viewed with a magnifying power of 120, the stars are visible; the cluster is insulated; some of the small stars scattered in the neighborhood are near it; but they are larger than those belonging to the cluster. With 240 it is better resolved, and is much condensed in the centre. With 300 no nucleus or central body can be seen. The diameter with the 10 feet is 3’16”, and the stars in the centre are too accumulated to be separately seen. It will not be necessary to add that the two last mentioned globular clusters, viewed with more powerful instruments, are of equal beauty with the rest; and from what has been said it is obvious that here the exertion of a clustering power has brought the accumulation and artificial construction of these wonderful celestial objects to the highest degree of mysterious perfection.”
While you may – or may not – resolve Messier 19’s individual stars, even small telescopes can pick up on some of its ellipticity and larger telescopes will make out a definite blue tinge to its coloration. Before you yawn at viewing another globular cluster, remember that you are looking at the other side of our galactic center and think on the words about M19 from Admiral Symth.
“The whole vicinity,” he wrote, “afford a grand conception of the grandeur and richness even of the exterior creation; and indicate the beautious gradation and variety of the heaven of heavens. Truly has it been said, “Stars teach us as well as shine.” This is near the large opening or hole, about 4deg broad, in the Scorpion’s body, which WH [William Herschel] found almost destitute of stars.”
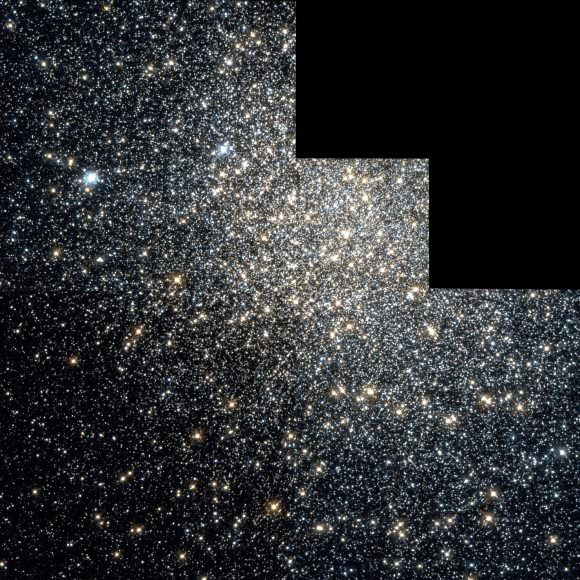

Locating Messier 19:
Finding M19’s location in binoculars is quite easy – it’s less than a fistwidth (8 degrees) east of Antares (Alpha Scorpi). However, ‘seeing’ M19 in binoculars (especially smaller ones) is a little more problematic. The steadier the binoculars are, the better your chances, since it will appear almost stellar at first glance. A good indicator is to have optical double 26 Ophiuchi in the field at the 2:00 position and look for the star that won’t quite come to focus in the 8:00 position.
Star 26 also makes for a great finderscope lead when locating M19 in a telescope as well. Even for aperture sizes as small as 114mm, this globular cluster will show quite easily in a telescope and reveal its oblate nature. When aperture size increase to the 8″ range, it will begin resolution and as it nears 12″ or more, you’ll pick up on blue stars.
And for your convenience, here are the quick facts of M19:
Object Name: Messier 19
Alternative Designations: M19, NGC 6273
Object Type: Class VIII Globular Star Cluster
Constellation: Ophiuchus
Right Ascension: 17 : 02.6 (h:m)
Declination: -26 : 16 (deg:m)
Distance: 28.0 (kly)
Visual Brightness: 6.8 (mag)
Apparent Dimension: 17.0 (arc min)
We have written many interesting articles about Messier Objects here at Universe Today. Here’s Tammy Plotner’s Introduction to the Messier Objects, , M1 – The Crab Nebula, M8 – The Lagoon Nebula, and David Dickison’s articles on the 2013 and 2014 Messier Marathons.
Be to sure to check out our complete Messier Catalog. And for more information, check out the SEDS Messier Database.
Re-engined’ Antares Rocket Completes Crucial Engine Test Firing
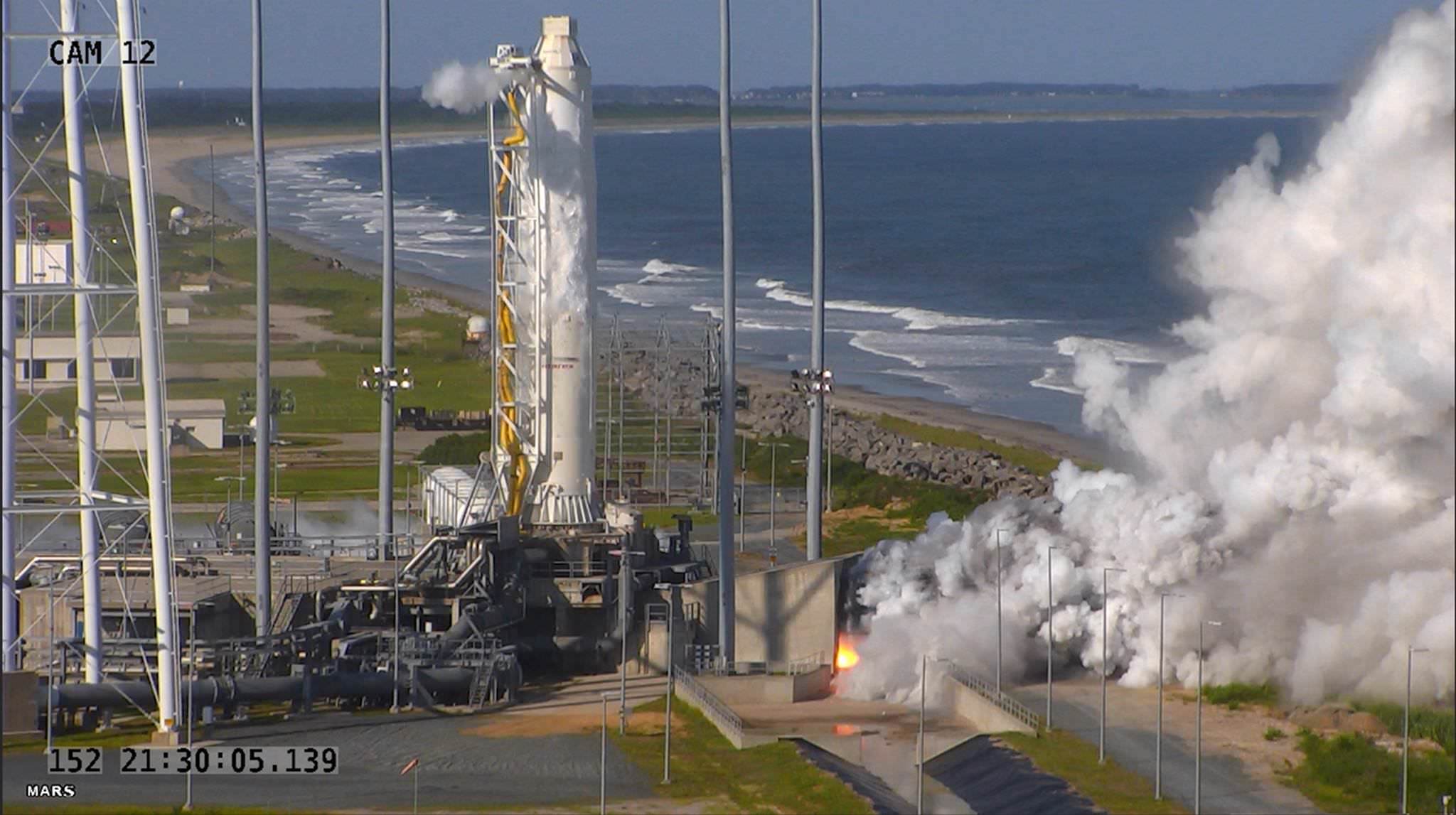


Orbital ATK announced late Tuesday that the company’s Antares medium-class commercial rocket outfitted with new first stage RD-181 engines has successfully completed a test firing of the powerplants.
The 30-second long static test firing took place at 5:30 p.m. Tuesday evening, May 31, at Virginia Space’s Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) Pad 0A.
The now revamped launch vehicle – dubbed Antares 230 – has been ‘re-engined’ and upgraded with a pair of modern and more powerful first stage engines – the Russian-built RD-181 fueled by LOX/kerosene.
The engine test was conducted using only the first stage of Antares at the MARS Pad 0A at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility.
“Early indications show the upgraded propulsion system, core stage and launch complex all worked together as planned,” said Mike Pinkston, Orbital ATK General Manager and Vice President, Antares Program.
“Congratulations to the combined NASA, Orbital ATK and Virginia Space team on a successful test.”
Orbital ATK engineers will now “review test data over the next several days to confirm that all test parameters were met”

If all goes well with the intensive data review, the company could launch Antares as soon as July on its next NASA contracted mission – known as OA-5 – to resupply the International Space Station (ISS).
The test involved firing up Antares dual first stage RD-181 engines at full 100% power (thrust) for a scheduled duration of approximately 30 seconds. Hold down restraints kept the rocket firmly anchored at the pad during the test.
The RD-181 replaces the previously used AJ26 which failed moments after liftoff during the last launch on Oct. 28, 2014 resulting in a catastrophic failure of the rocket and the Cygnus cargo freighter.
The RD-181 flight engines are built by Energomash in Russia and had to be tested via the static hot fire test to ensure their readiness.
“They are a good drop in replacement for the AJ26. And they offer 13% higher thrust compared to the AJ26,” said Kurt Eberly, Orbital ATK Antares deputy program manager, in an interview with Universe Today.

As a result of switching to the new RD-181 engines, the first stage also had to be modified to incorporate new thrust adapter structures, actuators, and propellant feed lines between the engines and core stage structure.
So the primary goal was to confirm the effectiveness of the new engines and all the changes in the integrated rocket stage.
“The successful stage test, along with the extensive testing of each new RD-181, gives us further confidence in the first stage propulsion and in moving forward to launch,” said Pinkston.
“We are now focused on the OA-5 mission and launching the enhanced Cygnus spacecraft to the International Space Station on our upgraded, higher-performing Antares rocket.”
The test used the first stage core planned to launch the OA-7 mission from Wallops late this year.
With the engine test is completed, the OA-7 stage will be rolled back to the HIF and a new stage fully integrated with the Cygnus cargo freighter will be rolled out to the pad for the OA-5 ‘Return to Flight’ mission as soon as July.
“Each of the new flight RD-181 engines has undergone hot fire acceptance testing at the manufacturer’s facility prior to being shipped to Orbital ATK. A certification test series was successfully completed in the spring of 2015 where a single engine was test fired seven times, accumulating 1,650 seconds of test time and replicating the Antares flight profile, before being disassembled for inspection,” said Orbital ATK officials.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
Messier 8 (M8) – The Lagoon Nebula

Welcome to another Messier Monday. In our ongoing tribute to the great Tammy Plotner, we bring you another item from the Messier Catalog!
In the 18th century, while searching the night sky for comets, French astronomer Charles Messier kept noting the presence of fixed, diffuse objects in the night sky. In time, he would come to compile a list of approximately 100 of these objects, with the purpose of making sure that astronomers did not mistake them for comets. However, this list – known as the Messier Catalog – would go on to serve a more important function, acting as a milestone in the history of the study of Deep Sky Objects.
However, not all objects in the catalog were first discovered by Charles Messier himself. Some, like the Lagoon Nebula, were observed sooner, owing to the fact that they are visible to the naked eye. This interstellar cloud, which is located in the Sagittarius constellation, has been known of since the late 17th century, and is one of only two star-forming nebulae that is visible to the naked eye from mid-northern latitudes.


