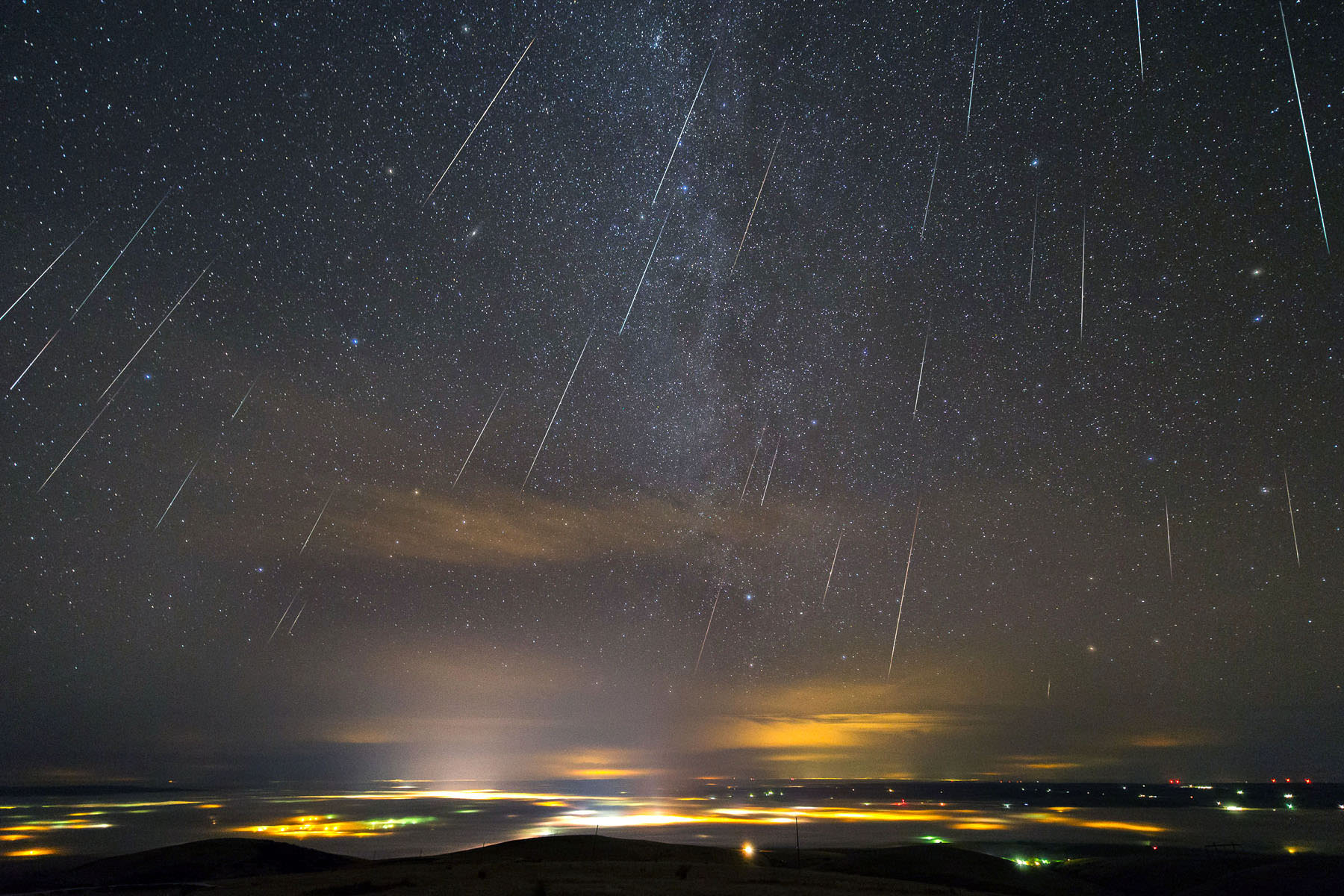
Wouldn’t it be nice if a meteor shower peaked on a weekend instead of 3 a.m. Monday morning? Maybe even showed good activity in the evening hours, so we could get our fill and still get to bed at a decent hour. Wait a minute – this year’s Geminids will do exactly that!
What’s more, since the return of this rich and reliable annual meteor shower occurs around 6 a.m. (CST) on Sunday December 14th, both Saturday and Sunday nights will be equally good for meteor watching. After the Perseids took a battering from the Moon last August, the Geminids will provide the best meteor display of 2014. They do anyway! The shower’s been strengthening in recent years and now surpasses every major shower of the year.
The official literature touts a rate of 120 meteors per hour visible from a dark sky site, but I’ve found 60-80 per hour a more realistic expectation. Either way, what’s to complain?
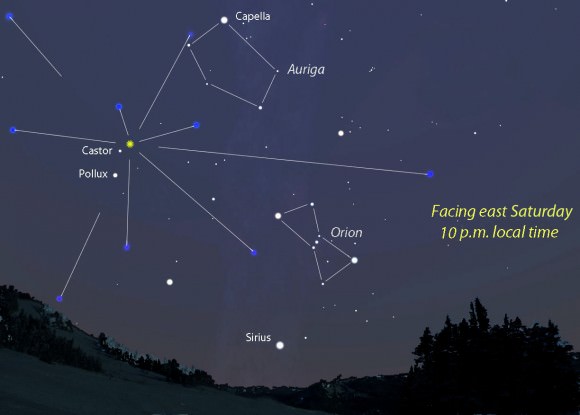
The third quarter Moon rises around midnight Saturday and 1 a.m. on Monday morning. Normally, moonlight would be cause for concern, but unlike many meteor showers the Geminids put on a decent show before midnight. The radiant, the location in the sky from which the meteors will appear to stream, will be well up in the east by 9:30 p.m. local time. That’s a good 2-3 hours of meteor awesomeness before moonrise.

Shower watching is a total blast because it’s so simple. Your only task is to dress warmly and get comfortable in a reclining chair aware from the unholy glare of unshielded lighting. The rest is looking up. Geminid meteors will flash anywhere in the sky, so picking a direction to watch the shower isn’t critical. I usually face east or southeast for the bonus view of Orion lumbering up from the horizon.
Bring your camera, too. I use a moderately wide angle lens (24-35mm) at f/2.8 (widest setting), set my ISO to 800 or 1600 and make 30-second exposures. The more photos you take, the better chance of capturing a meteor. You can also automate the process by hooking up a relatively inexpensive intervalometer to your camera and have it take the pictures for you.
As you ease back and let the night pass, you’ll see other meteors unrelated to the shower, too. Called sporadics, they trickle in at the rate of 2-5 an hour. You can always tell a Geminid from an interloper because its path traces back to the radiant. Sporadics drop down from any direction.
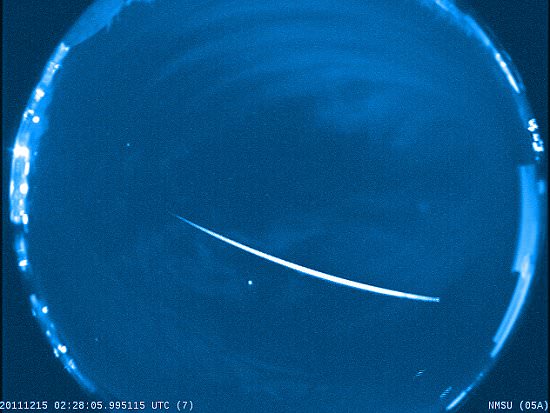
Geminid meteors immolate in Earth’s atmosphere at a moderate speed compared to some showers – 22 miles per second (35 km/sec) – and often flare brightly. Green, red, blue, white and yellow colors have been recorded, making the shower one of the more colorful. Most interesting, the meteoroid stream appears to be sorted according to size with faint, telescopic meteors maxing out a day before the naked eye peak. Larger particles continue to produce unusually bright meteors up to a few days after maximum.
Most meteor showers are the offspring of comets. Dust liberated from vaporizing ice gets pushed back by the pressure of sunlight to form a tail and fans out over the comet’s orbital path. When Earth’s orbit intersects a ribbon of this debris, sand and gravel-sized bits of rock crash into our atmosphere at high speed and burn up in multiple flashes of meteoric light.
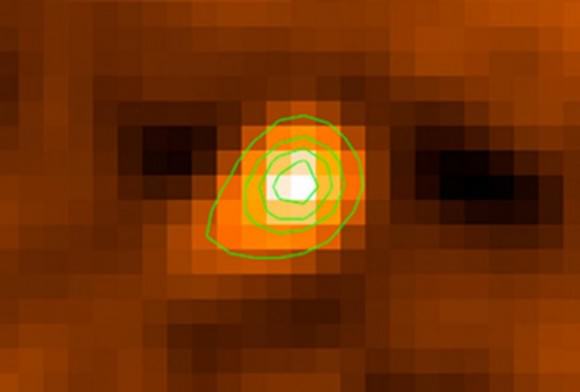
But the Geminids are a peculiar lot. Every year in mid-December, Earth crosses not a comet’s path but that of 3200 Phaethon (FAY-eh-thon), a 3.2 mile diameter (5.1 km) asteroid. Phaethon’s elongated orbit brings it scorchingly close (13 million miles) to the Sun every 1.4 years. Normally a quiet, well-behaved asteroid, Phaethon brightened by a factor of two and was caught spewing jets of dust when nearest the Sun in 2009, 2010 and 2012. Apparently the intense heat solar heating either fractured the surface or heated rocks to the point of desiccation, creating enough dust to form temporary tails like a comet.
While it looks like an asteroid most of the time, Phaethon may really be a comet that’s still occasionally active. Periodic eruptions provide the fuel for the annual December show.
Most of us will head out Saturday or Sunday night and take in the shower for pure enjoyment, but if you’d like to share your observations and contribute a bit of knowledge to our understanding of the Geminids, consider reporting your meteor sightings to the International Meteor Organization. Here’s the link to get started.
And this just in … Italian astronomer Gianluca Masi will webcast the shower starting at 8 p.m. CST December 13th (2 a.m. UT Dec. 14) on his Virtual Telescope Project site.