Scientists have detected magmatic water — water that originates from deep within the Moon’s interior — on the surface of the Moon. These findings represent the first such remote detection of this type of lunar water, and were arrived at using data from NASA’s Moon Mineralogy Mapper (M3) carried aboard India’s Chandrayaan-1 lunar orbiter.
The discovery represents an exciting contribution to the rapidly changing understanding of lunar water according to Rachel Klima, a planetary geologist at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Md., and lead author of the paper, “Remote detection of magmatic water in Bullialdus Crater on the Moon” published in the August 25 issue of the journal Nature Geoscience.

“For many years, researchers believed that the rocks from the Moon were ‘bone dry’ and that any water detected in the Apollo samples had to be contamination from Earth,” said Klima, a member of the NASA Lunar Science Institute’s (NLSI) Scientific and Exploration Potential of the Lunar Poles team. “About five years ago, new laboratory techniques used to investigate lunar samples revealed that the interior of the Moon is not as dry as we previously thought. Around the same time, data from orbital spacecraft detected water on the lunar surface, which is thought to be a thin layer formed from solar wind hitting the lunar surface.”
Read more: The Moon’s Water Comes From the Sun
“This surficial water unfortunately did not give us any information about the magmatic water that exists deeper within the lunar crust and mantle, but we were able to identify the rock types in and around Bullialdus crater,” said co-author Justin Hagerty, of the U.S. Geological Survey. “Such studies can help us understand how the surficial water originated and where it might exist in the lunar mantle.”
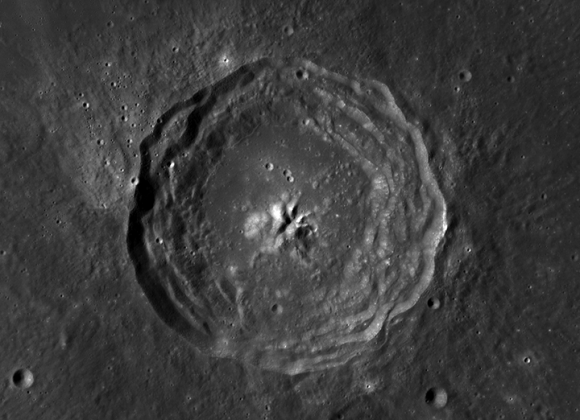

M3 (pronounced “M-cube”) fully imaged the large impact crater Bullialdus in 2009. “It’s within 25 degrees latitude of the equator and so not in a favorable location for the solar wind to produce significant surface water,” Klima explained. “The rocks in the central peak of the crater are of a type called norite that usually crystallizes when magma ascends but gets trapped underground instead of erupting at the surface as lava. Bullialdus crater is not the only location where this rock type is found, but the exposure of these rocks combined with a generally low regional water abundance enabled us to quantify the amount of internal water in these rocks.”

After examining the M3 data, Klima and her colleagues found that the crater has significantly more hydroxyl — a molecule consisting of one oxygen atom and one hydrogen atom — compared to its surroundings. “The hydroxyl absorption features were consistent with hydroxyl bound to magmatic minerals that were excavated from depth by the impact that formed Bullialdus crater,” Klima writes.
The internal magmatic water provides information about the Moon’s volcanic processes and internal composition, Klima said. “Understanding this internal composition helps us address questions about how the Moon formed, and how magmatic processes changed as it cooled. There have been some measurements of internal water in lunar samples, but until now this form of native lunar water has not been detected from orbit.”
“This impressive research confirms earlier lab analyses of Apollo samples, and will help broaden our understanding of how this water originated and where it might exist in the lunar mantle.”
– Yvonne Pendleton, NLSI Director
Source: JHUAPL News Release