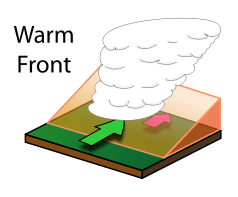
[/caption]A warm front is the transition zone that marks where a warm air mass starts replacing a cold air mass. Warm fronts tend to move from southwest to southeast. Normally the air behind a warm front is warmer than the air in front of it. Normally when a warm front passes through an area the air will get warmer and more humid. Warm fronts signal significant changes in the weather. Here are some of the weather signs that appear as a warm front passes over a region.
First before the warm front arrives the pressure in area start to steadily decrease and temperatures remain cool. The winds tend to blow south to southeast in the northern hemisphere and north to northeast in the southern hemisphere. The precipitation is normally rain, sleet, or snow. Common cloud types that appear would various types of stratus, cumulus, and nimbus clouds. The dew point also rises steadily
While the front is passing through a region temperatures start to warm rapidly. The atmospheric pressure in the area that was dropping starts to level off. The winds become variable and precipitation turns into a light drizzle. Clouds are mostly stratus type clouds formations. The dew point then starts to level off.
After the warm front passes conditions completely reverse. The atmospheric pressure rises slightly before falling. The temperatures are warmer then they level off. The winds in the northern hemisphere blow south-southwest in the northern hemisphere and north-northwest in the southern hemisphere. Cloudy conditions start to clear with only cumulonimbus and stratus clouds. The dew point rises then levels off.
Knowing about how warm fronts work gives a better understanding of how pressure systems interact with geography to create weather. Looking at warm fronts we learn that they are the transition zone between warm humid air masses and cool, dry air masses. We know that these masses interact in a cycle of rising and falling air that alters the pressure of atmosphere causing changes in weather.
We have written many articles about warm front for Universe Today. Here’s an article about cyclones, and here’s an article about cloud formations.
If you’d like more info on warm front, check out NOAA National Weather Service. And here’s a link to NASA’s Earth Observatory.
We’ve also recorded an episode of Astronomy Cast all about planet Earth. Listen here, Episode 51: Earth.
Reference:
http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides/mtr/af/frnts/wfrnt/def.rxml