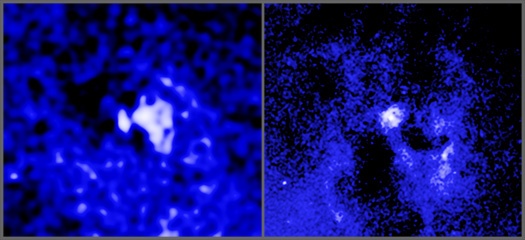
Black holes seem to provide endless fascination to astronomers. This is at least partly due to the extreme physics that takes place in and around them, but sometimes, it might harken back to cultural touchpoints that made them interested in astronomy in the first place. That seems to be the case for the authors of a new paper on the movement of jets coming out of black holes. Dubbing them “Death Star” black holes, researchers used data from the Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) and the Chandra X-ray Observatory to look at where these black holes fired jets of superheated particles. And over time the found they did something the fiction Death Star could also do – move.
Continue reading “Black Holes are Firing Beams of Particles, Changing Targets Over Time”Gravitational Lenses Could Pin Down Black Hole Mergers with Unprecedented Accuracy
Gravitational wave astronomy has been one of the hottest new types of astronomy ever since the LIGO consortium officially detected the first gravitational wave (GW) back in 2016. Astronomers were excited about the number of new questions that could be answered using this sensing technique that had never been considered before. But a lot of the nuance of the GWs that LIGO and other detectors have found in the 90 gravitational wave candidates they have found since 2016 is lost.
Researchers have a hard time determining which galaxy a gravitational wave comes from. But now, a new paper from researchers in the Netherlands has a strategy and developed some simulations that could help narrow down the search for the birthplace of GWs. To do so, they use another darling of astronomers everywhere—gravitational lensing.
Continue reading “Gravitational Lenses Could Pin Down Black Hole Mergers with Unprecedented Accuracy”Astronomers Will Get Gravitational Wave Alerts Within 30 Seconds
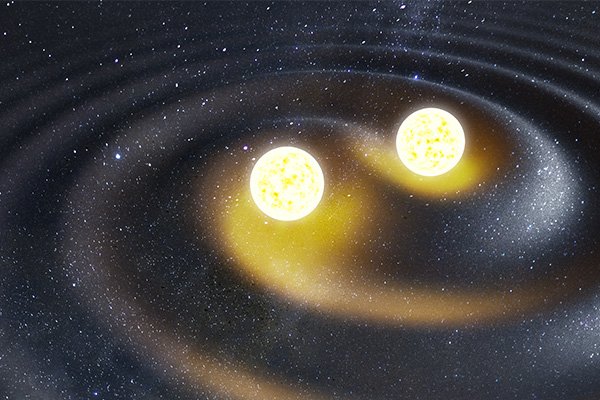

Any event in the cosmos generates gravitational waves, the bigger the event, the more disturbance. Events where black holes and neutron stars collide can send out waves detectable here on Earth. It is possible that there can be an event in visible light when neutron stars collide so to take advantage of every opportunity an early warning is essential. The teams at LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA observatories are working on an alert system that will alert astronomers within 30 seconds fo a gravity wave event. If warning is early enough it may be possible to identify the source and watch the after glow.
Continue reading “Astronomers Will Get Gravitational Wave Alerts Within 30 Seconds”The Brightest Gamma Ray Burst Ever Seen Came from a Collapsing Star
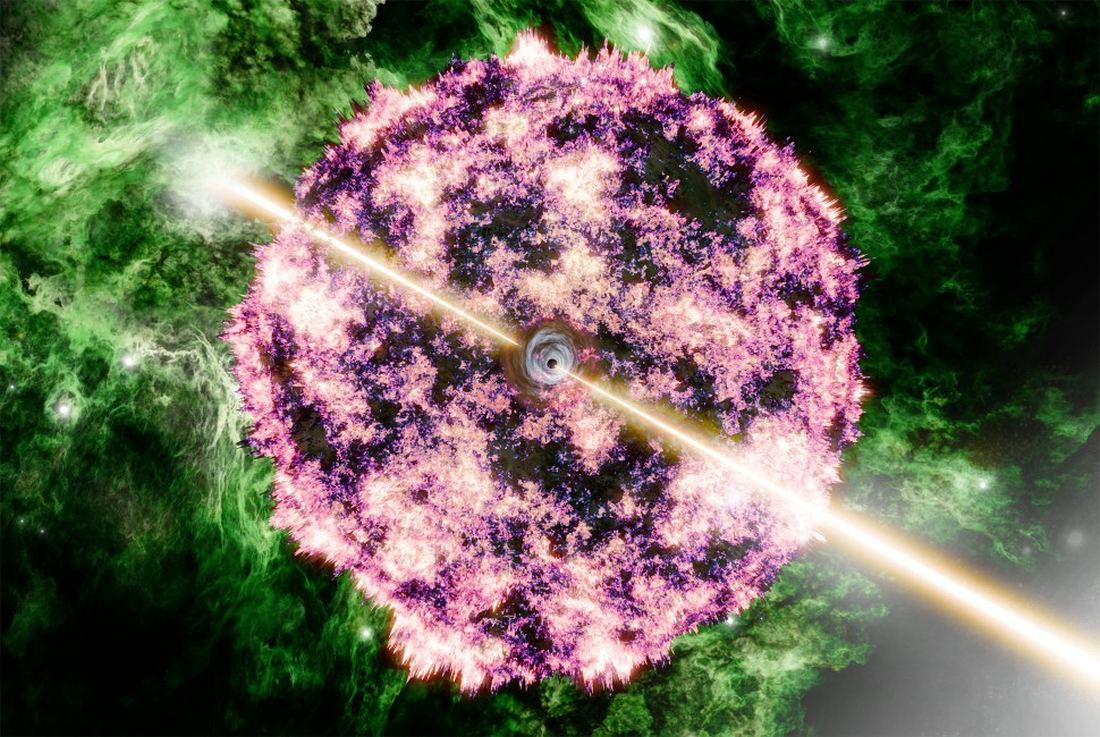

After a journey lasting about two billion years, photons from an extremely energetic gamma-ray burst (GRB) struck the sensors on the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory and the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope on October 9th, 2022. The GRB lasted seven minutes but was visible for much longer. Even amateur astronomers spotted the powerful burst in visible frequencies.
It was so powerful that it affected Earth’s atmosphere, a remarkable feat for something more than two billion light-years away. It’s the brightest GRB ever observed, and since then, astrophysicists have searched for its source.
Continue reading “The Brightest Gamma Ray Burst Ever Seen Came from a Collapsing Star”A Supermassive Black Hole with a Case of the Hiccups
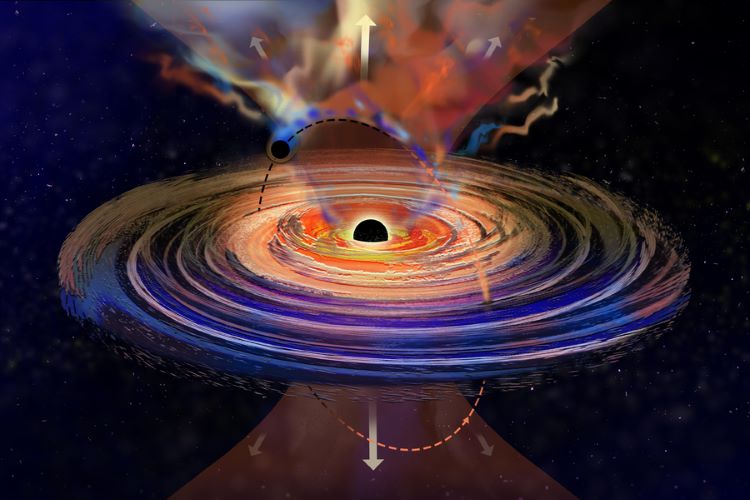

Can binary black holes, two black holes orbiting each other, influence their respective behaviors? This is what a recent study published in Science Advances hopes to address as a team of more than two dozen international researchers led by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) investigated how a smaller black hole orbiting a supermassive black hole could alter the outbursts of the energy being emitted by the latter, essentially giving it “hiccups”. This study holds the potential to help astronomers better understand the behavior of binary black holes while producing new methods in finding more binary black holes throughout the cosmos.
Continue reading “A Supermassive Black Hole with a Case of the Hiccups”New View Reveals Magnetic Fields Around Our Galaxy’s Giant Black Hole
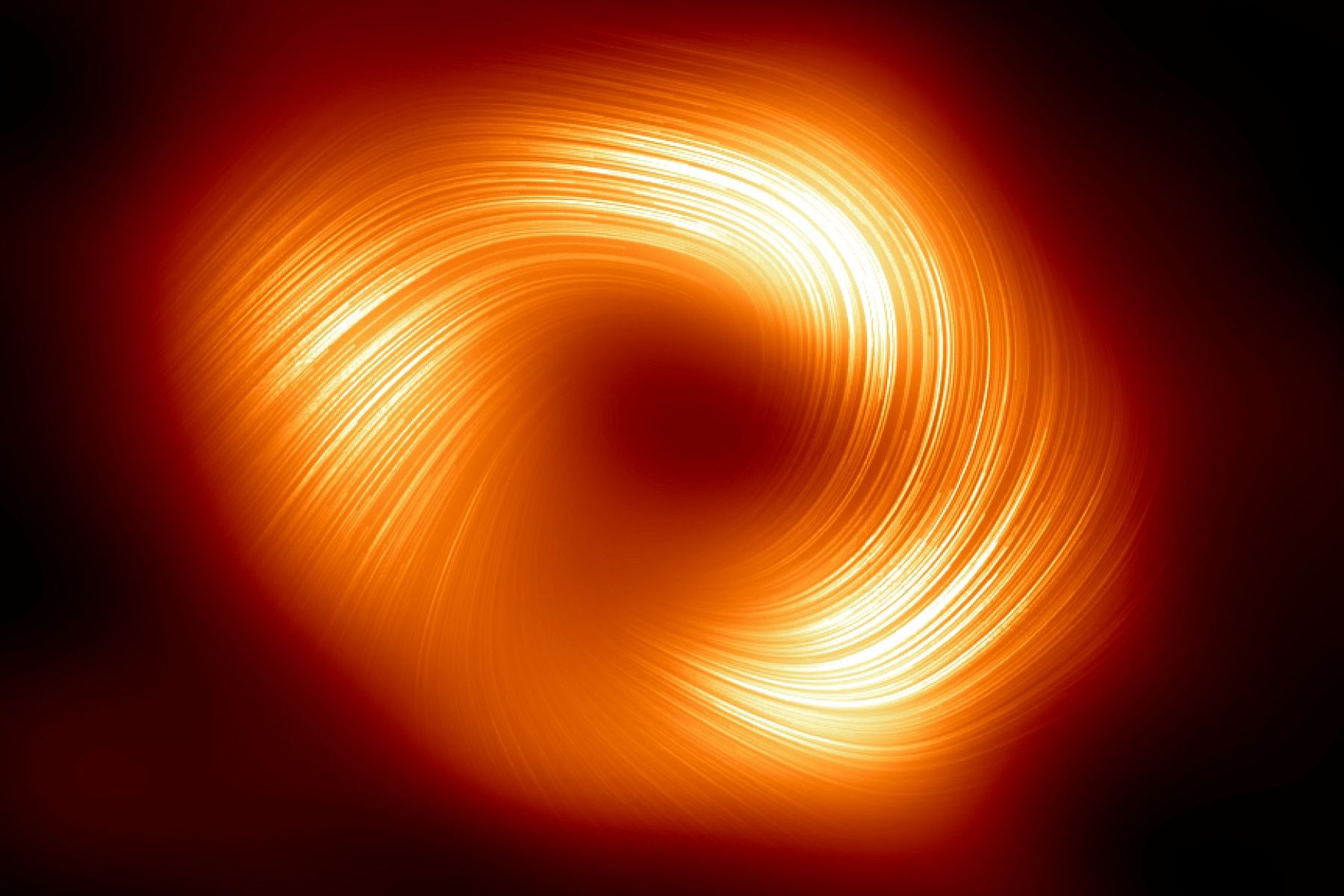

Fresh imagery from the Event Horizon Telescope traces the lines of powerful magnetic fields spiraling out from the edge of the supermassive black hole at the center of our Milky Way galaxy, and suggests that strong magnetism may be common to all supermassive black holes.
Continue reading “New View Reveals Magnetic Fields Around Our Galaxy’s Giant Black Hole”Powerful Jets From a Black Hole are Spawning Star Clusters
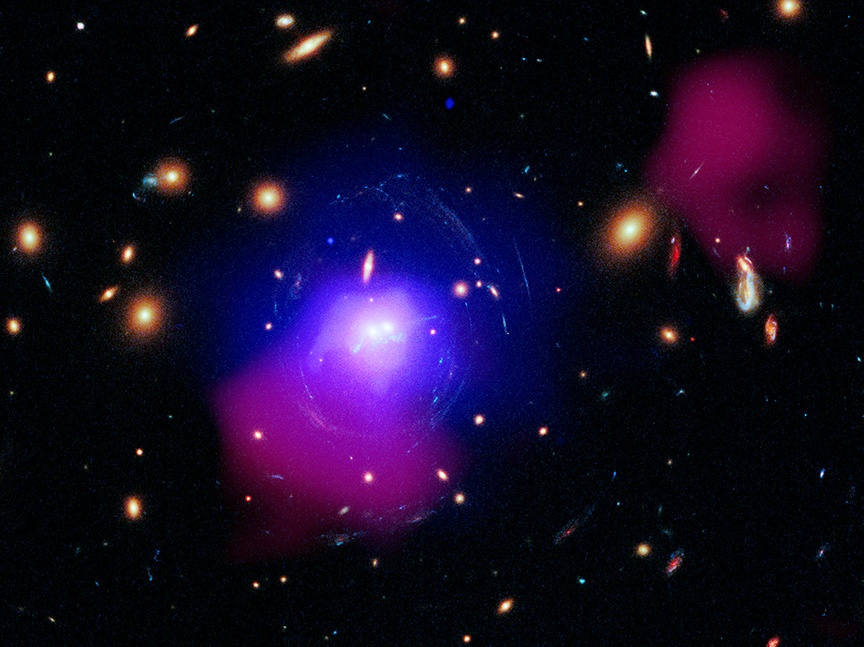
Supermassive black holes are messy feeders, and when they’re gorging on too much material, they can hurl high-energy jets into the surrounding Universe. Astronomers have found one of the most powerful eruptions ever seen, emanating from a black hole 3.8 billion light-years away. The powerful jets are blowing out cavities in intergalactic space and triggering the formation of a huge chain of star clusters.
Continue reading “Powerful Jets From a Black Hole are Spawning Star Clusters”Is this the Lightest Black Hole or Heaviest Neutron Star?
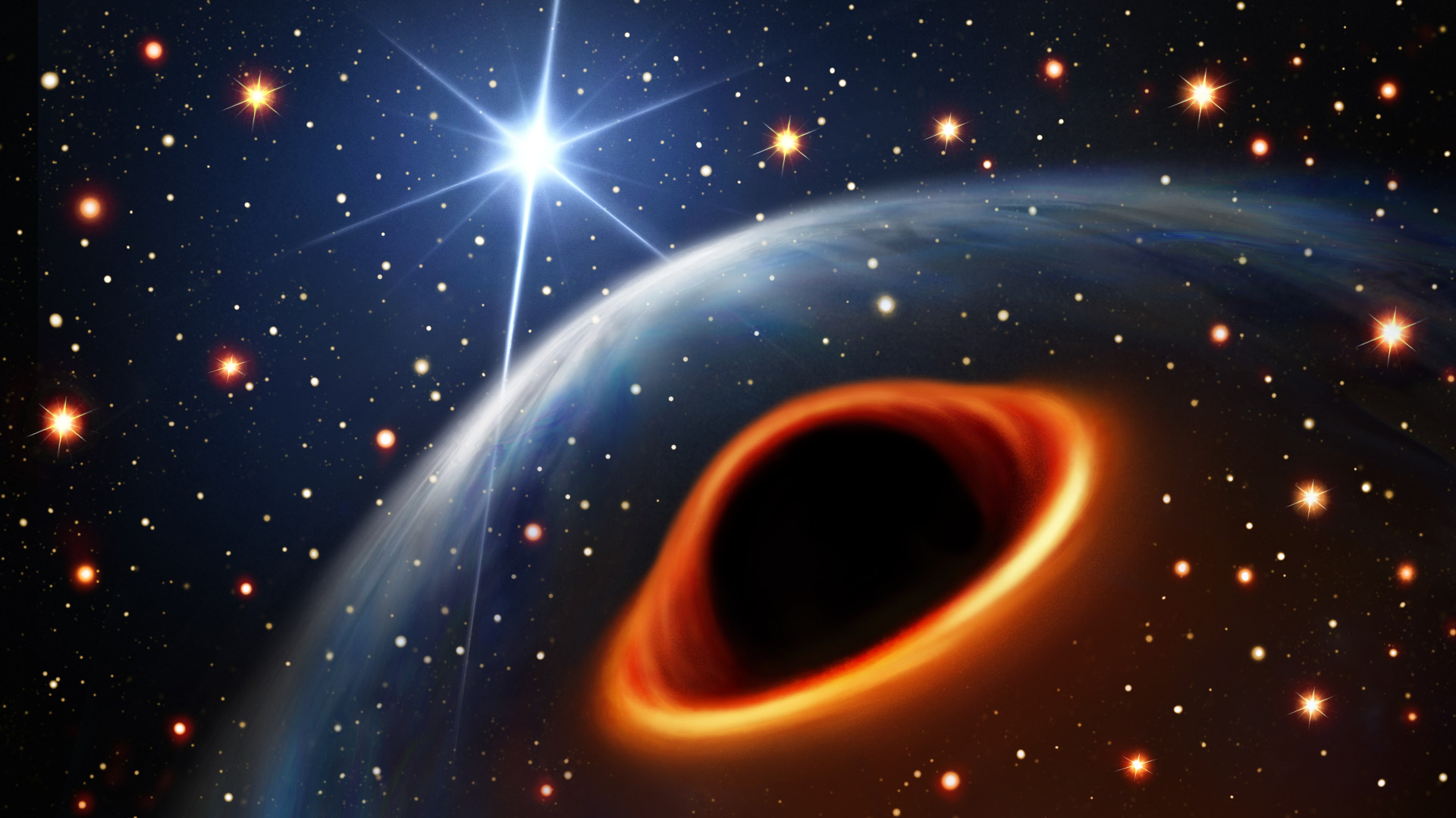

About 40,000 light-years away, a rapidly spinning object has a companion that’s confounding astronomers. It’s heavier than the heaviest neutron stars, yet at the same time, it’s lighter than the lightest black holes. Measurements place it in the so-called black hole mass gap, an observed gap in the stellar population between two to five solar masses. There appear to be no neutron stars larger than two solar masses and no black holes smaller than five solar masses.
Continue reading “Is this the Lightest Black Hole or Heaviest Neutron Star?”What Could a Next Generation Event Horizon Telescope Do?

Telescopes have come a long way in a little over four hundred years! It was 1608 that Dutch spectacle maker Hans Lippershey who was said to be working with a case of myopia and, in working with lenses discovered the magnifying powers if arranged in certain configurations. Now, centuries on and we have many different telescope designs and even telescopes in orbit but none are more incredible than the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT). Images las year revealed the supermassive black hole at the centre of our Galaxy and around M87 but now a team of astronomers have explored the potential of an even more powerful system the Next Generation EHT (ngEHT).
Continue reading “What Could a Next Generation Event Horizon Telescope Do?”Everything in the Universe Fits in This One Graph. Even the Impossible Stuff
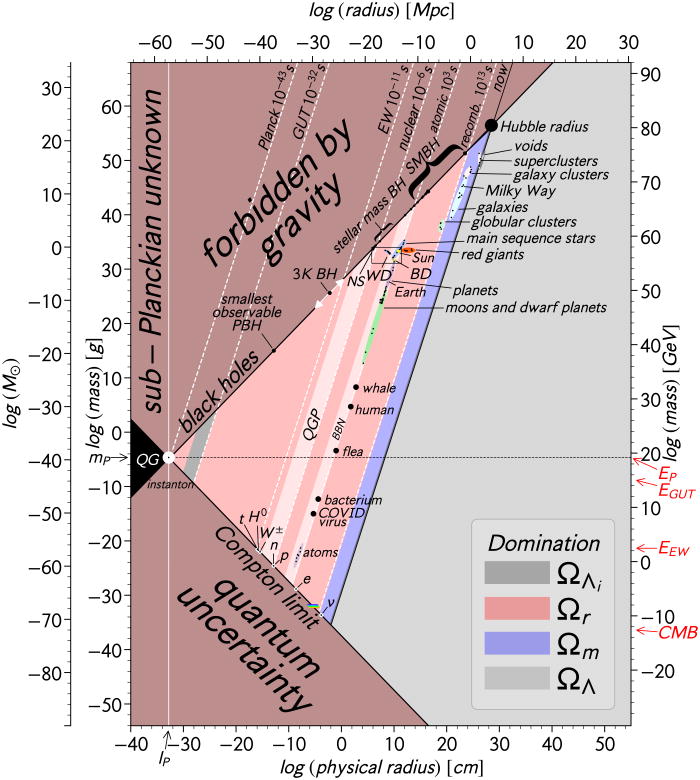
The Universe has physical constants, such as the force of gravity that define everything. If these constants were any different, our Universe would look quite different. When you consider the types of objects that exist in our Universe – from quarks and bacteria to fleas and superclusters — different forces dominate their existence.
A fascinating new graph plots everything in the known Universe and shows us what’s possible. It also shows what types of objects are prohibited by the laws of physics as we understand them.
Continue reading “Everything in the Universe Fits in This One Graph. Even the Impossible Stuff”