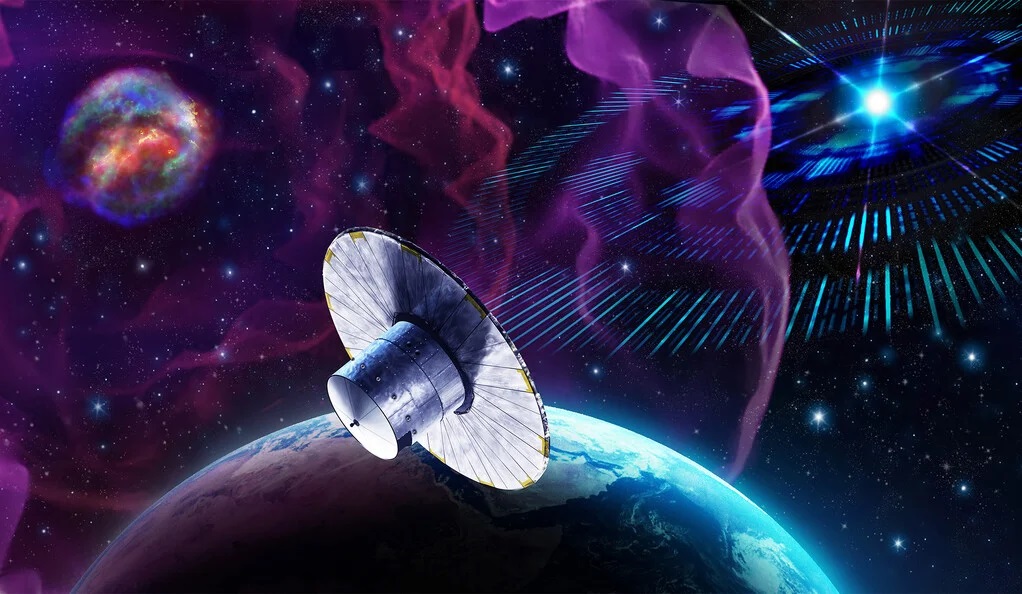
For over ten years, the ESA’s Gaia Observatory has monitored the proper motion, luminosity, temperature, and composition of over a billion stars throughout our Milky Way galaxy and beyond. This data will be used to construct the largest and most precise 3D map of the cosmos ever made and provide insight into the origins, structure, and evolutionary history of our galaxy. Unfortunately, this sophisticated astrometry telescope is positioned at the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrange Point, far beyond the protection of Earth’s atmosphere and magnetosphere.
As a result, Gaia has experienced two major hazards in recent months that could endanger the mission. These included a micrometeoroid impact in April that disrupted some of Gaia‘s very sensitive sensors. This was followed by a solar storm in May—the strongest in 20 years—that caused electrical problems for the mission. These two incidents could threaten Gaia‘s ability to continue mapping stars, planets, comets, asteroids, quasars, and other objects in the Universe until its planned completion date of 2025.
Continue reading “Gaia Hit by a Micrometeoroid AND Caught in a Solar Storm”