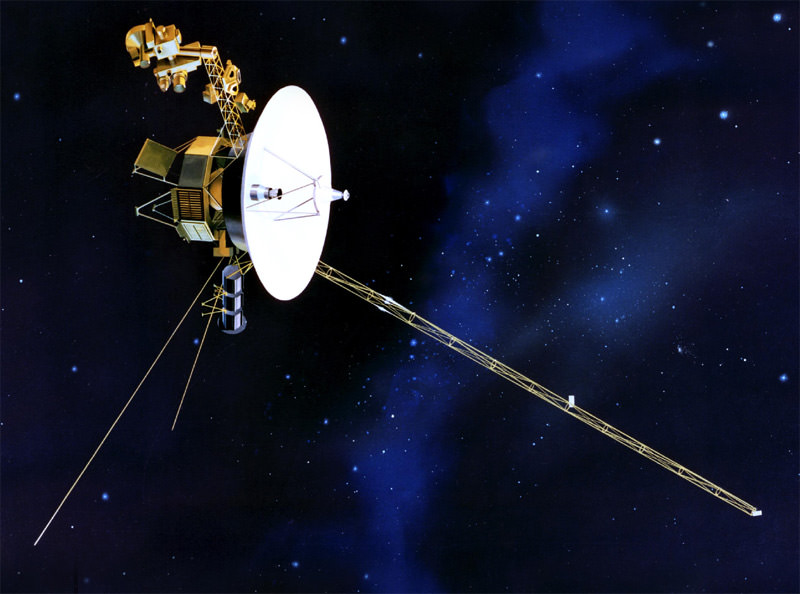
Yesterday, NASA announced that as of August 2012, Voyager 1 is in a new frontier to humanity: interstellar space. Our most distant spacecraft is now in a region where the plasma (really hot gas) environment comes more from between the stars than from the sun itself. (There’s still debate as to whether it’s in or out of the solar system, as this article explains.)
The plucky spacecraft is close to 12 billion miles (19 million kilometers) from home, and in its 36 years of voyaging has taught us a lot about the planets, their moons and other parts of space. Here are 10 of some of its most historic moments. Did we miss any? Let us know in the comments.
10. The launch: Aug. 20, 1977

Voyager 1 blasted off from Cape Canaveral on Sept. 5, 1977. Its twin, Voyager 2, departed Earth 16 days earlier. Each spacecraft carried various scientific instruments on board as well as a “Golden Record” that had sounds of Earth on it, as well as a diagram showing where Earth is in the universe.
9. Capturing the Earth and Moon together for the first time
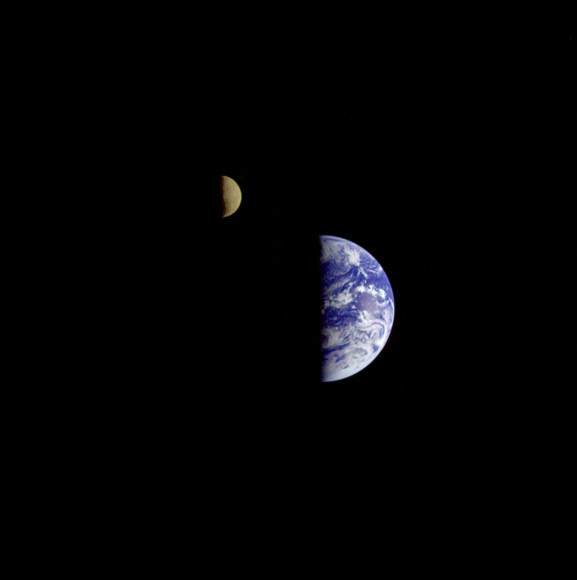

About two weeks after launching, Voyager 1 turned back towards Earth and took three images, which were combined into this single view of the Earth and Moon together in space. This was the first time both bodies were pictured together, NASA said.
8. The ‘Pale Blue Dot’ image

On February 14, 1990, Voyager 1 was about 3.7 billion miles (6 billion kilometers) away from Earth. Scientists commanded the spacecraft to turn its face towards the solar system and snap some pictures of the planets. Among them was this famous image of Earth, which astronomer Carl Sagan called the Pale Blue Dot. “Look again at that dot. That’s here. That’s home. That’s us,” wrote Sagan in his 1997 book of the same name. In 2013, the spacecraft Cassini also took a picture of Earth, and NASA encouraged everyone to wave back.
7. Finding moons “shepherding” Saturn’s F ring
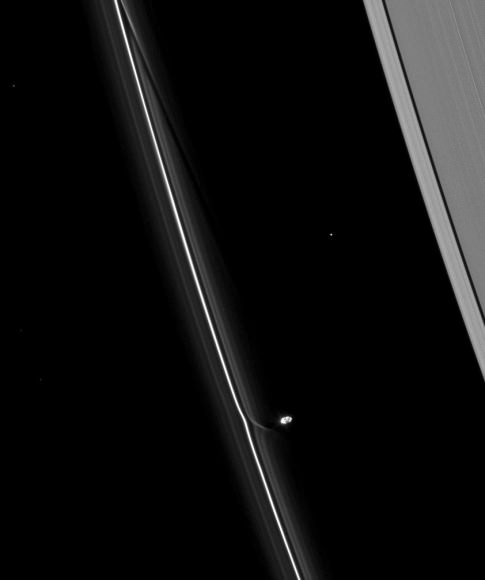

Voyager 1 spotted Prometheus and Pandora, two moons of Saturn that keep the F ring separate from the rest of the debris, as well as Atlas, which “shepherds” the A ring. More recently, astronomers have found even more interesting things in Saturn’s rings — such as rain.
6. Spotting what appeared to be a LOT of water ice on Saturn’s moons

After many years of seeing Saturn’s moons as mere points of light, Voyager 1 buzzed several of them in its quick flyby through the system: Dione, Enceladus, Mimas, Rhea, Tethys and Titan among them. Many of these moons appeared to be icy, which was a surprising find since astronomers previously thought water was pretty rare in the Solar System. We know better now.
5. Imaging Titan’s orange haze
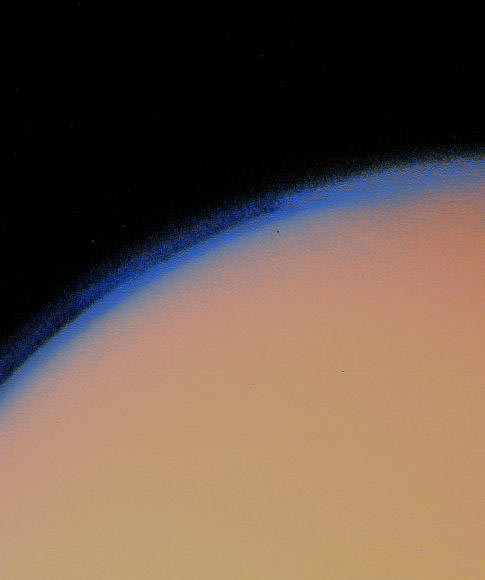
Voyager 1 pictures such as this tortured astronomers for decades — what lies beneath this mysterious haze surrounding Titan, Saturn’s moon? That mystery, in fact, inspired the European Space Agency to send a lander to the moon, called Huygens, which successfully reached the surface in 2005.
4. Finding active volcanoes on Io

Voyager 1 helped show us that the Solar System is full of very interesting moons. At Io — a moon of Jupiter — it turns out the moon flexes during its 42-hour orbit of massive Jupiter, which powers a lot of volcanic activity.
3. Voyager 1 becomes the most distant human object
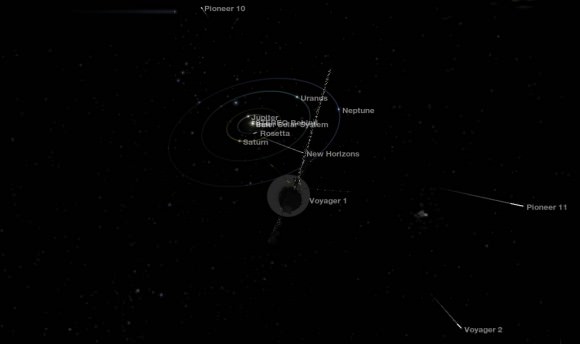
On Feb. 17, 1998, Voyager 1’s distance surpassed that of another long-flying probe, Pioneer 10. This made Voyager 1 the farthest-flung human object in space.
2. Riding the “magnetic highway”
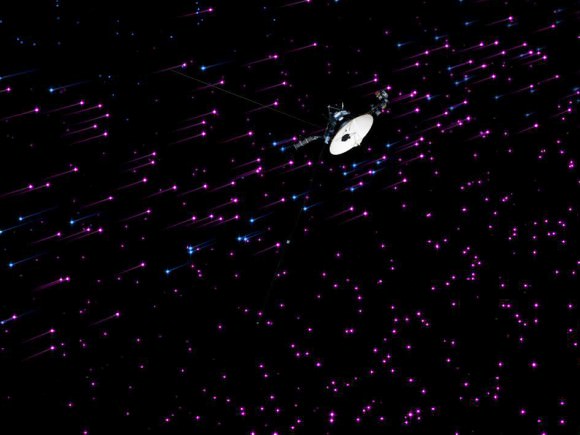

In December, NASA said Voyager 1 had reached an area (as of July 28, 2012) where high-energy magnetic particles were starting to bleed through the bubble of lower-energy particles from our sun. “Voyager’s discovered a new region of the heliosphere that we had not realized was there. It’s a magnetic highway where the magnetic field of the Sun is connected to the outside. So it’s like a highway, letting particles in and out,” said project scientist Ed Stone at the time. After that point, as more measurements were analyzed by different teams, there was a lot of debate as to whether Voyager had reached interstellar space.
1. Reaching interstellar space
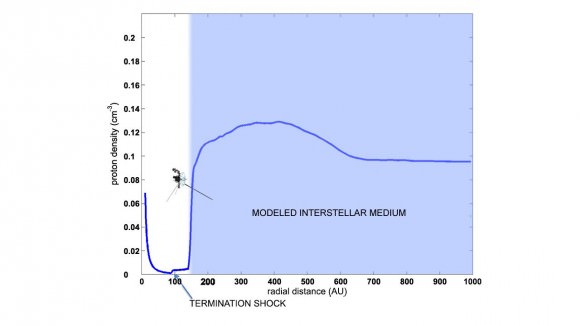
With Voyager 1 now known to be in interstellar space, we’re lucky enough to have a few years left to communicate with it before it runs out of power. All of the instruments will be turned off by 2025, and then engineering data will be available for about 10 years beyond that. The silent emissary from humanity will then come within 1.7 light years of an obscure star in the constellation Ursa Minor (the Little Bear) called AC+79 3888 in the year 40,272 AD and then orbit the center of the Milky Way for millions of years.

