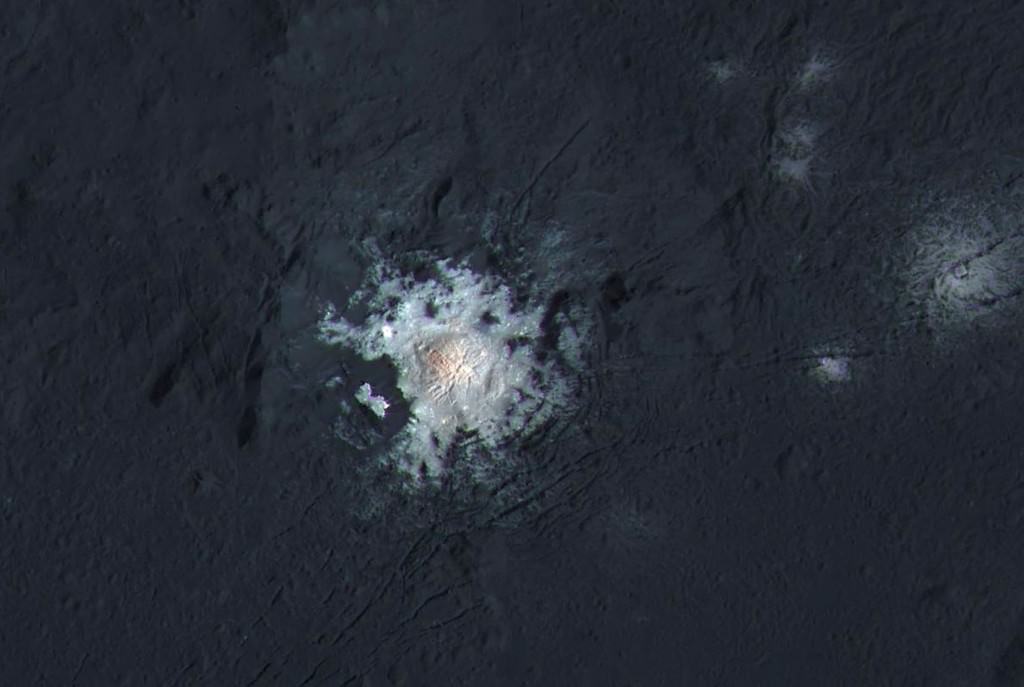
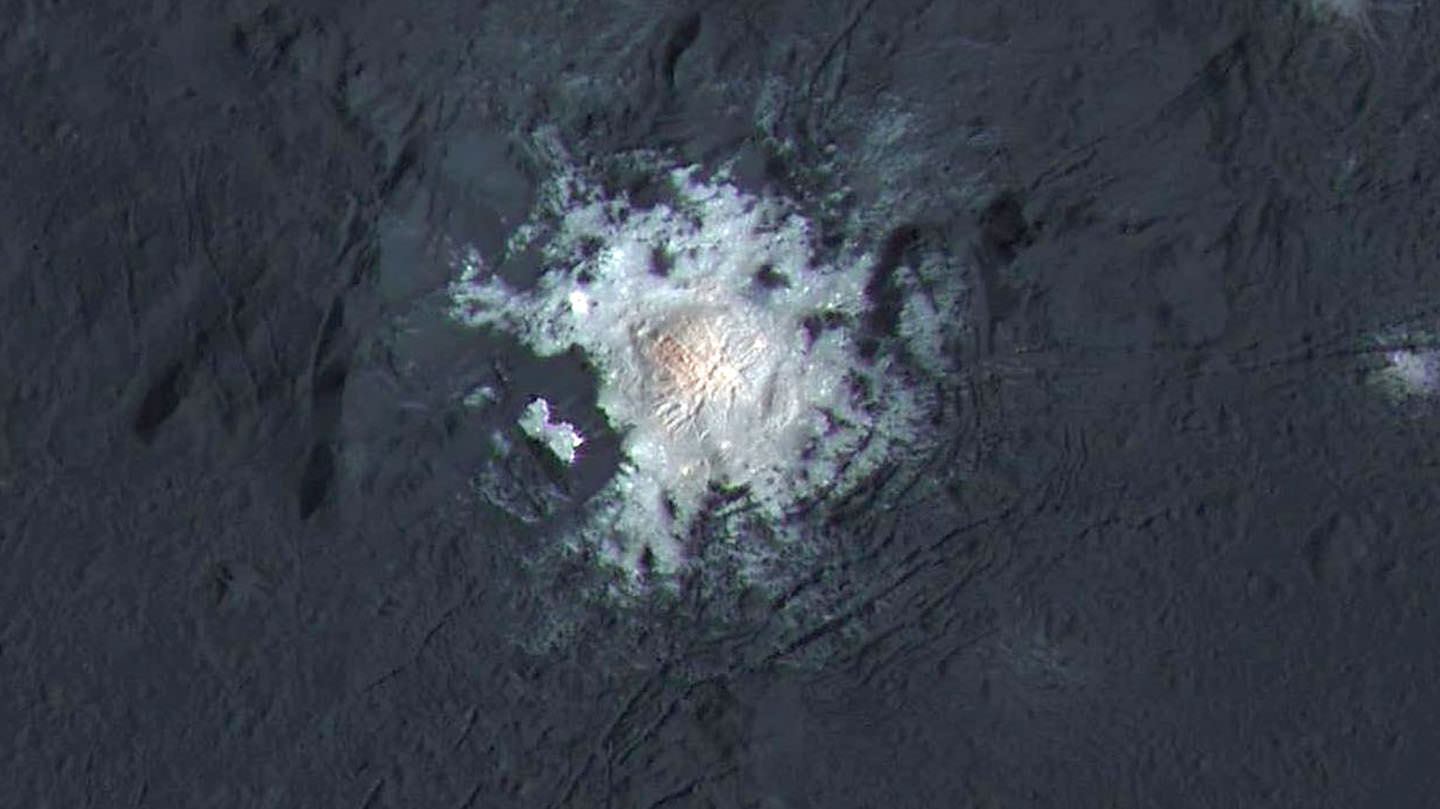
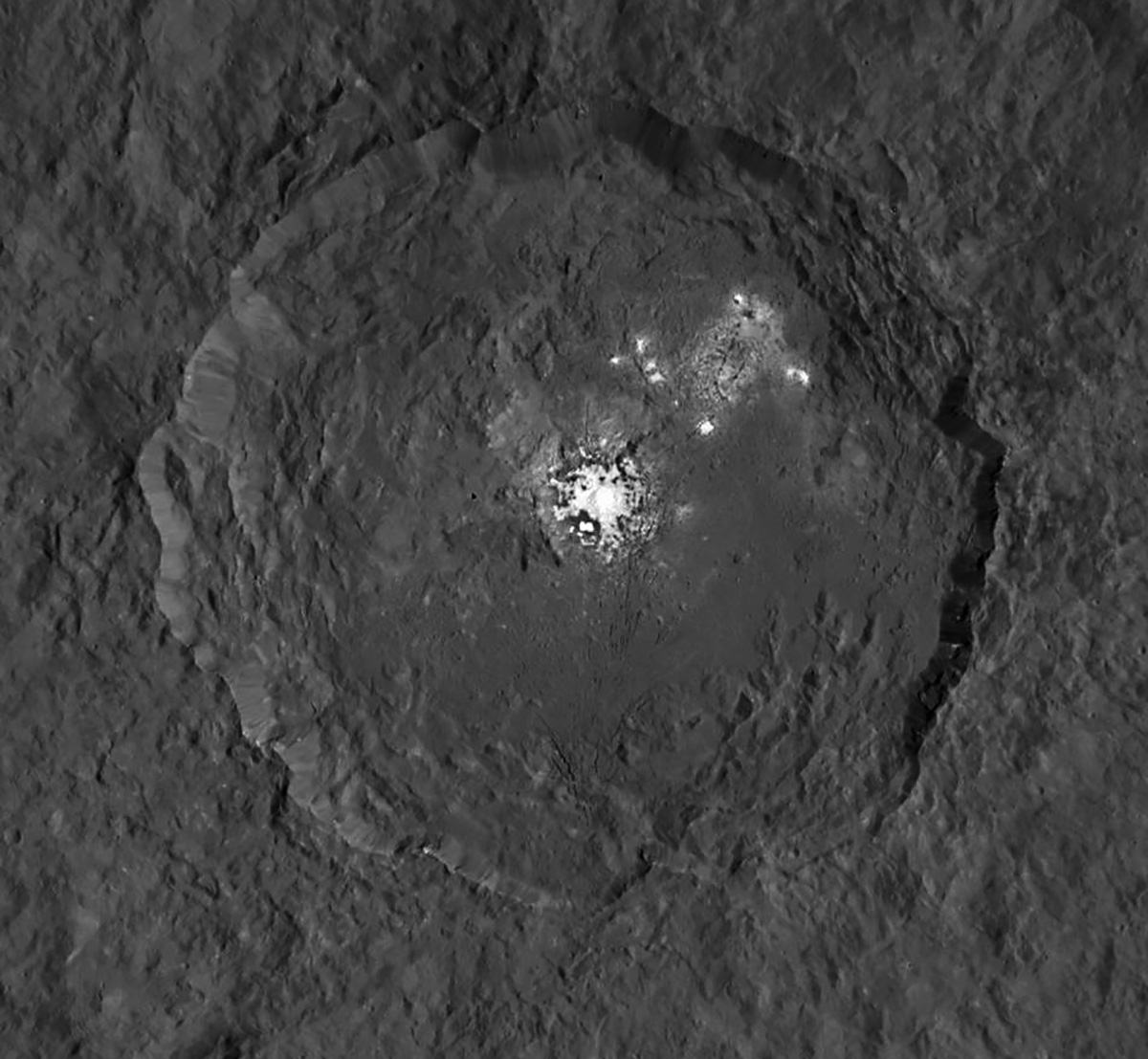
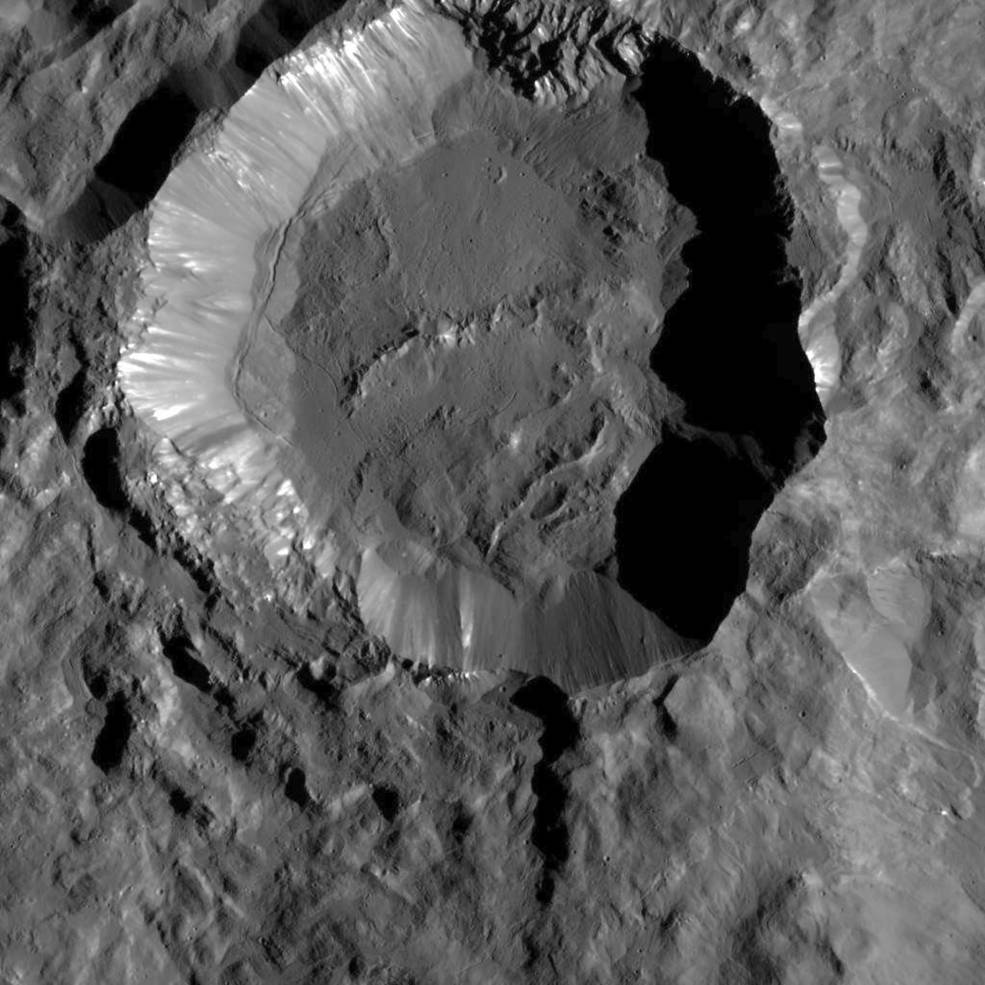
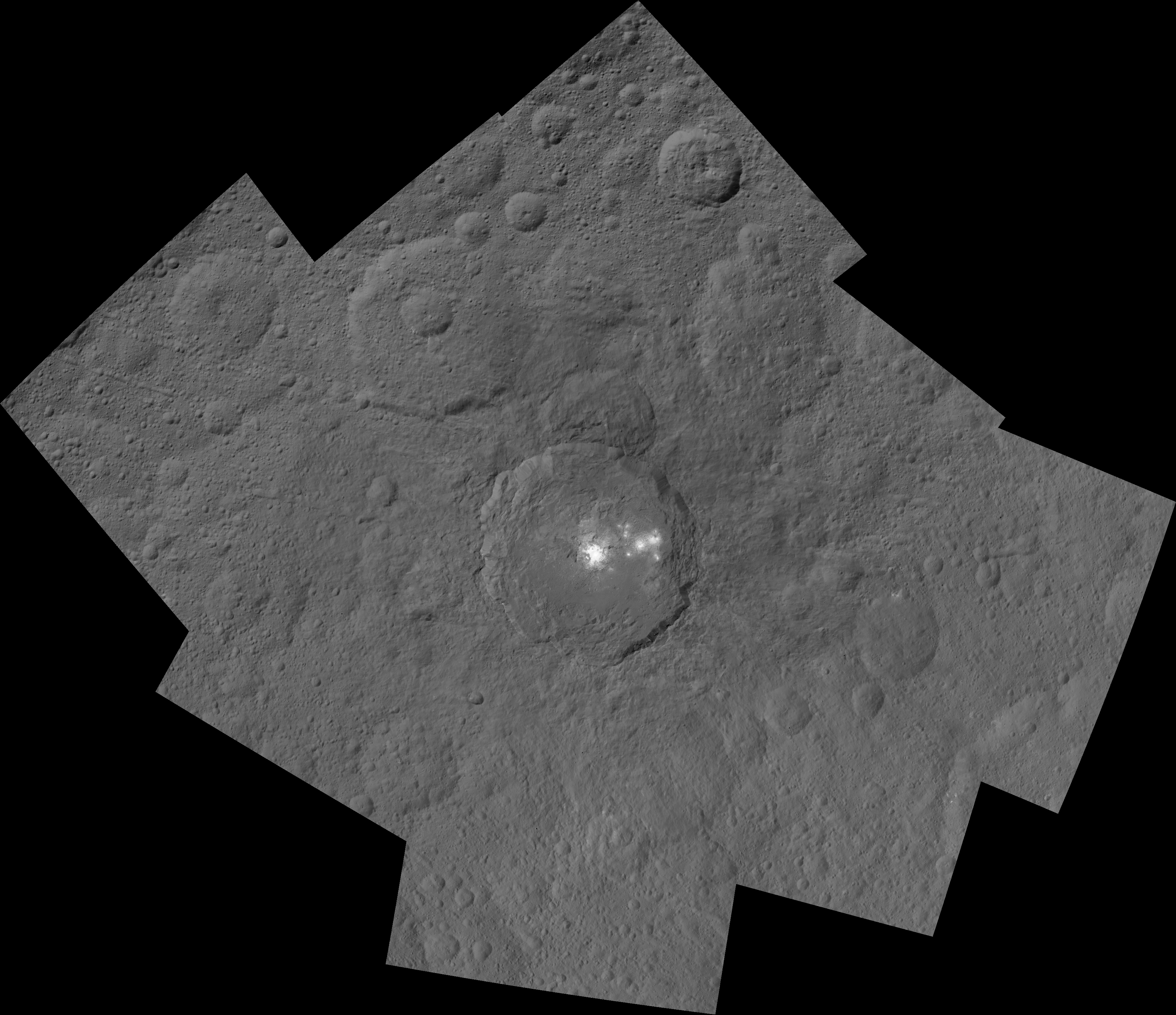
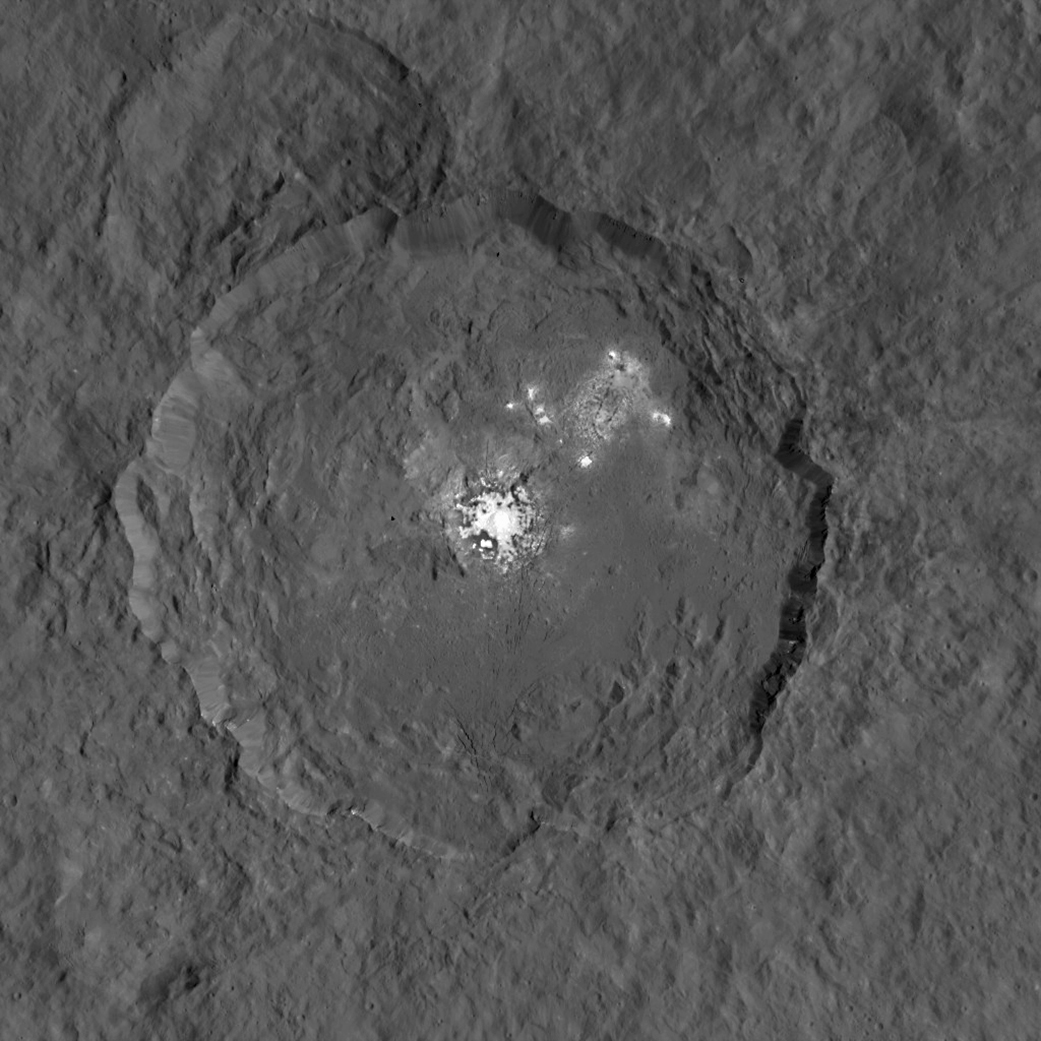
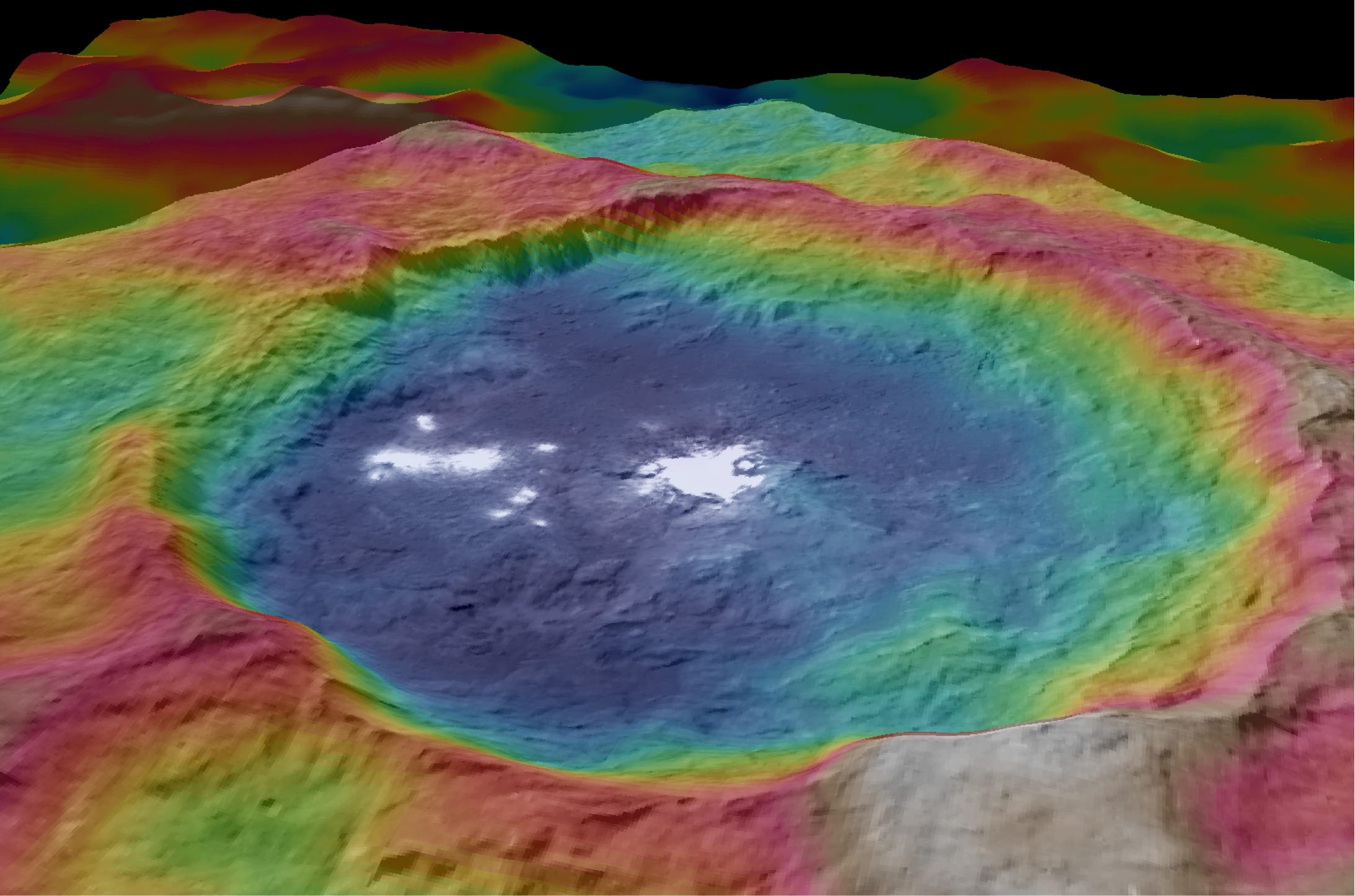
Ah, dome sweet dome. Scientists from NASA’s Dawn mission unveiled new images from the spacecraft’s lowest orbit at Ceres, including highly anticipated views of Occator Crater, at the 47th annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference in The Woodlands, Texas, on Tuesday. The new images, taken from Dawn’s low-altitude mapping orbit (LAMO) of 240 miles (385 kilometers) above Ceres, reveal a dome in a smooth-walled pit in the bright center of the crater. Linear fractures crisscross the top and flanks of the dome with still more fractures slicing across the nearby plains.

“Before Dawn began its intensive observations of Ceres last year, Occator Crater looked to be one large bright area. Now, with the latest close views, we can see complex features that provide new mysteries to investigate,” said Ralf Jaumann, planetary scientist and Dawn co-investigator at the German Aerospace Center (DLR) in Berlin. “The intricate geometry of the crater interior suggests geologic activity in the recent past, but we will need to complete detailed geologic mapping of the crater in order to test hypotheses for its formation.”
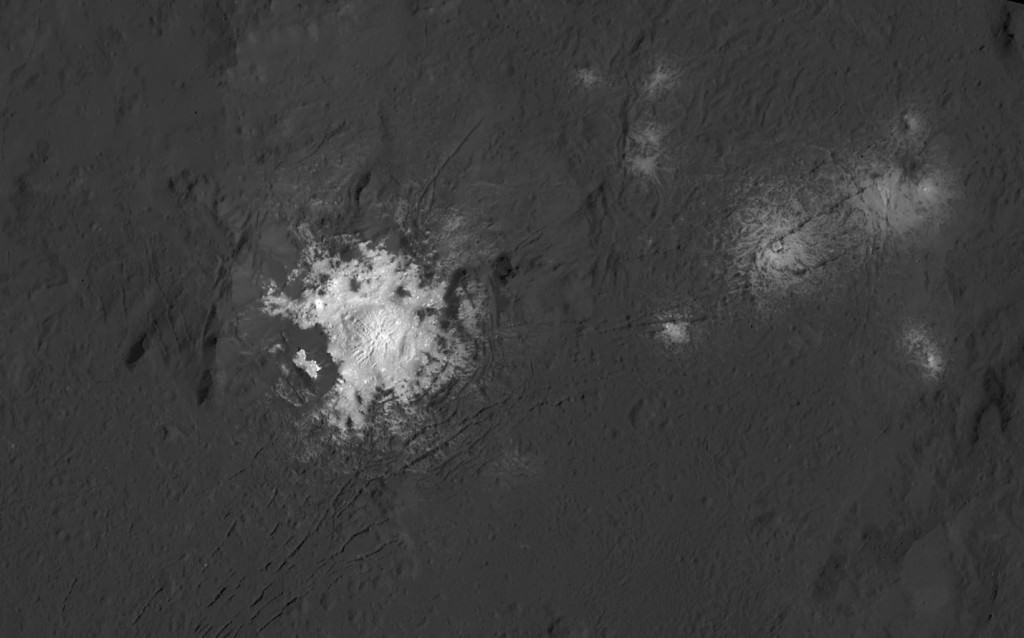

Like me, you’ve probably been anticipating LAMO for months, when we’d finally get our clearest view of the famous “bright spots”. Spectral observations have shown that the patches are consistent with a magnesium sulfate called hexahydrite that resembles the more familiar Epsom salts here on Earth. Scientists think these salt-rich areas were residue left behind when water-ice sublimated in the past. Impacts from asteroids could have broken into Ceres’ crust and possibly unearthed salt-rich ices. Exposed to the vacuum of space, the ice would have sublimated (vaporized), leaving the salt behind.
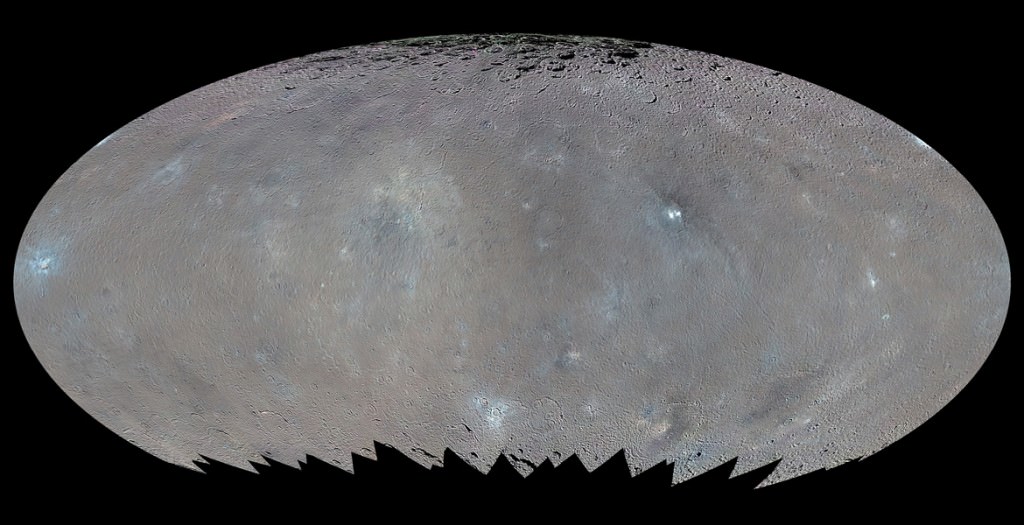

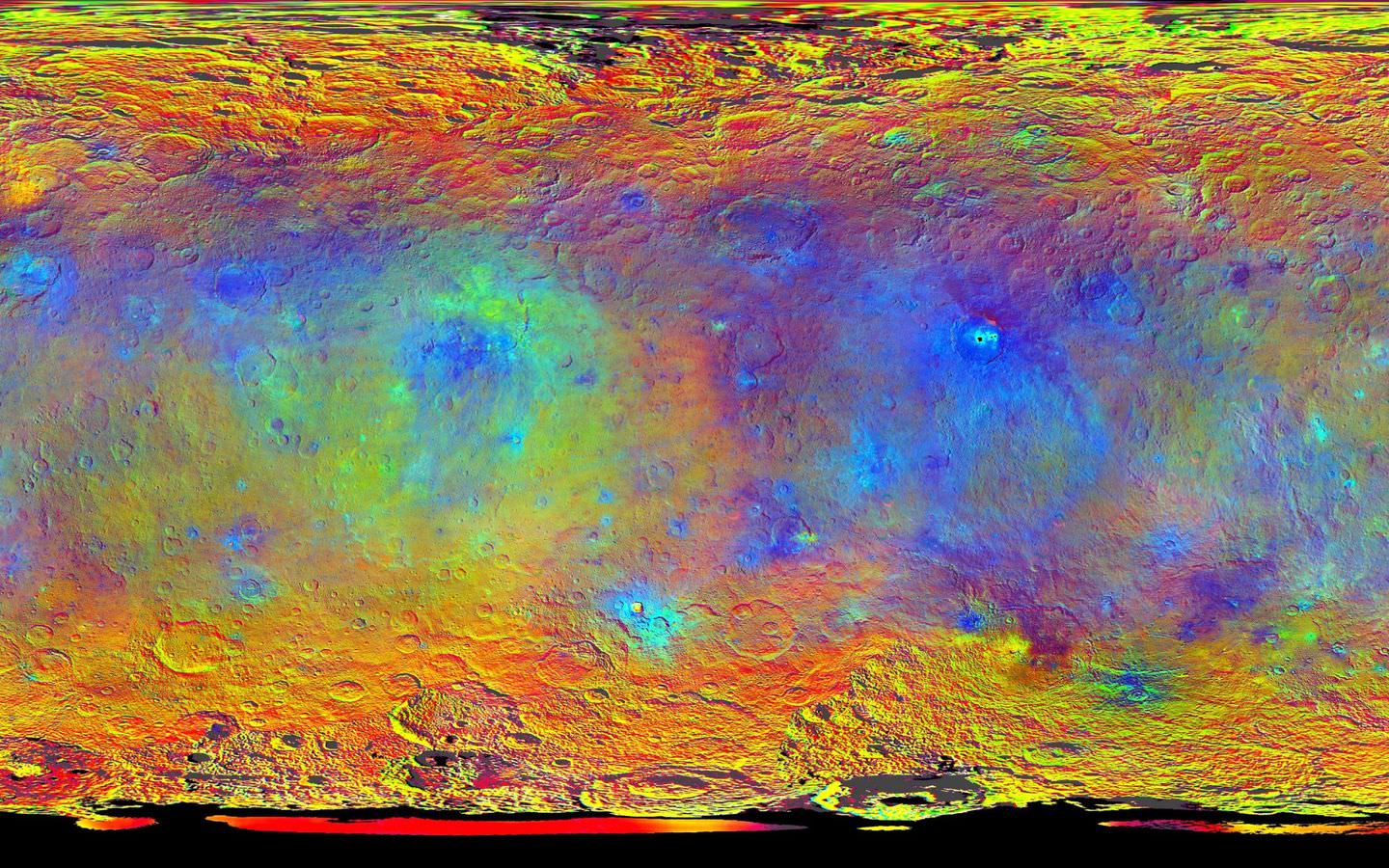
The team also released an enhanced color map of the surface of Ceres that reveals a diversity of surface materials and how they relate to Ceres’ landforms. The dwarf planet doesn’t have as many large impact basins as scientists expected, but the number of smaller craters generally matches their predictions. The blue material highlighted in the color map is related to flows, smooth plains and mountains, which appear to be very young surface features.
“Although impact processes dominate the surface geology on Ceres, we have identified specific color variations on the surface indicating material alterations that are due to a complex interaction of the impact process and the subsurface composition,” Jaumann said. “Additionally, this gives evidence for a subsurface layer enriched in ice and volatiles.”
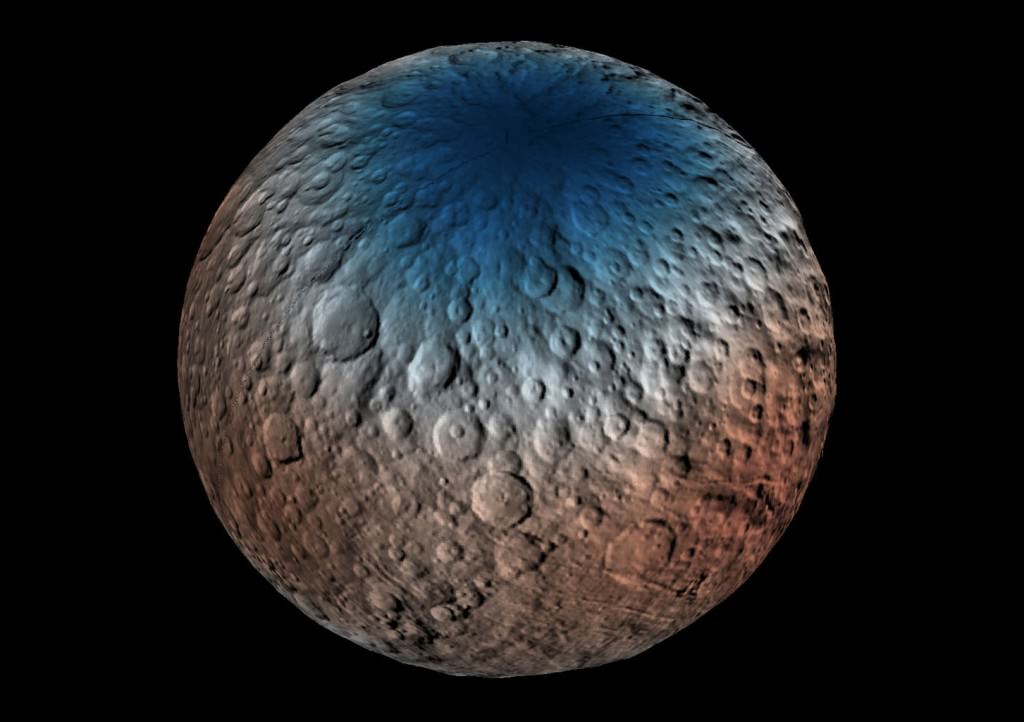

This map shows part of Ceres’ northern hemisphere with neutron counting data from Dawn’s gamma ray and neutron detector (GRaND) instrument and reflect the concentration of hydrogen in the upper yard (or meter) of regolith, the loose surface material on Ceres. Colors are based on the number of neutrons detected per second by GRaND. Counts decrease with increasing hydrogen concentration. The color scale of the map is from blue (lowest neutron count) to red (highest neutron count). Lower neutron counts near the pole suggest the presence of water ice within about a yard (meter) of the surface at high latitudes. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA/PSI
We’re learning more about that subsurface ice thanks to Dawn’s Gamma Ray and Neutron Detector (GRaND). Neutrons and gamma rays produced by cosmic rays interacting with the topmost yard (meter) of the loose rock and dust called regolith provide a fingerprint of Ceres’ chemical makeup. Lower counts indicate the presence of hydrogen, and since water’s rich in hydrogen (H2o), the results from GRanD suggest concentrations of water ice in the near-surface at high latitudes.
“Our analyses will test a longstanding prediction that water ice can survive just beneath Ceres’ cold, high-latitude surface for billions of years,” said Tom Prettyman, the lead for GRaND and Dawn co-investigator at the Planetary Science Institute, Tucson, Arizona.
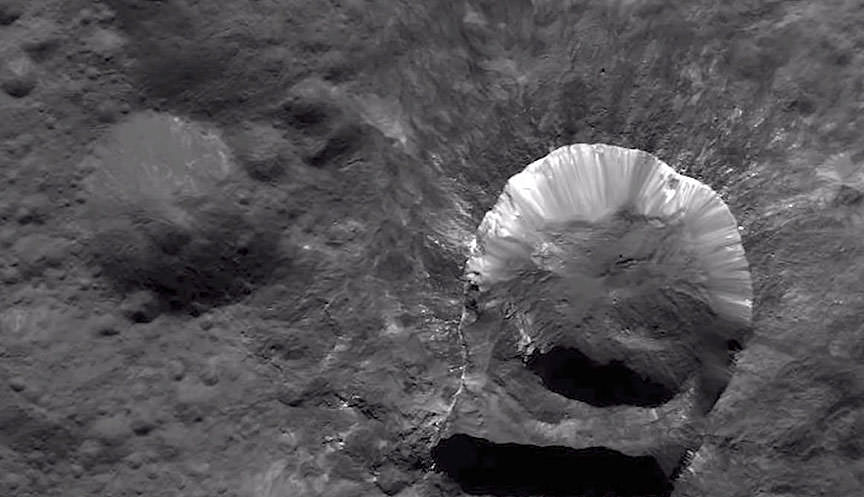

Dawn scientists also reported that the Visual and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIR) has detected water at Oxo Crater, a young, 6-mile-wide (9-kilometer-wide) feature in Ceres’ northern hemisphere. This water could either be bound up in minerals or exist as ice and may have been exposed during a landslide or impact or a combination of the two events. Oxo is the only place on Ceres where water has been detected at the surface so far.
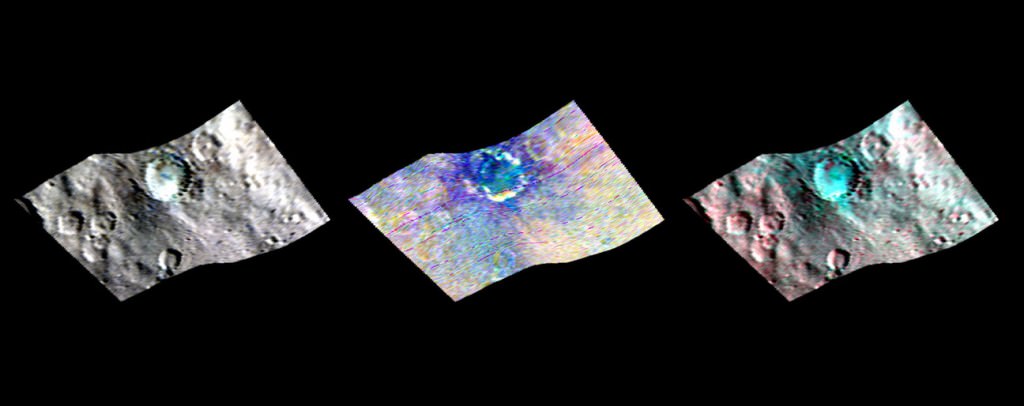
Not only have scientists found evidence of possible extensive subsurface ice, but the composition of the surface is variable. Using VIR, which measures mineral composition by how those minerals reflect sunlight, they found that Haulani Crater shows a different proportion of surface materials than its surroundings. While the surface of Ceres is mostly made of a mixture of materials containing carbonates and phyllosilicates (clays), their relative proportion varies across the surface.
“False-color images of Haulani show that material excavated by an impact is different than the general surface composition of Ceres. The diversity of materials implies either that there is a mixed layer underneath, or that the impact itself changed the properties of the materials,” said Maria Cristina de Sanctis, the VIR instrument lead scientist.
All these cool stuff we’re finding out about this small body makes it nearly as exciting as Pluto. Taking a closer look is the best form of education.