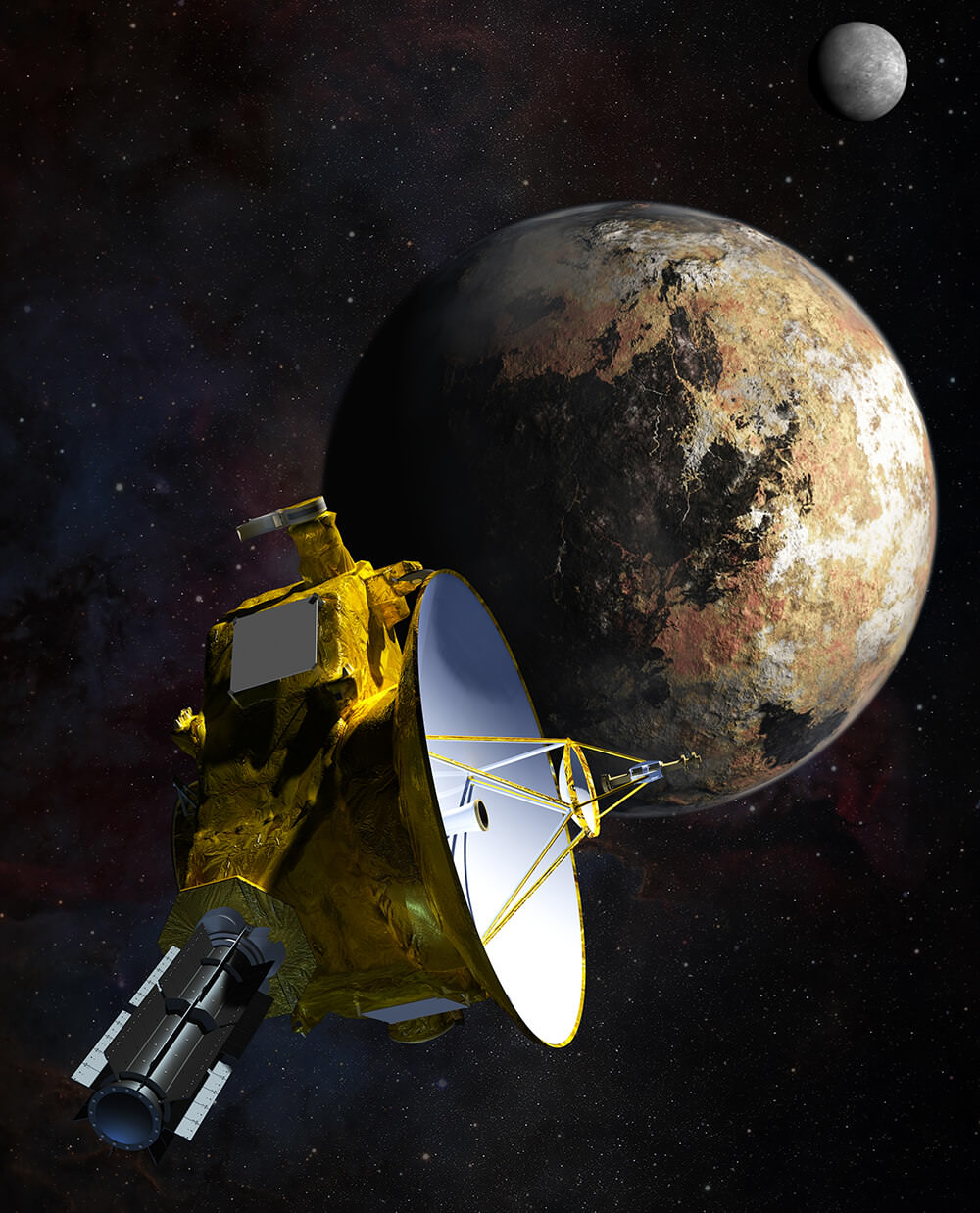
On July 14th, 2015, the New Horizons probe made history by accomplishing the first flyby of Pluto and its largest satellite, Charon. The stunning images this mission took of these icy worlds have helped scientists address some of the key questions about Pluto and its massive moon, which have been shrouded in mystery for decades (owing to their great distance from Earth). One of the biggest mysteries that scientists have contemplated since Charon was first discovered in 1978 is how it came together with Pluto in the first place.
For decades, astronomers suspected that Pluto and Charon formed through a process similar to Earth and the Moon. This theory, known as the Giant Impact Hypothesis, states that roughly 4.5 billion years ago, primordial Earth was struck by a Mars-sized body named Theia. In a new study, a team of researchers from the University of Arizona challenged this assumption and offered an alternate theory known as “kiss and capture.” Their findings could help scientists better understand how planetary bodies in the outer Solar System form and evolve.
Continue reading “Here's How Pluto and Charon Became a Bizarre Double Planet”