China has a fabulously rich history when it comes to space travel and was among the first to experiment in rocket technology. The invention of the rocket is often attributed to the Sung Dynasty (AD 960-1279.) Since then, China has been keen to develop and build its own space industry. The Chinese National Space Administration has already successfully landed probes on the Moon but is preparing for their first human landers. Chinese astronauts are sometimes known as taikonauts and CNSA has just confirmed their fourth batch of taikonauts are set for a lunar landing.
Continue reading “China Trains Next Batch of Taikonauts”China is Going Back to the Moon Again With Chang'e-6
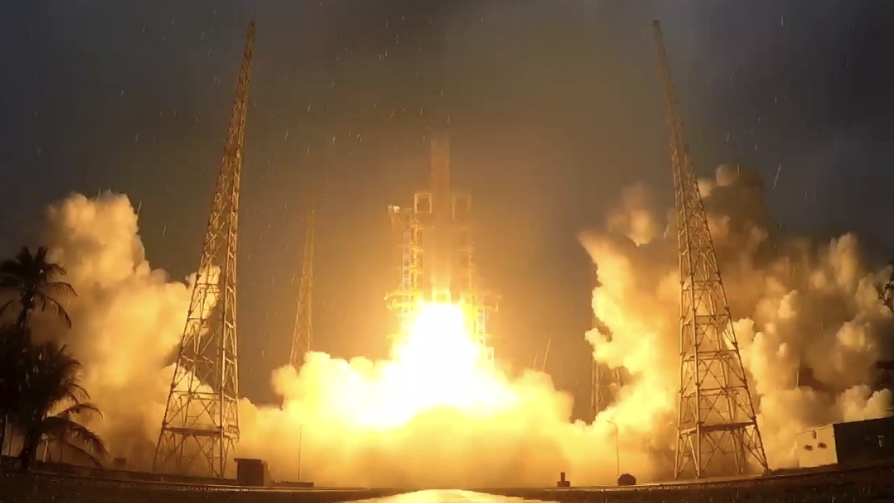
On Friday, May 3rd, the sixth mission in the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program (Chang’e-6) launched from the Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site in southern China. Shortly after, China announced that the spacecraft separated successfully from its Long March 5 Y8 rocket. The mission, consisting of an orbiter and lander element, is now on its way to the Moon and will arrive there in a few weeks. By June, the lander element will touch down on the far side of the Moon, where it will gather about 2 kg (4.4 lbs) of rock and soil samples for return to Earth.
Continue reading “China is Going Back to the Moon Again With Chang'e-6”China's Relay Satellite is in Lunar Orbit
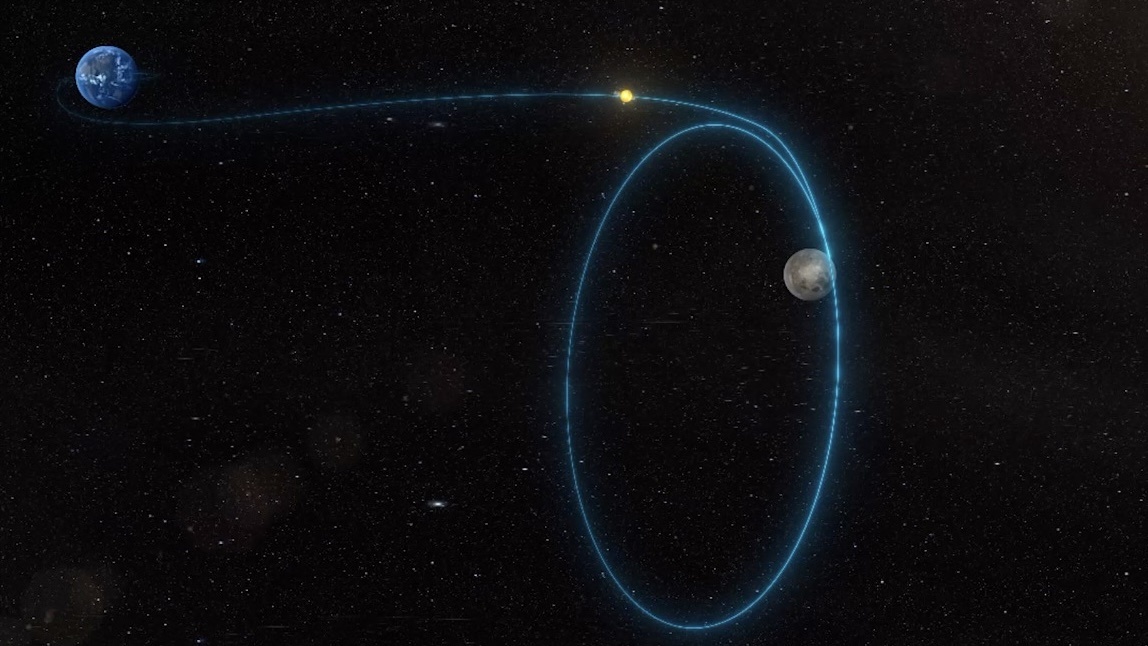
On March 20th, China’s Queqiao-2 (“Magpie Bridge-2”) satellite launched from the Wenchang Space Launch Site LC-2 on the island of Hainan (in southern China) atop a Long March-8 Y3 carrier rocket. This mission is the second in a series of communications relay and radio astronomy satellites designed to support the fourth phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program (Chang’e). On March 24th, after 119 hours in transit, the satellite reached the Moon and began a perilune braking maneuver at a distance of 440 km (~270 mi) from the lunar surface.
The maneuver lasted 19 minutes, after which the satellite entered lunar orbit, where it will soon relay communications from missions on the far side of the Moon around the South Pole region. This includes the Chang’e-4 lander and rover and will extend to the Chang’e-6 sample-return mission, which is scheduled to launch in May. It will also assist Chang’e-7 and -8 (scheduled for 2026 and 2028, respectively), consisting of an orbiter, rover, and lander mission, and a platform that will test technologies necessary for the construction of the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS).
Continue reading “China's Relay Satellite is in Lunar Orbit”Chinese Astronauts May Build a Base Inside a Lunar Lava Tube
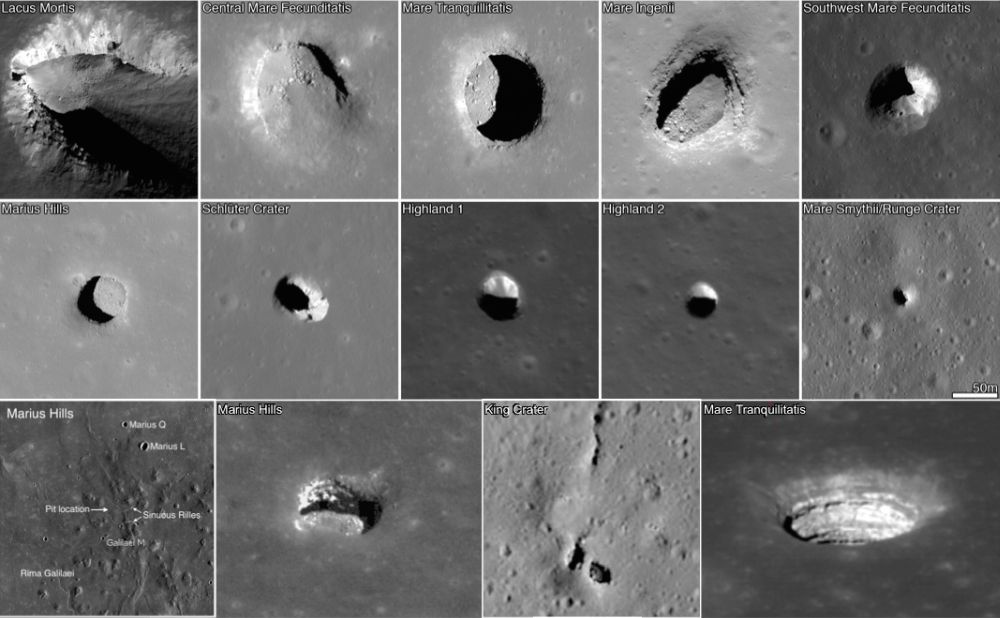
Caves were some of humanity’s first shelters. Who knows what our distant ancestors were thinking as they sought refuge there, huddling and cooking meat over a fire, maybe drawing animals on the walls. Caves protected our ancient ancestors from the elements, and from predators and rivals, back when sticks, stones, furs and fire were our only technologies.
So there’s a poetic parallel between early humans and us. We’re visiting the Moon again, and lunar caves could shelter us the way caves sheltered our ancestors on Earth.
Continue reading “Chinese Astronauts May Build a Base Inside a Lunar Lava Tube”
China is Planning to Have Humans on the Moon by 2030

As NASA prepares to return astronauts to the Moon with Artemis III, China is ramping up its efforts for a crewed lunar landing, targeting earlier than 2030. Lin Xiqiang, the deputy director of China’s Manned Space Agency announced that the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program (CLEP) is preparing for a “short stay on the lunar surface and human-robotic joint exploration.”
Continue reading “China is Planning to Have Humans on the Moon by 2030”


