A team of astronomers has caught glimpses of gas giants forming around a very young star.
The nascent giants are having a chilling effect on their potential siblings.
Continue reading “Baby Gas Giants Cast Shadows on Their Siblings”
A team of astronomers has caught glimpses of gas giants forming around a very young star.
The nascent giants are having a chilling effect on their potential siblings.
Continue reading “Baby Gas Giants Cast Shadows on Their Siblings”A lot of the headlines and discussion around the habitability of exoplanets is focused on their proximity to their star and on the presence of water. It makes sense, because those are severely limiting factors. But those planetary characteristics are really just a starting point for the habitable/not habitable discussion. What happens in a planet’s interior is also important.
Continue reading “Habitability of Planets Will Depend on Their Interiors”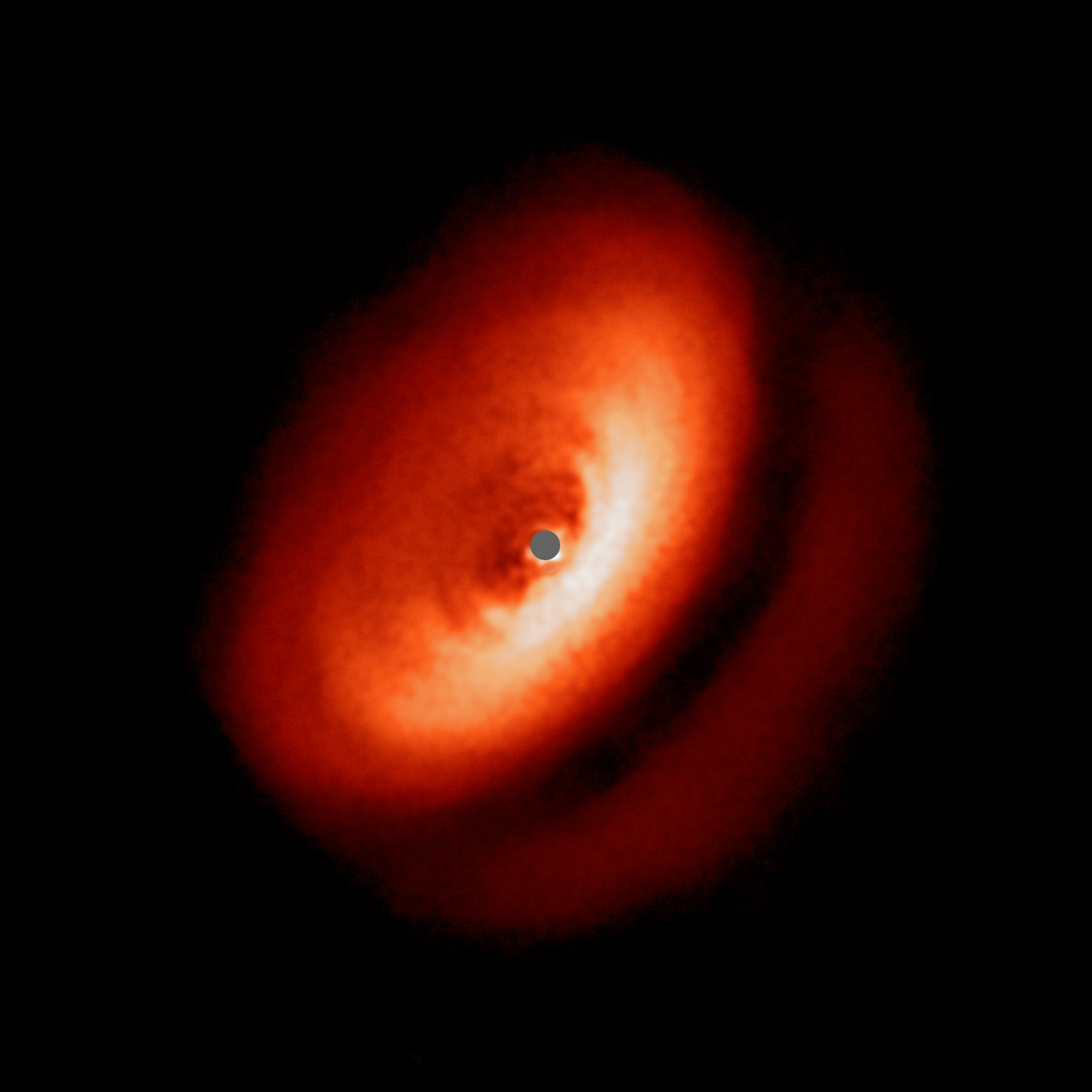
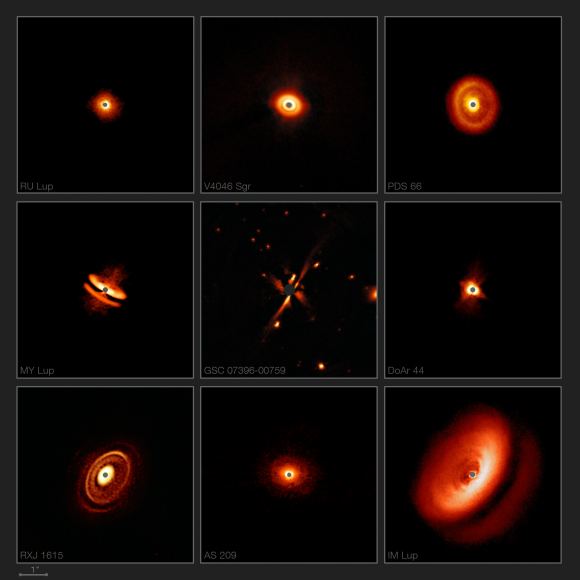
The European Southern Observatory (ESO) has released a stunning collection of images of the circumstellar discs that surround young stars. The images were captured with the SPHERE (Spectro-Polarimetric High-contrast Exoplanet REsearch) instrument on the ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile. We’ve been looking at images of circumstellar disks for quite some time, but this collection reveals the fascinating variety of shapes an sizes that these disks can take.

We have a widely-accepted model of star formation supported by ample evidence, including images like these ones from the ESO. The model starts with a cloud of gas and dust called a giant molecular cloud. Within that cloud, a pocket of gas and dust begins to coalesce. Eventually, as gravity causes material to fall inward, the pocket becomes more massive, and exerts even more gravitational pull. More gas and dust continues to be drawn in.
The material that falls in also gives some angular momentum to the pocket, which causes rotation. Once enough material is accumulated, fusion ignites and a star is born. At that point, there is a proto-star inside the cloud, with unused gas and dust remaining in a rotating ring around the proto-star. That left over rotating ring is called a circumstellar disc, out of which planets eventually form.
There are other images of circumstellar discs, but they’ve been challenging to capture. To image any amount of detail in the disks requires blocking out the light of the star at the center of the disk. That’s where SPHERE comes in.
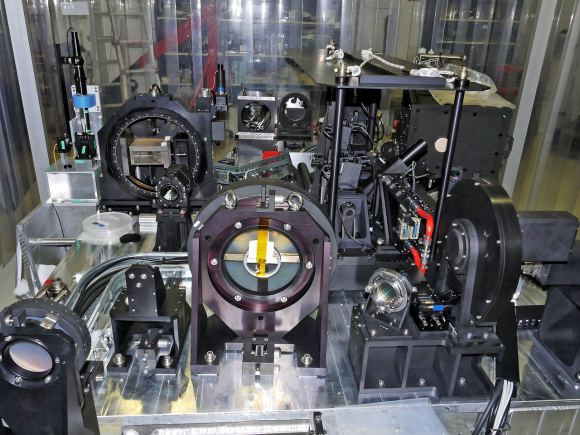
SPHERE was added to the ESO’s Very Large Telescope in 2014. It’s primary job is to directly image exoplanets, but it also has the ability to capture images of circumstellar discs. To do that, it separates two types of light: polarized, and non-polarized.
Light coming directly from a star—in these images, a young star still surrounded by a circumstellar disc—is non-polarized. But once that starlight is scattered by the material in the disk itself, the light becomes polarized. SPHERE, as its name suggests, is able to separate the two types of light and isolate just the light from the disk. That is how the instrument captures such fascinating images of the disks.
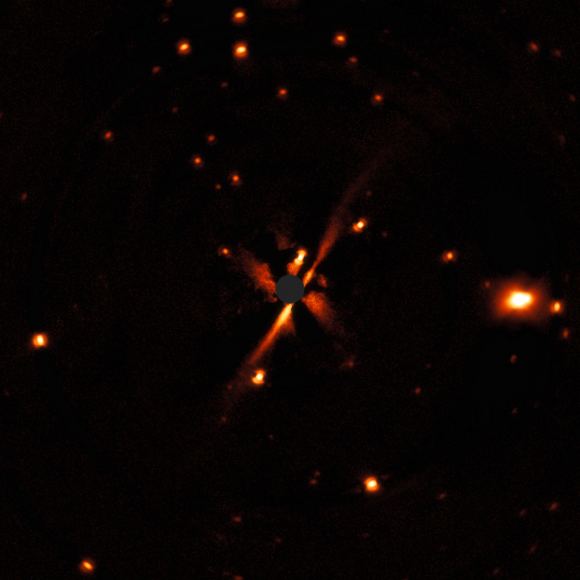
ESO/E. Sissa et al.
Ever since it became clear that exoplanets are not rare, and that most stars—maybe all stars—have planets orbiting them, understanding solar system formation has become a hot topic. The problem has been that we can’t really see it happening in real time. We can look at our own Solar System, and other fully formed ones, and make guesses about how they formed. But planet formation is hidden inside those circumstellar disss. Seeing into those disks is crucial to understanding the link between the properties of the disk itself and the planets that form in the system.
The discs imaged in this collection are mostly from a study called the DARTTS-S (Discs ARound T Tauri Stars with SPHERE) survey. T Tauri stars are young stars less than 10 million years old. At that age, planets are still in the process of forming. The stars range from 230 to 550 light-years away from Earth. In astronomical terms, that’s pretty close. But the blinding bright light of the stars still makes it very difficult to capture the faint light of the discs.
One of the images is not a T Tauri star and is not from the DARTTS-S study. The disc around the star GSC 07396-00759, in the image above, is actually from the SHINE (SpHere INfrared survey for Exoplanets) survey, though the images itself was captured with SPHERE. GSC 07396-00759 is a red star that’s part of a multiple star system that was part of the DARTTS-S study. The puzzling thing is that red star is the same age as the T TAURI star in the same system, but the ring around the red star is much more evolved. Why the two discs around two stars the same age are so different from each other in terms of time-scale and evolution is a puzzle, and is one of the reasons why astronomers want to study these discs much more closely.
We can study our own Solar System, and look at the positions and characteristics of the planets and the asteroid belt and Kuiper Belt. From that we can try to guess how it all formed, but our only chance to understand how it all came together is to look at other younger solar systems as they form.
The SPHERE instrument, and other future instruments like the James Webb Space Telescope, will allow us to look into the circumstellar discs around other stars, and to tease out the details of planetary formation. These new images from SPHERE are a tantalizing taste of the detail and variety we can expect to see.