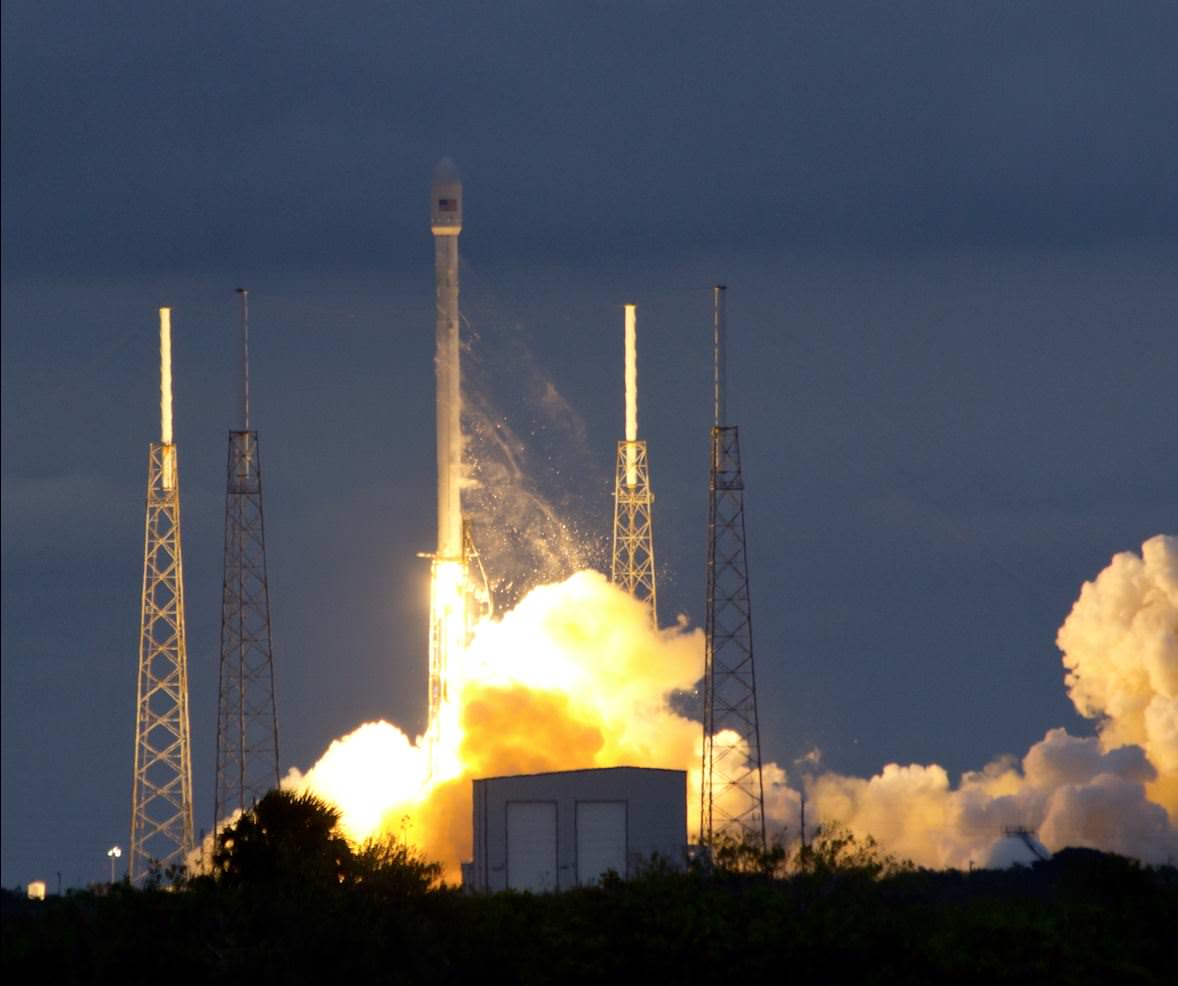
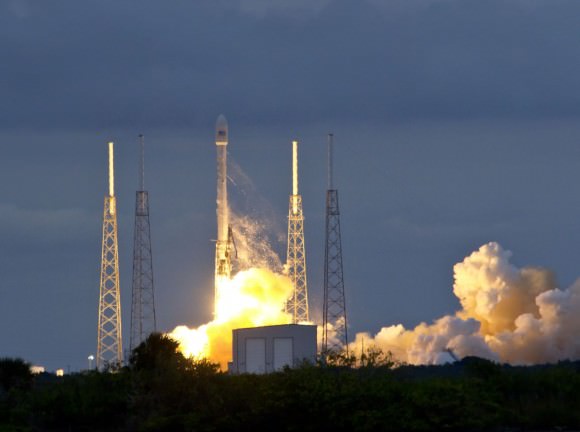
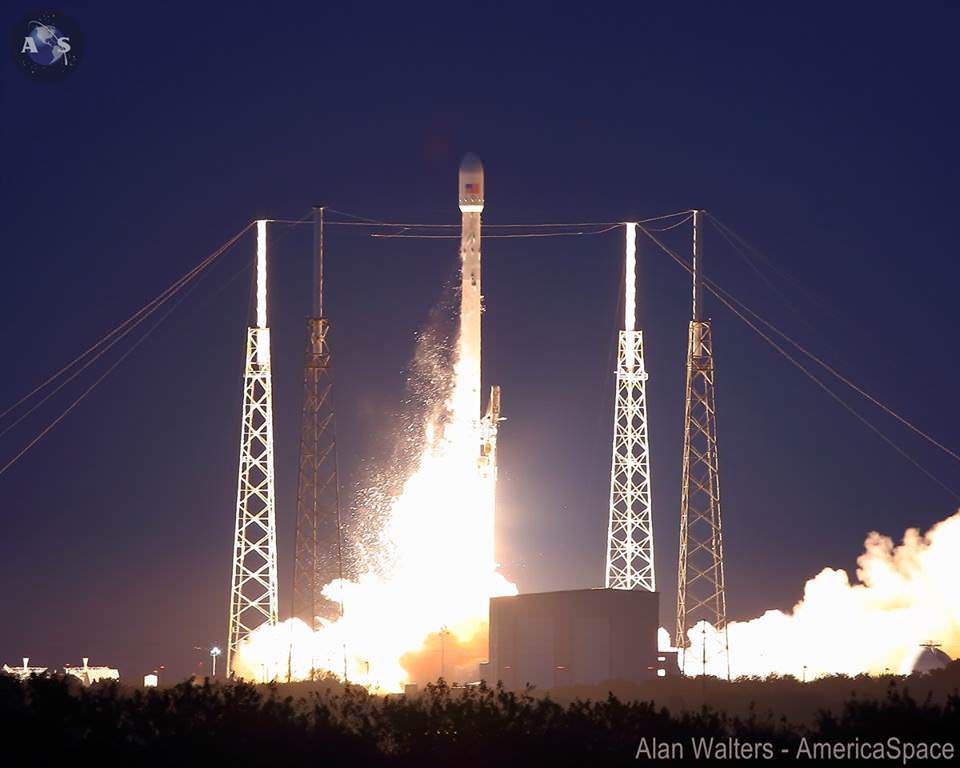
SpaceX began 2014 with a spectacular big bang for private space today, Jan. 6, when the firms next generation Falcon 9 rocket blasted off for the first time this year and successfully delivered the Thaicom 6 commercial broadcasting satellite to its target orbit.
The new, next generation Falcon 9 rocket lifted off at 5:06 p.m. EST (2206 GMT) from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida with the Thai payload.
The sunset SpaceX launch from the Florida Space Coast took place precisely on time with ignition of the nine Merlin 1-D first stage engines at Space Launch Complex 40.
The launch was broadcast live via a SpaceX webcast.
The nine engines on the 224 foot tall Falcon 9 v1.1 rocket generate 1.3 million pounds of thrust, about 50% more than the initial Falcon 9.
The second stage Merlin vacuum engine fired twice as planned.
The first firing began approximately 184 seconds into flight and lasted five minutes and 35 second to deliver Thaicom 6 into its parking orbit.

The engine relit for a second burn eighteen minutes later and lasted just over one minute to carry the satellite to its final geostationary transfer orbit.
The restart of the Falcon 9 second stage is a requirement for all geostationary transfer missions.
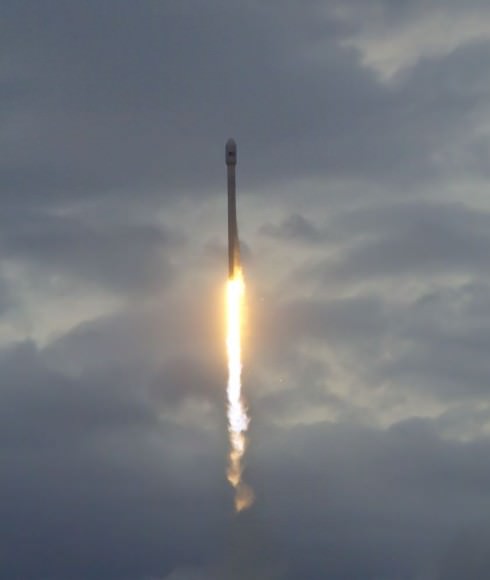

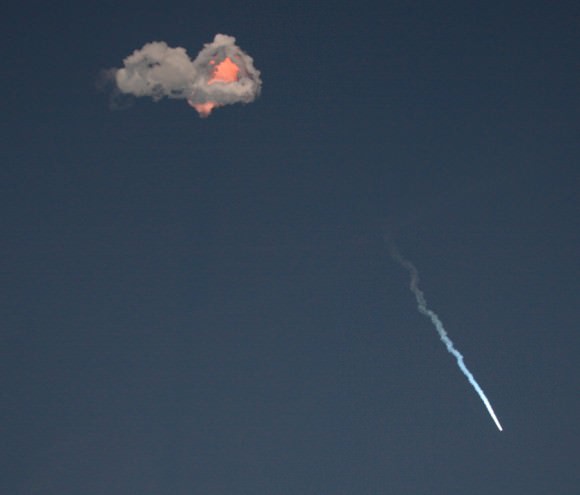
31 minutes after liftoff the Thaicom 6 spacecraft separated from the Falcon 9 launch vehicle and was placed into the desired geosynchronous transfer orbit of 295 x 90,000 km geosynchronous at 22.5 degrees inclination.
SpaceX said in a statement that, “The Falcon 9 launch vehicle performed as expected, meeting 100% of mission objectives.”
SpaceX did not attempt to recover the first stage booster on this mission, SpaceX spokeswoman Emily Shanklin told me. “We may try on the next flight.”

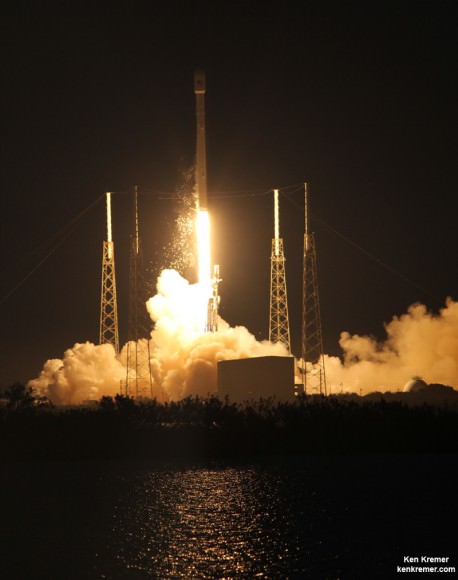
This marks the second launch of the upgraded Falcon 9 in just over a month, following closely on the heels of the maiden flight from Cape Canaveral on Dec. 3 with another commercial satellite, namely SES-8.
“Today’s successful launch of the THAICOM 6 satellite marks the eighth successful flight in a row for Falcon 9,” said Gwynne Shotwell, President of SpaceX. “SpaceX greatly appreciates THAICOM’s support throughout this campaign and we look forward to a busy launch schedule in 2014.”
Both the Thaicom-6 and SES-8 satellites were built by Orbital Sciences, one of SpaceX’s chief competitors in the commercial space race, making for strange bedfellows.

Indeed it’s a very busy week for private rockets.
Orbital Sciences is poised to launch their Antares rocket in less than 48 hours on Wednesday, Jan. 8 on a commercial resupply mission for NASA that’s bound for the international Space Station (ISS).
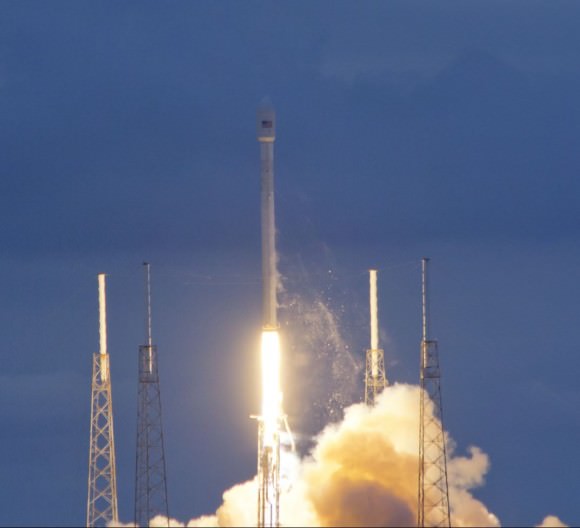
The new Falcon 9 is the key to fulfilling SpaceX’s future launch manifest of nearly 50 payloads worth billions of dollars for a diverse customer base.

The next gen Falcon 9 will also launch the human rated SpaceX Dragon to the ISS in a bid to restore America’s human spaceflight capability.
A pair of critical Falcon 9/Dragon abort tests are planned for 2014. Read my new article and discussion with SpaceX CEO Elon Musk – here.
The next SpaceX Dragon cargo launch to the ISS is currently scheduled for Feb. 22, said SpaceX spokeswoman Emily Shanklin told Universe Today.


Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing SpaceX, Orbital Sciences, commercial space, Chang’e-3, LADEE, Mars and more news.
…………….
Learn more about SpaceX, Orbital Sciences Antares Jan. 8 launch, Curiosity, Orion, MAVEN, MOM, Mars rovers and more at Ken’s upcoming presentations
Jan 7-9: “Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launch from Virginia on Jan. 8” & “Space mission updates”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA, evening