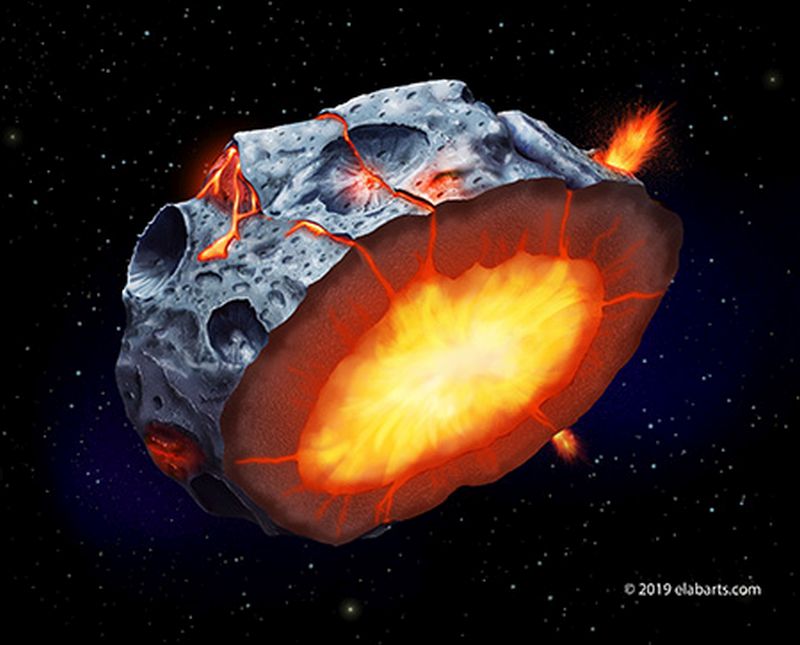
Imagine a time in the Solar System’s past, when the asteroids were not solid rock, but blobs of molten iron. It sounds strange, but that may have been the case. And in the right conditions, some of those asteroids would have sprouted volcanoes. One of those asteroids, Psyche, is the destination for a NASA mission.
Continue reading “Metal Asteroid Psyche Might Have Had Volcanoes of Molten Iron”Sorry Hollywood, it’s Going to Take a Lot More to Destroy an Asteroid

It’s become something of an action movie cliche: an asteroid is hurling towards Earth, its impact will cause a mass extinction, and the only hope for humanity is a ragtag group of astronauts and average Joes who will fly to the asteroid and blow it to pieces using nukes. The idea has been explored so many times by Hollywood that it seems like this is actually something space agencies have planned.
And in truth, they are, though the execution may be a little more sophisticated. For decades, space agencies have considered various methods for destroying asteroids that threaten Earth. But according to a new study led by researchers from John Hopkins University, incoming asteroids may be harder to break apart than we thought.
Continue reading “Sorry Hollywood, it’s Going to Take a Lot More to Destroy an Asteroid”Steam-Powered Spacecraft Could Explore the Asteroid Belt Forever, Refueling Itself in Space
The era of renewed space exploration has led to some rather ambitious proposals. While many have been on the books for decades, it has only been in recent years that some of these plans have become technologically feasible. A good example is asteroid mining, where robotic spacecraft would travel to Near-Earth Asteroids and the Main Asteroid Belt to harvest minerals and other resources.
At the moment, one of the main challenges is how these craft would be able to get around and refuel once they are in space. To address this, the New York-based company Honeybee Robotics has teemed up with the University of Central Florida (UFC) to develop a steam-powered robotic spacecraft. The company recently released a demonstration video that shows their prototype World is Not Enough (WINE) “steam hopper” in action.
Continue reading “Steam-Powered Spacecraft Could Explore the Asteroid Belt Forever, Refueling Itself in Space”OSIRIS-REx Has Already Found Water on Bennu
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer) has found water on the asteroid Bennu. Bennu is OSIRIS-REx’s only target, and though the spacecraft arrived at the asteroid on December 3rd, some of its instruments have been trained on the asteroid since mid-August. And two of those instruments detected water on Bennu.
OSIRIS-REx wasn’t sent to Bennu just to find water. The mission is NASA’s first asteroid sample-return mission. The presence of water on Bennu confirms what the science team hoped would be true when they selected the asteroid as the spacecraft’s destination: Bennu is an excellent target for scientific inquiry into the early Solar System.
“The presence of hydrated minerals across the asteroid confirms that Bennu, a remnant from early in the formation of the solar system, is an excellent specimen for the OSIRIS-REx mission to study the composition of primitive volatiles and organics.” – Amy Simon, OVIRS deputy instrument scientist, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
Continue reading “OSIRIS-REx Has Already Found Water on Bennu”
OSIRIS-REx has Finally Caught up with Asteroid Bennu. Let the Analysis and Sample Collection Commence!
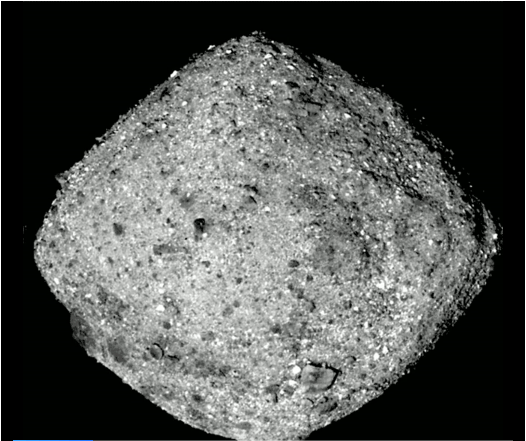

NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft has reached its destination and is now in orbit around asteroid Bennu. The spacecraft travelled for over two years and covered more than 2 billion kms. It will spend a year in orbit, surveying the surface of the Potentially Hazardous Object (PHO) before settling on a location for the key phase of its mission: a sample return to Earth.
Not all the Earth’s Water Came From Comets

We have comets and asteroids to thank for Earth’s water, according to the most widely-held theory among scientists. But it’s not that cut-and-dried. It’s still a bit of a mystery, and a new study suggests that not all of Earth’s water was delivered to our planet that way.
Continue reading “Not all the Earth’s Water Came From Comets”
The Path that MASCOT Took Across Asteroid Ryugu During its 17 Hours of Life
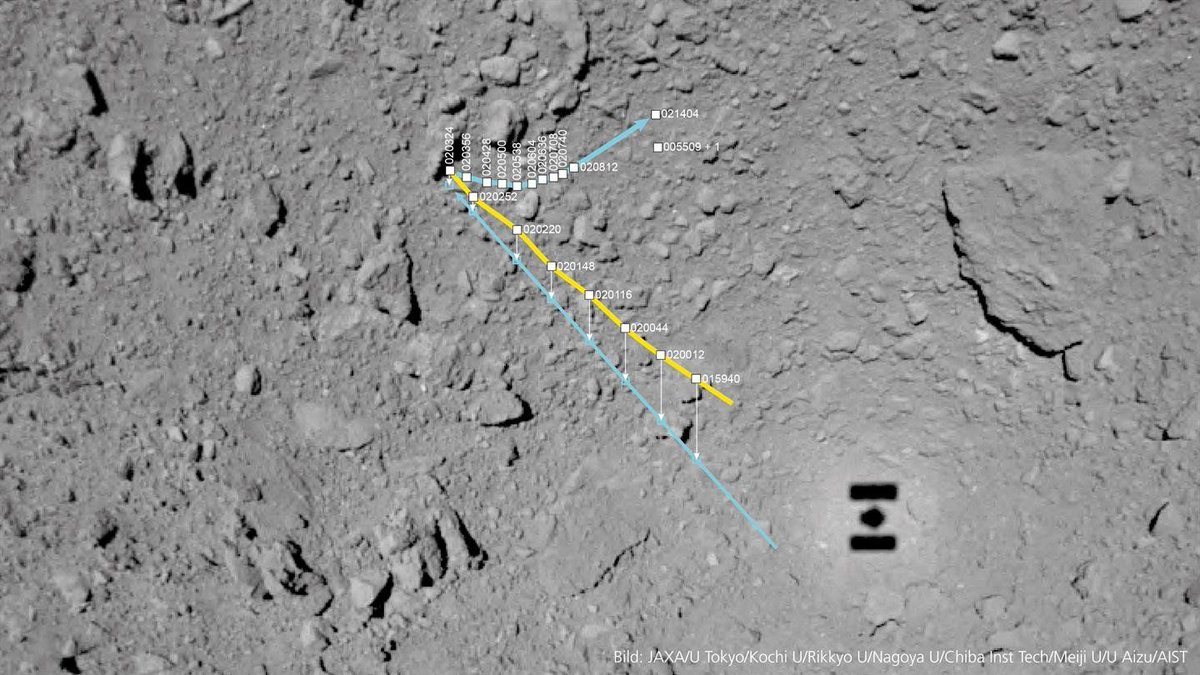
The tiny hopping-robot MASCOT completed its 17 hour mission on the asteroid Ryugu in early October. Now the German Aerospace Center (DLR) has released an image of MASCOT’s path across the asteroid. Surprised by what MASCOT found on the surface, they’ve named the landing spot “Alice’s Wonderland.”
Continue reading “The Path that MASCOT Took Across Asteroid Ryugu During its 17 Hours of Life”
A German-French Hopping Robot Just Landed on the Surface of Asteroid Ryugu
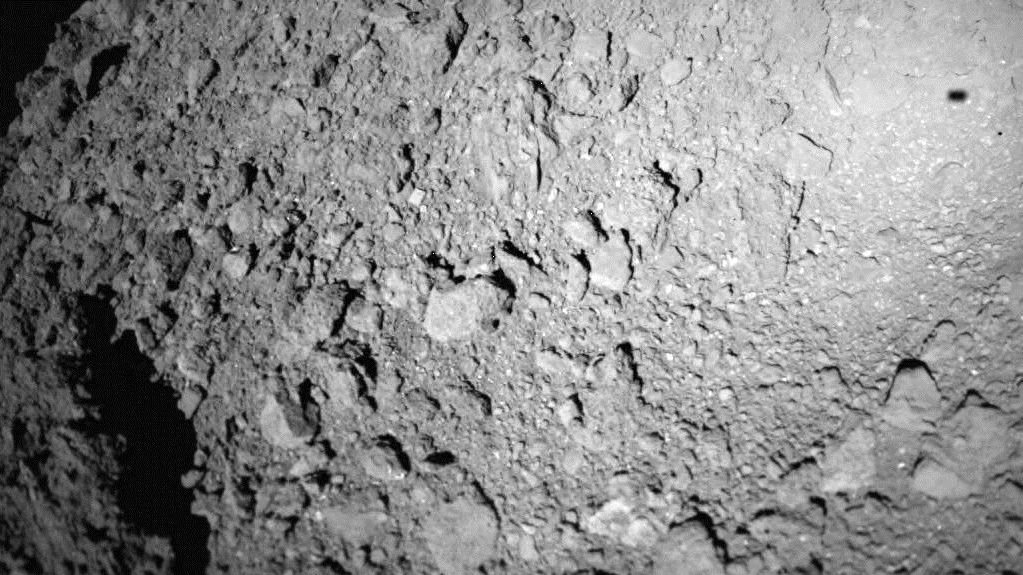

Earlier this week asteroid Ryugu had a visitor. The Mobile Asteroid Surface Scout (MASCOT) landed on Ryugu on October 3rd after it was successfully deployed from the Japanese Hayabusa2 space probe. The little hopping robot’s visit was brief however, and it stopped functioning on Oct. 4th.
Continue reading “A German-French Hopping Robot Just Landed on the Surface of Asteroid Ryugu”
A Mission to Deflect an Asteroid Just Moved into the Final Design and Assembly Phase

Within near-Earth space, there are over 18,000 asteroids whose orbit occasionally brings them close to Earth. Over the course of millions of years, some of these Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) – which range from a few meters to tens of kilometers in diameter – may even collide with Earth. It is for this reason that the ESA and other space agencies around the world are engaged in coordinated efforts to routinely monitor larger NEOs and track their orbits.
In addition, NASA and other space agencies have been developing counter-measures in case any of these objects stray too close to our planet in the future. One proposal is NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART), the world’s first spacecraft specifically designed to deflect incoming asteroids. This spacecraft recently moved into the final design and assembly phase and will launch to space in the next few years.
Carnival of Space #575
Welcome to the 575th Carnival of Space! The Carnival is a community of space science and astronomy writers and bloggers, who submit their best work each week for your benefit. We have a fantastic roundup today including news from the IAU, so now, on to this week’s worth of stories!
Continue reading “Carnival of Space #575”




