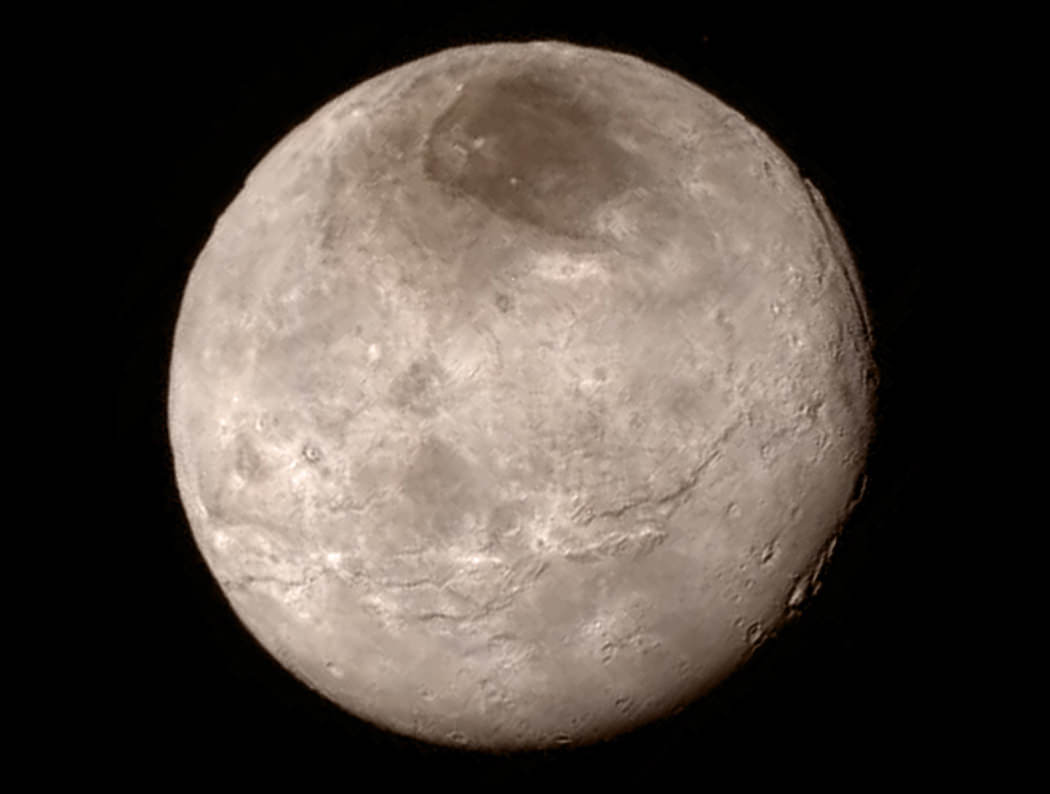
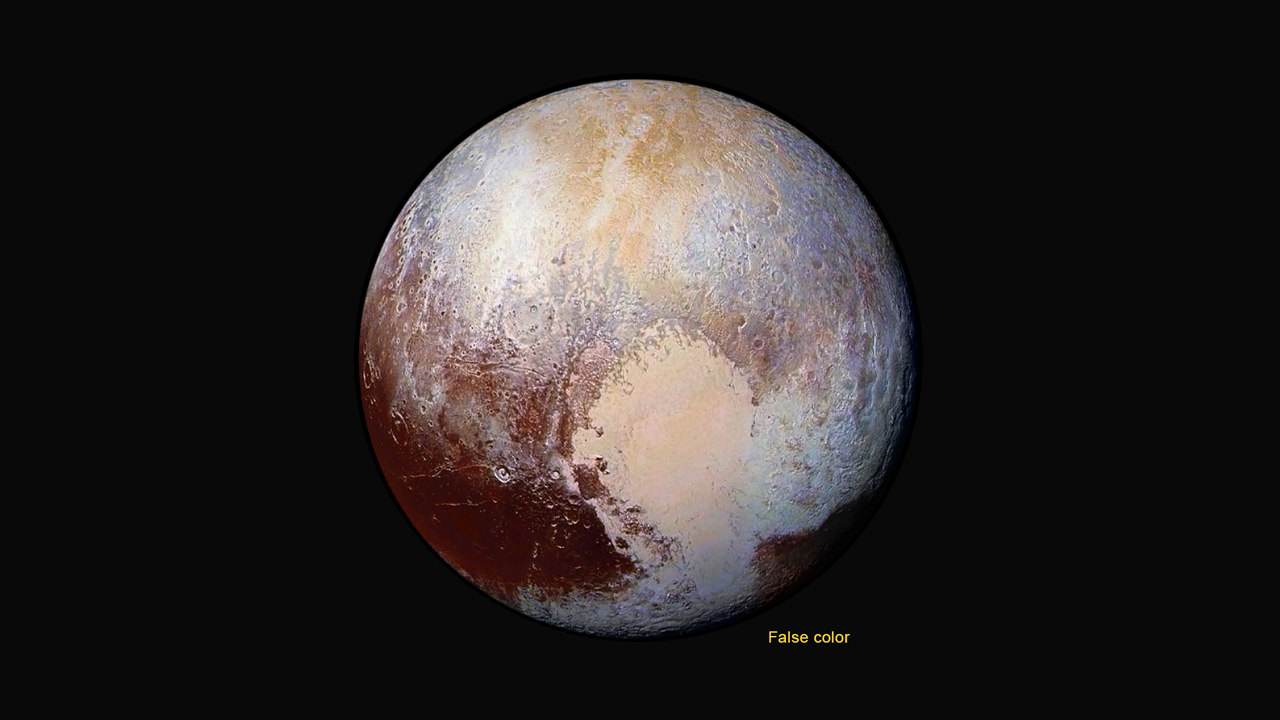
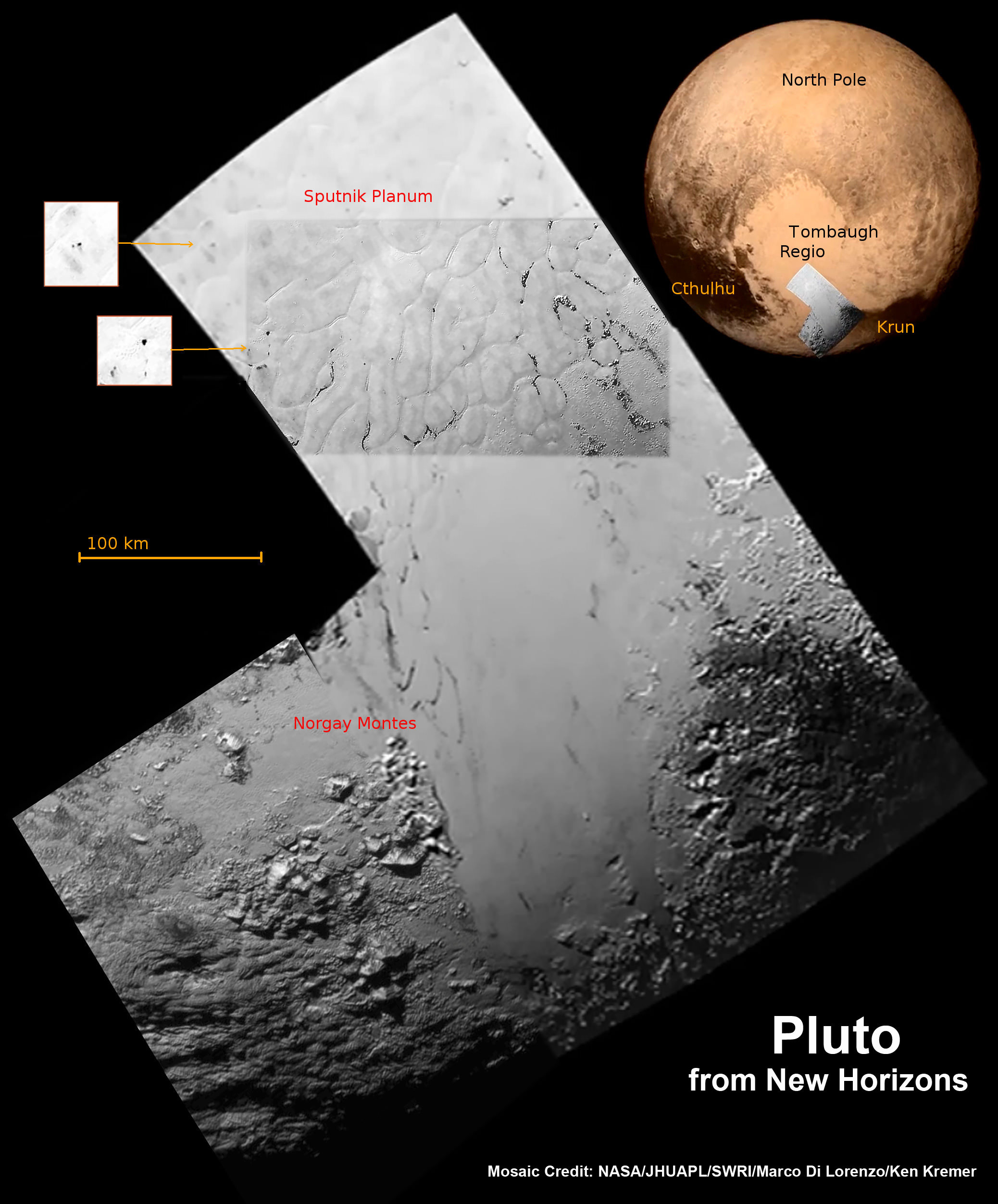
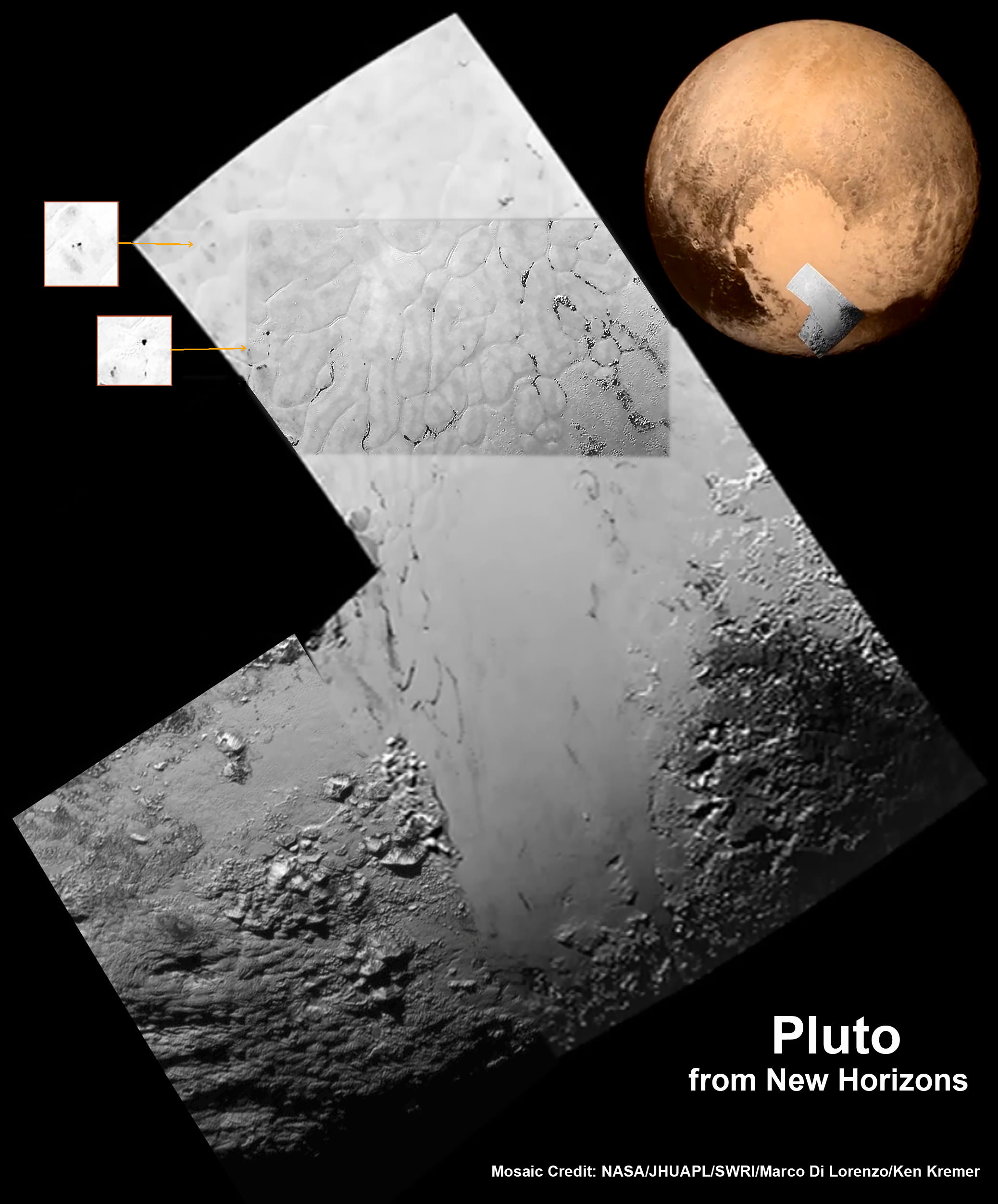
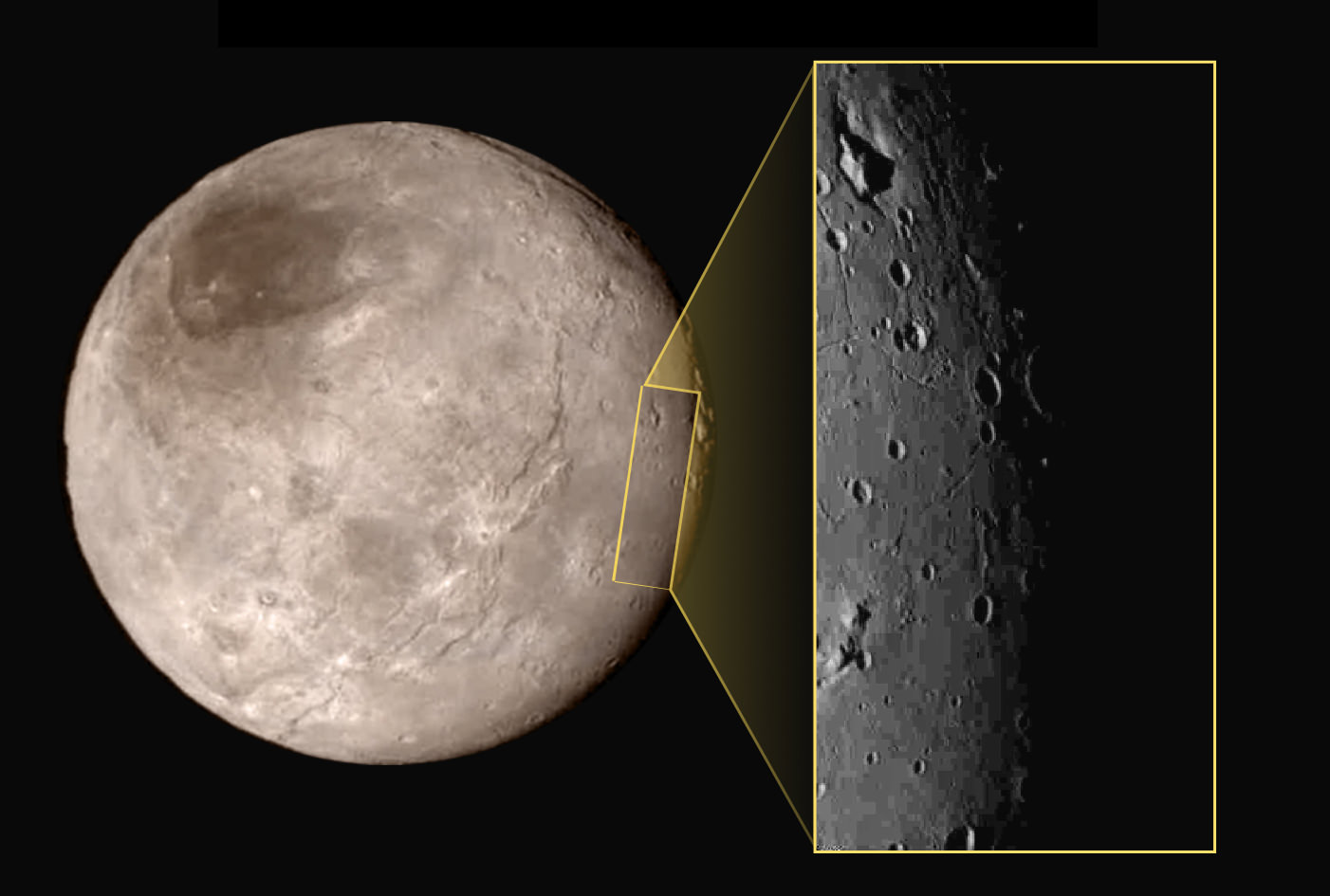
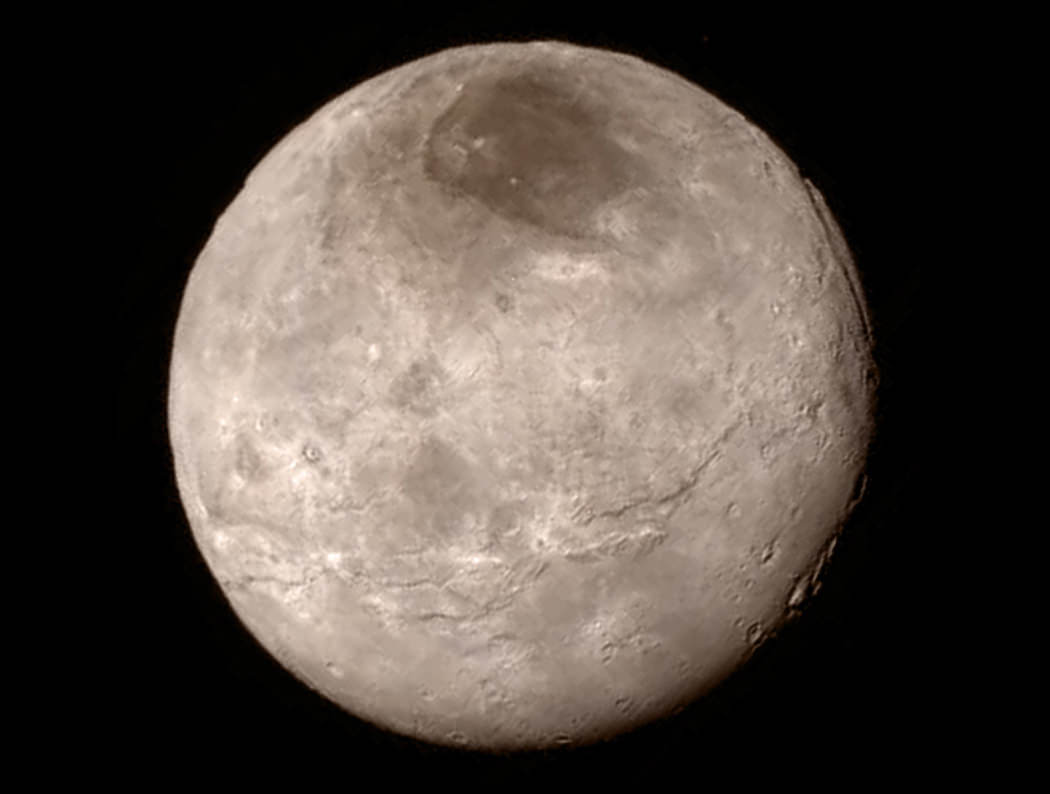
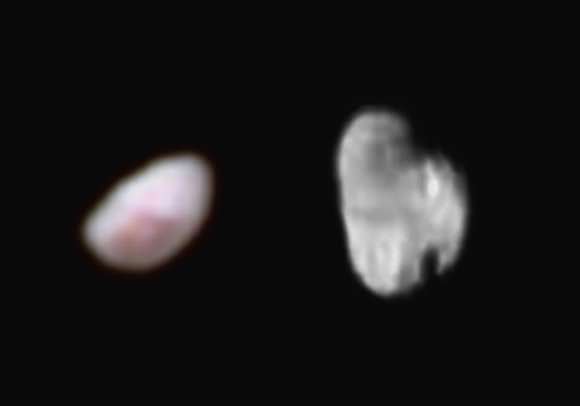
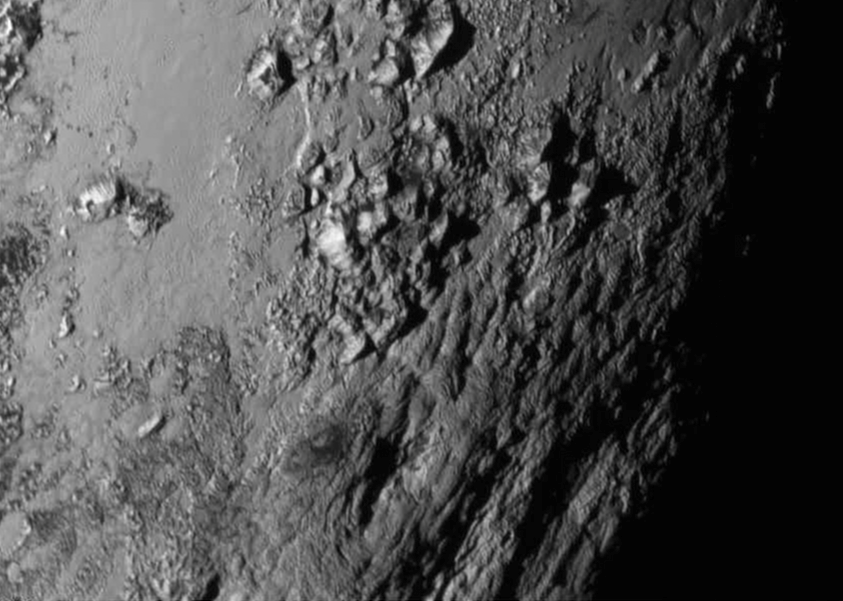
As we await new imagery and data from the New Horizons’ flyby of the Pluto system to be transmitted to Earth, one piece of the Pluto-Charon puzzle that scientists are looking forward learning more about is the mysterious “dark pole” on Charon. Images sent immediately after the flyby reveal Charon’s north polar region is much darker than the lighter-colored material surrounding it, and it actually has a reddish cast to it.
The New Horizons team says the red pole appears to be a thin deposit of dark material over a distinct, sharply bounded, angular feature – perhaps and impact basin – and scientists hope to learn more by studying higher-resolution images that are currently being beamed back to Earth from the spacecraft.
Carly Howett, a senior research scientist at the Southwest Research Institute, is one of the scientists studying the mystery of what is causing this color difference and why it shows up at Charon’s north pole.
“Looking at Charon, it’s very clear that the northern polar region is much redder than the rest of the moon,” said Howett in a post on the New Horizons website. “Surfaces vary in color when something about them changes.”
So what is this red material? The leading theory right now is that material from Pluto’s atmosphere is falling to Charon and being ensnared in the polar region by what is known as “cold-trapping.”
It’s is so cold at Charon’s poles – temperatures there vary are just a tad warmer than absolute zero, between -433 and -351 °F (-258 and -213 °C) – that any gases settling there would freeze solid instead of escaping. And with the combination of extremely cold temperatures and solar radiation, the material is transformed to a new substance, and is being trapped on the pole. Howett said it likely won’t disappear with any seasonal changes on Charon.
“We know Pluto’s atmosphere is mainly nitrogen, with some methane and carbon monoxide,” she said, “so we expect that these same constituents are slowly coating Charon’s winter pole. The frozen ices would sublimate away again as soon as Charon’s winter pole emerges back into sunlight, except for one important detail: solar radiation modifies these ices to produce a new substance, which has a higher sublimation temperature and can’t sublimate and then escape from Charon.”
What is the new substance? Scientists can’t say for sure yet, but it might be a tholin.

What is a tholin? Tholins were first created in a laboratory by in the 1970s by Carl Sagan and his team at Cornell. According to planetary scientist Sarah Hörst, who wrote about tholins on The Planetary Society website, Sagan and his team would take mixtures of cosmically relevant gases and irradiate them with various energy sources. The result was “a brown, sometimes sticky, residue,” as Sagan described them in a paper he wrote in 1979.
Hörst said Sagan and team “were searching for answers to questions ranging from ‘why is the Great Red Spot red’ to ‘how did life on Earth originate’ and in the process produced material for which there was no name.”
They came up with the name “tholin,” and theorized that tholins could be a constituent of the Earth’s primitive oceans and therefore as relevant to the origin of life.
In the article Hörst wrote, “I have been studying tholin for almost a decade and in my experience the most frequently used synonyms for tholin are “gunk”, “brown gunk”, and “complex organic gunk”. Tholin is also often described as a “tar-like” substance. Words like tar, kerogen, bitumen, petroleum, asphalt, etc. all describe substances that are potentially similar to tholin in some ways. However, these materials all result from life; they are’biotic.’”

Finding out more about what is going on at Charon’s north pole is indeed intriguing. Tholins might be the same material that give Pluto its reddish-brown hue in some regions, too.
Howett told Universe Today that the main instrument on New Horizons that will really pin down the compositional information is LEISA (Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array).
“This instrument observes 250 wavelengths between 1.25-2.5 microns, making it ideal for detecting the spectral signature of solid features,” she said via email. “We don’t know exactly the composition of the tholin on Charon (many different types are possible) but with LEISA we can look for differences in the spectra between the Charon’s anomalous red region and those surrounding it – to give us some hints of the change in surface composition and the “raw ingredients” for the tholin.”
For example, Howett said, maybe they’ll see more hydrogen cyanide (HCN) around the north pole region, which would open up a lot of complex chemistry options.
“We will start getting this data down in the next few weeks, so hopefully we’ll have some answers soon!” she said.
Further reading: New Horizons website, The Planetary Society