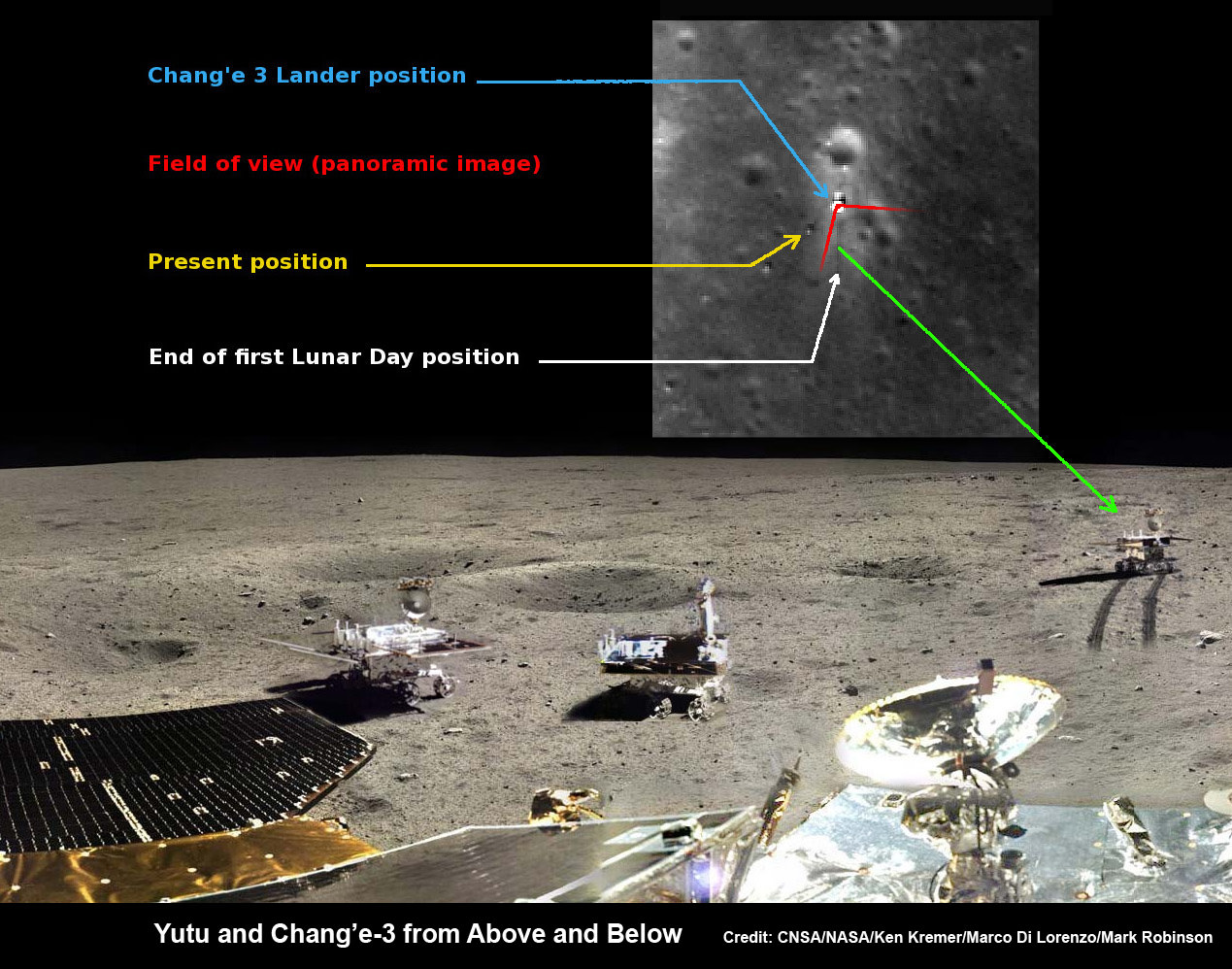
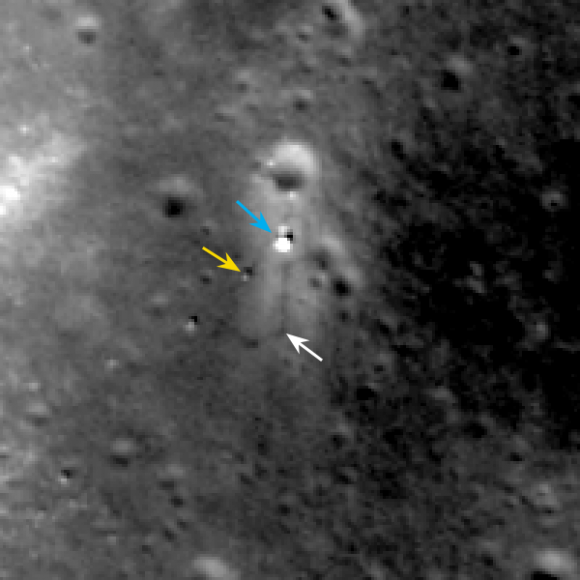
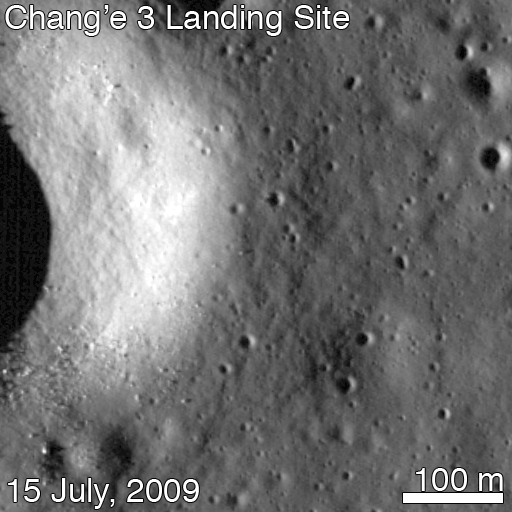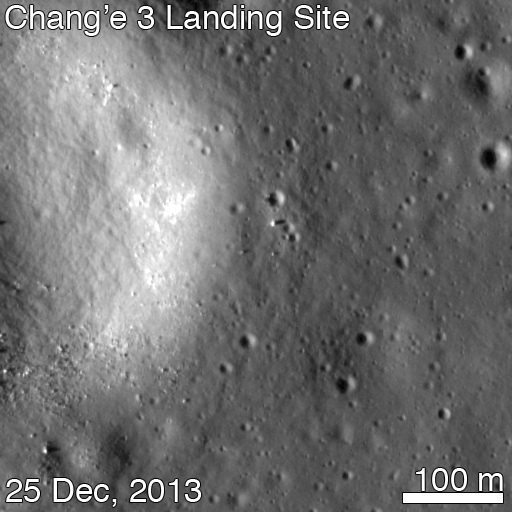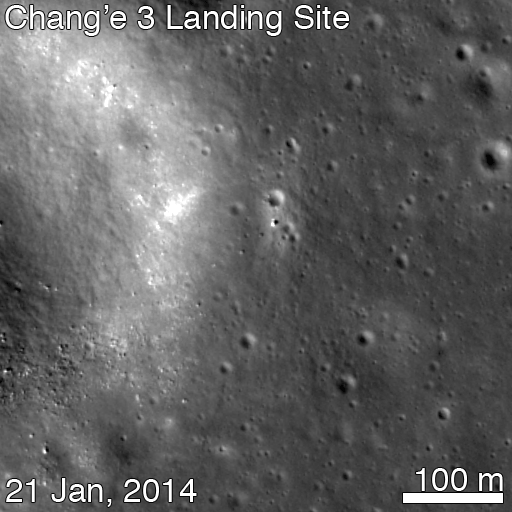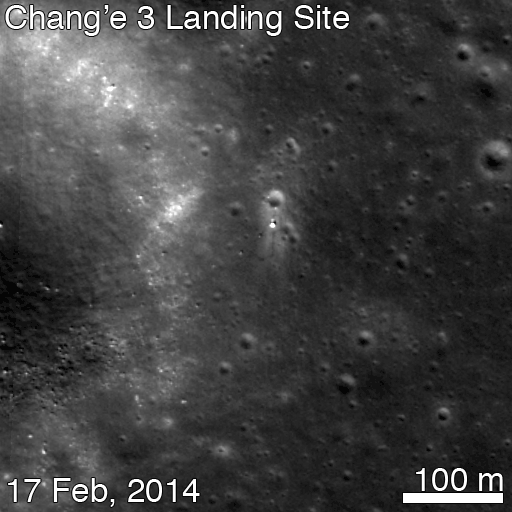
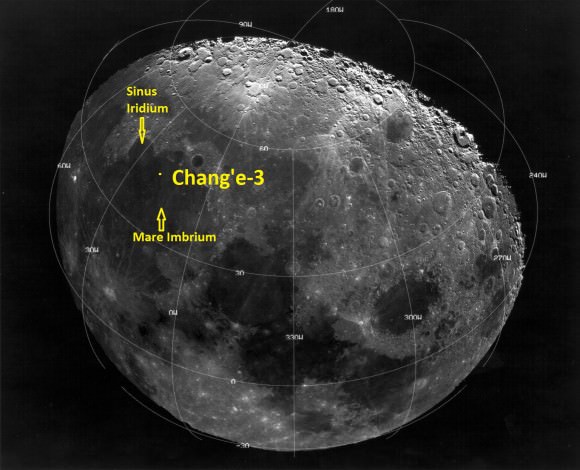
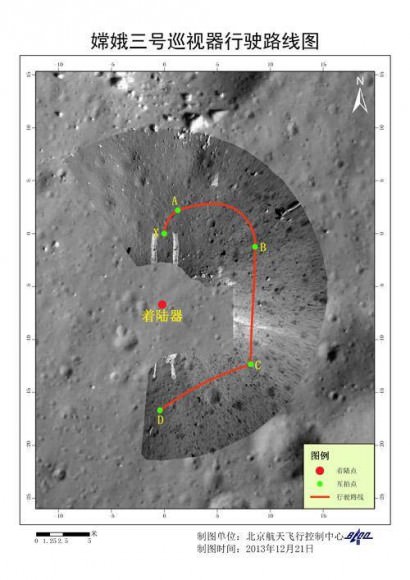
For many space-faring nations, ambitions for Mars run broad and deep. Now, add China to the list of countries with Mars in their sights. News reports from China disclosed that country is considering a future Mars rover mission, with a potential 2020 launch date. Additionally came other hints that China may be looking to develop a next-generation heavy-lift launch system.
This new project, while early in development, reveals how Chinese aspirations are growing rapidly. Human space flight successes have been followed by recent lunar mission successes of the Yutu lunar rover and the Chang’e-5 T1 test of a sample return mission. The Chinese Mars missions could influence future plans of ESA, India and NASA or more simply raise the urgency to execute missions in concept or early development without hesitation.

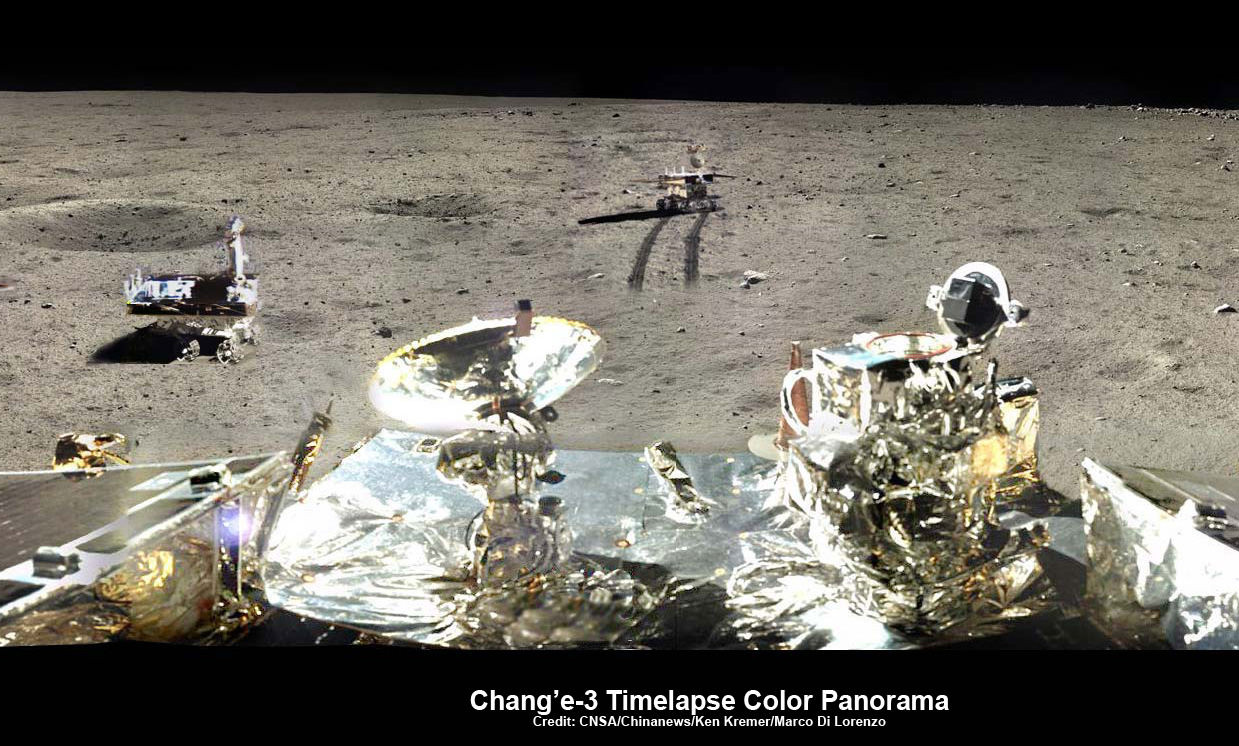
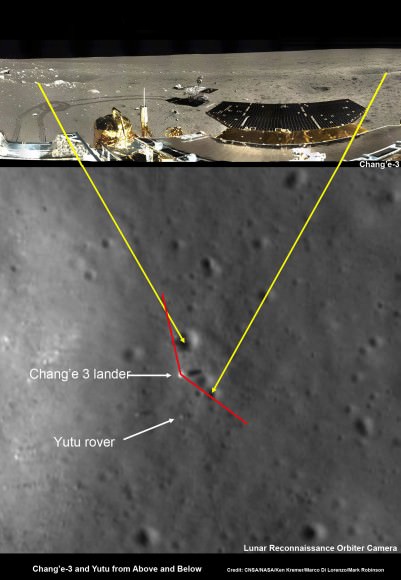
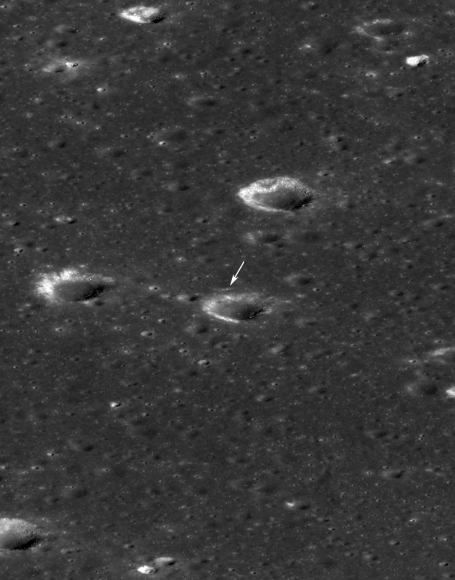
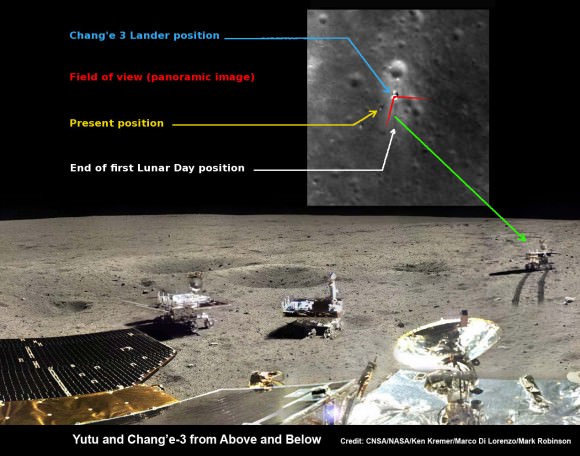
The Mars rover mock-up display was presented at the aerospace show by China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC). The design appears similar to the Yutu rover which landed successfully on the Moon late in 2013. While Yutu’s mobility system failed prematurely, many mission milestones were achieved.
The Mars rover design is significantly larger than Yutu but includes changes that can be attributed to the challenges of roving Mars at tens of millions of kilometers distance and under more gravitational force. The wheels are beefed up, since it must withstand more force and rugged martian terrain (gravity on Mars is 37% of the Earth’s in strength but 2.25 times the strength of gravity on the Moon’s surface.) The the solar panels are larger due to 1.) less sunlight at Mars – 35% to 50% of Earth’s, and 2.) more electrically demanding instruments.
The goals of the Chinese Mars rover will be to search for life and water. The NASA missions searching for indicators of habitable environments and for water has cost billions of dollars but the Chinese space program is operating on a fraction of what NASA’s annual budget is. Whereas the Chinese Mars program will be competing with the lunar program for government funds, it remains to be seen how quickly they can make progress and actually meet milestones for a 2020 launch date.
Besides video of the China View reporter presenting and discussing the Mars rover (link to photo above), the video also includes a simulation of the Chinese lunar sample return spacecraft, which is underdevelopment and was tested early this month during a the Chang’e-5 T1 circum-lunar mission that proved a small re-entry vehicle.

The actual dimensions of this rover were not reported but an estimate of the size can be determined by the size of the high-gain directional antenna. Assuming it is an X-Band dish, like the one on the MER Rovers and Curiosity, then this Sino-rover would be near the same size as the MER rovers – Spirit and Opportunity. The Sino-rover shares a six wheel design like MER and MSL rovers.
Other reports from the China Daily indicated that industry leaders in China are urging China’s space agency to develop a more powerful heavy-lift launch system. It could be used for the nation’s human spaceflight goals to send a space station in to orbit, as well as send missions to Mars and beyond.
“It is a must for us to develop a more powerful heavy-lift rocket if we want to reach and explore deep space,” Zhang Zhi, a senior rocket researcher at the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology the aerospace exhibition.
Plans also call for an orbiter to likely function as a communication relay as MGS, Mars Odyssey and MRO have done for the American rovers. Whether this would involve a single spacecraft such as the NASA Vikings or dual crafts such as the present American rovers with supporting orbiters is unknown. Given the successful landing of the Yutu rover encapsuled in a soft-lander, one might expect the same for the Chinese Mars rover rather than an airbag landing used by MER. Either way, they will be challenged by the seven minutes of terror just like the American rovers. They will have to solve for themselves the entry, descent and landing of a rover. Only American-made rovers have successfully landed on Mars; all Russian attempts have ended in failure.

The presentation also stated future plans for a sample-return mission by 2030. If the first Chineses Mars rover lands successfully in 2020, it will join up to four active rovers on the surface. Curiosity, ExoMars (ESA/NASA), Mars Rover 2020 and MER Opportunity. Six years seems like a long time but MER’s Oppy is a proven trooper having lasted over ten years. Curiosity, barring the unexpected, might last beyond 2020. ExoMars and NASA’s 2020 rover are still in development phases. Using ExoMars or 2020, NASA has plans to recover collected samples from rovers and return them to Earth in the 2020s and possibly as soon as 2022.
References:
China unveils first Mars rover and exploration system for red planet
China Daily