KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – The next generation of America’s human spaceships is rapidly taking shape and “making fantastic progress” at the Kennedy Space Center as Boeing and NASA showcased the start of assembly of the first flightworthy version of the aerospace giants Starliner crew taxi vehicle to the media last week. Starliner will ferry NASA astronauts to and from the International Space Station (ISS) by early 2018.
“We are making fantastic progress across the board,” John Mulholland, vice president and program manager of Boeing Commercial Programs, told Universe Today at the July 26 media event in Boeing’s new Starliner factory.
“It so nice to move from design to firm configuration, which was an incredibly important milestone, to now moving into the integrated qual phase of the campaign.”
Boeing is swiftly making tangible progress towards once again flying Americans astronauts to space from American soil as was quite visibly demonstrated when the firm showed off their spanking new Starliner ‘clean-floor factory’ to the media last week, including Universe Today – and it’s already humming with activity by simultaneously building two full scale Starliner crew vehicles.
“We are on track to support launch by the end of 2017 [of the uncrewed orbital test flight],” Mulholland told me.
“The Structural Test Article (STA) crew module is almost ready to be delivered to the test site in California. The service module is already delivered at the test site. So we are ready to move into the qualification campaign.”
“We are also in the middle of component qualification and qualifying more than one component every week as we really progress into assembly, integration and test of flight design spacecrafts.”
Starliner is being manufactured in what is officially known as Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida under contract with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP).
And the Boeing CST-100 Starliner assembly line aiming to send our astronauts to low Earth orbit and the space station is now operating full speed ahead at KSC.
Formerly known as Orbiter Processing Facility-3, or OPF-3, the facility was previously used as a servicing hanger to prepare NASA’s space shuttle orbiters for flight.
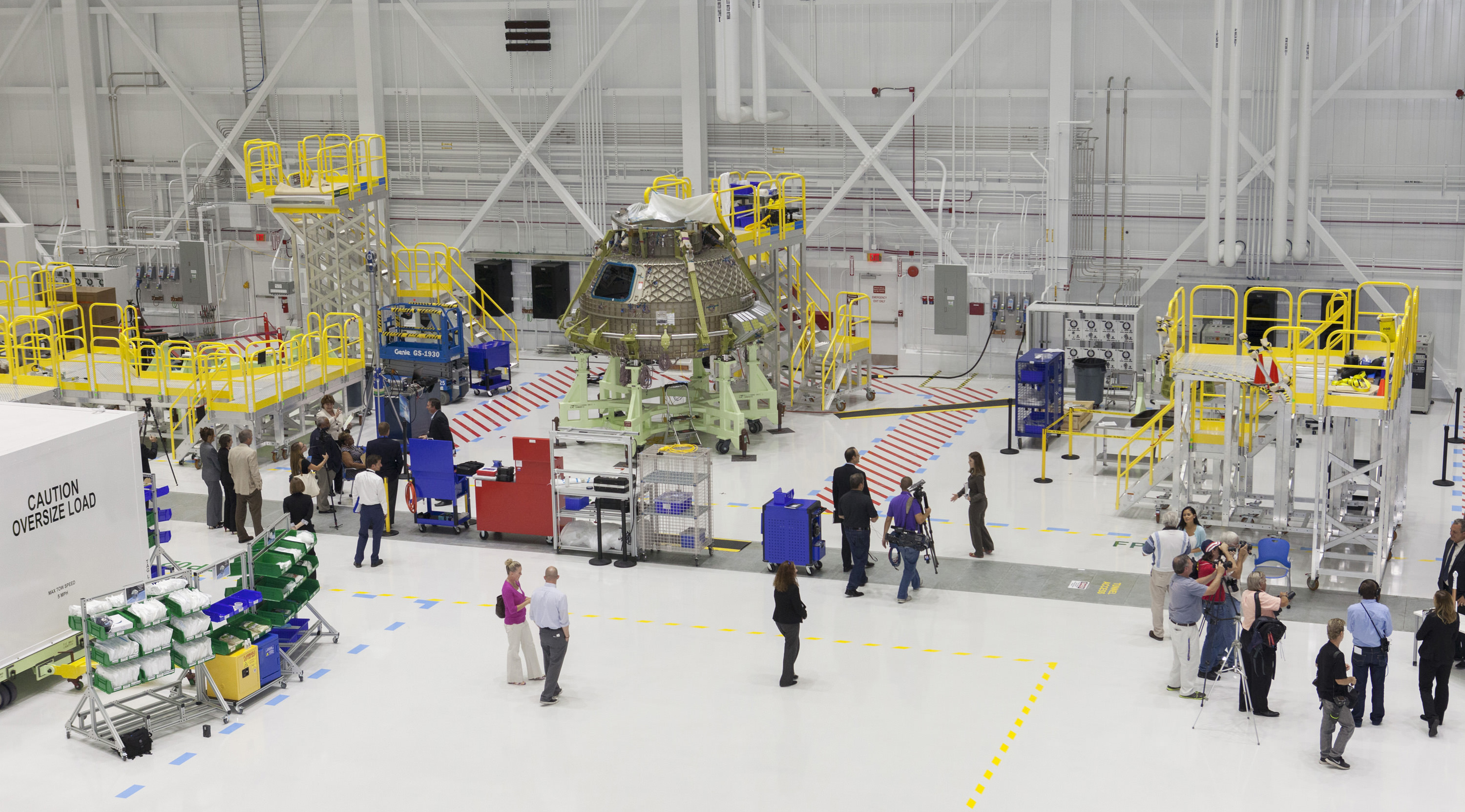

The facility has now been completely renovated and refurbished by removing about 11,000 tons of massive steel work platforms that once enshrouded the space shuttle orbiters for servicing and refurbishment for flight – and been transformed into Boeings gleaming white C3PF Starliner manufacturing facility.
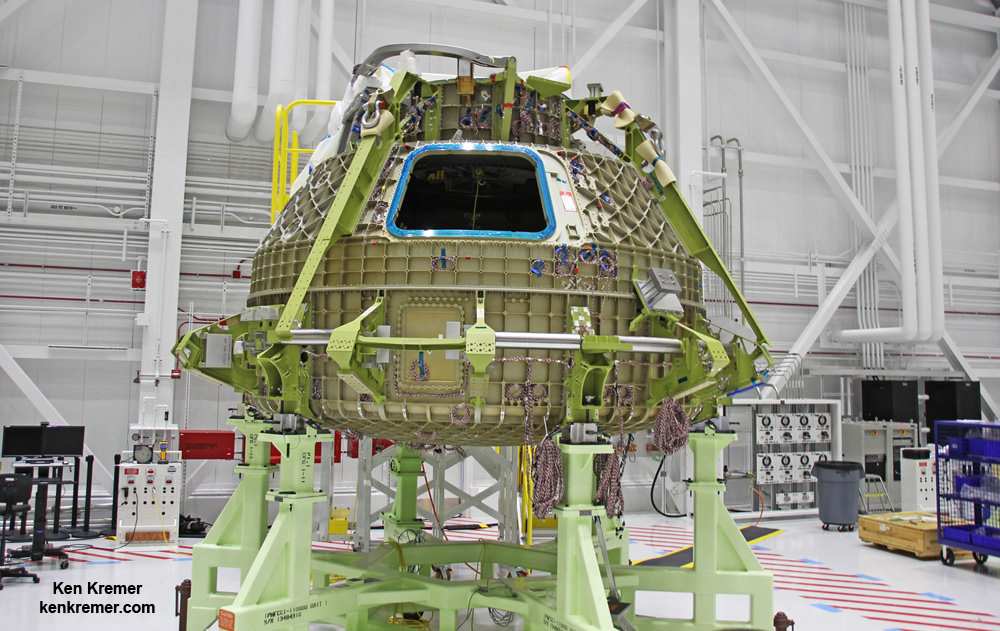
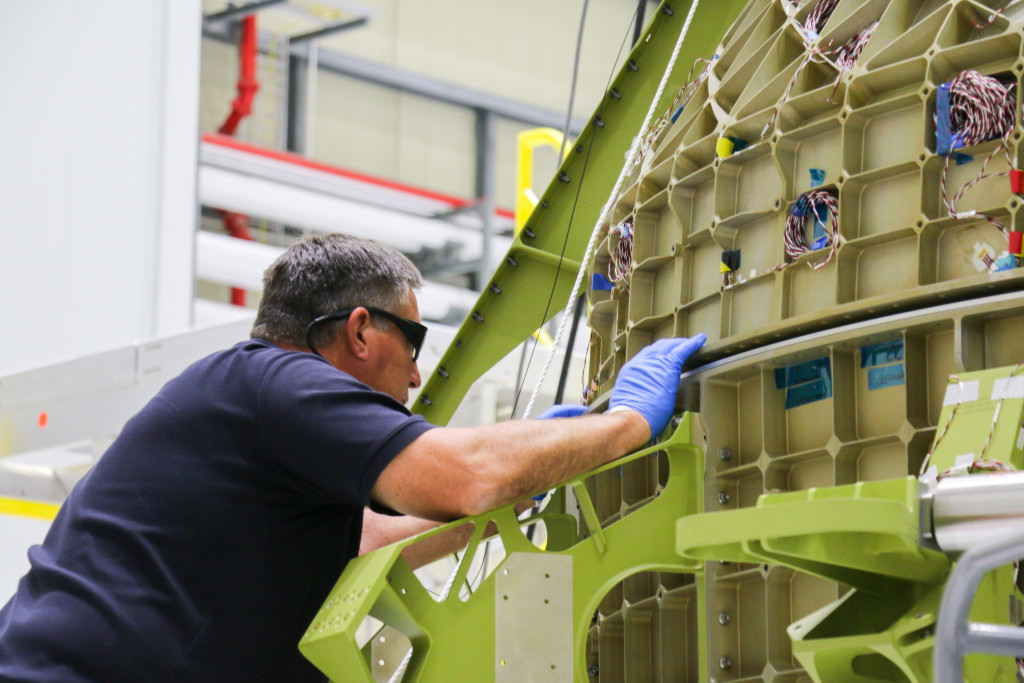
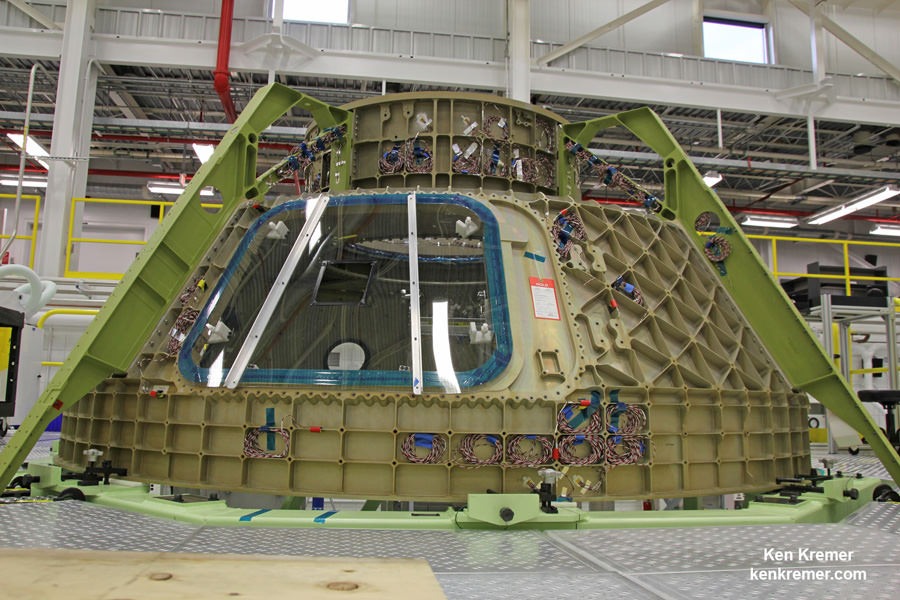
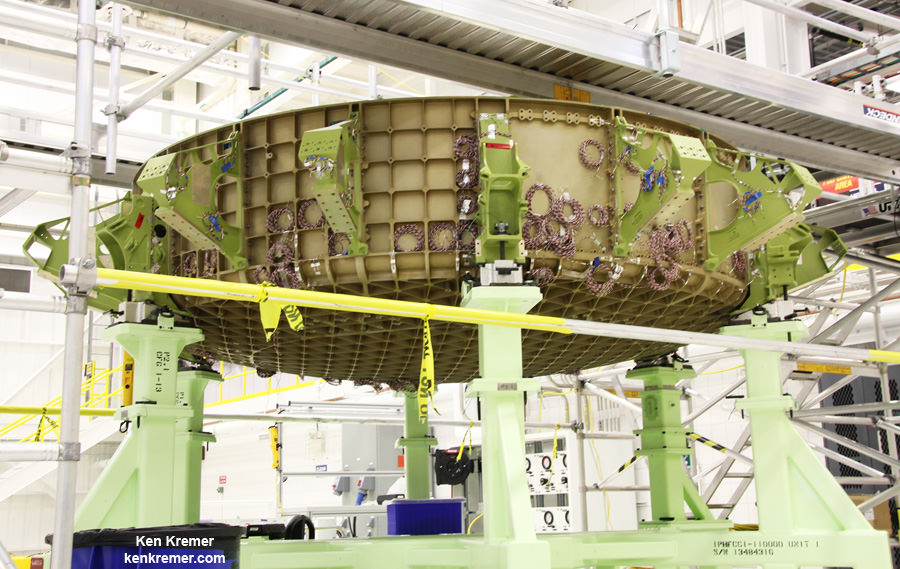
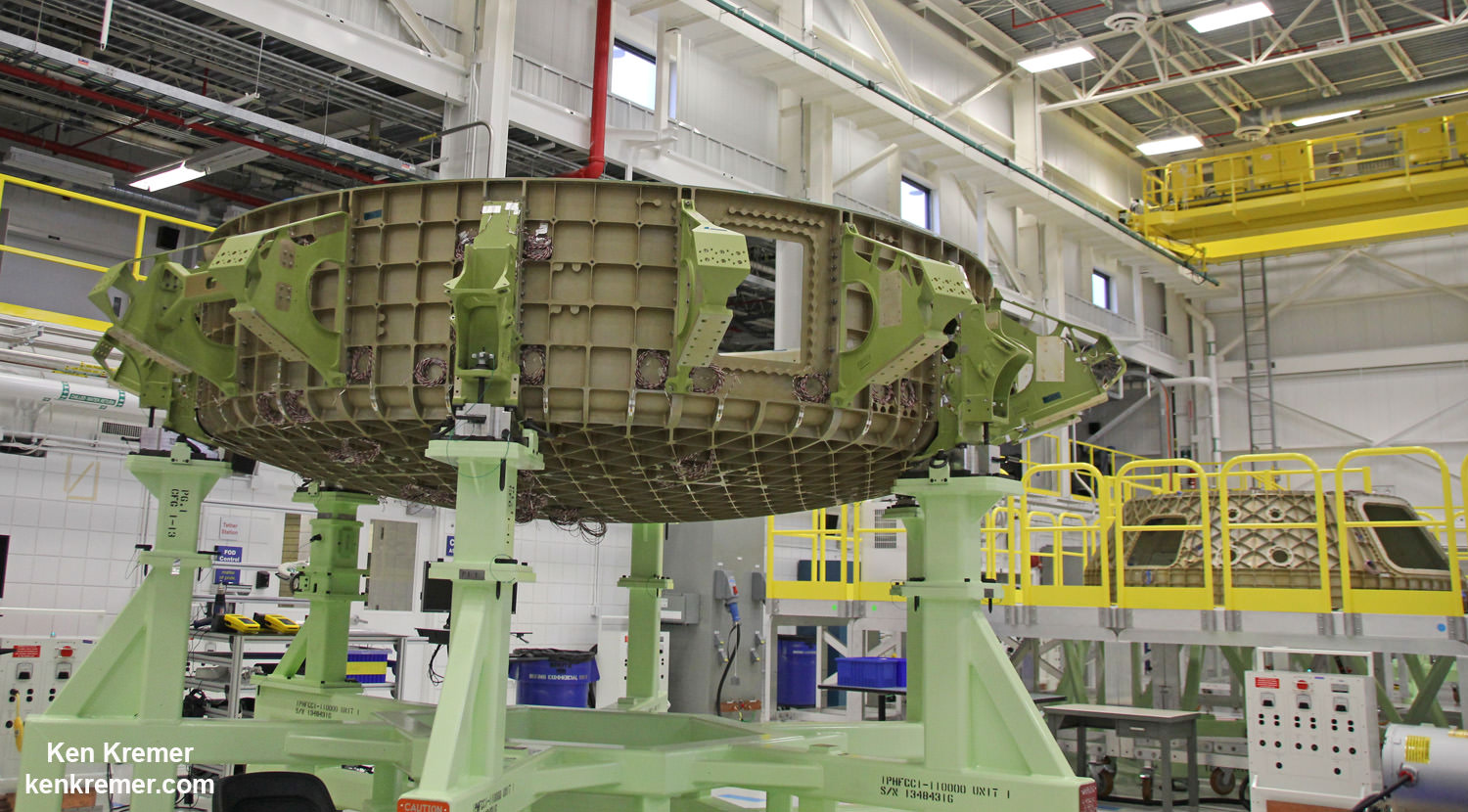
Components for the first Starliner that will actually fly in space – known as Spacecraft 1 – began arriving recently at the C3PF. These include the upper and lower domes, as well as the docking hatch for the spacecrafts pressure vessel.
“You can see the beginning of Spacecraft 1. To build it all of the major structural elements are here,” Mulholland explained.
“The lower dome will be populated and get to first power on early next year. We are really looking forward to that. Then we will mate that to the upper dome and start in on the ground qualification on Spacecraft 1.”
Altogether Boeing is fabricating three Starliner flight spacecraft.
“We will start building Spacecraft 2 in the Fall of this year. And then we will start Spacecraft 3 early next year.”
“So we will have three Starliner spacecraft flight crew module builds as we move into the flight campaign.”
Technicians are outfitting these individual components of the pressure vessel with wiring and lines, avionics and other systems, before they are bolted together.
Spacecraft 1 is actually the second Starliner being manufactured at the Kennedy Space Center.
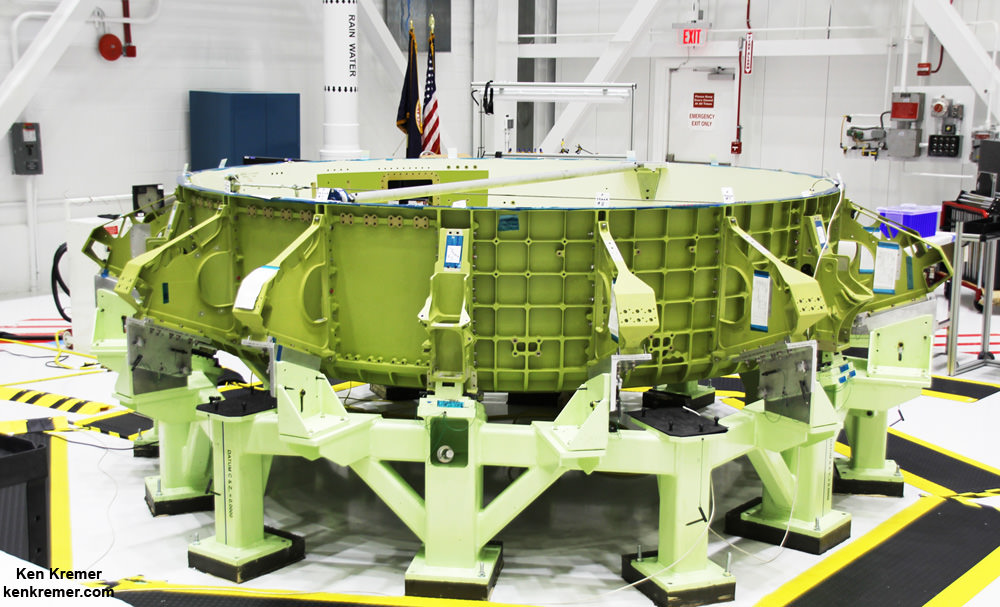
The first full scale Starliner vehicle to be built is known as the Structural Test Article (STA) and is nearing completion.

Notably Spacecraft 1 will be the first Starliner to fly in the company’s pad abort test.
“Spacecraft 1 will go into the ground campaign and then the pad abort,” Mulholland stated.
“The test is designed to prove the launch abort system planned for the spacecraft will be able to lift astronauts away from danger in the event of an emergency during launch operations,” says NASA.
The Pad Abort test is currently slated for October 2017 in New Mexico. Boeing will fly an uncrewed orbital flight test in December 2017 and a crewed orbital flight test in February 2018.
“Spacecraft 3 will be the first to fly in orbit on the uncrewed flight test by the end of 2017,” Mulholland confirmed.
‘Spacecraft 2 will go through a several month long thermal vac testing and EMI and EMC in California in the middle of next year and then go into the crewed flight test [in 2018].”
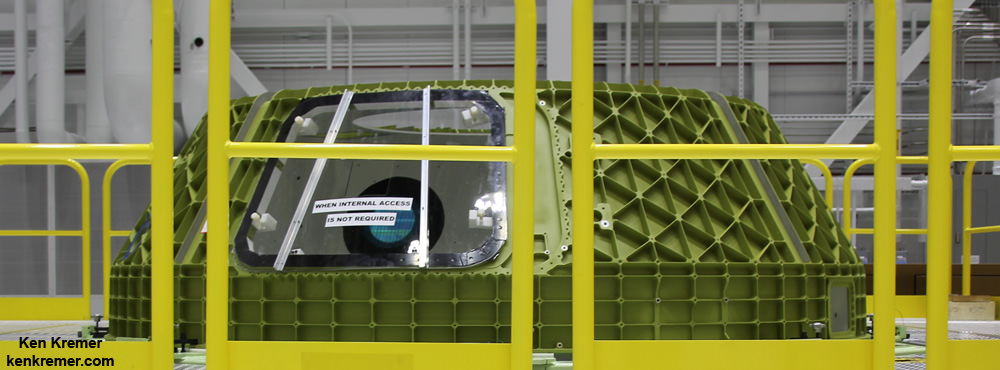
The rather distinctive, olive colored aluminum domes are manufactured using a weldless spin forming process by Spincraft, based in North Billerica, Massachusetts.
They take on their honeycombed look after being machined for the purposes of reducing weight and increasing strength to handle the extreme stresses of spaceflight. The lower dome is machined by Janicki Industries in Layton, Utah, and the upper dome is machined by Major Tool & Machine in Indianapolis.
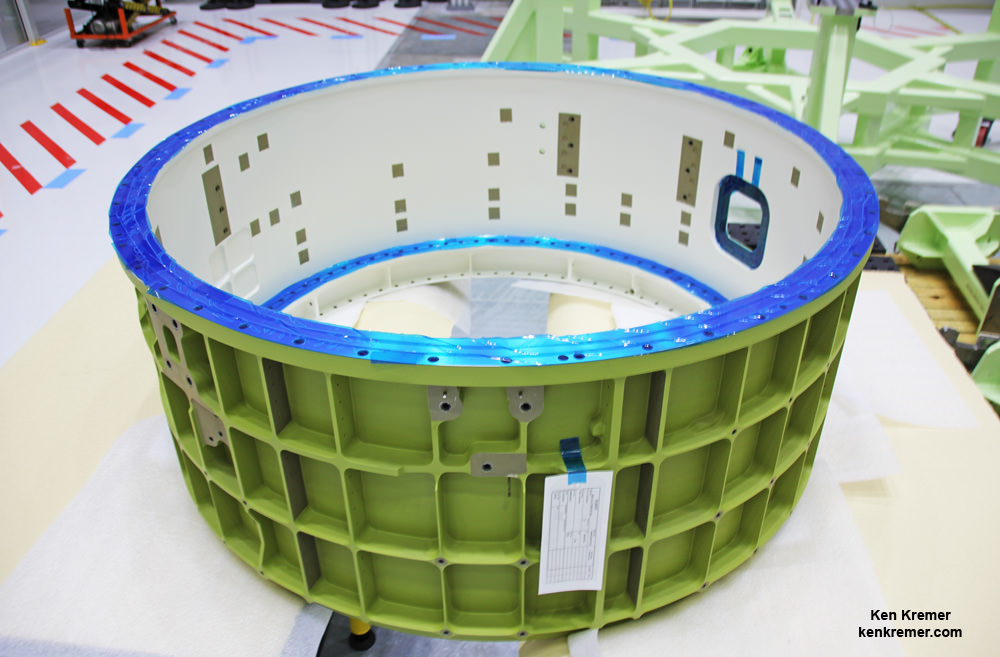

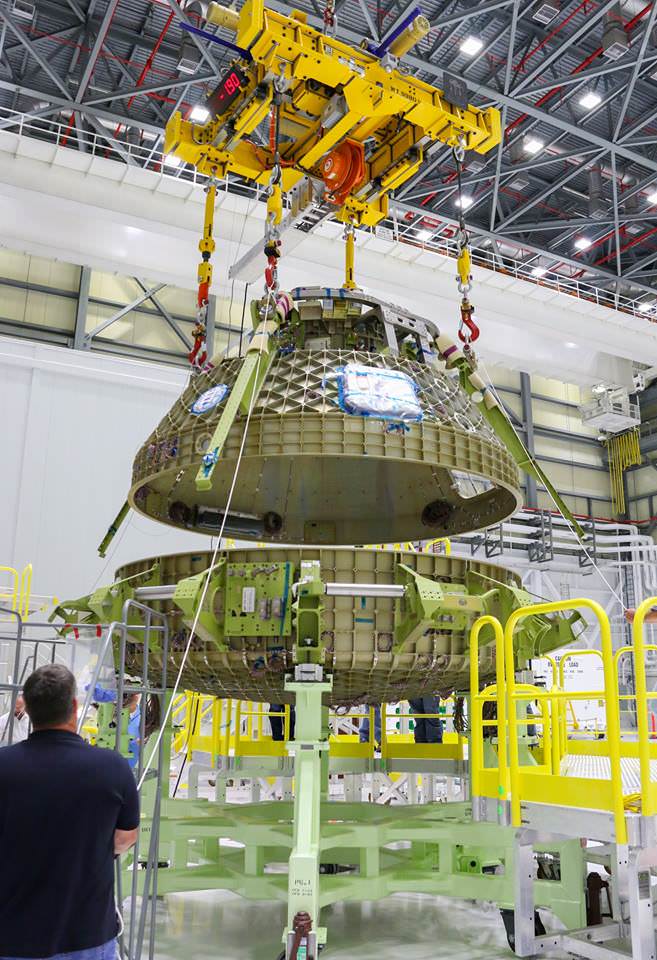
Engineers bolted together the upper and lower domes of Boeings maiden Starliner crew module in early May to form the complete hull of the pressure vessel for the Structural Test Article (STA).
Altogether they are held together by 216 bolts. They have to line up perfectly. And the seals are checked to make sure there are no leaks, which could be deadly in space.
Boeing expects to finish fabricating the STA by August.
The completed Starliner STA will then be transported to Boeing’s facility in Huntington Beach, California for a period of critical stress testing that verifies the capabilities and worthiness of the spacecraft.
“Boeing’s testing facility in Huntington Beach, California has all the facilities to do the structural testing and apply loads. They are set up to test spacecraft,” said Danom Buck, manager of Boeing’s Manufacturing and Engineering team at KSC, during an interview in the C3PF.
“At Huntington Beach we will test for all of the load cases that the vehicle will fly in and land in – so all of the worst stressing cases.”
“So we have predicted loads and will compare that to what we actually see in testing and see whether that matches what we predicted.”
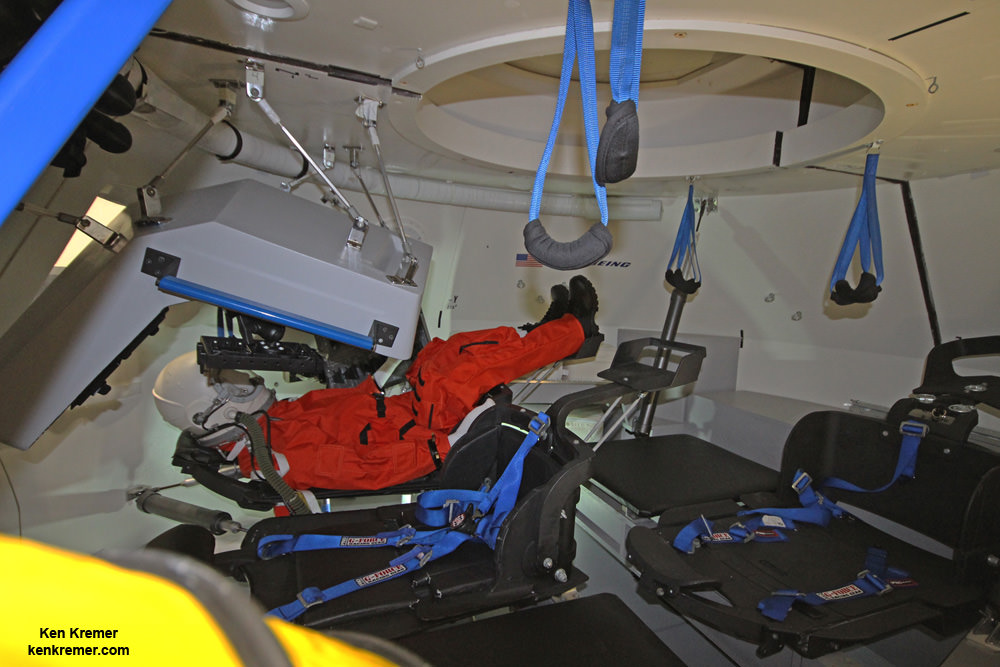
Boeing has also vastly updated the mockup Starliner to reflect the latest spacecraft advances and assist in manufacturing the three planned flight units.
Bastian Technologies built many of the components for the mockup and signed as new 18-month new Mentor-Protégé Program agreement with Boeing and NASA at the media event.
The mock up “is used as a hands-on way to test the design, accessibility and human factors during the early design and development phase of the program. The mock-up is currently being used for rapid fire engineering verification activities, ergonomic evaluations [including the seats and display panels], and crew ingress and egress training,” says NASA.

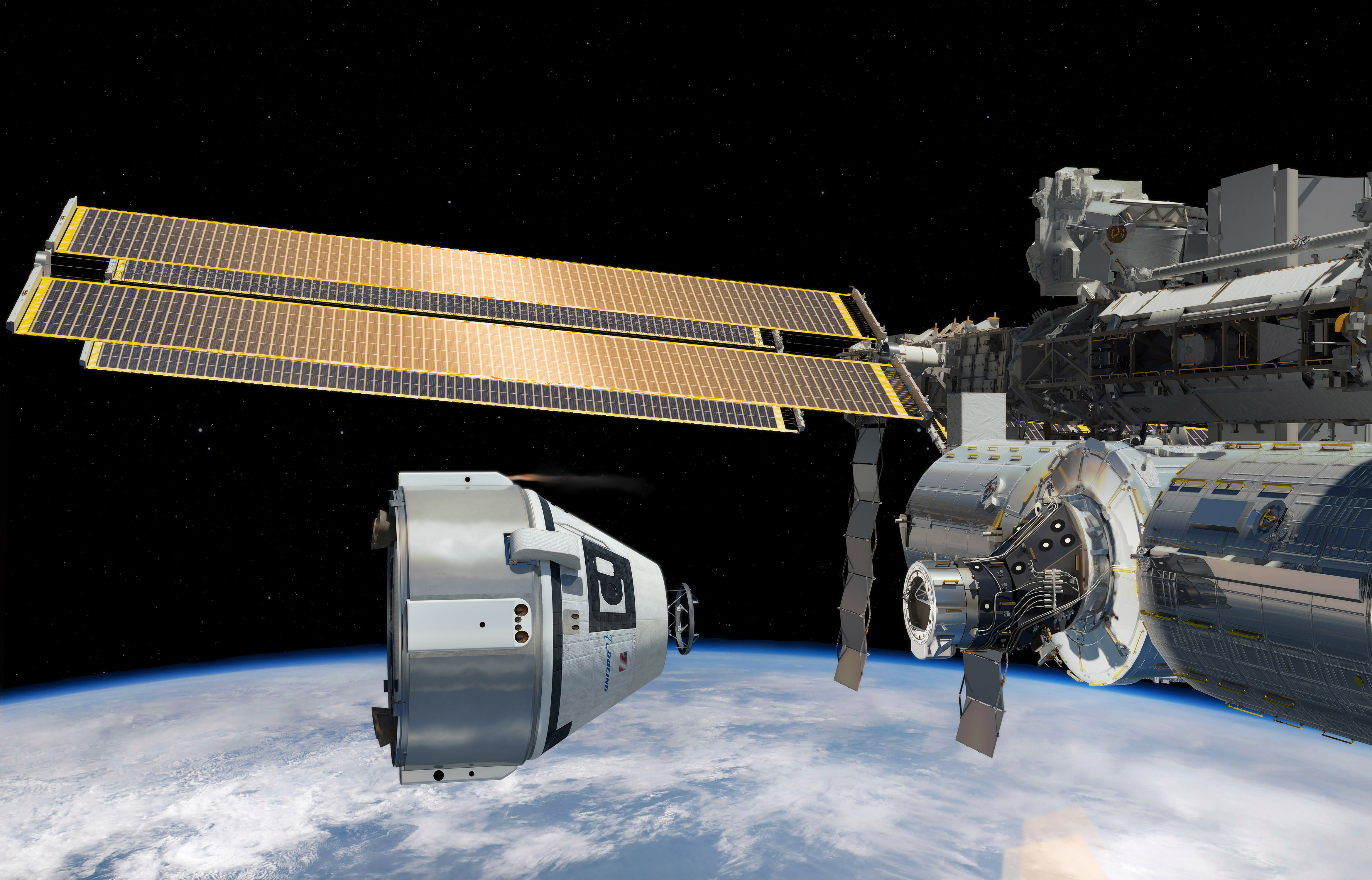
The Boeing CST 100 Starliner is one of two private astronaut capsules – along with the SpaceX Crew Dragon – being developed under a commercial partnership contract with NASA to end our sole reliance on Russia for crew launches back and forth to the International Space Station (ISS).
The goal of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP) is to restore America’s capability to launch American astronauts on American rockets from American soil to the ISS, as soon as possible.
Boeing was awarded a $4.2 Billion contract in September 2014 by NASA Administrator Charles Bolden to complete development and manufacture of the CST-100 Starliner space taxi under the agency’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) program and NASA’s Launch America initiative.
Since the retirement of NASA’s space shuttle program in 2011, the US was been 100% dependent on the Russian Soyuz capsule for astronauts rides to the ISS at a cost exceeding $70 million per seat.
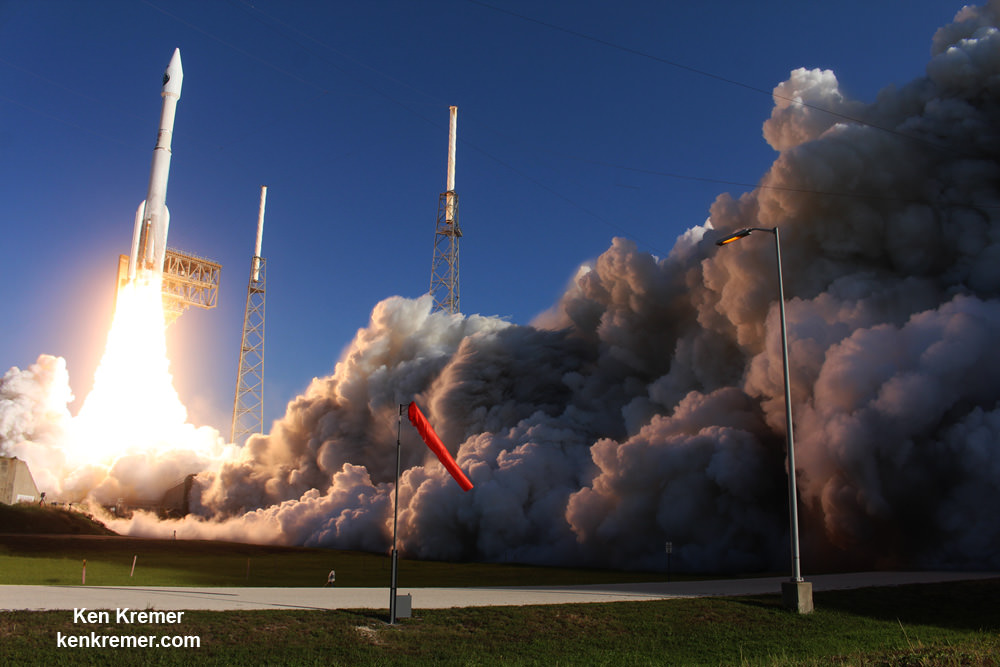
Starliners will launch to space atop the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket from pad 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
Ken Kremer
















