Have you heard?
I remember, getting into astronomy as a kid back in the 1970s, building a pinhole projector in a shoe box and watching the partial solar eclipse of February 26th, 1979 from our living room in northern Maine. I had no Learjet, no magic carpet to whisk me off to that thin thread of a path of totality way out west along the Pacific coast. As I settled for the 66% partial solar eclipse, I remember news reports stating that a total solar eclipse won’t cross the United States again until… August 21st, 2017.
That date is almost upon us now, only one month from this coming Friday.
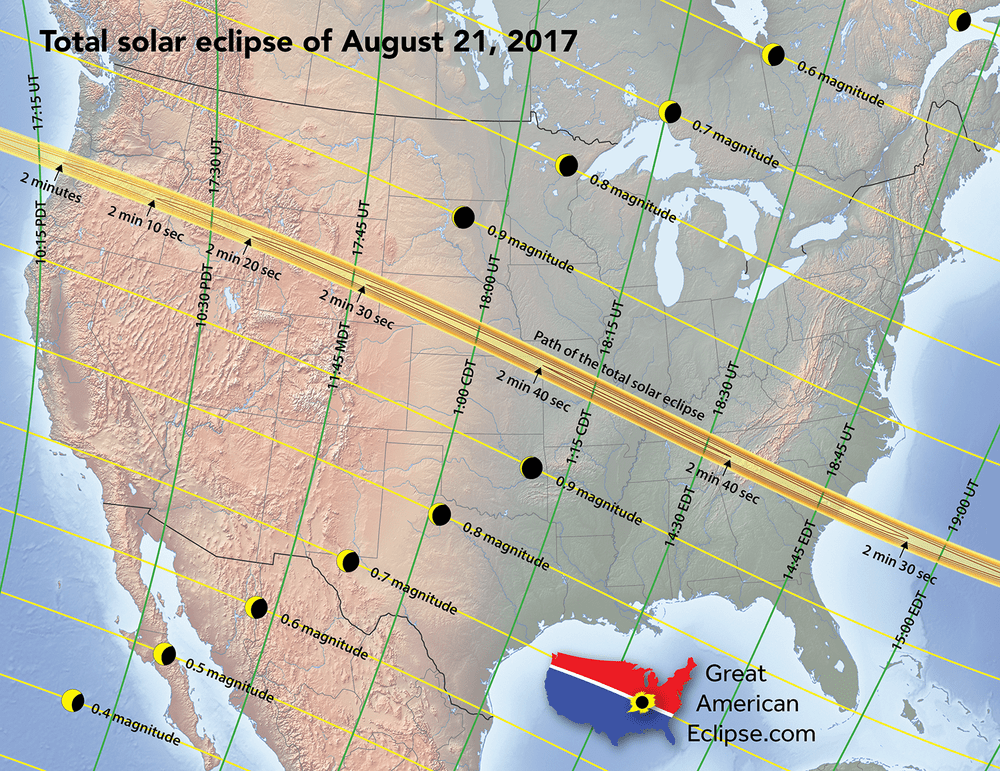
This total solar eclipse is one for the ages, THE big ticket event for 2017. Umbraphiles (those who chase eclipses) have been planning for this one for decades, and it’s already hard to find a room along the path. Fear not, as you only need to be within striking distance the day of the eclipse to reach totality, though expect the roads to be congested that Monday morn.
The eclipse is indeed the first time totality touches the contiguous (“lower 48”) United States since 1979, and the first total solar eclipse to cross the United States since almost a century ago on June 8th 1918. A total solar eclipse did cross Hawaii on July 11th, 1991.
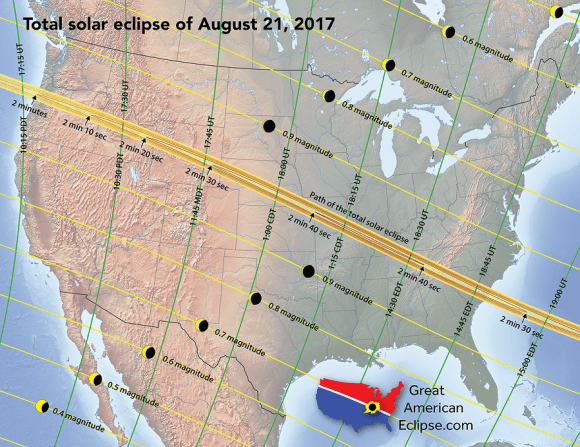
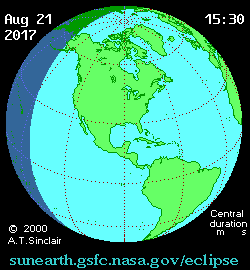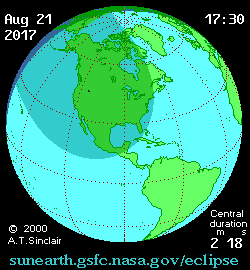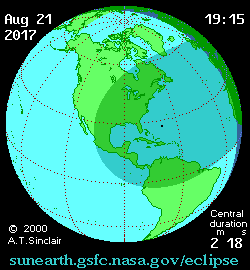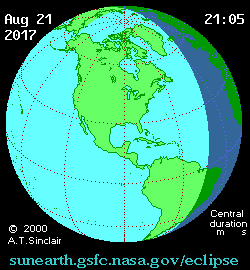
Partial phases for the eclipse begin at 15:47 Universal Time (UT) and span 5 hours and 18 minutes until 21:04 UT. The partial aspect of the eclipse touches all continents except Antarctica and Australia. The 115 kilometer wide shadow of Earth’s moon (known as the umbra) first makes landfall over the Oregon coast at 17:16 UT /10:16 Pacific Daylight Saving time (PDT) and races eastward at 3,900 kilometers per second. The shadow touches 14 states, just briefly nicking Montana and Iowa. Maximum totality of 2 minutes, 40 seconds occurs near Carbondale, Illinois.
Seen a partial solar eclipse before and wonder what the big deal is? You really need to get to the path of totality for the full eclipse experience. Millions live in the path of the August 21st eclipse, and millions more within an easy day drive. We witnessed the May 10th, 1994 annular eclipse from the shores of Lake Erie in Sandusky, Ohio, and can attest that 1% of the Sun at midday is still pretty darned bright.

Action really gets interesting moments before totality sweeps over the landscape. Be sure to keep an eye out for shadow bands flitting across the ground, an effect notoriously hard to photograph. It’s safe to drop those glasses moments before totality, when you’ll see those final rays of sunlight streaming through the valleys along the limb of the Moon, creating what’s known as Baily’s Beads or the Diamond Ring Effect. You’re now in the realm of the shadow of the Moon, an ethereal shadow world turned on its head. I dare you to blink. Looking sunward, you’ll see the pearly corona of the Sun, a white halo about as bright as a Full Moon spied only during totality.
Think about it: you knew this moment was coming, perhaps you’d been planning for it for years… but would you think as an average citizen thousands or millions of years ago if you were suddenly confronted with such as strange sky?
And all too soon, it’s over.
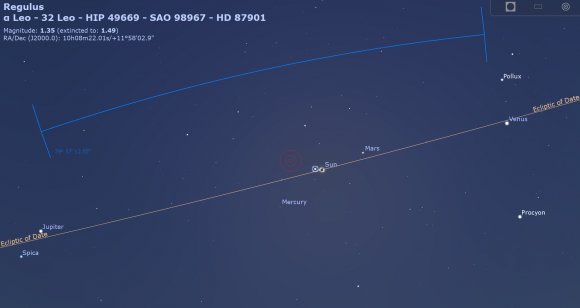
Be sure to keep an eye out for planets and bright stars during the eclipse. Totality is a late morning affair out west, and an early afternoon event for the US East Coast. All naked eye planets except Saturn are above the horizon during totality, covering a span of about 80 degrees from Jupiter to Venus. Look just one degree from the eclipsed Sun and you might just spy the star Regulus occulted by the Moon shortly after the eclipse.
Perhaps you’re planning on aiming a battery of cameras skyward during the eclipse, or maybe, you’re simply planning on simply enjoying the moment, then photographing the next one. The Eclipse MegaMovie project is planning on capturing the scene down the eclipse path. NASA will also be flying overhead with converted WB-57F aircraft, looking to capture high definition video in the visible and infrared wavelengths during the eclipse.

You need to take the same safety precautions observing the partial phases of the eclipse as you would during ordinary solar observing. Use only a filtered telescope designed to look at the Sun, or solar eclipse glasses with an ISO 12312-2 rating. Make sure that filter fits snugly over the aperture of the telescope and cannot be removed by curious prying hands or high winds, and that all finder-scopes are removed, stowed and/or covered. Also, don’t try and use one of those old screw-on eyepiece solar filters that came with old department store 60mm refractors, as they can heat up and crack. Likewise, be careful when projecting the Sun through a telescope onto a piece of paper, as it can heat up and damage the optics.
If you don’t think the danger is real, read this amazing recent interview with an optometrist on Space.com, where he states you can actually see the crescent Sun burned into the backs of patient’s eyes who stared too long at a partial solar eclipse (!) It’s a permanent souvenir you don’t want to have. Don’t be like 18th century psychologist Gustav Fechner who blinded himself staring at the Sun, mesmerized by the glare of lingering afterimages.

And though we can predict eclipses centuries out, there’s one thing we won’t know eclipse day: what the weather plans on doing. Best bets are for clear skies out west, though you only need a gap in the clouds to see the Sun. We’ll be running a final post on Universe Today just days prior to the eclipse looking at weather prospects, solar activity and prospects for transits of the International Space Station and possible views from space.

The second eclipse season for 2017 begins with a partial lunar eclipse favoring on August 7th… we’ve got you covered on that as well. And us? We’ll be watching the event from the Pisgah Astronomical Research Institute (PARI) in Smoky Mountains just outside of Asheville, North Carolina for a glorious 107 seconds of totality.
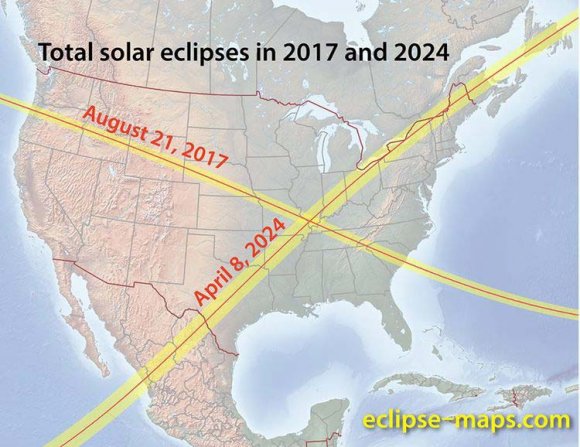
And after that? Well, totality visits that same living room in northern Maine on April 8th, 2024… I think I know where I’ll be then.
A request- observing the eclipse from the path of totality? I’m planning on doing a state-by-state roundup post eclipse, perhaps with a paragraph of personal impressions from each observer. Let us know what your plans are!
-Read more about the August 21st total solar eclipse, plus the true tale of Edison’s Chickens and the 1878 total solar eclipse in out free e-guide to 101 Astronomical Events for 2017.
-Eclipse… fiction? Read our original eclipse-fueled sci-fi tales Exeligmos, Peak Season, Shadowfall and more!