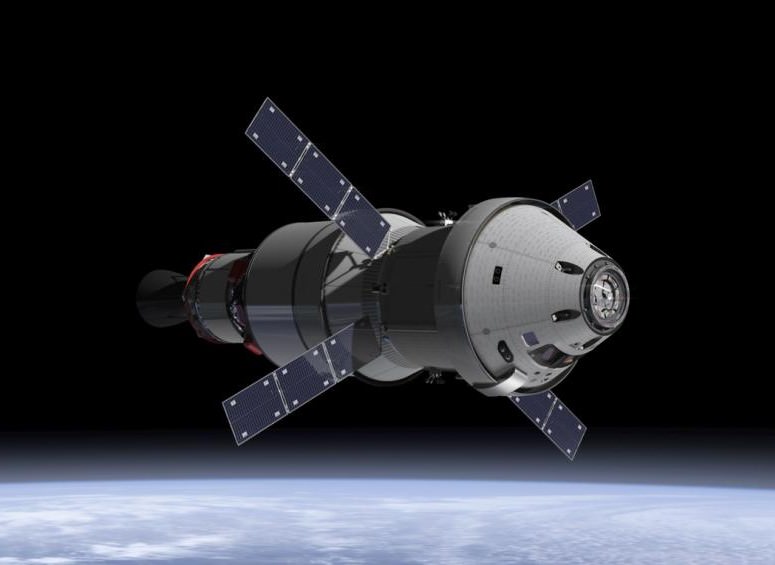
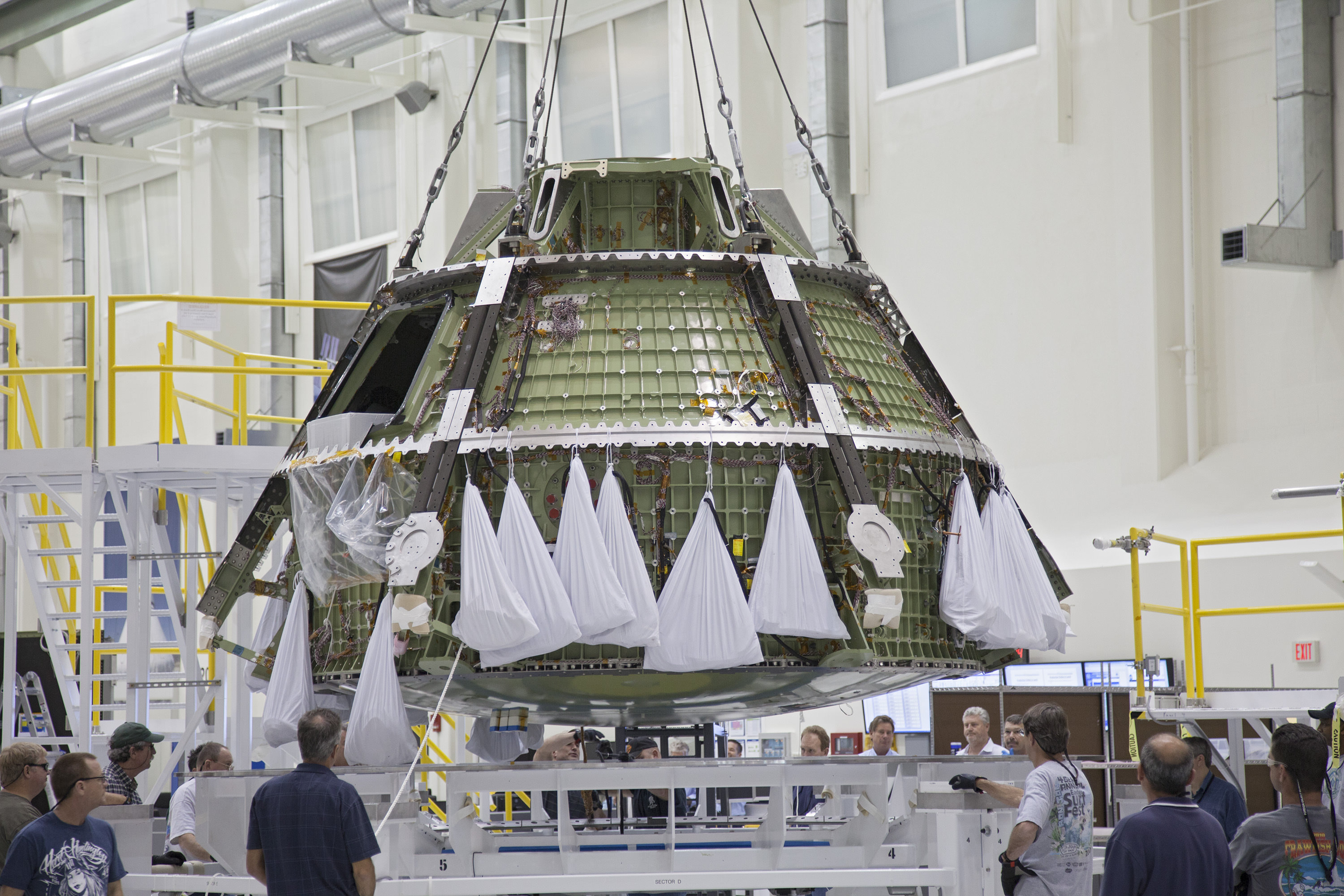
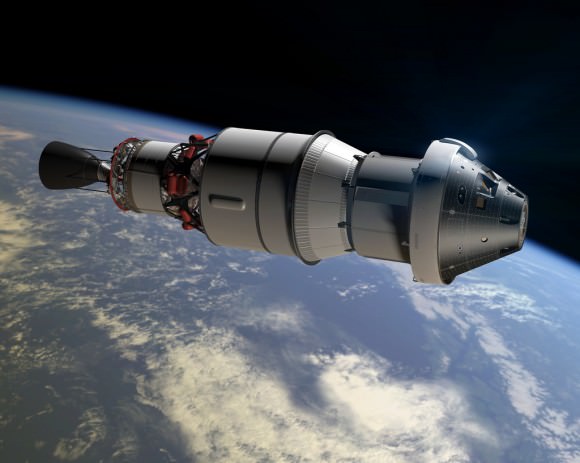
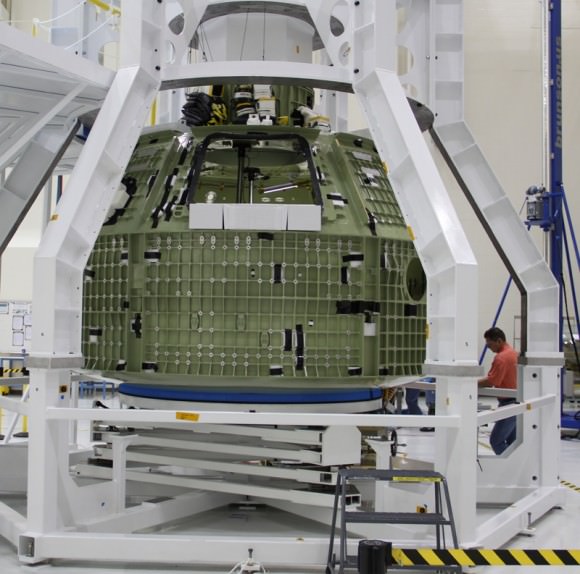
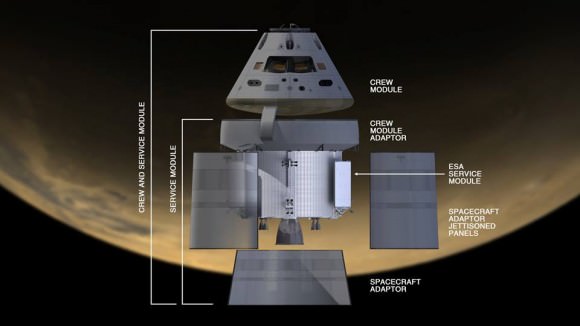
NASA Orion spacecraft blasts off atop 1st Space Launch System rocket in 2017 – attached to European provided service module – on an ambitious mission to explore Deep Space some 40,000 miles beyond the Moon, where an asteroid could be relocated as early as 2021. Credit: NASA
Story updated with further details[/caption]
NASA managers have announced a bold new plan to significantly alter and upgrade the goals and complexity of the 1st mission of the integrated Orion/Space Launch System (SLS) human exploration architecture – planned for blastoff in late 2017.
The ambitious first flight, called Exploration Mission 1 (EM-1), would be targeted to send an unpiloted Orion spacecraft to a point more than 40,000 miles (70,000 kilometers) beyond the Moon as a forerunner supporting NASA’s new Asteroid Redirect Initiative – recently approved by the Obama Administration.
The EM-1 flight will now serve as an elaborate harbinger to NASA’s likewise enhanced EM-2 mission, which would dispatch a crew of astronauts for up close investigation of a small Near Earth Asteroid relocated to the Moon’s vicinity.

Until recently NASA’s plan had been to launch the first crewed Orion atop the 2nd SLS rocket in 2021 to a high orbit around the moon on the EM-2 mission, said NASA Associate Administrator Lori Garver in an prior interview with me at the Kennedy Space Center.
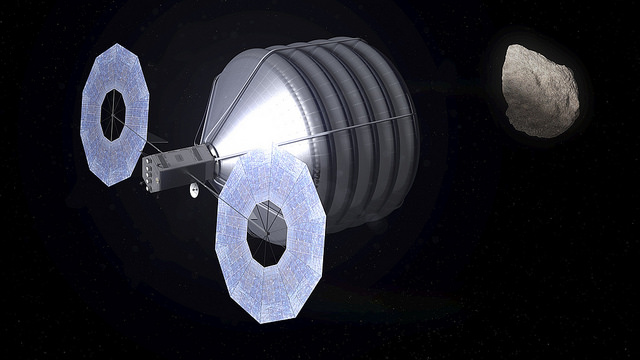
The enhanced EM-1 flight would involve launching an unmanned Orion, fully integrated with the Block 1 SLS to a Deep Retrograde Orbit (DRO) near the moon, a stable orbit in the Earth-moon system where an asteroid could be moved to as early as 2021.
Orion’s mission duration would be nearly tripled to 25 days from the original 10 days.
“The EM-1 mission with include approximately nine days outbound, three to six days in deep retrograde orbit and nine days back,” Brandi Dean, NASA Johnson Space Center spokeswoman told Universe Today exclusively.
The proposed much more technologically difficult EM-1 mission would allow for an exceptionally more vigorous work out and evaluation of the design of all flight systems for both Orion and SLS before risking a flight with humans aboard.
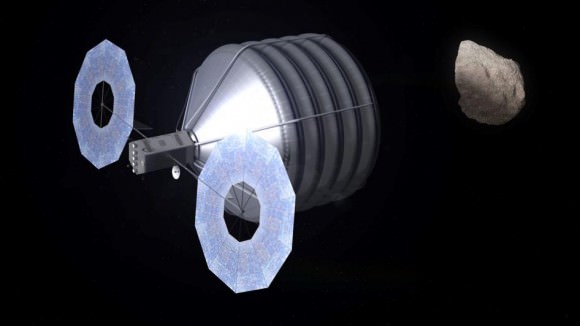
A slew of additional thruster firings would exercise the engines to change orbital parameters outbound, around the moon and inbound for reentry.
The current Deep Retrograde Orbit (DRO) plan includes several thruster firings from the Orion service module, including a powered lunar flyby, an insertion at DRO, an extraction maneuver from the DRO and a powered flyby on return to Earth.
Orion would be outfitted with sensors to collect a wide variety of measurements to evaluate its operation in the harsh space environment.
“EM-1 will have a compliment of both operational flight instrumentation and development flight instrumentation. This instrumentation suite gives us the ability to measure many attributes of system functionality and performance, including thermal, stress, displacement, acceleration, pressure and radiation,” Dean told me.
The EM-1 flight has many years of planning and development ahead and further revisions prior to the 2017 liftoff are likely.
“Final flight test objectives and the exact set of instrumentation required to meet those objectives is currently under development,” Dean explained.
Orion is NASA’s next generation manned space vehicle following the retirement of NASA’s trio of Space Shuttles in 2011.
The SLS launcher will be the most powerful and capable rocket ever built by humans – exceeding the liftoff thrust of the Apollo era Moon landing booster, the mighty Saturn V.
“We sent Apollo around the moon before we landed on it and tested the space shuttle’s landing performance before it ever returned from space.” said Dan Dumbacher, NASA’s deputy associate administrator for exploration systems development, in a statement.
“We’ve always planned for EM-1 to serve as the first test of SLS and Orion together and as a critical step in preparing for crewed flights. This change still gives us that opportunity and also gives us a chance to test operations planning ahead of our mission to a relocated asteroid.”
Both Orion and SLS are under active and accelerating development by NASA and its industrial partners.
The 1st Orion capsule is slated to blast off on the unpiloted EFT-1 test flight in September 2014 atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket on a two orbit test flight to an altitude of 3,600 miles above Earth’s surface.

It will then reenter Earth’s atmosphere at speeds of about 20,000 MPH (11 km/sec) and endure temperatures of 4,000 degrees Fahrenheit in a critical test designed to evaluate the performance of Orion’s heatshield and numerous spacecraft systems.
Orion EFT-1 is already under construction at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) by prime contractor Lockheed Martin – read my earlier story here.
Integration and stacking tests with Orion’s emergency Launch Abort System are also in progress at KSC – details here.
NASA says the SLS is also in the midst of a extensive review process called the Preliminary Design Review (PDR) to ensure that all launch vehicle components and systems will achieve the specified performance targets and be completed in time to meet the 2017 launch date. The PDR will be completed later this summer.
NASA’s goal with Orion/SLS is to send humans to the Moon and other Deep Space destinations like Asteroids and Mars for the first time in over forty years since the final manned lunar landing by Apollo 17 back in 1972.
NASA Headquarters will make a final decision on upgrading the EM-1 mission after extensive technical reviews this summer.