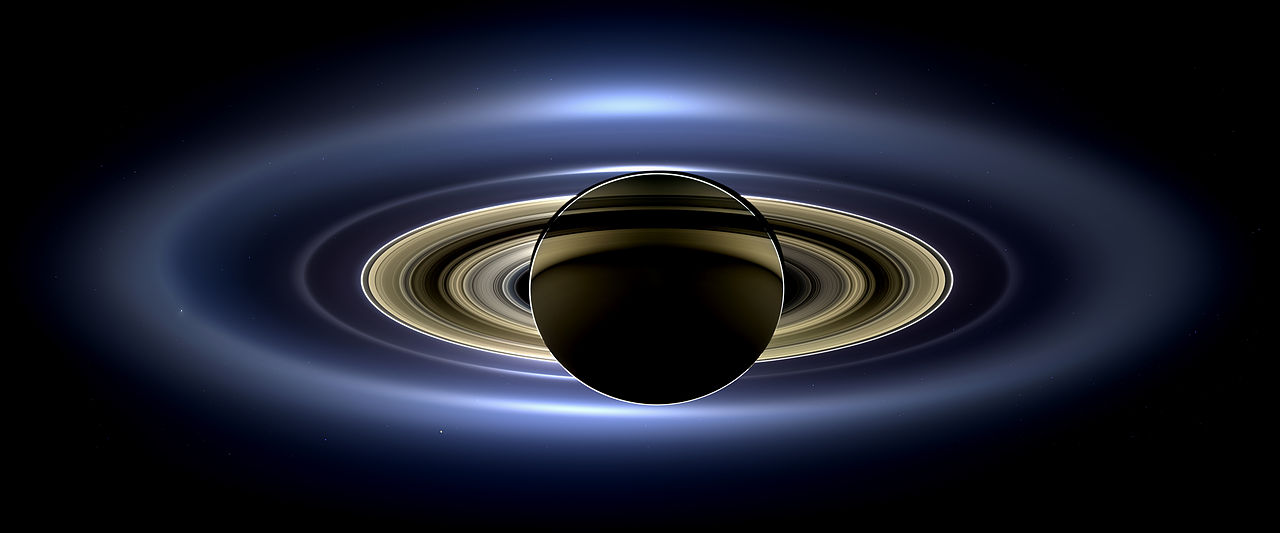
The rings of Saturn are an amazing sight. They are so iconic that it is hard to imagine Saturn without its rings. But throughout most of Saturn’s history, it didn’t have rings. The rings are much younger than the planet itself, and we now have good evidence to prove it.
Continue reading “Saturn's Rings are Much Younger Than the Planet”Will Enceladus finally answer, ‘Are we alone?’
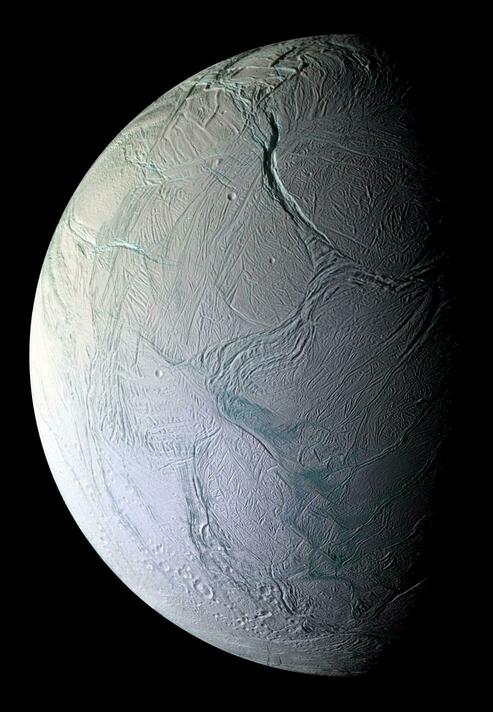
We recently examined how and why the planet Mars could answer the longstanding question: Are we alone? There is evidence to suggest that it was once a much warmer and wetter world thanks to countless spacecraft, landers, and rovers having explored—and currently exploring—its atmosphere, surface, and interior. Here, we will examine another one of Saturn’s 83 moons, an icy world that spews geysers of water ice from giant fissures near its south pole, which is strong evidence for an interior ocean, and possibly life. Here, we will examine Enceladus.
Continue reading “Will Enceladus finally answer, ‘Are we alone?’”Animation Shows how Saturn’s Rings Move at Different Speeds
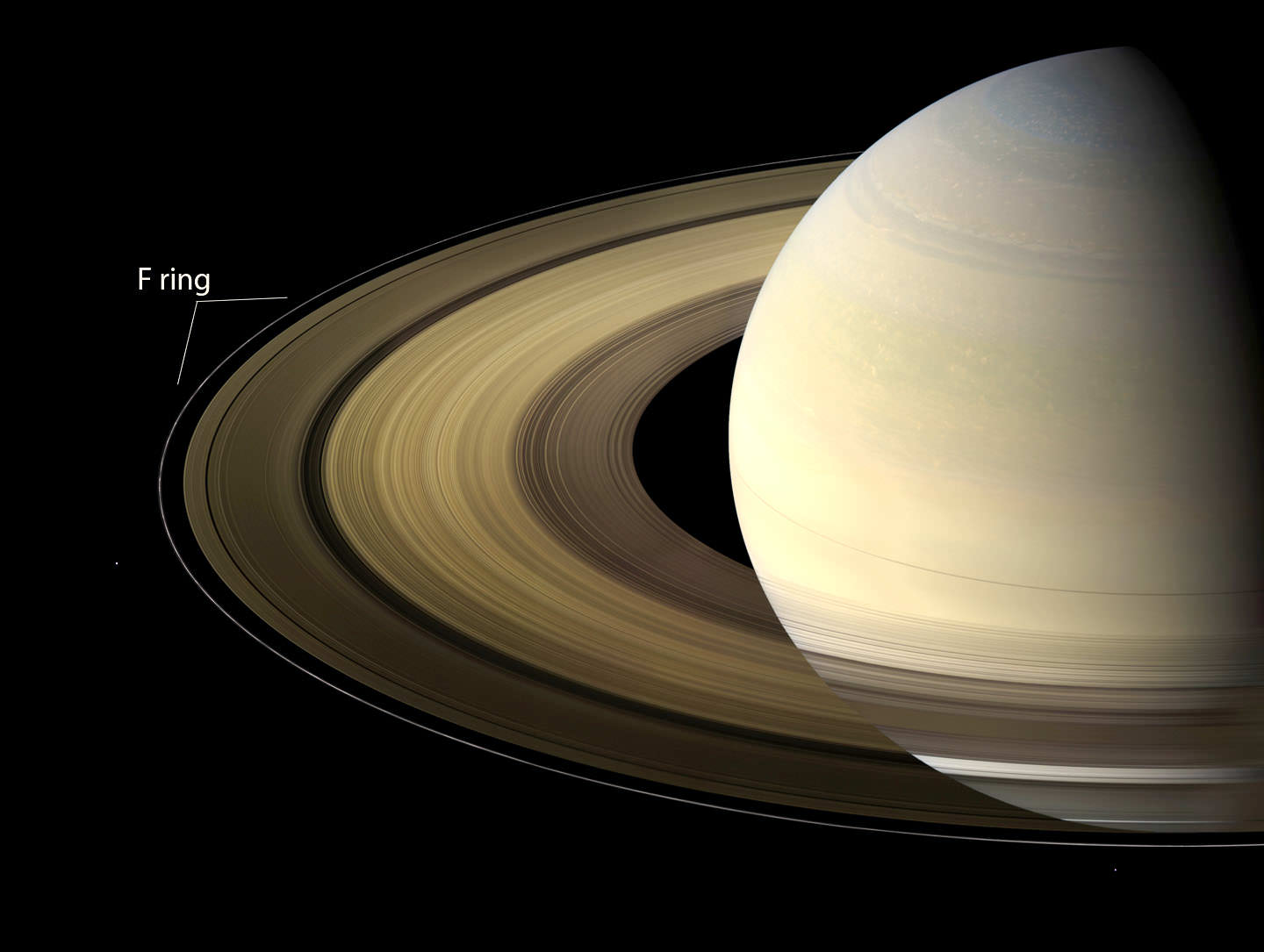
Saturn’s rings are one of the most recognized and revered celestial objects known to the human race. From a distance, they look like a disk of layered crystal or multicolored disks within disks that wrap around Saturn’s hazy umber face. When viewed up close, we see that these rings are actually particles of water ice (from microns to icebergs), as well as silicates, carbon dioxide, and ammonia.
We would also noticed that the rings have some interesting orbital mechanics. In fact, each ring has a different orbit that is the result of its proximity to Saturn (i.e., the closer they are, the faster they orbit). To illustrate what this complex system look like, NASA Fellow Dr. James O’Donoghue created a stunning animation that shows how each of Saturn’s major ring segments (A-Ring to F-Ring) orbit together around the planet.
Continue reading “Animation Shows how Saturn’s Rings Move at Different Speeds”Titan’s Atmosphere Recreated in an Earth Laboratory
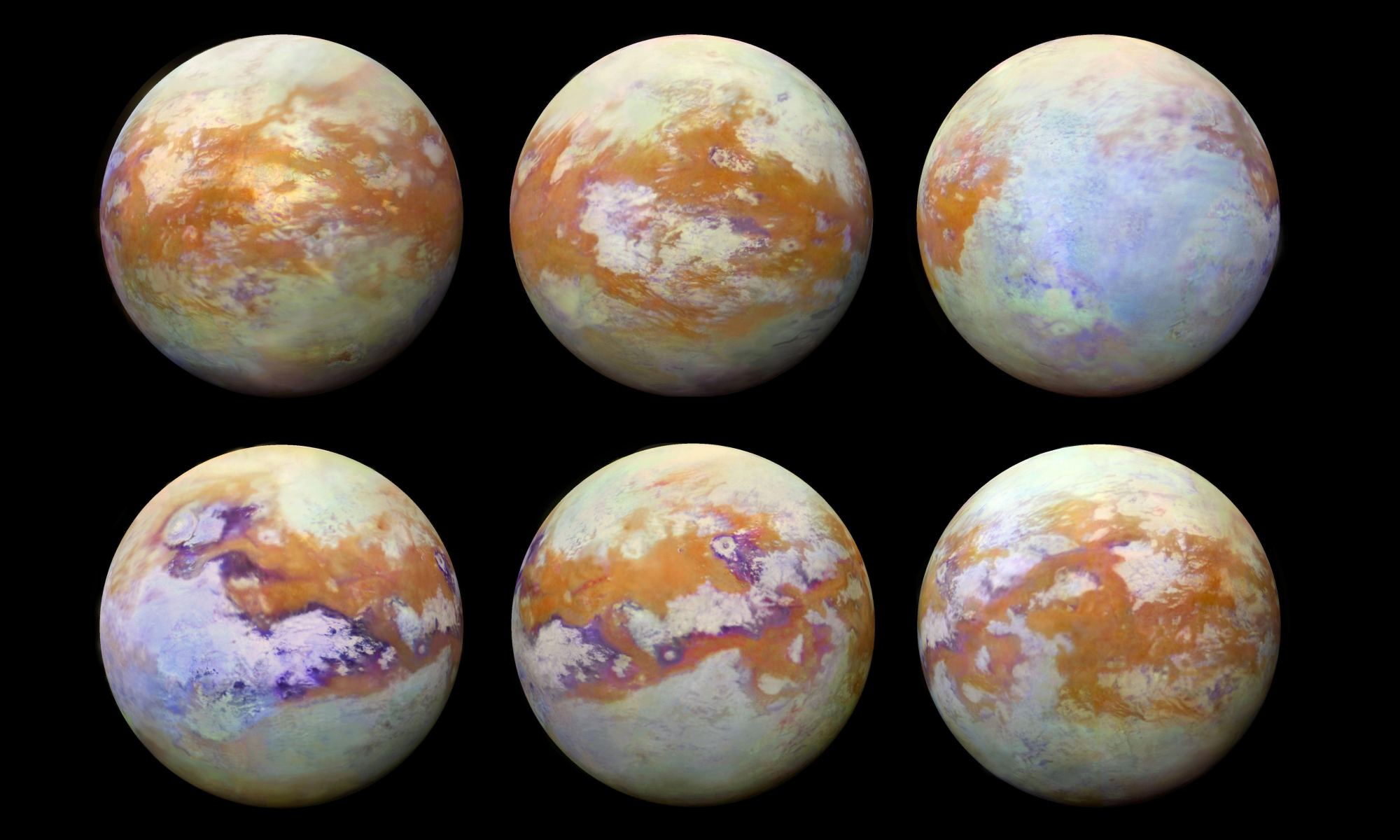
Beyond Earth, the general scientific consensus is that the best place to search for evidence of extraterrestrial life is Mars. However, it is by no means the only place. Aside from the many extrasolar planets that have been designated as “potentially-habitable,” there are plenty of other candidates right here in our Solar System. These include the many icy satellites that are thought to have interior oceans that could harbor life.
Among them is Titan, Saturn’s largest moon that has all kinds of organic chemistry taking place between its atmosphere and surface. For some time, scientists have suspected that the study of Titan’s atmosphere could yield vital clues to the early stages of the evolution of life on Earth. Thanks to new research led by tech-giant IBM, a team of researchers has managed to recreate atmospheric conditions on Titan in a laboratory.
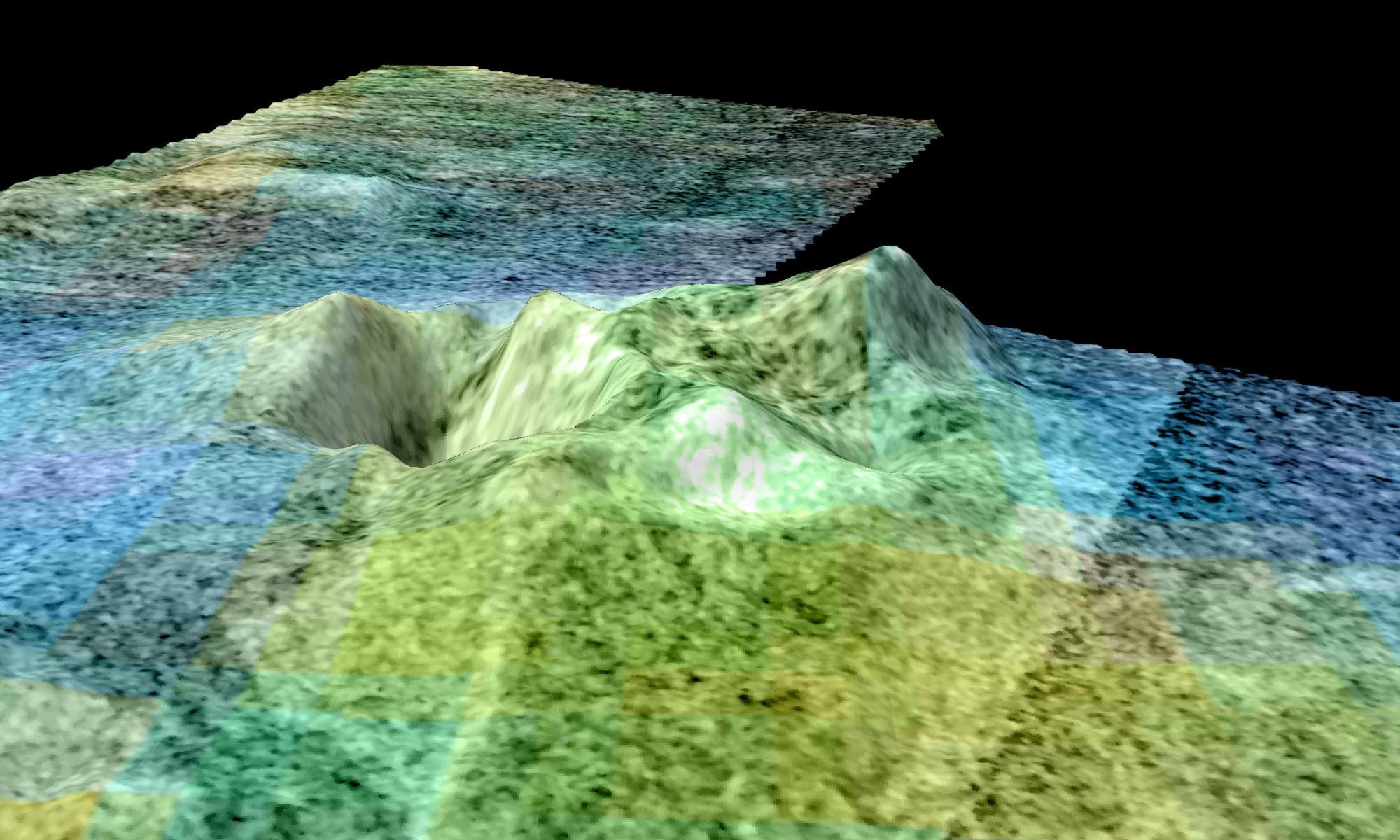
Continue reading “Titan’s Atmosphere Recreated in an Earth Laboratory”There are Features on Titan That Really Look Like Volcanic Craters
On Sept. 15th, 2017, NASA’s Cassini Orbiter concluded its mission by diving into Saturn’s atmosphere. Over the course of the 13 years it spent studying the Saturn system, it revealed a great deal about this gas giant and its largest moon, Titan. In the coming years, scientists are eager to send another mission to Titan to follow up on Cassini and get a better look at its surface features, methane lakes, and other curious properties.
These include the morphological features in the northern polar region that are strikingly similar to volcanic features here on Earth. According to a recent study by the Planetary Science Institute (PSI), these features could be evidence of cryovolcanism that continues to this day. These findings are the latest evidence that Titan has an interior ocean and internal heating mechanisms, which could also mean the planet harbors life in his interior.
Continue reading “There are Features on Titan That Really Look Like Volcanic Craters”Scientists Construct a Global Map of Titan’s Geology
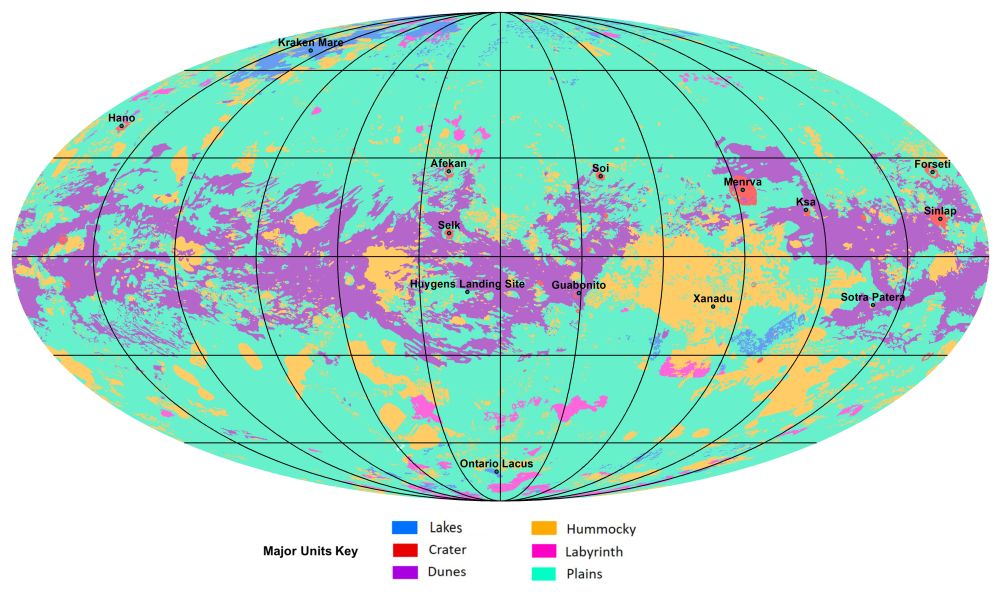
Titan’s methane-based hydrologic cycle makes it one of the Solar System’s most geologically diverse bodies. There are lakes of methane, methane rainfall, and even “snow” made of complex organic molecules. But all of that detail is hidden under the moon’s dense, hazy atmosphere.
Now a team of scientists have used data from the Cassini mission to create our first global geological map of Titan.
Continue reading “Scientists Construct a Global Map of Titan’s Geology”Whoa. Lakes on Titan Might be the Craters from Massive Underground Explosions
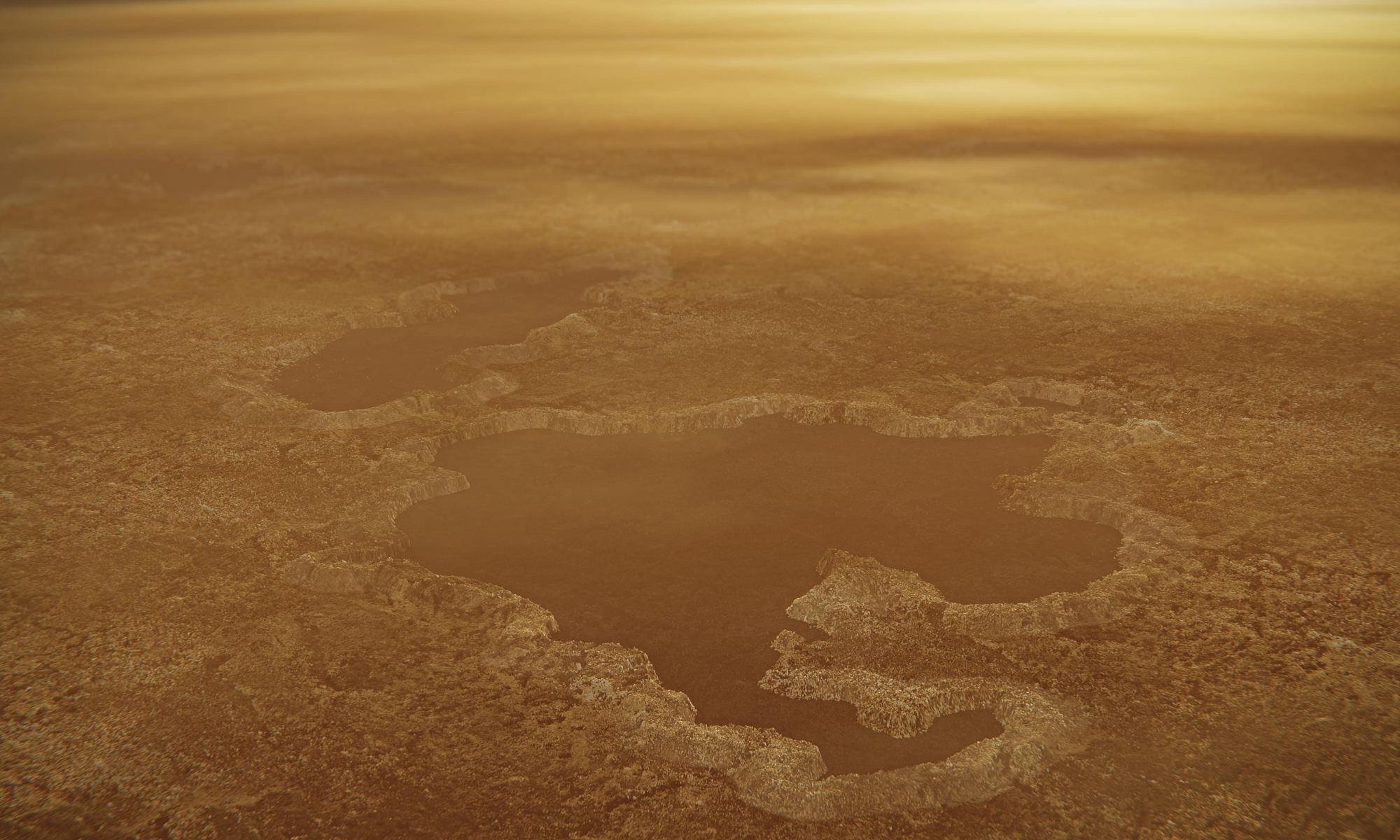

The Cassini spacecraft ended its mission to Saturn and its moons two years ago when it was sent plunging into Saturn to be destroyed. But after two years, scientists are still studying the data from the Cassini mission. A new paper based on Cassini data proposes a new explanation for how some lakes on Titan may have formed.
Continue reading “Whoa. Lakes on Titan Might be the Craters from Massive Underground Explosions”Enceladus is Filled with Tasty Food for Bacteria
As soon as the Cassini-Huygens mission arrived the Saturn system in 2004, it began to send back a number of startling discoveries. One of the biggest was the discovery of plume activity around the southern polar region of Saturn’s moon Enceladus’, which appears to be the result of geothermal activity and an ocean in the moon’s interior. This naturally gave rise to a debate about whether or not this interior ocean could support life.
Since then, multiple studies have been conducted to get a better idea of just how likely it is that life exists inside Enceladus. The latest comes from the University of Washington’s Department of Earth and Space Sciences (ESS), which shows that concentrations of carbon dioxide, hydrogen and methane in Enceladus’ interior ocean (as well as its pH levels) are more conducive to life than previously thought.
Continue reading “Enceladus is Filled with Tasty Food for Bacteria”Stunning Image Shows How Saturn’s Tiny Moon Sculpts the Planet’s Rings
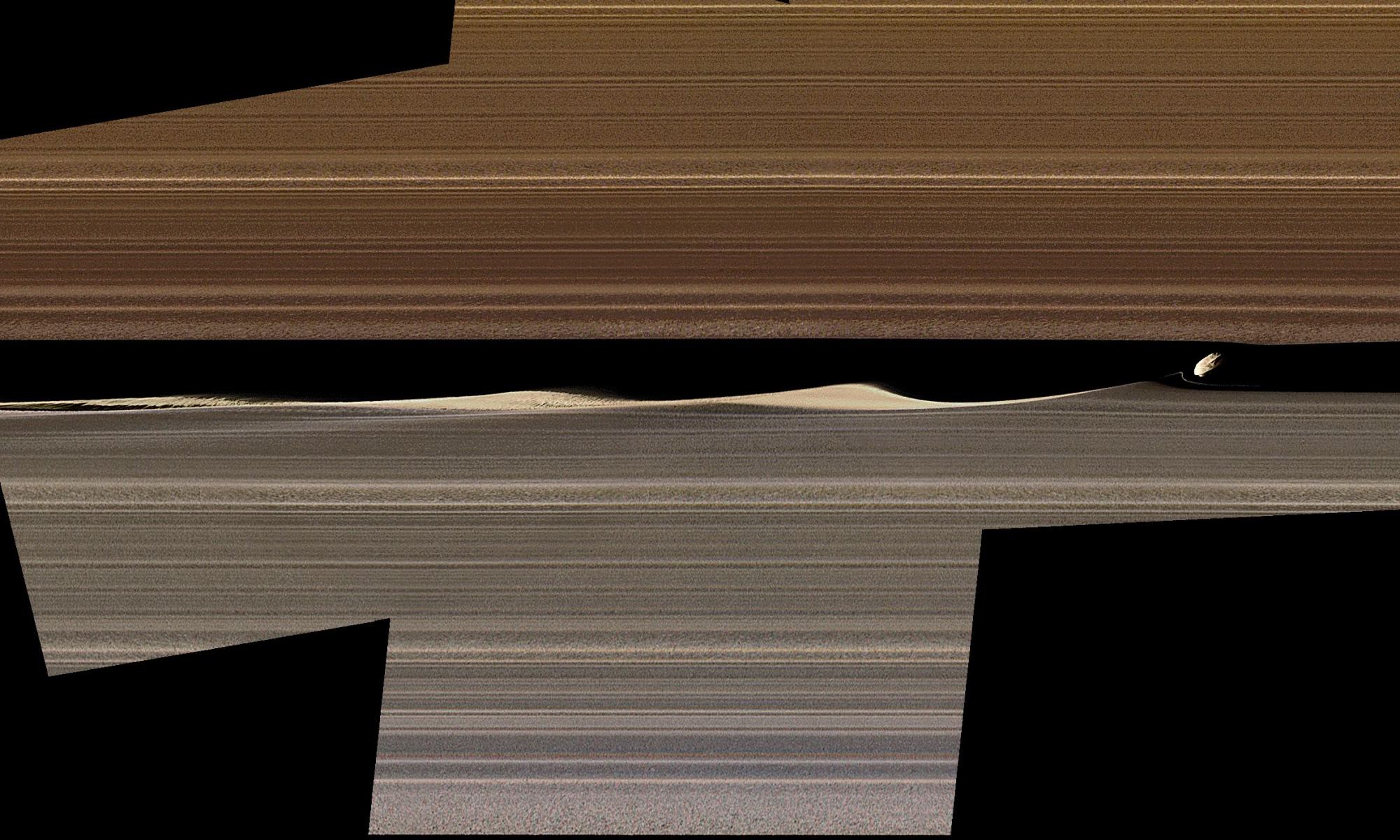
The Cassini mission to Saturn ended a year and a half ago, but scientific results are still coming from all of the data it collected. When Cassini moved in closer to Saturn in its final months, it took a very detailed look at the gas giant’s rings, travelling between them and the planet itself. That detailed inspection raised quite a few questions about all the interactions shaping those rings.
A new paper published in Science presents some of the results from Cassini’s close-up look at the rings.
Continue reading “Stunning Image Shows How Saturn’s Tiny Moon Sculpts the Planet’s Rings”Methane-Filled Lakes on Titan are “Surprisingly Deep”

The Cassini mission to Saturn and its moons wrapped up in 2017, when the spacecraft was sent plunging into the gas giant to meet its end. But there’s still a lot of data from the mission to keep scientists busy. A team of scientists working with Cassini data have made a surprising discovery: Titan’s methane-filled lakes are much deeper, and weirder, than expected.
Continue reading “Methane-Filled Lakes on Titan are “Surprisingly Deep””