The Universe is filled with hot fusion, in the cores of stars. And scientists have even been able to replicate this stellar process in expensive experiments. But wouldn’t it be amazing if you could produce energy from fusion without all that equipment, and high temperatures and pressures? Pons and Fleischmann announced exactly that back in 1989, but things didn’t quite turn out as planned…
Cold Fusion Experiment Maybe Holds Promise … Possibly … Hang on a Sec ….
Cold fusion has been called one of the greatest scientific breakthroughs that might likely never happen. On the surface, it seems simple – a room-temperature reaction occurring under normal pressure. But it is a nuclear reaction, and figuring it out and getting it to work has not been simple, and any success in this area could ultimately – and seriously — change the world. Despite various claims of victory over the years since 1920, none have been able to be replicated consistently and reliably.
But there’s buzz this week of a cold fusion experiment that has been replicated, twice. The tests have reportedly produced excess heat with roughly 10,000 times the energy density and 1,000 times the power density of gasoline.
The names involved are familiar in the cold fusion circles: Italian entrepreneur Andrea Rossi has been claiming for several years that his E-Cat device produces heat through a process called a Low Energy Nuclear Reaction (LENR), and puts out more energy than goes in. In the past, Rossi didn’t allow anyone to verify his device because he claimed his device was an “industrial trade secret.”
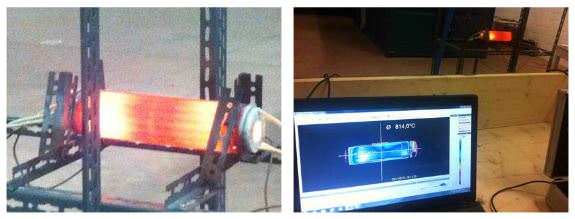
But a new paper published on arXiv last week says that seven independent scientists have performed tests of two E-Cat prototypes under controlled conditions, using high-precision instrumentation. Although the authors of the paper wrote that they weren’t allowed to see what was going on inside the sealed steel cylinder reactor, they did write in their paper, “Even by the most conservative assumptions as to the errors in the measurements, the result is still one order of magnitude greater than conventional energy sources.“
The team did two tests:
The first test experiment, lasting 96 hours (from Dec. 13th 2012, to Dec. 17th 2012), was carried out by the two first authors of this paper, Levi and Foschi, while the second experiment, lasting for 116 hours (from March 18th 2013, to March 23rd 2013), was carried out by all authors.
Previously, Rossi and his colleague Sergio Focardi have said their device works by infusing hydrogen into nickel, transmuting the nickel into copper and releasing a large amount of heat.
As expected, the paper – which is not peer-reviewed – and Rossi’s work have both been met with lots of skepticism.
Steven Krivit, writing in the New Energy Times said that the paper by Levi, Foschi et al doesn’t describe any independent test but that authors were just witnesses of a Rossi demonstration.
Ethan Seigel from “Starts With a Bang” said its just another magic trick of a charlatan that people are falling for, again.
The folks at the Martin Fleishman Memorial Project website – a group that facilitates the wide-spread replication and validation of things like LENR in an open and scientific manner – say they have an overall positive impression of the paper by Levi and Foschi.
“Our preliminary assessment among the team is that it is a generally good report with no obvious errors or glaring omissions,” they wrote on their website. “It is easily the best evidence to date that Rossi has a working technology, and, if verified openly and widely, this report could be remembered as historic.”
But they also don’t have total confidence in the paper. “It is unfortunate that there are some justified concerns about the independence of the test team, since many of the authors are names that we have seen before in the context of Rossi.” Plus, they are disappointed that none of the authors of the Levi and Foschi paper are willing to present their findings at an upcoming conference.
They also have several other technical questions and criticisms, as do many others.
Articles on Forbes and ExtremeTech are more enthusiastic.
It’s too soon to say if this latest buzz about cold fusion will amount to anything. Only time and more tests and scrutiny will reveal whether this is anything to get excited about.