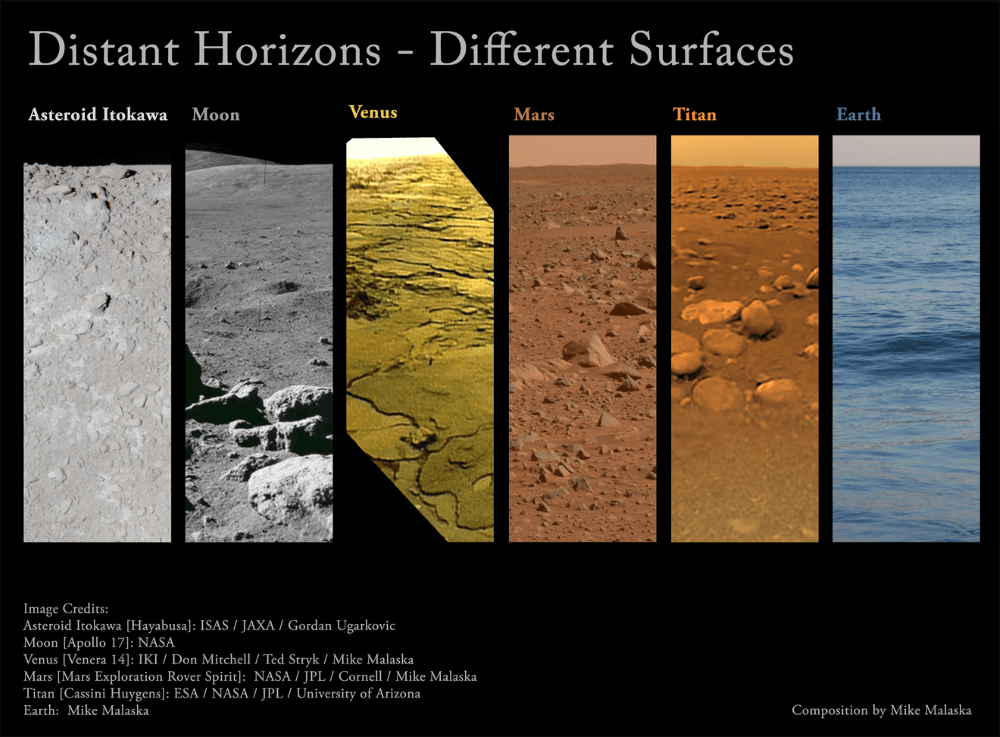
Universe Today recently explored the importance of studying impact craters and what they can teach us about finding life beyond Earth. Impact craters are considered one of the many surface processes—others include volcanism, weathering, erosion, and plate tectonics—that shape surfaces on numerous planetary bodies, with all of them simultaneously occurring on Earth. Here, we will explore how and why planetary scientists study planetary surfaces, the challenges faced when studying other planetary surfaces, what planetary surfaces can teach us about finding life, and how upcoming students can pursue studying planetary surfaces, as well. So, why is it so important to study planetary surfaces throughout the solar system?
Continue reading “Planetary Surfaces: Why study them? Can they help us find life elsewhere?”Impact Craters: Why study them and can they help us find life elsewhere?
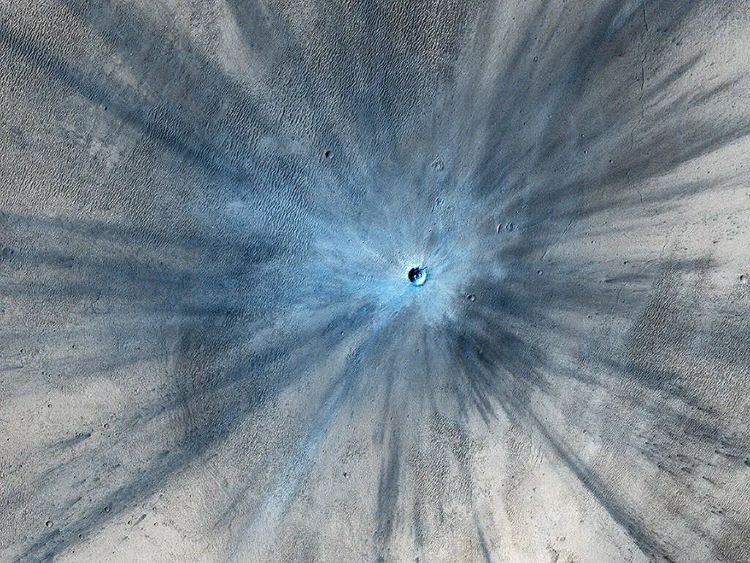

When we look at the Moon, either through a pair of binoculars, a telescope, or past footage from the Apollo missions, we see a landscape that’s riddled with what appear to be massive sinkholes. But these “sinkholes” aren’t just on the Moon, as they are evident on nearly every planetary body throughout the solar system, from planets, to other moons, to asteroids. They are called impact craters and can range in size from cities to small countries.
Continue reading “Impact Craters: Why study them and can they help us find life elsewhere?”DART Showed We Can Move an Asteroid. Can We Do It More Efficiently?

Like many of you, I loved Deep Impact and Armageddon. Great films, loads of action and of course, an asteroid on collision course with Earth. What more is there to love! Both movies touched upon the options for humanity to try and avoid such a collision but the reality is a little less Hollywood. One of the most common options is to try some sort of single impact style event as was demonstrated by the DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) mission but a new paper offer an intriguing and perhaps more efficient alternative.
Continue reading “DART Showed We Can Move an Asteroid. Can We Do It More Efficiently?”For its Next Trick, Gaia Could Help Detect Background Gravitational Waves in the Universe

Ripples in a pond can be captivating on a nice sunny day as can ripples in the very fabric of space, although the latter are a little harder to observe. Using the highly tuned Gaia probe, a team of astronomers propose that it might just be possible to detect gravitational waves through the disturbance they impart on the movement of asteroids in our Solar System!
Continue reading “For its Next Trick, Gaia Could Help Detect Background Gravitational Waves in the Universe”JWST Detects Carbon Dioxide in a Centaur for the First Time

A study published today in The Planetary Science Journal examines how NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has conducted a first-time detection of carbon dioxide in a Centaur, this one designated 39P/Oterma. A Centaur is a small planetary body that orbits between Jupiter and Neptune and frequently crosses the orbits of one or more of the gas giant planets within our solar system. While no Centaur has been imaged up-close, they typically exhibit a combination of attributes between comets and asteroids. While carbon monoxide has been detected in two known centaurs, this recent discovery could mark a turning point in how scientists understand the formation, evolution, and composition of not only Centaurs, but of the early solar system, as well.
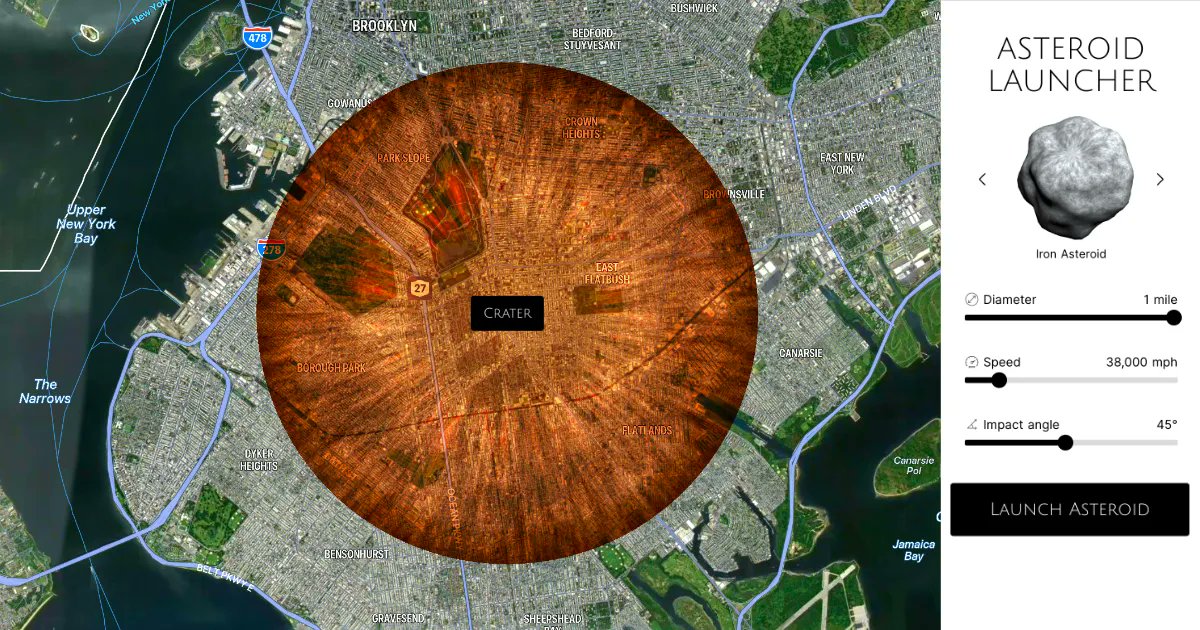
Continue reading “JWST Detects Carbon Dioxide in a Centaur for the First Time”This Interactive Tool Lets you Simulate Asteroid Impacts Anywhere on Earth
Asteroid impacts rank highest on the UN’s list of potentially species-ending calamities. They’ve been the subject of countless movies and books, some of which are accurate depictions of what would happen, and some of which are not. Now, if you’ve ever been interested to see what would happen if different sizes of asteroid impact different areas of the globe, the internet has a tool for you!
Continue reading “This Interactive Tool Lets you Simulate Asteroid Impacts Anywhere on Earth”Astronomers Spotted a Tiny Asteroid A Few Hours Before it Impacted the Earth, and Predicted Exactly Where and When it Would Crash
Humanity is getting better a planetary defense. At least from external threats from outer space. As long as they’re just dumb rocks that follow the laws of physics. And a group of extraordinary humans proved it last week when the planetary defense community jumped into action to accurately track and predict exactly where a relatively small meteor would fall on November 19th.
Continue reading “Astronomers Spotted a Tiny Asteroid A Few Hours Before it Impacted the Earth, and Predicted Exactly Where and When it Would Crash”OSIRIS-REx Would Have Sunk Deep into Asteroid Bennu if it Tried to Land
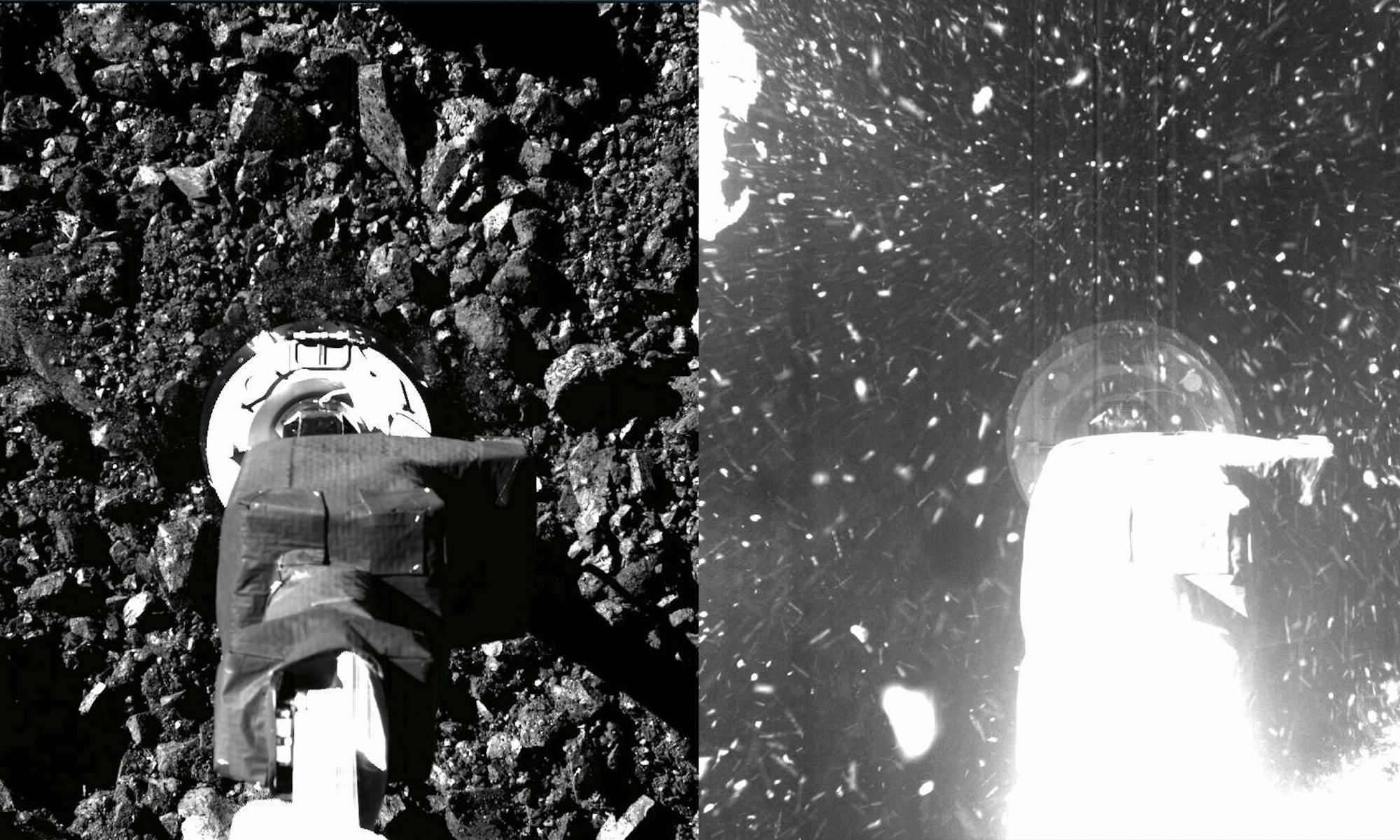
A pair of studies published in Science and Science Advances have helped identify that NASA’s OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer) spacecraft would have sunk into the asteroid Bennu had the spacecraft not fired its thrusters immediately after collecting samples from the surface of the small planetary body in October 2020. The respective studies examined the loosely packed exterior of Bennu, comparing its surface to stepping into a pit of plastic balls that people of all ages enjoy. The paper in Science was led by Dr. David Lauretta, Principal Investigator of OSIRIS-REx and a Regents Professor at the University of Arizona, and the paper in Science Advances was led by Dr. David Walsh, a member of the OSIRIS-REx team from the Southwest Research Institute in Boulder, Colorado.
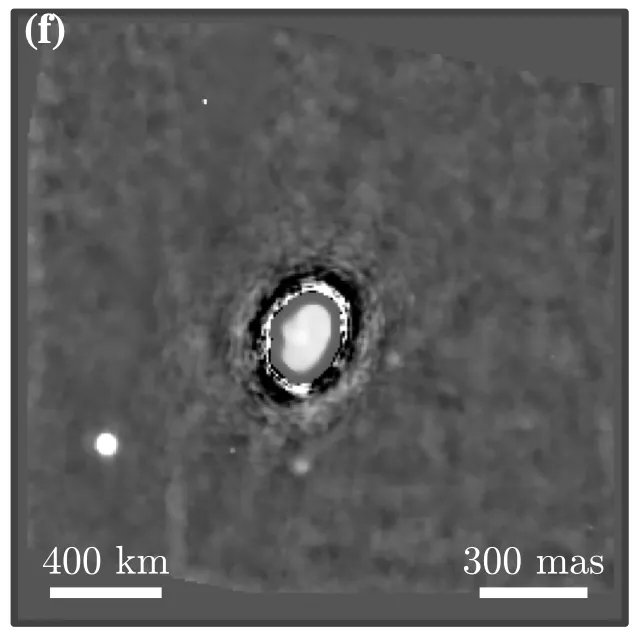
Continue reading “OSIRIS-REx Would Have Sunk Deep into Asteroid Bennu if it Tried to Land”An Asteroid has Been Discovered With Three Moons!
Planets aren’t the only celestial objects with moons – asteroids can have them too. They are usually other, smaller asteroids in orbit around a larger central one. Now, a team of Thai and French astronomers found an asteroid system with three satellites. The new four-body system makes complex gravitational problems like the three-body problem look simple by comparison.
Continue reading “An Asteroid has Been Discovered With Three Moons!”This Object is Both an Asteroid and a Comet
In astronomy, comets and asteroids are defined very differently. Comets have a “nucleus,” usually made of ice and dust, and a tail when they get near the sun, which is the nucleus material shedding off from the comet itself. Asteroids, on the other hand, are small balls of rock orbiting the sun. Occasionally though, some objects meet the criteria to be both an asteroid and a comet – and a team from the Planetary Science Institute (PSI) think they have found a new one.
Continue reading “This Object is Both an Asteroid and a Comet”