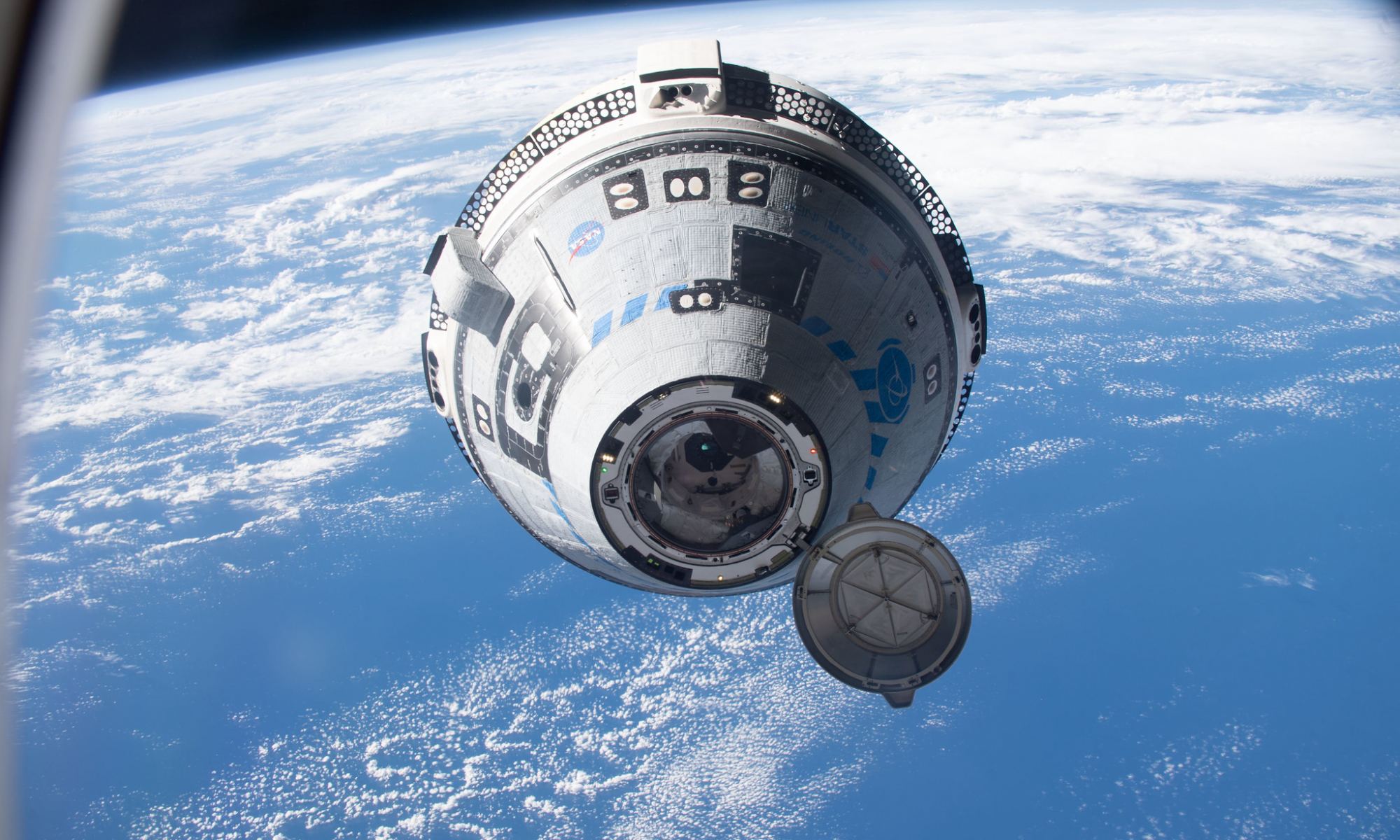
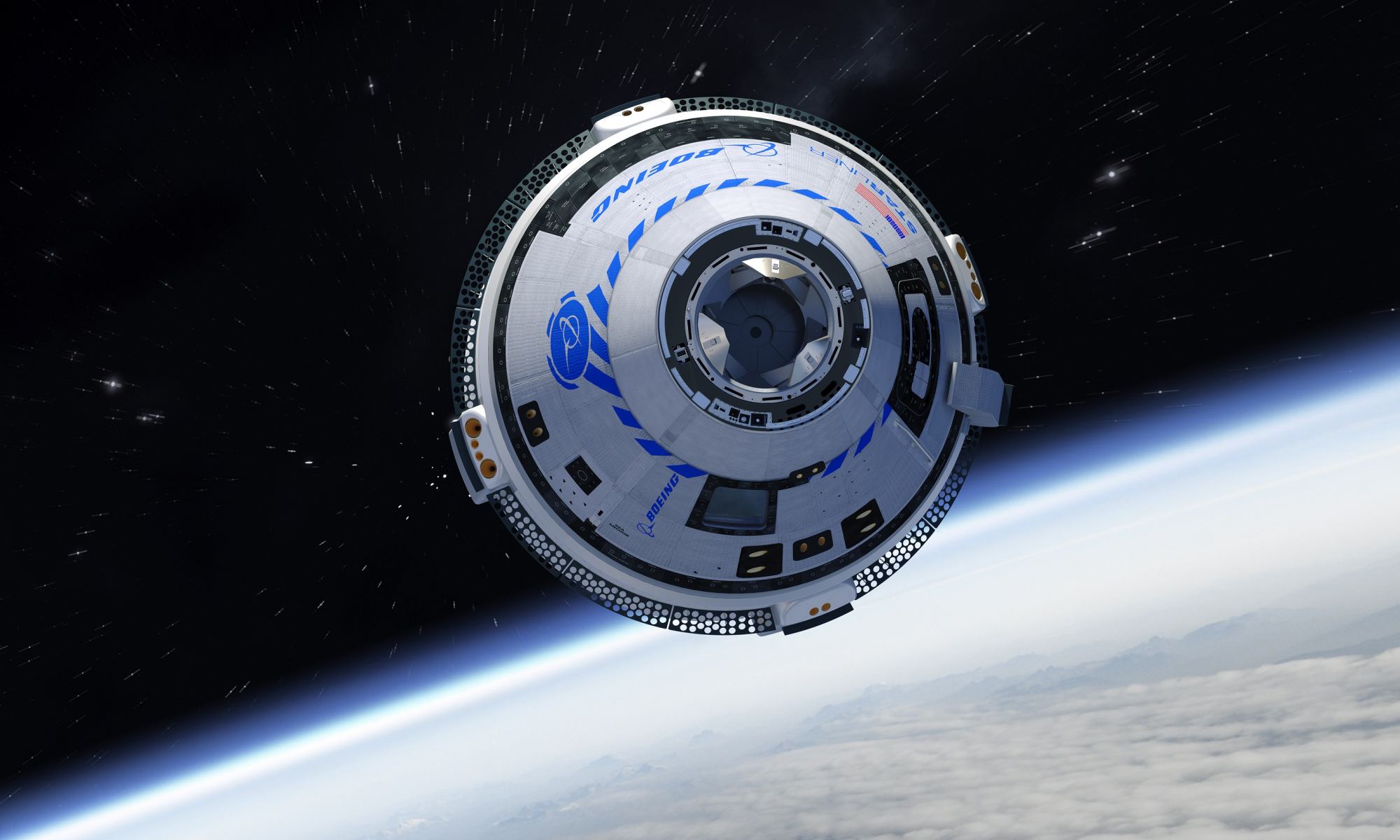
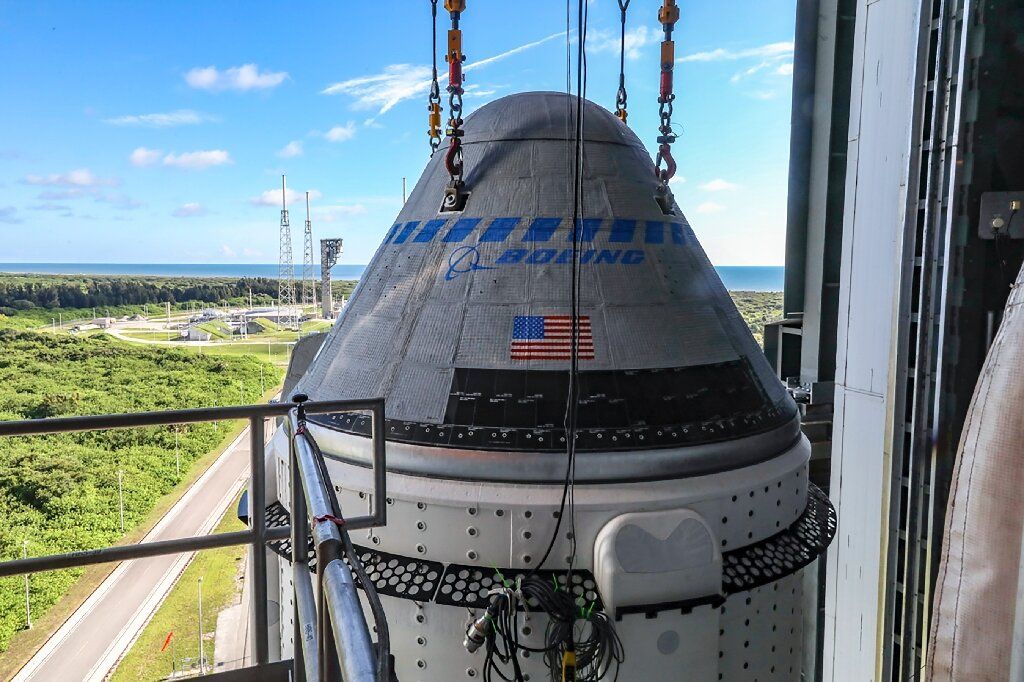
Astronauts Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams will remain on board the International Space Station until February, returning to Earth on a SpaceX Crew Dragon. NASA announced its decision over the weekend, citing concerns about the safety of the Boeing Starliner capsule due to helium leaks and thruster issues. The troublesome Starliner is slated to undock from the ISS without a crew in early September and attempt to return on autopilot, landing in the New Mexico desert.
NASA said this allows them and Boeing to continue gathering test data on Starliner during its uncrewed flight home, while also not accepting more risk than necessary for the crew.
Continue reading “NASA Decides to Play it Safe. Wilmore and Williams are Coming Home on a Crew Dragon in February”