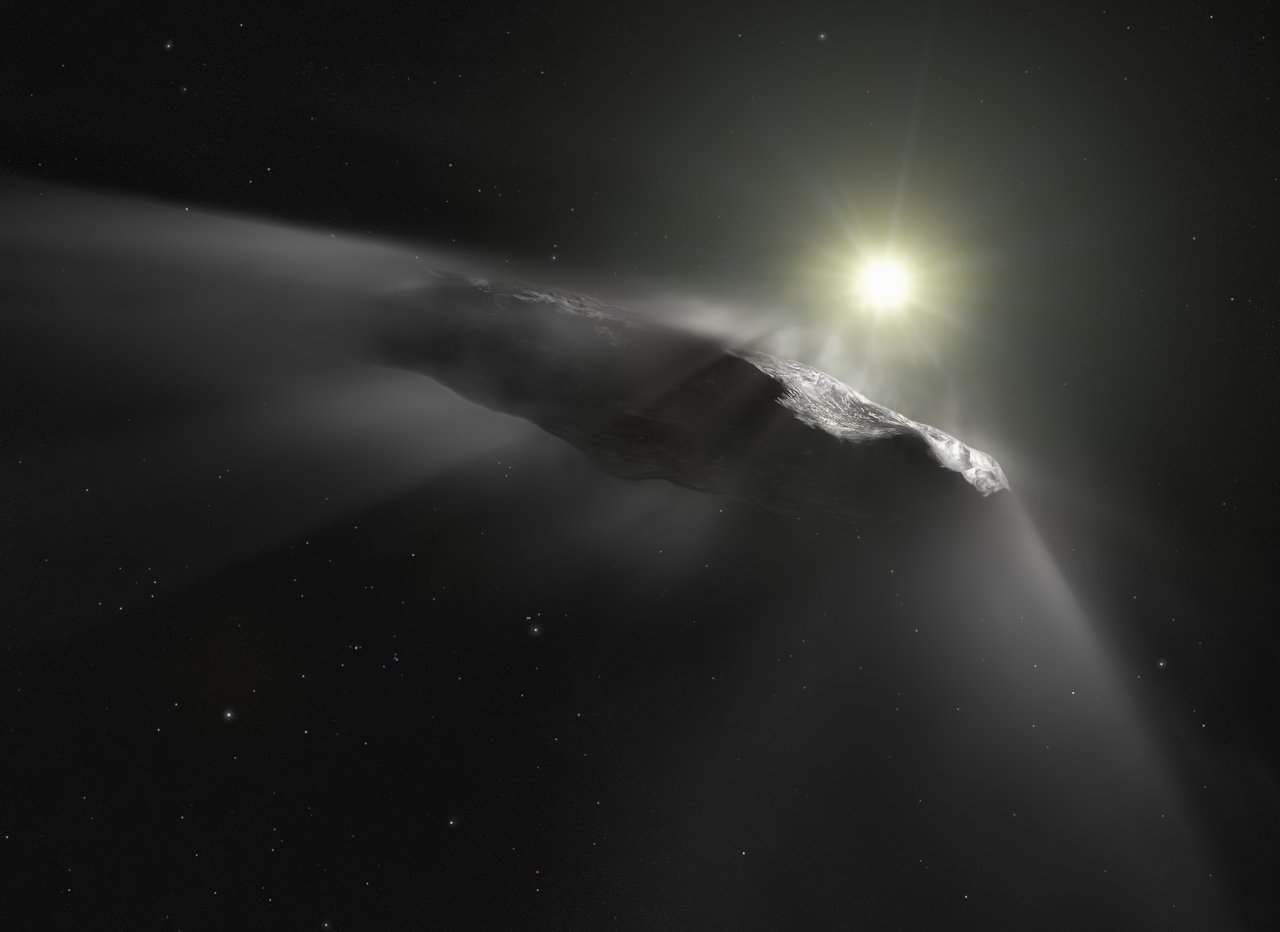
On October 19th, 2017, astronomers were astounded to learn that an interstellar object (named ‘Oumuamua) flew by Earth on its way out of the Solar System. Years later, astronomers are still debating what this object was – a comet fragment, a hydrogen iceberg, or an extraterrestrial solar sail? What’s more, the arrival of 2I/Borisov two years later showed how interstellar objects (ISOs) regularly enter our Solar System (some even stay!)
It’s little wonder then why proposals are in place to design missions that could rendezvous with an interstellar object the next time one passes by. One such mission is Project Lyra, a concept proposed by researchers from the Initiative for Interstellar Studies (i4is). Recently, an international team led from the I4IS drafted a White Paper that was submitted to the 2023-2032 Planetary Science and Astrobiology Decadal Survey.
Continue reading “We Have the Technology to Retrieve a Sample From an Interstellar Object Like Oumuamua”