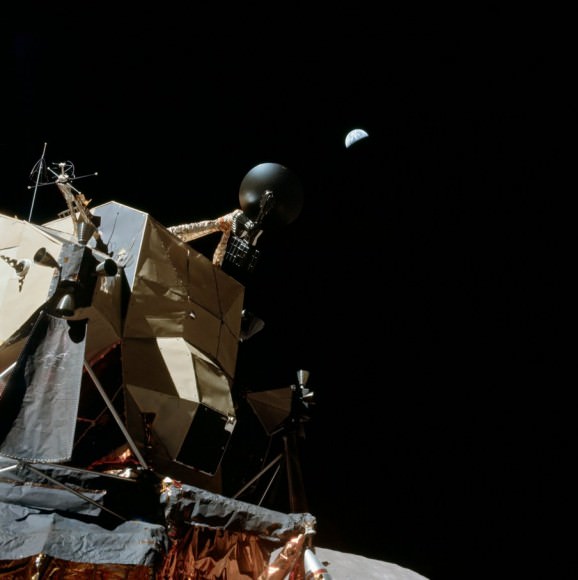
45 years ago today — on July 16th, 1969 — the Apollo 11 crew left Earth for the first human mission to land on the Moon. Launching on at Saturn V rocket from Cape Kennedy, the mission sent Commander Neil Armstrong, Command Module Pilot Michael Collins and Lunar Module Pilot Edwin “Buzz” Aldrin into an initial Earth-orbit, and then two hours and 44 minutes after launch, another burn of the engines put Apollo 11 into a translunar orbit.
If you want to re-live the launch and the mission, there are several ways you can participate. We’ve included here a few different replays of the launch, varying from a quick recap to a detailed look at the launch itself. Above is the newscast of the launch from CBS news with Walter Cronkite, and we’ve got more below.
Also below is information on several webcasts and other events that NASA has planned to commemorate the anniversary.
Here’s a detailed look at the launch in ultra-slow motion, with narration:
Here is some remastered high definition footage from NASA of the Apollo 11 launch, but there’s no audio.
And here’s a quick look at the entire Apollo 11 mission, all in just 100 seconds from Spacecraft Films:
Here are some ways to participate in the anniversary:
On Twitter, @ReliveApollo11 from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum is reliving the highlights from Apollo 11 mission to the Moon in “real time” 45 years later.
Also @NASAHistory is tweeting images and events from the mission, and journalist Amy Shira Teitel (@astVintageSpace ) is tweeting out some interesting pictures, facts and quotes from the mission, in “real time” (again 45 years later).
To join the ongoing conversation on social media about the anniversary and NASA’s deep space exploration plans, use the hashtags #NextGiantLeap and #Apollo45.
On Friday, July 18 at 10:30 a.m. PDT (1:30 p.m. EDT), NASA TV will air a live conversation about the future of space exploration with actor, director and narrator Morgan Freeman. He will speak at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, about his personal vision for space. The event also will include NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman participating from the International Space Station.
If you don’t have NASA TV on your cable or satellite feeds, you can watch online here.
Also on Friday at 3:30 p.m. EDT, NASA will host a discussion with Buzz Aldrin and astronaut Mike Massimino at the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in New York during the Intrepid Space and Science Festival. NASA also will have exhibits and activities at the festival Thursday, July 17 through Saturday, July 19. There’s more information about the festival here.
On Sunday, July 20 at 7:39 p.m. PDT (10:39 p.m. EDT), when Armstrong opened the spacecraft hatch to begin the first spacewalk on the moon, NASA TV will replay the restored footage of Armstrong and Aldrin’s historic steps on the lunar surface.
On Monday, July 21 at 7 a.m. PDT (10 a.m. EDT) from the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA TV will air live coverage of the renaming of the center’s Operations and Checkout Building in honor of Armstrong, who passed away in 2012. The renaming ceremony will include NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, Kennedy Center Director Robert Cabana, Apollo 11’s Collins, Aldrin and astronaut Jim Lovell, who was the mission’s back-up commander. International Space Station NASA astronauts Wiseman and Steve Swanson, who is the current station commander, also will take part in the ceremony from their orbiting laboratory 260 miles above Earth.
Kennedy’s Operations and Checkout Building has played a vital role in NASA’s spaceflight history. It was used during the Apollo program to process and test the command, service and lunar modules. Today, the facility is being used to process and assemble NASA’s Orion spacecraft, which the agency will use to send astronauts to an asteroid in the 2020s and Mars in the 2030s.
On Thursday, July 24 at 3 p.m. PDT (6 p.m. EDT), which is the 45th anniversary of Apollo 11’s return to Earth, the agency will host a panel discussion — called NASA’s Next Giant Leap — from Comic-Con International in San Diego. Moderated by actor Seth Green, the panel includes Aldrin, NASA Planetary Science Division Director Jim Green, JPL systems engineer Bobak Ferdowsi, and NASA astronaut Mike Fincke, who will talk about Orion and the Space Launch System rocket, which will carry humans on America’s next great adventure in space.
The NASA.gov website will host features, videos, and historic images and audio clips that highlight the Apollo 11 anniversary, as well as the future of human spaceflight. Find it all here.
Also, the Slooh telescope team will celebrate the 45th anniversary of the Apollo 11 landing with a high-definition broadcast of the lunar surface on Sunday, July 20th starting at 5:30 PM PDT / 8:30 PM EDT / 00:30 UTC (7/21) – (check International Times here) Slooh will broadcast the event live from a special feed located in Dubai in the United Arab Emirates.
Viewers can watch the event unfold free on Slooh.com, or in the webcast below. The image stream will be accompanied by discussions led by Slooh host, Geoff Fox, Slooh astronomer, Bob Berman, Slooh Observatory Engineer, Paul Cox, along with numerous special guests, including documentary filmmaker, Duncan Copp, and science journalist, Andrew Chaikin. Viewers can follow updates on the show by using the hashtag #SloohApollo11.