Following is Part 2 of an excerpt from my new book, “Incredible Stories From Space: A Behind-the-Scenes Look at the Missions Changing Our View of the Cosmos.” The book is an inside look at several current NASA robotic missions, and this excerpt is part 2 of 3 which will be posted here on Universe Today, of Chapter 2, “Roving Mars with Curiosity.” You can read Part 1 here. The book is available in print or e-book (Kindle or Nook) Amazon and Barnes & Noble.
Living on Mars Time
The landing occurred at 10:30 pm in California. The MSL team had little time to celebrate, transitioning immediately to mission operations and planning the rover’s first day of activity. The team’s first planning meeting started at 1 o’clock in the morning, ending about 8 a.m. They had been up all night, putting in a nearly 40-hour day.
This was a rough beginning of the mission for the scientists and engineers who needed to live on ‘Mars Time.’
A day on Mars day is 40 minutes longer than Earth’s day, and for the first 90 Mars days – called sols — of the mission, the entire team worked in shifts around the clock to constantly monitor the newly landed rover. To operate on the same daily schedule as the rover meant a perpetually shifting sleep/wake cycle where the MSL team would alter their schedules 40 minutes every day to stay in sync with the day and night schedules on Mars. If team members came into work at 9:00 a.m., the next day, they’d come in at 9:40 a.m., and the next day at 10:20 a.m., and so on.
Those who have lived through Mars Time say their bodies continually feel jet-lagged. Some people slept at JPL so as not to disrupt their family’s schedule, some wore two watches so they would know what time it was on two planets.
About 350 scientists from around the world were involved with MSL and many of them stayed at JPL for the first 90 sols of the mission, living on Mars Time.
But it took less than 60 Earth days for the team to announce Curiosity’s first big discovery.
Water, Water …

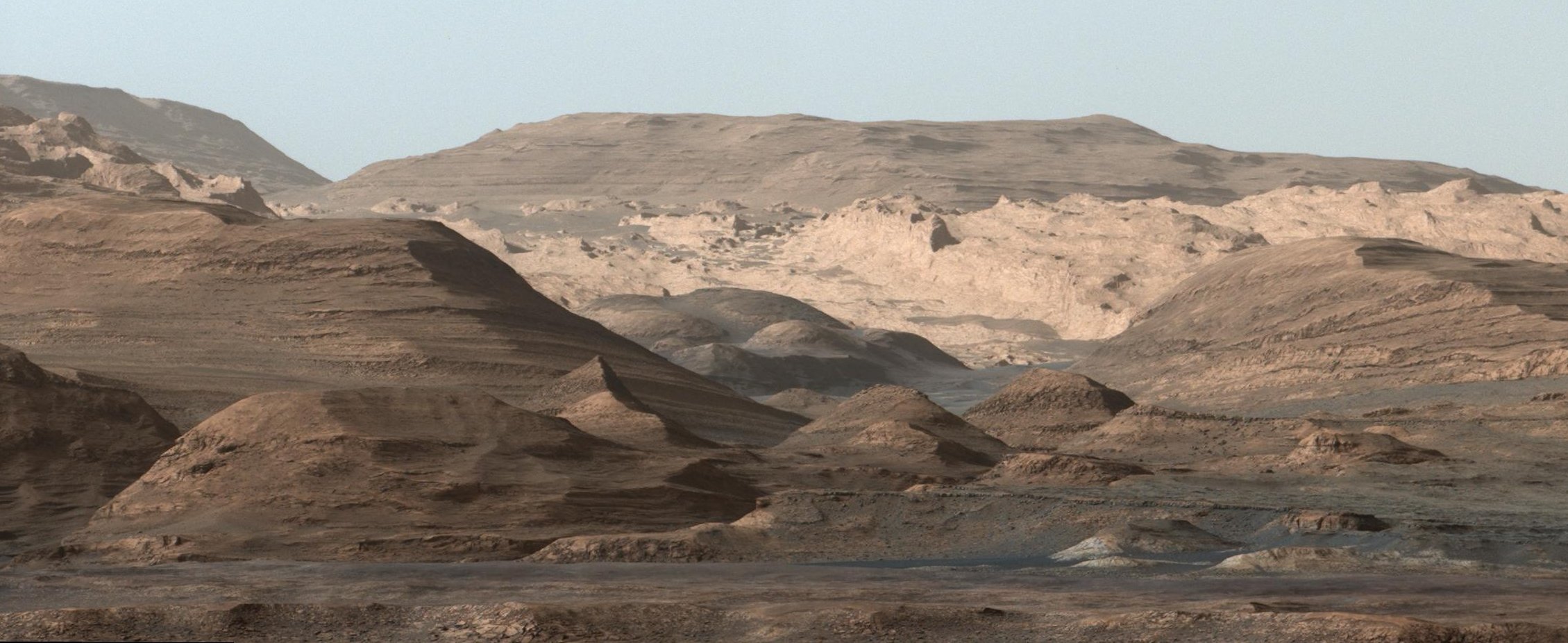
Ashwin Vasavada grew up in California and has fond childhood memories of visiting state and national parks in the southwest United States with his family, playing among sand dunes and hiking in the mountains. He’s now able to do both on another planet, vicariously through Curiosity. The day I visited Vasavada at his office at JPL in early 2016, the rover was navigating through a field of giant sand dunes at the base of Mount Sharp, with some dunes towering 30 feet (9 meters) above the rover.
“It’s just fascinating to see dunes close up on another planet,” Vasavada said. “And the closer we get to the mountain, the more fantastic the geology gets. So much has gone on there, and we have so little understanding of it … as of yet.”
At the time we talked, Curiosity was approaching four Earth years on Mars. The rover is now studying those enticing sedimentary layers on Mt. Sharp in closer detail. But first, it needed to navigate through the “Bagnold Dunes” which form a barrier along the northwestern flank of the mountain. Here, Curiosity is doing what Vasavada calls “flyby science,” stopping briefly to sample and study the sand grains of the dunes while moving through the area as quickly as possible.
Now working as the lead Project Scientist for the mission, Vasavada plays an even larger role in coordinating the mission.
“It’s a constant balance of doing things quickly, carefully and efficiently, as well as using the instruments to their fullest,” he said.
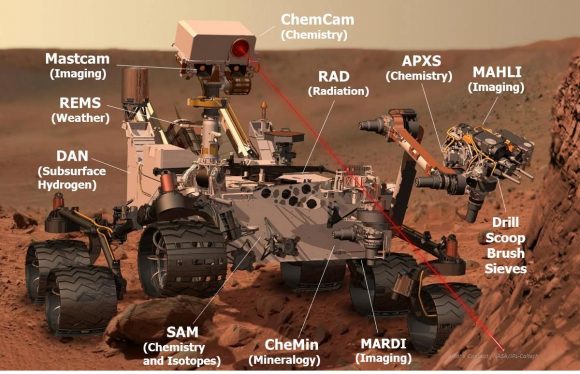
Since the successful August 2012 landing, Curiosity has sent back tens of thousands of images from Mars – from expansive panoramas to extreme close-ups of rocks and sand grains, all of which are helping to tell the story of Mars’ past.

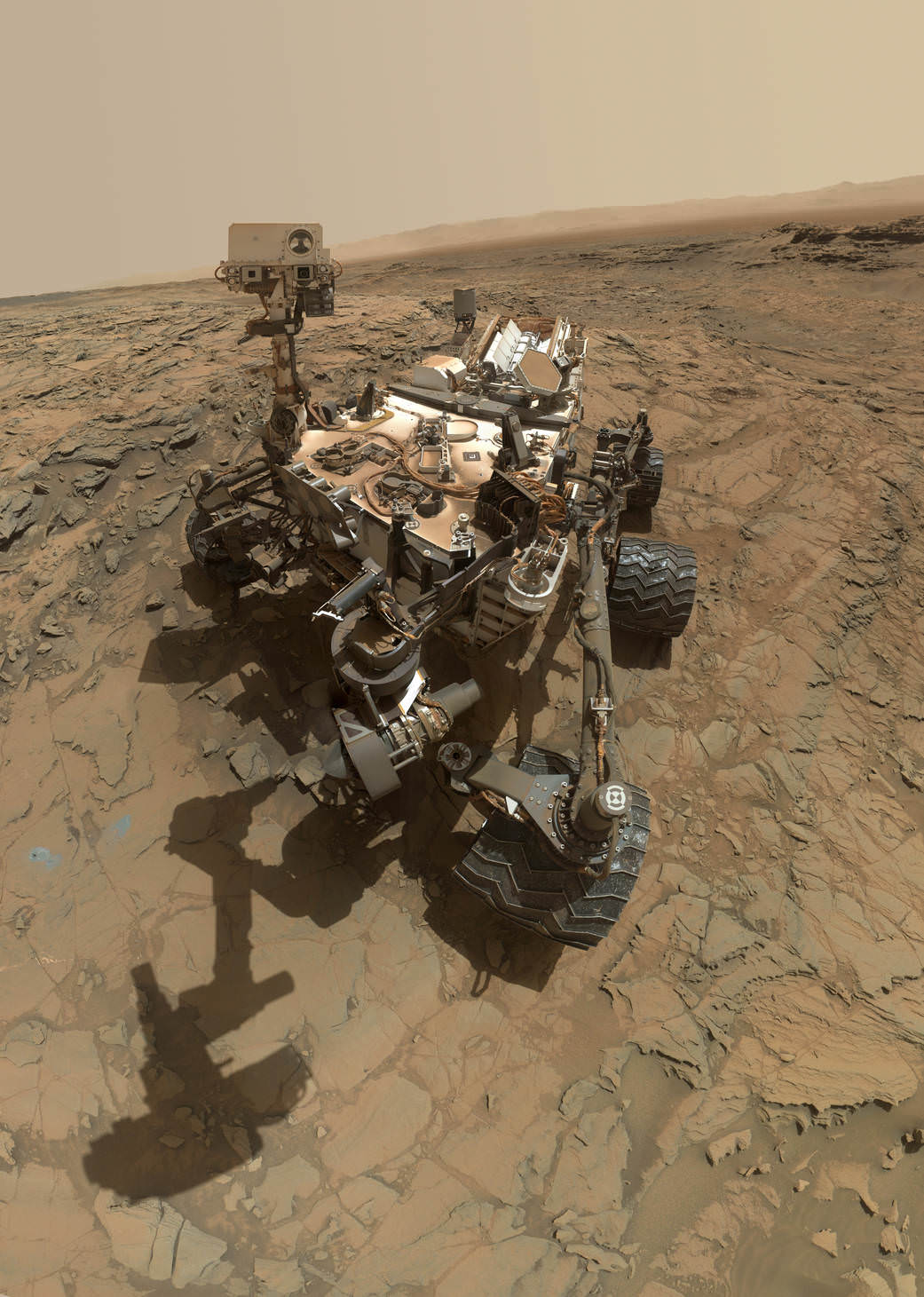
The images the public seems to love the most are the ‘selfies,’ the photos the rover takes of itself sitting on Mars. The selfies aren’t just a single image like the ones we take with our cell phones, but a mosaic created from dozens of separate images taken with the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera at the end of the rover’s robotic arm. Other fan favorites are the pictures Curiosity takes of the magnificent Martian landscape, like a tourist documenting its journey.
Vasavada has a unique personal favorite.
“For me, the most meaningful picture from Curiosity really isn’t that great of an image,” he said, “but it was one of our first discoveries so it has an emotional tie to it.”
Within the first 50 sols, Curiosity took pictures of what geologists call conglomerates: a rock made of pebbles cemented together. But these were no ordinary pebbles — they were pebbles worn by flowing water. Serendipitously, the rover had found an ancient streambed where water once flowed vigorously. From the size of pebbles, the science team could interpret the water was moving about 3 feet (1 meter) per second, with a depth somewhere between a few inches to several feet.
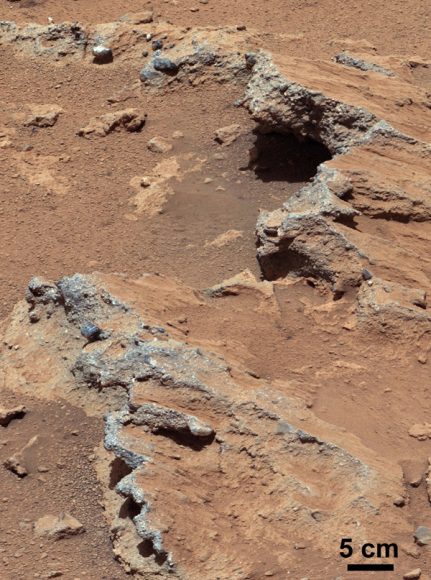

“When you see this picture, and whether you are a gardener or geologist, you know what this means,” Vasasvada said excitedly. “At Home Depot, the rounded rock for landscaping are called river pebbles! It was mind-blowing to me to think that the rover was driving through a streambed. That picture really brought home there was actually water flowing here long ago, probably ankle to hip deep.”
Vasavada looked down. “It still gives me the shivers, just thinking about it,” he said, with his passion for exploration and discovery visibly evident.
From that early discovery, Curiosity continued to find more water-related evidence. The team took a calculated gamble and instead of driving straight towards Mt. Sharp, took a slight detour to the east to an area dubbed ‘Yellowknife Bay.’
“Yellowknife Bay was something we saw with the orbiters,” Vasavada explained, “and there appeared to be a debris fan fed by a river—evidence for flowing water in the ancient past.”
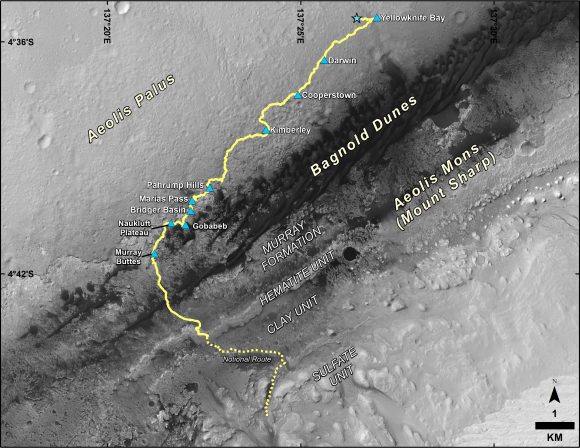
Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona
Here, Curiosity fulfilled ones of its main goals: determining whether Gale Crater ever was habitable for simple life forms. The answer was a resounding yes. The rover sampled two stone slabs with the drill, feeding half-baby-aspirin-sized portions to SAM, the onboard lab. SAM identified traces of elements like carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and more —the basic building blocks of life. It also found sulfur compounds in different chemical forms, a possible energy source for microbes.
Data gathered by Curiosity’s other instruments constructed a portrait detailing how this site was once a muddy lakebed with mild – not acidic – water. Add in the essential elemental ingredients for life, and long ago, Yellowknife Bay would have been the perfect spot for living organisms to hang out. While this finding doesn’t necessarily mean there is past or present life on Mars, it shows the raw ingredients existed for life to get started there at one time, in a benign environment.
“Finding the habitable environment in Yellowknife Bay was wonderful because it really showed the capability our mission has to measure so many different things,” Vasavada said. “A wonderful picture came together of streams that flowed into a lake environment. This was exactly what we were sent there to find, but we didn’t think we’d find it that early in the mission.”
Still, this lakebed could have been created by a one-time event over just hundreds of years. The ‘jackpot’ would be to find evidence of long-term water and warmth.
That discovery took a little longer. But personally, it means more to Vasavada.
Mars’ climate was one of Vasavada’s early interests in his career and he spent years creating models, trying to understand Mars’ ancient history.
“I grew up with pictures of Mars from the Viking mission,” he said, “and thinking of it as a barren place with jagged volcanic rock and a bunch of sand. Then I had done all this theoretical work about Mars climate, that rivers and oceans perhaps once existed on Mars, but we had no real evidence.”
That’s why the discovery made by Curiosity in late 2015 is so exciting to Vasavada and his team.
“We didn’t just see the rounded pebbles and remnants of the muddy lake bottom at Yellowknife Bay, but all along the route,” Vasavada said. “We saw river pebbles first, then tilted sandstones where the river emptied into lakes. Then as we got to Mt. Sharp, we saw huge expanses of rock made of the silt that settled out from the lakes.”
The explanation that best fits the “morphology” in this region — that is, the configuration and evolution of rocks and land forms – is rivers formed deltas as they emptied into a lake. This likely occurred 3.8 to 3.3 billion years ago. And the rivers delivered sediment that slowly built up the lower layers of Mt. Sharp.

“My gosh, we were seeing this full system now,” Vasavada explained, “showing how the entire lower few hundred meters of Mount Sharp were likely laid down by these river and lake sediments. That means this event didn’t take hundreds or thousands of years; it required millions of years for lakes and rivers to be present to slowly build up, millimeter by millimeter, the bottom of the mountain.”
For that, Mars also needed a thicker atmosphere than it has now, and a greenhouse gas composition that Vasavada said they haven’t quite figured out yet.
But then, somehow dramatic climate change caused the water to disappear and winds in the crater carved the mountain to its current shape.
The rover had landed in exactly the right place, because here in one area was a record of much of Mars’ environmental history, including evidence of a major shift in the planet’s climate, when the water that once covered Gale Crater with sediment dried up.
“This all is a significant driver now for what we need to explain about Mars’ early climate,” Vasavada said. “You don’t get millions of years of climate change from a single event like a meteor hit. This discovery has broad implications for the entire planet, not just Gale Crater.”
Other Discoveries
• Silica: The rover made a completely unanticipated discovery of high-content silica rocks as it approached Mt. Sharp. “This means that the rest of the normal elements that form rocks were stripped away, or that a lot of extra silica was added somehow,” Vasavada said, “both of which are very interesting, and very different from rocks we had seen before. It’s such a multifaceted and curious discovery, we’re going to take a while figuring it out.”
• Methane on Mars: Methane is usually a sign of activity involving organic matter — even, potentially, of life. On Earth, about 90 percent of atmospheric methane is produced from the breakdown of organic matter. On Mars, methane has been detected by other missions and telescopes over the years, but it was tenuous – the readings seemed to come and go, and are hard to verify. In 2014, the Tunable Laser Spectrometer within the SAM instrument observed a ten-fold increase in methane over a two-month period. What caused the brief and sudden increase? Curiosity will continue to monitor readings of methane, and hopefully provide an answer to the decades-long debate.
• Radiation Risks for Human Explorers: Both during her trip to Mars and on the surface, Curiosity measured the high-energy radiation from the Sun and space that poses a risk astronauts. NASA will use data from the Radiation Assessment Detector (RAD) instrument Curiosity’s data to design future missions to be safe for human explorers.
Tomorrow: The conclusion of this chapter, including ‘How To Drive a Mars Rover, and ‘The Beast.’ Part 1 is available here.
“Incredible Stories From Space: A Behind-the-Scenes Look at the Missions Changing Our View of the Cosmos” is published by Page Street Publishing, a subsidiary of Macmillan.