NASA’s ‘Journey to Mars’ is ramping up significantly with ‘InSight’ – as the agency’s next Red Planet lander has now been assembled into its flight configuration and begun a comprehensive series of rigorous and critical environmental stress tests that will pave the path to launch in 2016 on a mission to unlock the riddles of the Martian core.
The countdown clock is ticking relentlessly and in less than nine months time, NASA’s InSight Mars lander is slated to blastoff in March 2016.
InSight, which stands for Interior Exploration Using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is a stationary lander. It will join NASA’s surface science exploration fleet currently comprising of the Curiosity and Opportunity missions which by contrast are mobile rovers.
But before it will even be allowed to get to the launch pad, the Red Planet explorer must first prove its mettle and show that it can operate in and survive the harsh and unforgiving rigors of the space environment via a battery of prelaunch tests. That’s an absolute requirement in order for it to successfully carry out its unprecedented mission to investigate Mars deep interior structure.
InSight’s purpose is to elucidate the nature of the Martian core, measure heat flow and sense for “Marsquakes.” These completely new research findings will radically advance our understanding of the early history of all rocky planets, including Earth and could reveal how they formed and evolved.
“Today, our robotic scientific explorers are paving the way, making great progress on the journey to Mars,” said Jim Green, director of NASA’s Planetary Science Division at the agency’s headquarters in Washington, in a statement.
“Together, humans and robotics will pioneer Mars and the solar system.”

The launch window for InSight opens on March 4 and runs through March 30, 2016.
InSight will launch atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California.
InSight counts as NASA’s first ever interplanetary mission to launch from California.
The car sized probe will touch down near the Martian equator about six months later in the fall of 2016.
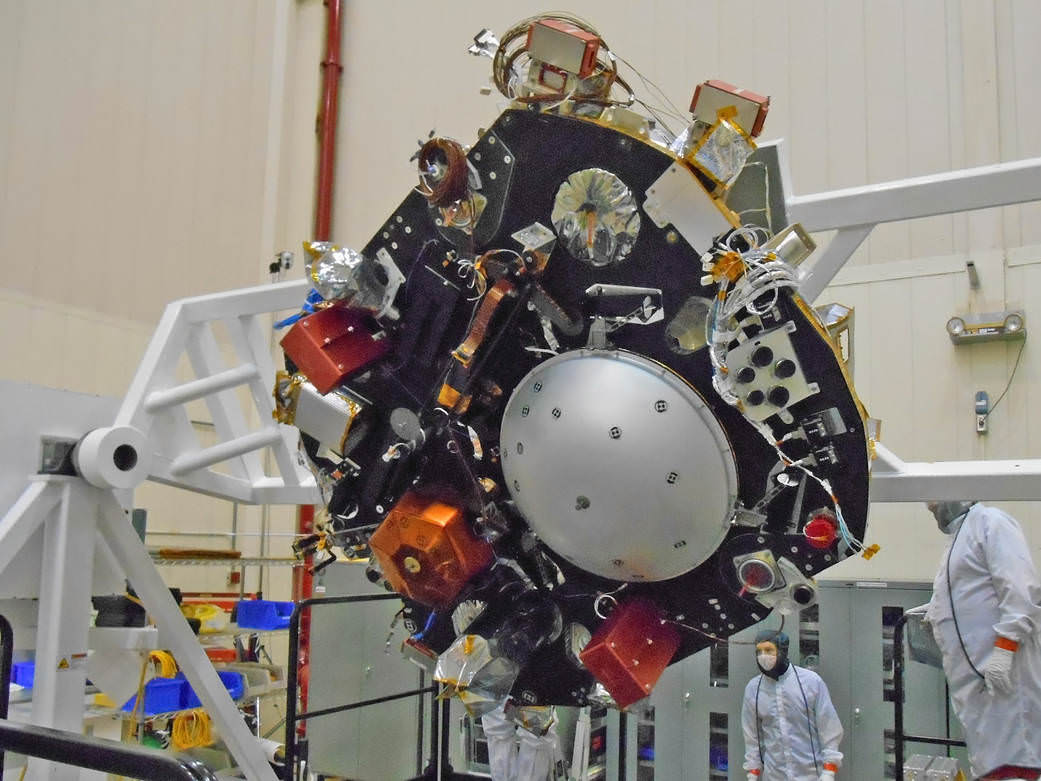
The prime contractor for InSight is Lockheed Martin Space Systems in Denver, Co and the engineering and technical team recently finished assembling the lander into its final configuration.
So now the time has begun to start the shakedown that literally involve “shaking and baking and zapping” the spacecraft to prove its ready and able to meet the March 2016 launch deadline.
During the next seven months of environmental testing at Lockheed’s Denver facility, “the lander will be exposed to extreme temperatures, vacuum conditions of nearly zero air pressure simulating interplanetary space, and a battery of other tests.”
“The assembly of InSight went very well and now it’s time to see how it performs,” said Stu Spath, InSight program manager at Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver, in a statement.
“The environmental testing regimen is designed to wring out any issues with the spacecraft so we can resolve them while it’s here on Earth. This phase takes nearly as long as assembly, but we want to make sure we deliver a vehicle to NASA that will perform as expected in extreme environments.”
The first test involves “a thermal vacuum test in the spacecraft’s “cruise” configuration, which will be used during its seven-month journey to Mars. In the cruise configuration, the lander is stowed inside an aeroshell capsule and the spacecraft’s cruise stage – for power, communications, course corrections and other functions on the way to Mars — is fastened to the capsule.”
After the vacuum test, InSight will be subjected to a series of tests simulating the vibrations of launch, separation and deployment shock, as well as checking for electronic interference between different parts of the spacecraft and compatibility testing.
Finally, a second thermal vacuum test will expose the probe “to the temperatures and atmospheric pressures it will experience as it operates on the Martian surface.”
The $425 million InSight mission is expected to operate for about two years on the Martian surface.

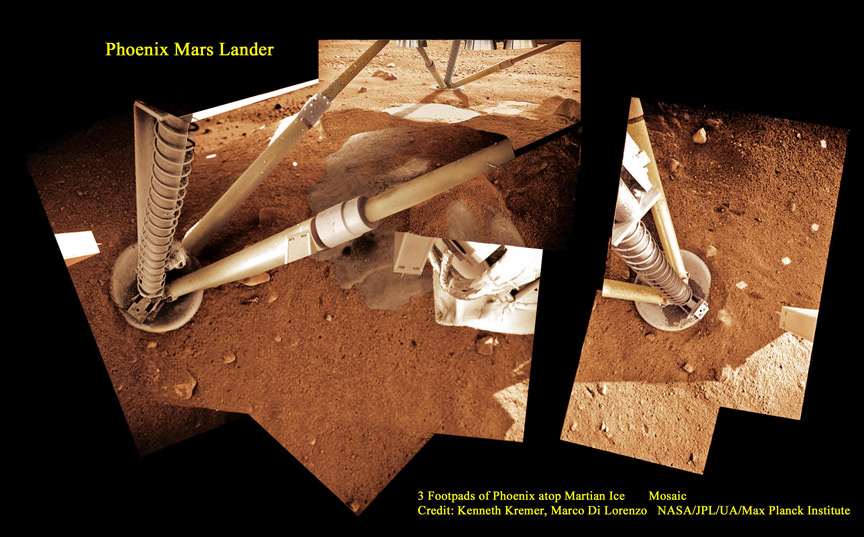
InSight is an international science mission and a near duplicate of NASA’s successful Phoenix Mars landing spacecraft, Bruce Banerdt, InSight Principal Investigator of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), Pasadena, California, told Universe Today.
“InSight is essentially built from scratch, but nearly build-to-print from the Phoenix design,” Banerdt, of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena , Calif, told me. The team can keep costs down by re-using the blueprints pioneered by Phoenix instead of creating an entirely new spacecraft.
It is funded by NASA’s Discovery Program as well as several European national space agency’s and countries. Germany and France are providing InSight’s two main science instruments; HP3 and SEIS through the Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt. or German Aerospace Center (DLR) and the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES).
“The seismometer (SEIS, stands for Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure) is from France (built by CNES and IPGP) and the heat flow probe (HP3, stands for Heat Flow and Physical Properties Probe) is from Germany (built by DLR),” Banerdt explained.
SEIS and HP3 are stationed on the lander deck. They will each be picked up and deployed by a robotic arm similar to that flown on Phoenix with some modifications.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.