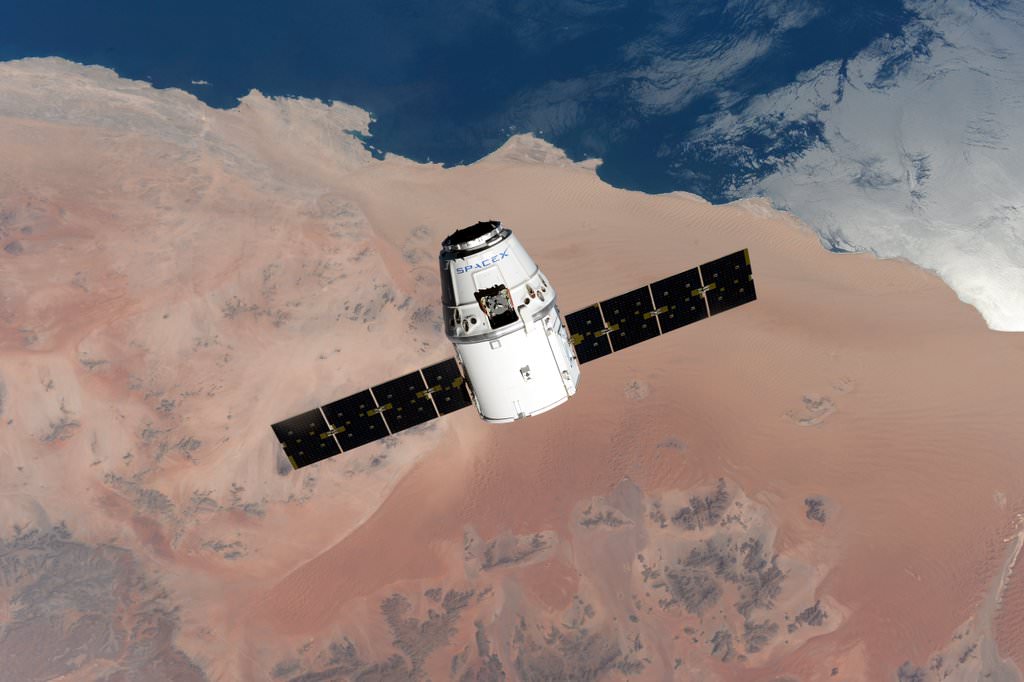
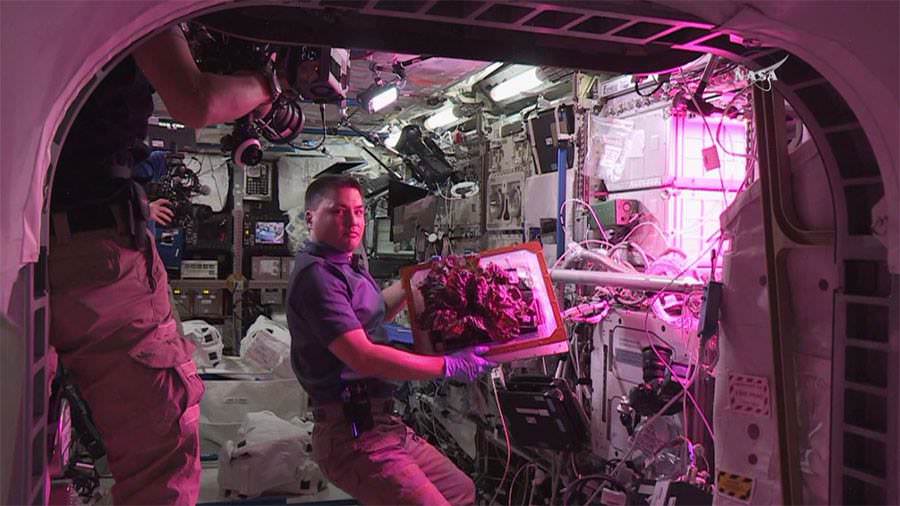
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – Following a flawless post midnight blastoff two mornings ago, a pair of NASA astronauts executed a flawless capture of the newest SpaceX Dragon supply ship at the International Space Station early this morning, July 20, carrying 2.5 tons of priceless research equipment and gear for the resident astronauts and cosmonauts.
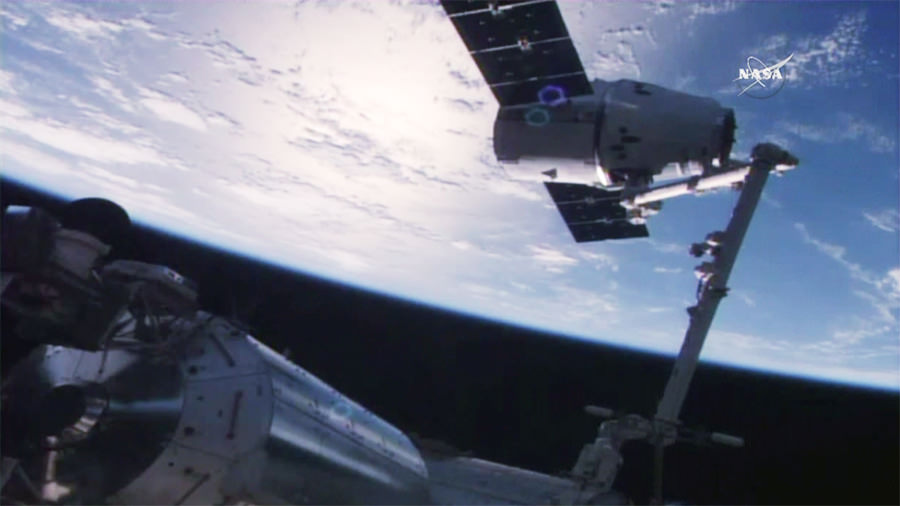
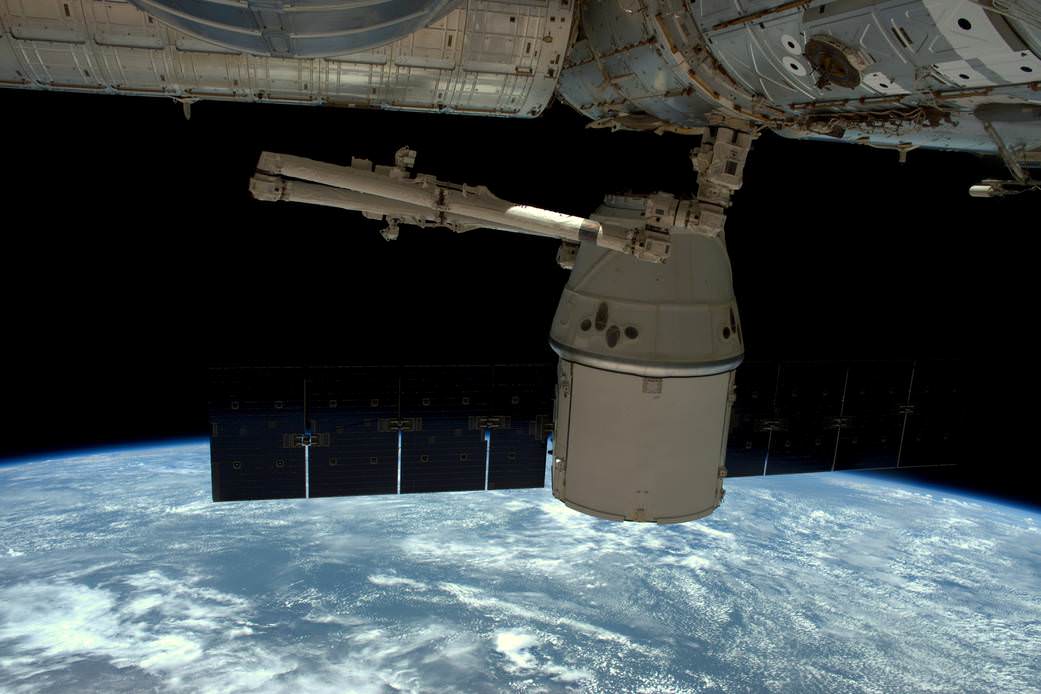
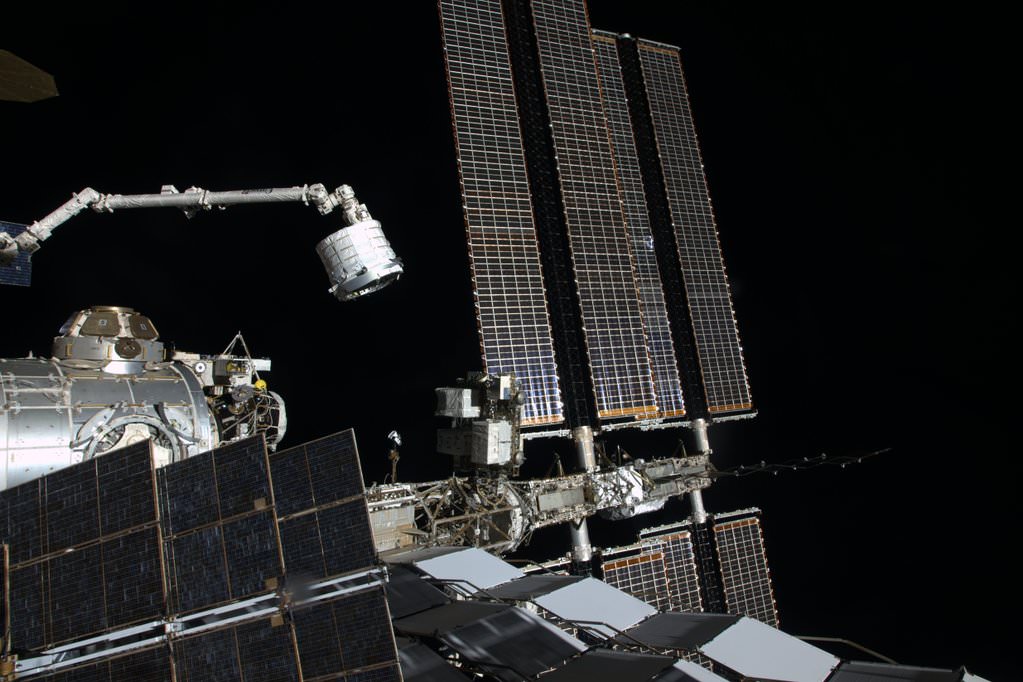
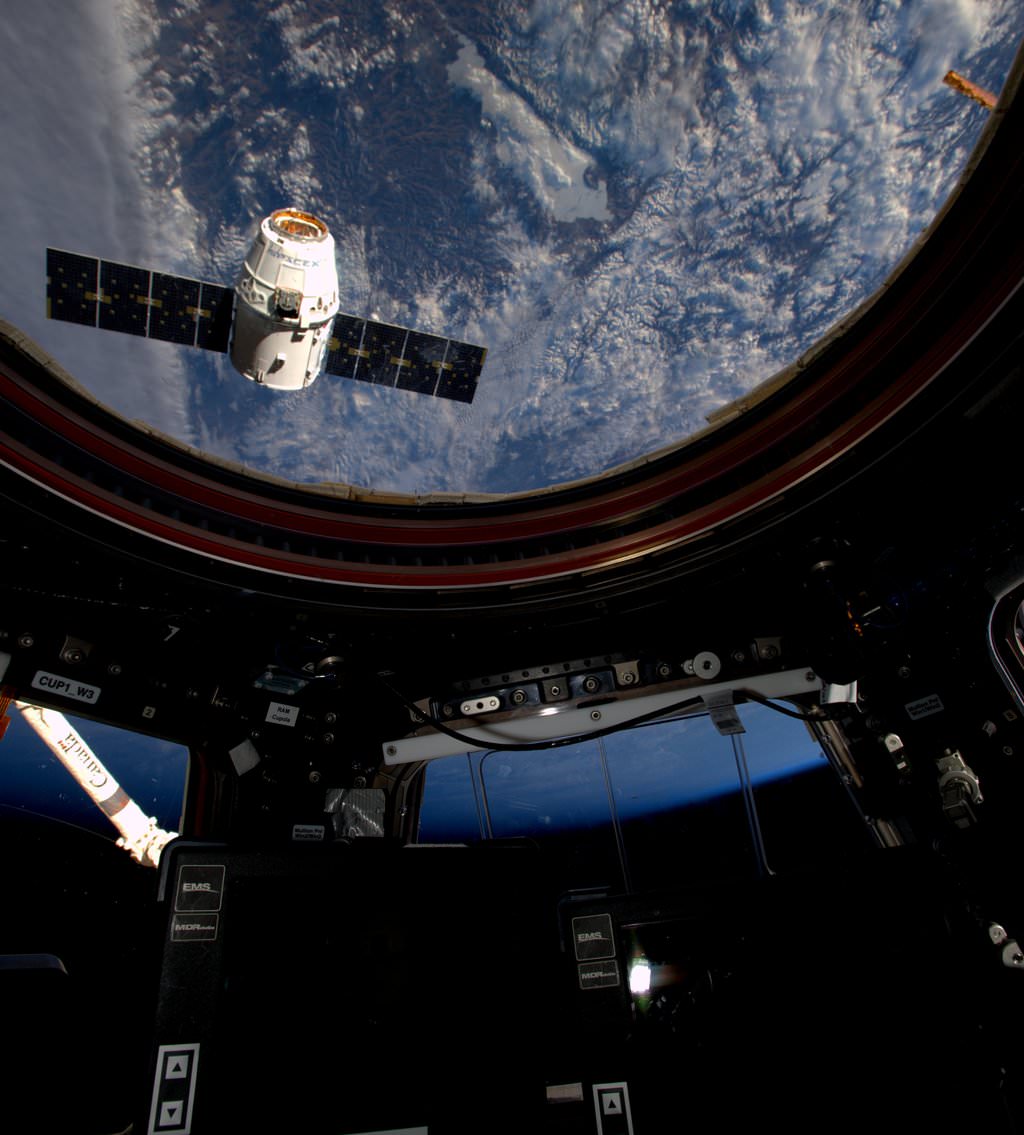
As the orbiting outpost was traveling 252 statute miles over the Great Lakes, NASA’s veteran Expedition 48 Commander Jeff Williams and newly arrived NASA Flight Engineer Kate Rubins used the station’s 57.7-foot (17.6-meter) Canadian-built robotic arm to reach out and capture the Dragon CRS-9 spacecraft at 6:56 a.m. EDT.
“Good capture confirmed after a two day rendezvous,” said Houston Mission Control at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, as Dragon was approximately 30 feet (10 meters) away from the station.
“We’ve captured us a Dragon,” radioed Williams.
“Congratulations to the entire team that put this thing together, launched it, and successfully rendezvoused it to the International Space Station. We look forward to the work that it brings.”
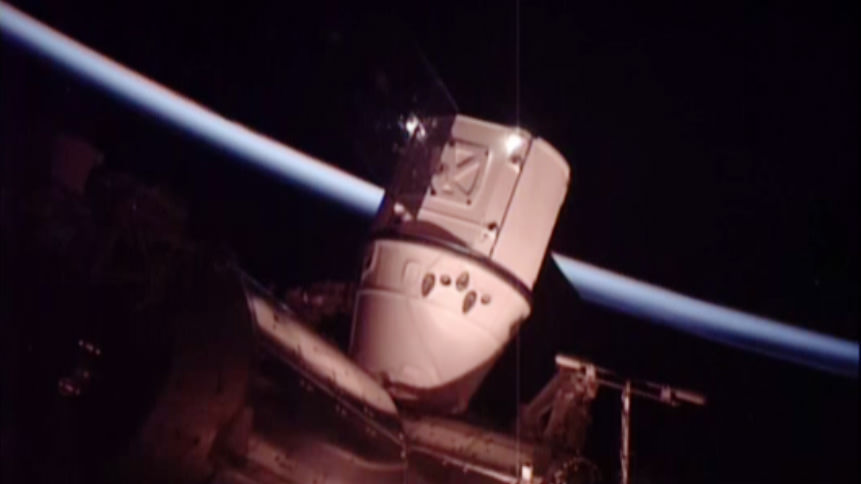

The events unfolded live on a NASA TV webcast for all to follow along.
Furthermore, today’s dramatic Dragon arrival coincides with a renowned day in the annuls of space history. Today coincides with the 40th anniversary of humanity’s first successful touchdown on the surface of Mars by NASA’s Viking 1 lander on July 20, 1976. It paved the way for many future missions.
And Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin were the first humans to land on another celestial body – the Moon – on July 20, 1969 during NASA’s Apollo 11 lunar landing mission.
Williams was working from a robotics work station in the station’s domed cupola. Rubins was Williams backup. She just arrived at the station on July 9 for a minimum 4 month stay, after launching to orbit on a Russian Soyuz on July 6 with two additional crew mates.
Ground controllers then used the robotic arm to maneuver the Dragon cargo spacecraft closer to its berthing port on the Earth facing side of the Harmony module, located at the front of the station.
Some three hours after the successful grappling, Dragon was joined to the station and bolted into place for initial berthing on the Harmony module at 10:03 a.m. EDT as the station flew about 252 statute miles over the California and Oregon border.
Controllers then activated four gangs of four bolts in the common berthing mechanism (CBM) to complete the second stage capture of the latching and berthing of Dragon to the station with a total of 16 bolts to ensure a snug connection, safety and no pressure leaks.
Crew members Williams and Rubins along with Japanese astronaut Takuya Onishi are now working to install power and data cables from the station to Dragon. They plan to open the hatch tomorrow after pressurizing the vestibule in the forward bulkhead between the station and Dragon.
Dragon reached the station after a carefully choreographed orbital chase and series of multiple thruster firings to propel the cargo ship from its preliminary post launch orbit up to the massive million pound science outpost with six resident crew members from the US, Russia and Japan.
Among the 5000 pounds of equipment on board is the first of two identical docking adapters essential for enabling station dockings next year by NASA’s new commercial astronaut taxis. This mission is all about supporting NASA’s ‘Journey to Mars’ by humans in the 2030s.
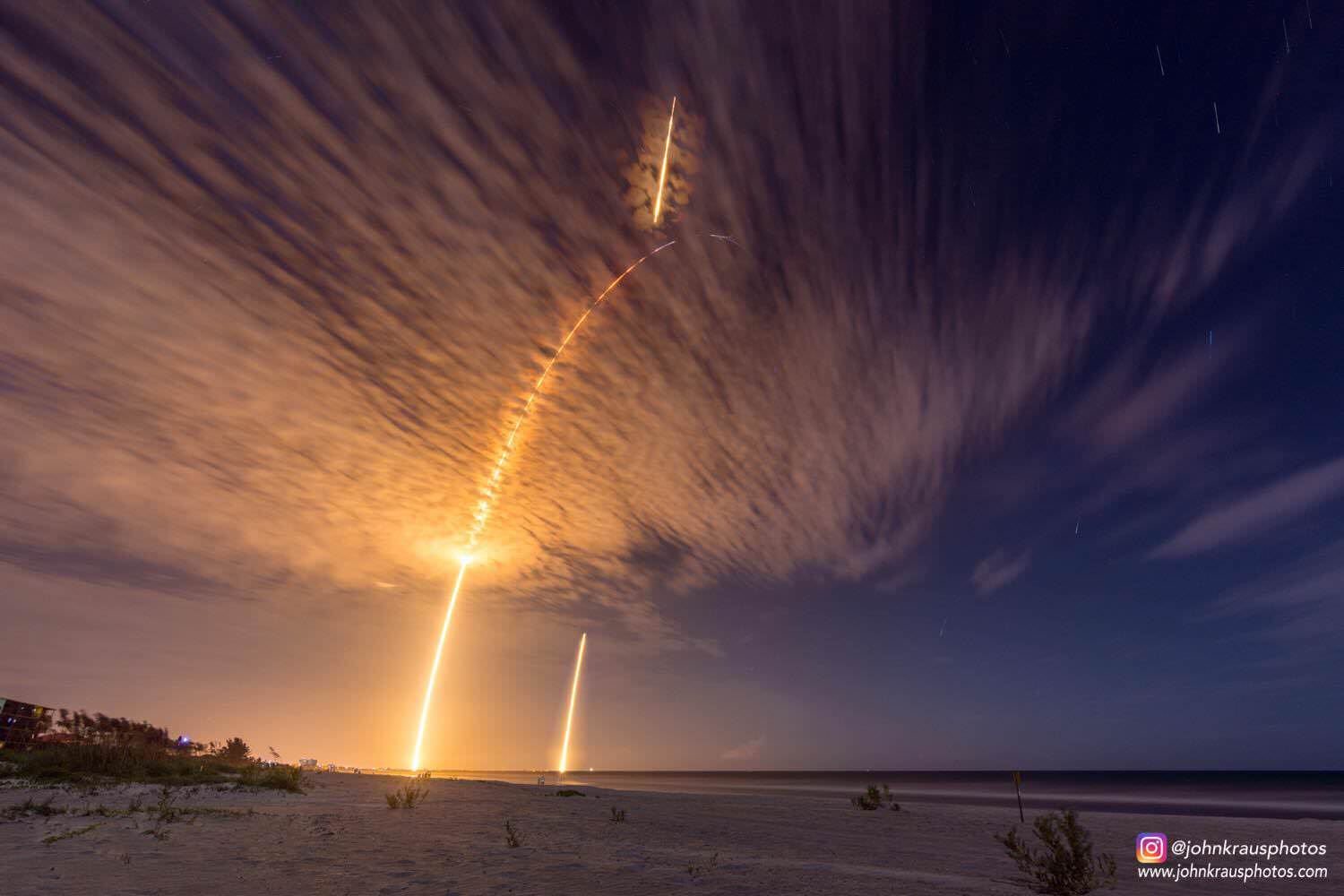
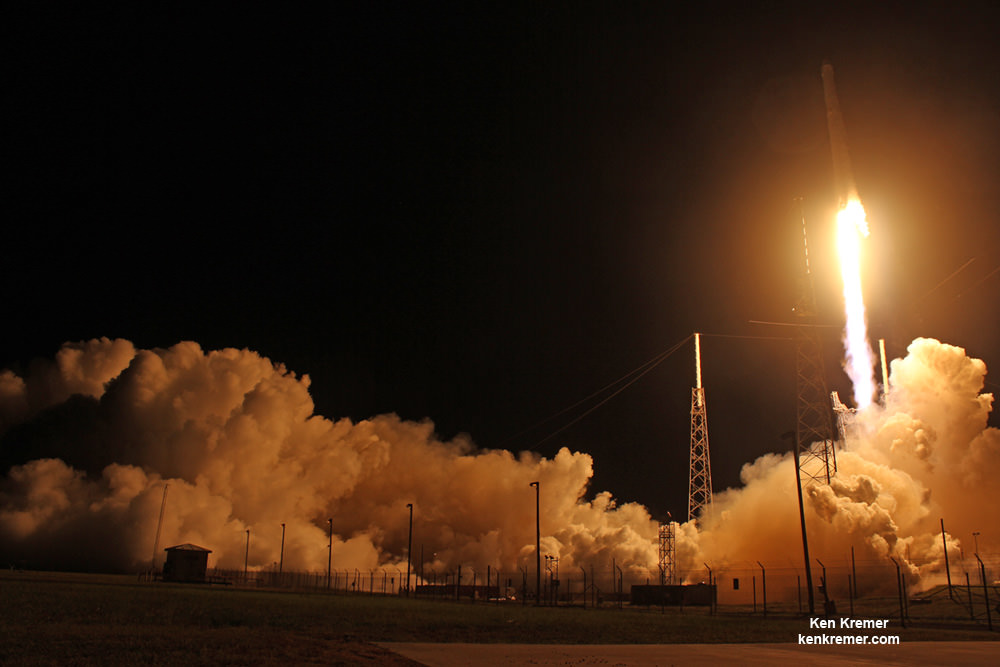
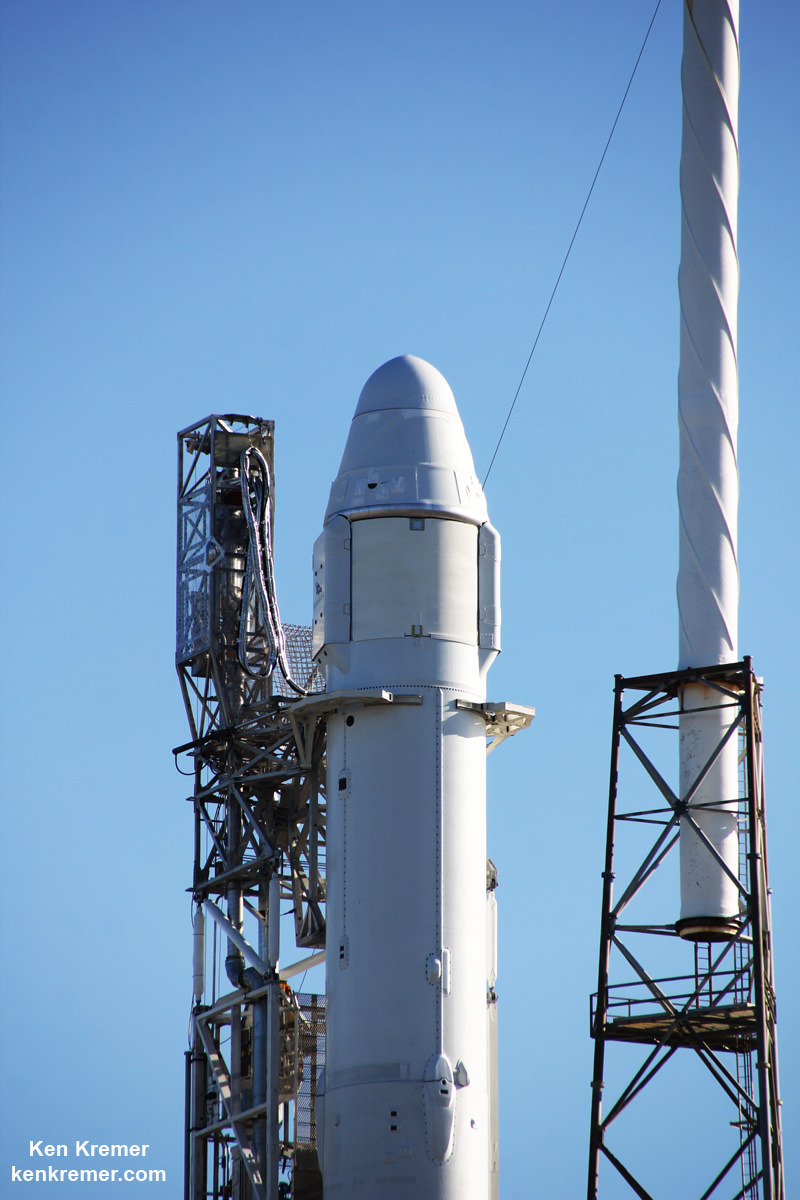
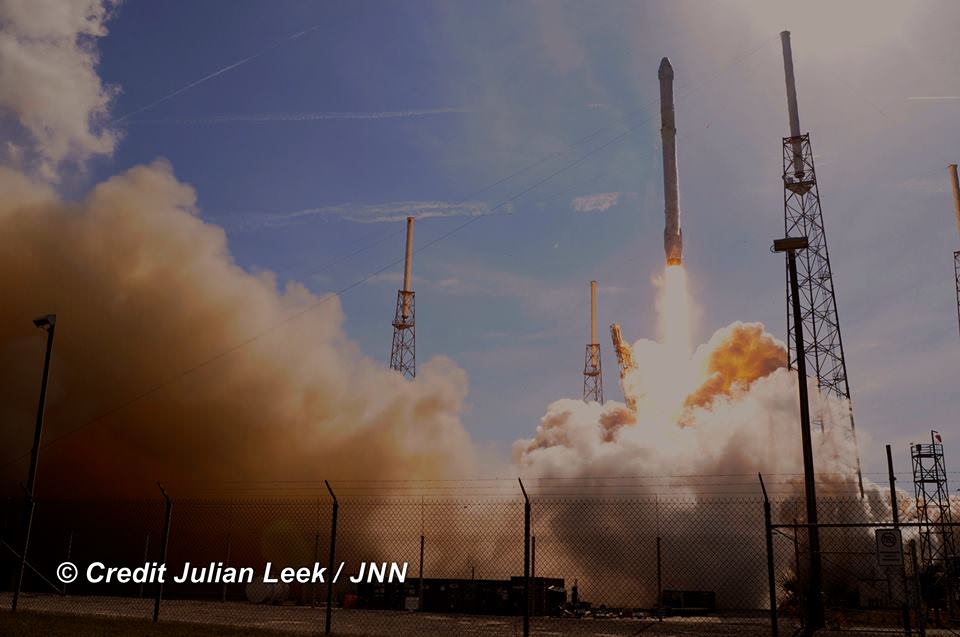
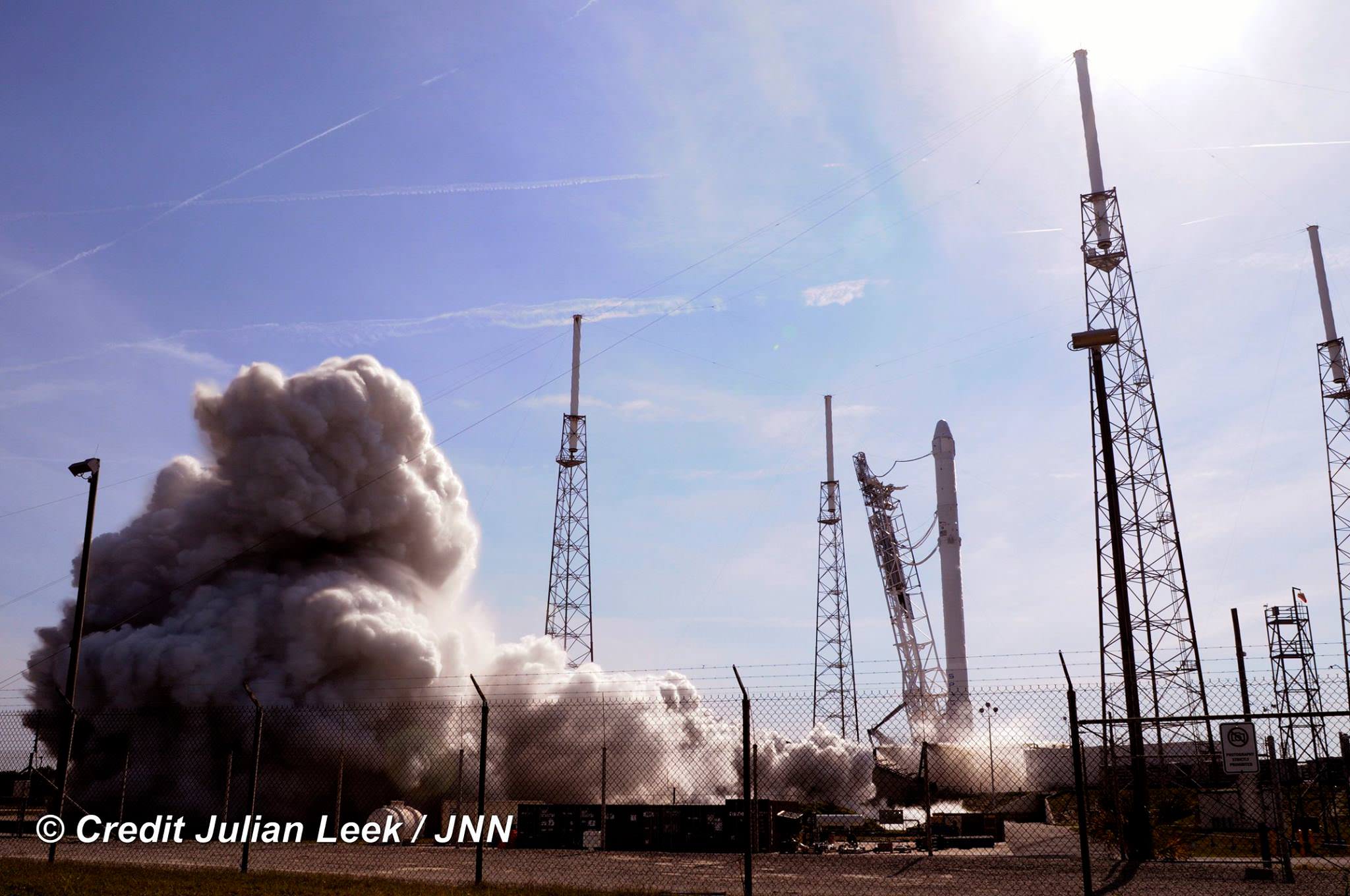
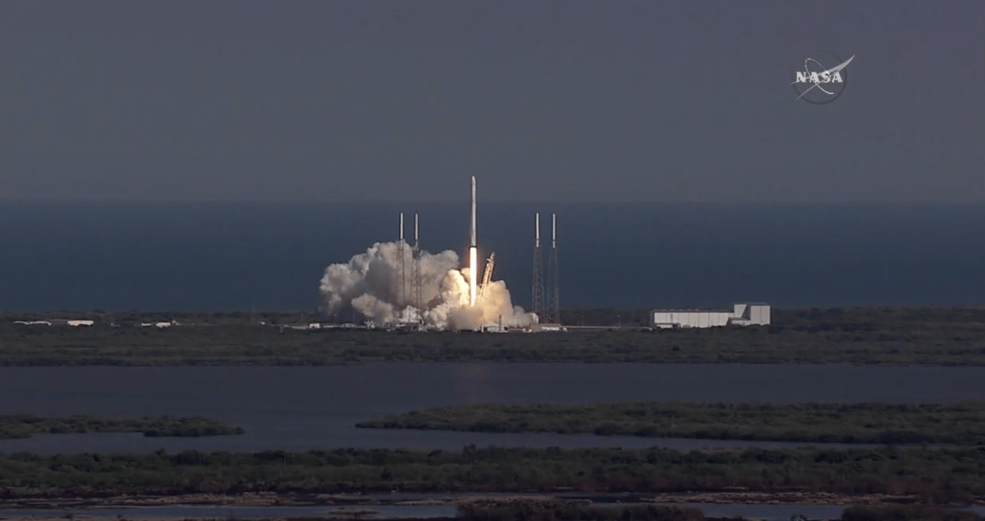
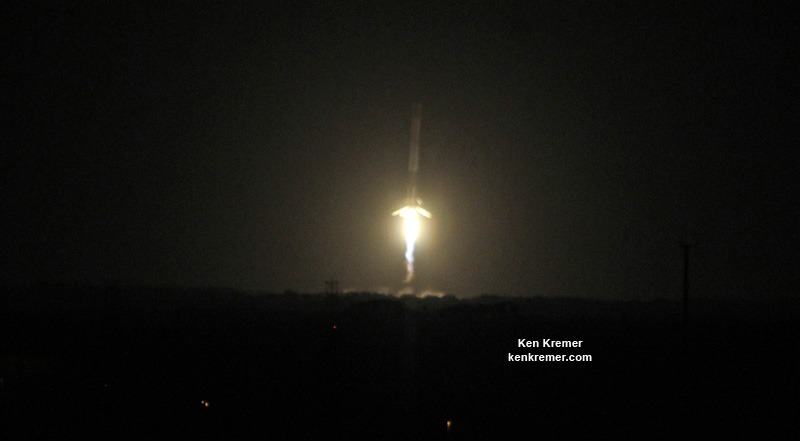
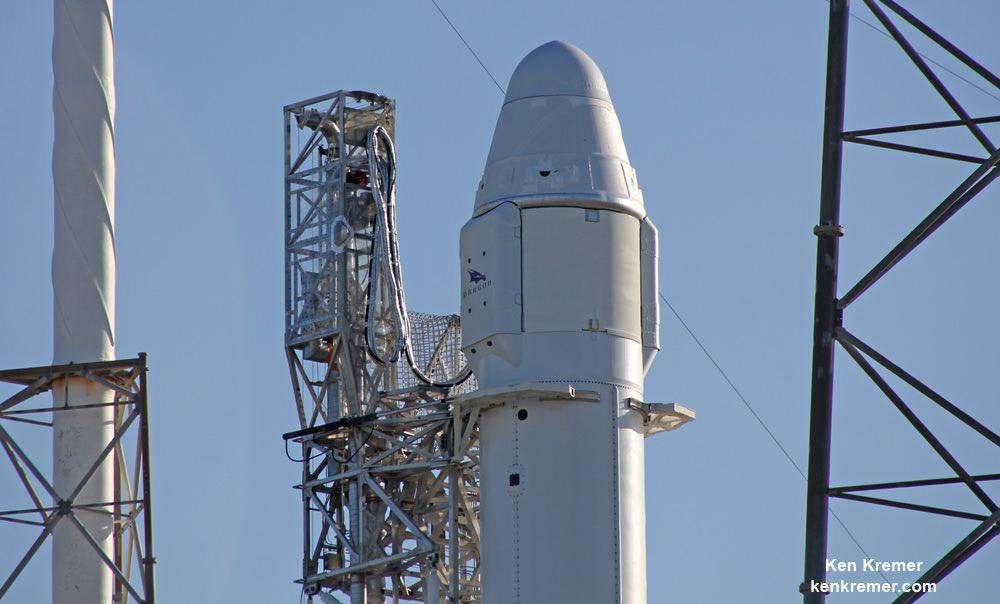
Liftoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in its upgraded, full thrust version and the Dragon CRS-9 resupply ship took place barely 48 hours ago at 12:45 a.m. EDT Monday, July 18, from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
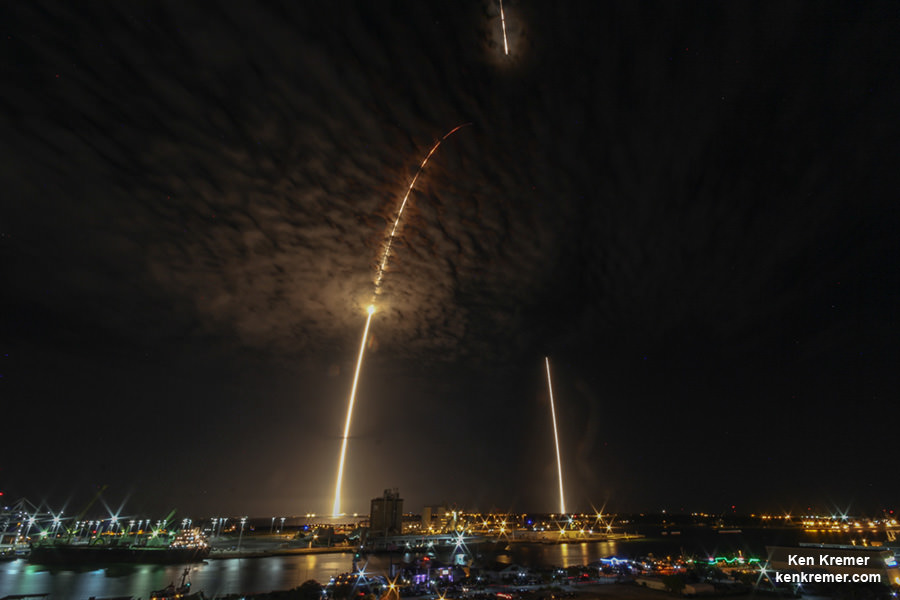

Dragon reached its preliminary orbit about 10 minutes after launch and then deployed a pair of solar arrays.
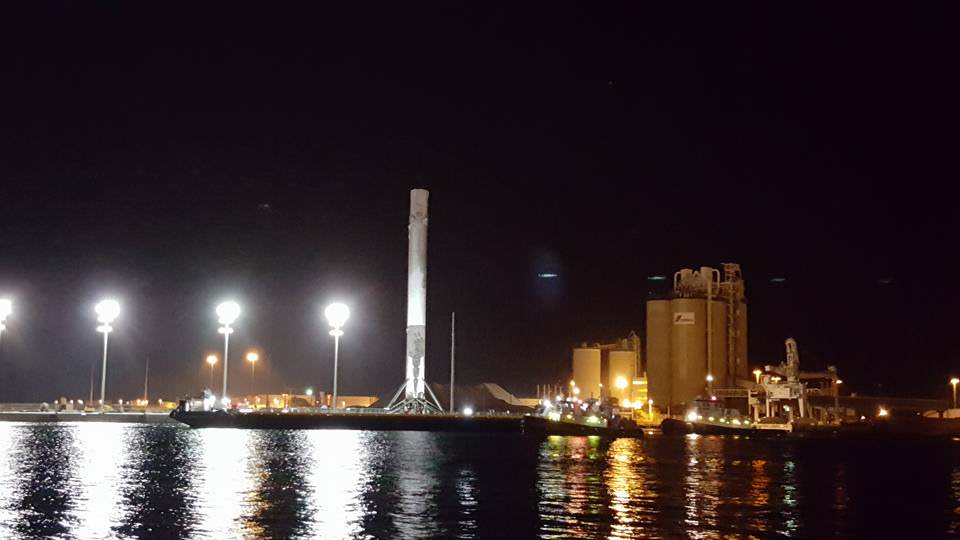
SpaceX also successfully executed a spellbinding ground landing of the Falcon 9 first stage back at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Landing Zone 1, located a few miles south of launch pad 40.
The dramatic ground landing of the 156 foot tall Falcon 9 first stage at LZ -1 took place about 9 minutes after liftoff. It marks only the second time a spent orbit class booster has touched down intact and upright on land.

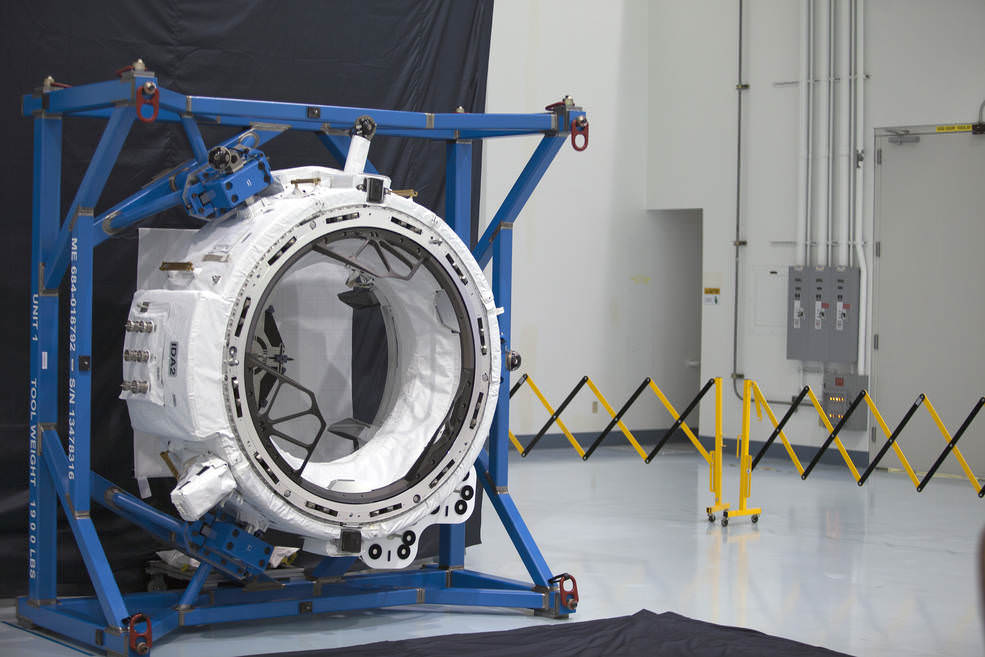
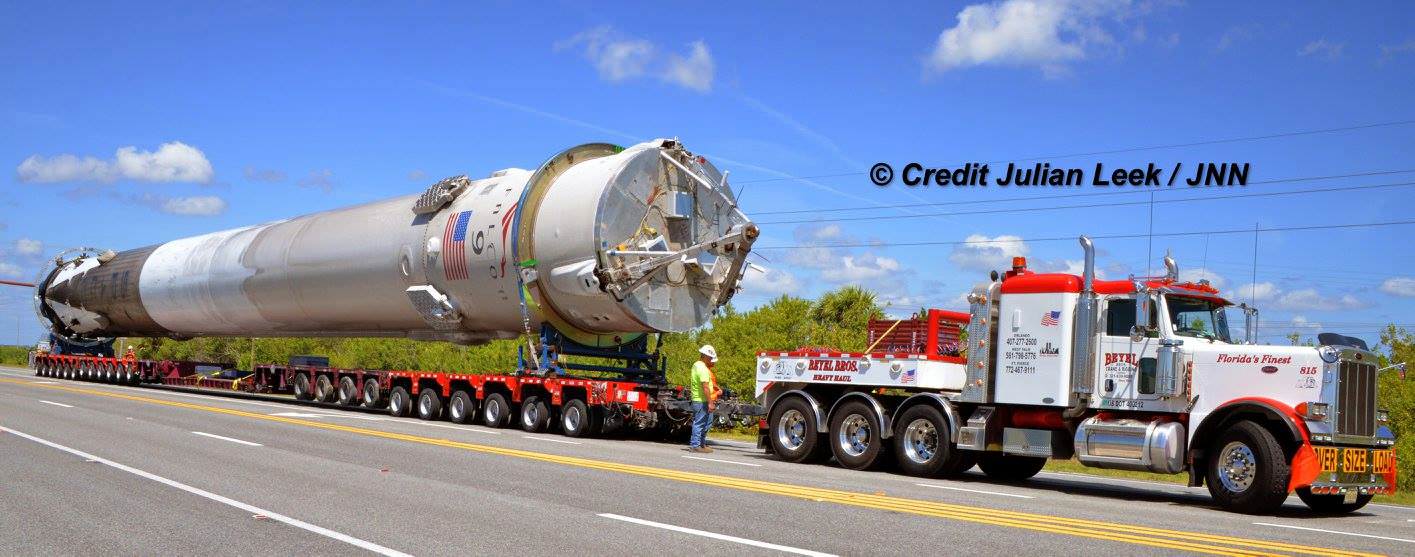
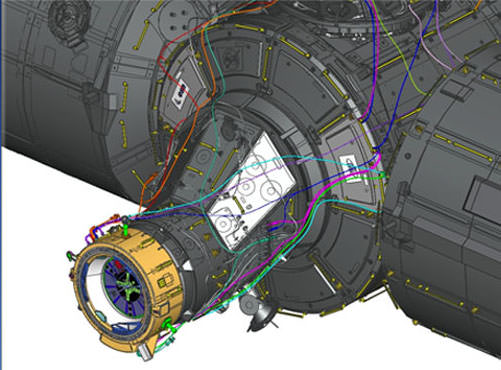
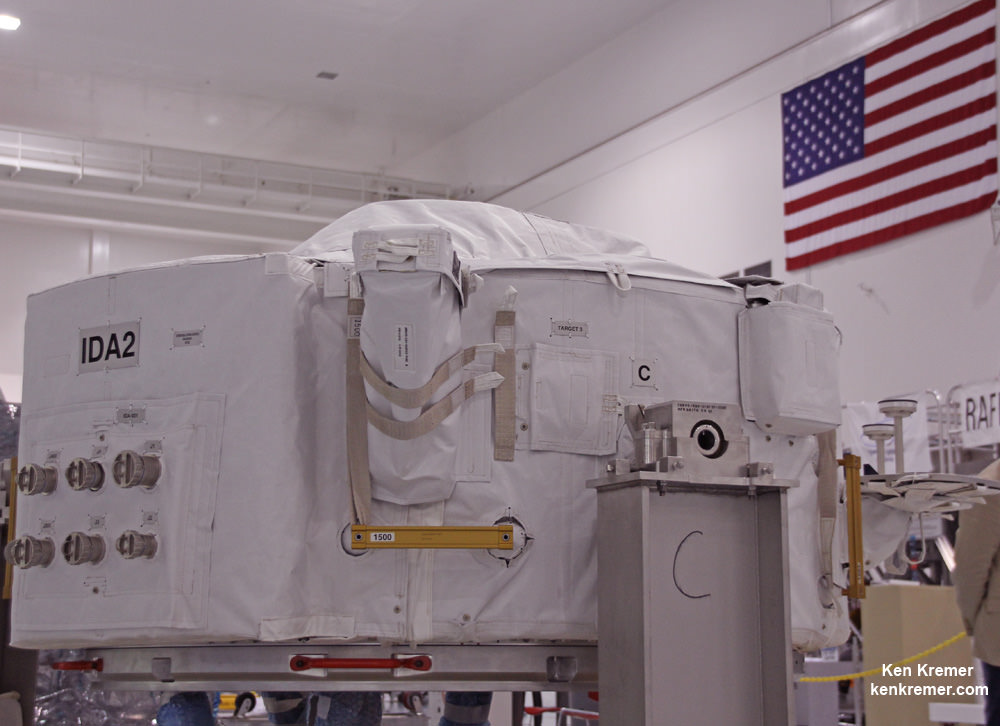
Among the wealth of over 3900 pounds (1790 kg) of research investigations loaded on board Dragon is an off the shelf instrument designed to perform the first-ever DNA sequencing in space and the first international docking adapter (IDA) that is absolutely essential for docking of the SpaceX and Boeing built human spaceflight taxis that will ferry our astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS) in some 18 months.
Other science experiments on board include OsteoOmics to test if magnetic levitation can accurately simulate microgravity to study different types of bone cells and contribute to treatments for diseases like osteoporosis, a Phase Change Heat Exchanger to test temperature control technology in space, the Heart Cells experiments that will culture heart cells on the station to study how microgravity changes the human heart, new and more efficient three-dimensional solar cells, and new marine vessel tracking hardware known as the Automatic Identification System (AIS) that will aid in locating and identifying commercial ships across the globe.
The ring shaped IDA-2 unit is stowed in the Dragon’s unpressurized truck section. It weighs 1029 lbs (467 kg), measures about 42 inches tall and sports an inside diameter of 63 inches in diameter – so astronauts and cargo can easily float through. The outer diameter measures about 94 inches.
“Outfitted with a host of sensors and systems, the adapter is built so spacecraft systems can automatically perform all the steps of rendezvous and dock with the station without input from the astronauts. Manual backup systems will be in place on the spacecraft to allow the crew to take over steering duties, if needed,” says NASA.

“It’s a passive system which means it doesn’t take any action by the crew to allow docking to happen and I think that’s really the key,” said David Clemen Boeing’s director of Development/Modifications for the space station.
“Spacecraft flying to the station will use the sensors on the IDA to track to and help the spacecraft’s navigation system steer the spacecraft to a safe docking without astronaut involvement.”
CRS-9 counts as the company’s ninth scheduled flight to deliver supplies, science experiments and technology demonstrations to the International Space Station (ISS).
The CRS-9 mission is for the crews of Expeditions 48 and 49 to support dozens of the approximately 250 science and research investigations in progress under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract.

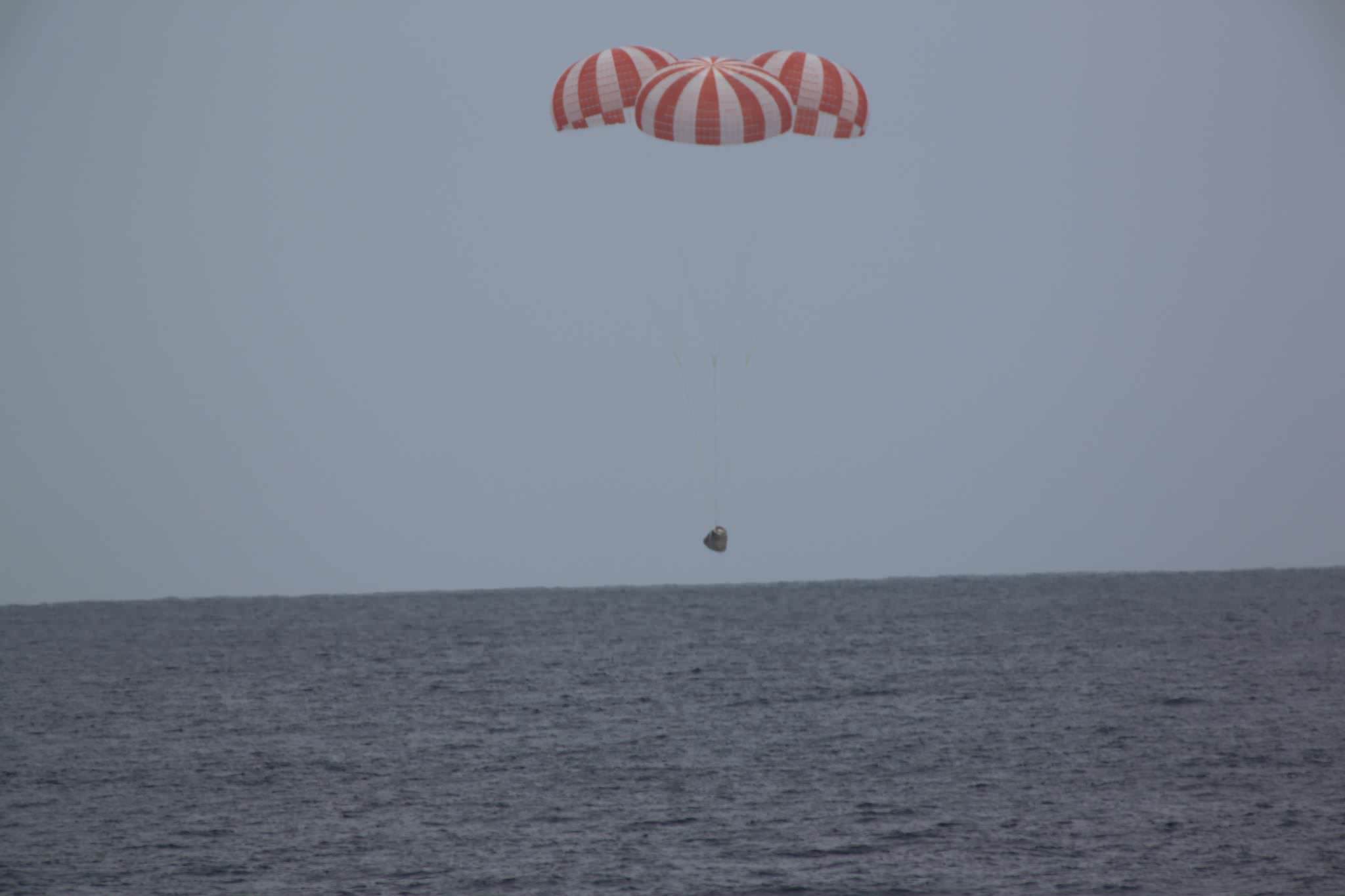
Dragon will remain at the station until its scheduled departure on Aug. 29 when it will return critical science research back to Earth via a parachute assisted splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the California coast.
Watch for Ken’s continuing CRS-9 mission coverage where he reported onsite direct from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.