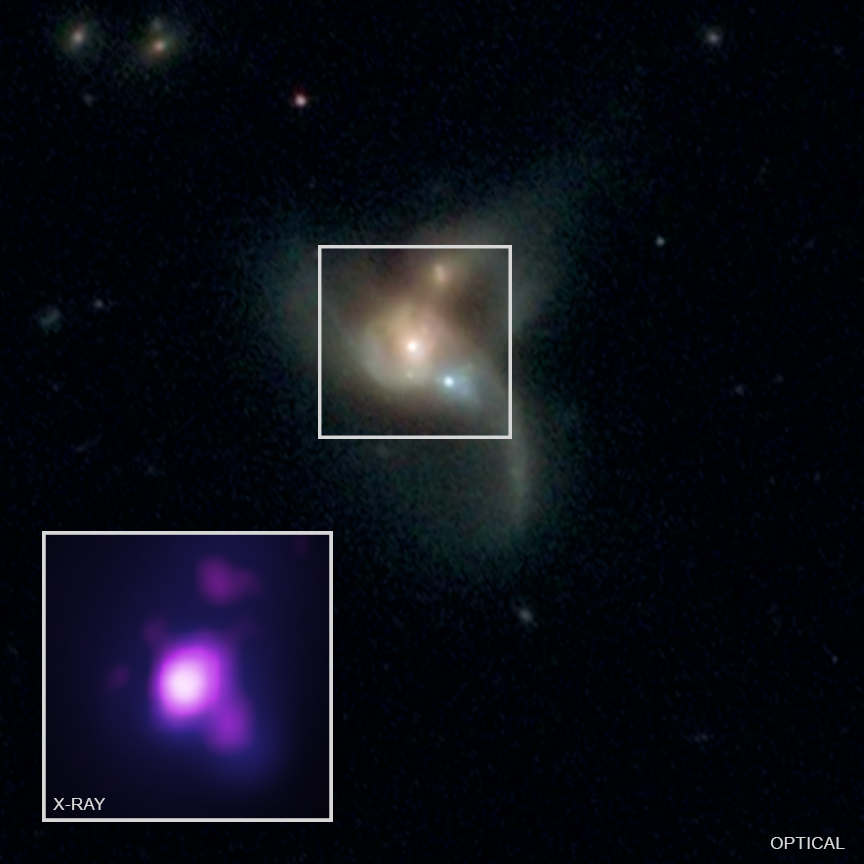
Black holes are one of the most awesome and mysterious forces of nature. At the same time, they are fundamental to our understanding of astrophysics. Not only are black holes the result of particularly massive stars that go supernova at the end of their lives, they are also key to our understanding of General Relativity and are believed to have played a role in cosmic evolution.
Because of this, astronomers have diligently been trying to create a census of black holes in the Milky Way galaxy for many years. However, new research indicates that astronomers may have overlooked an entire class of black holes. This comes from a recent discovery where a team of astronomers observed a black hole that is just over three Solar masses, making it the smallest black hole discovered to date.
Continue reading “The Lowest Mass Black Hole has Been Found, only 3.3 Times the Mass of the Sun”