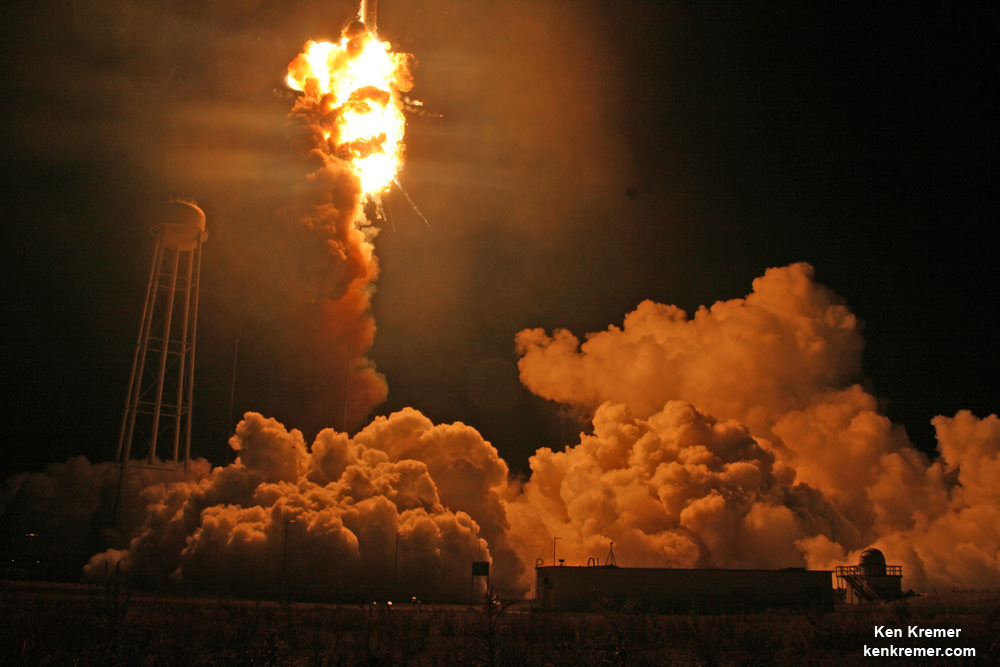
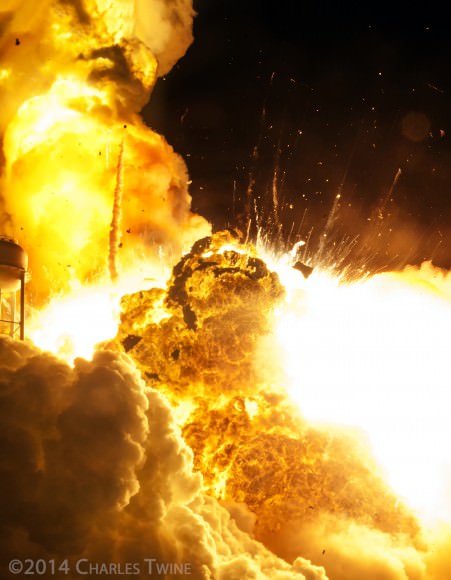
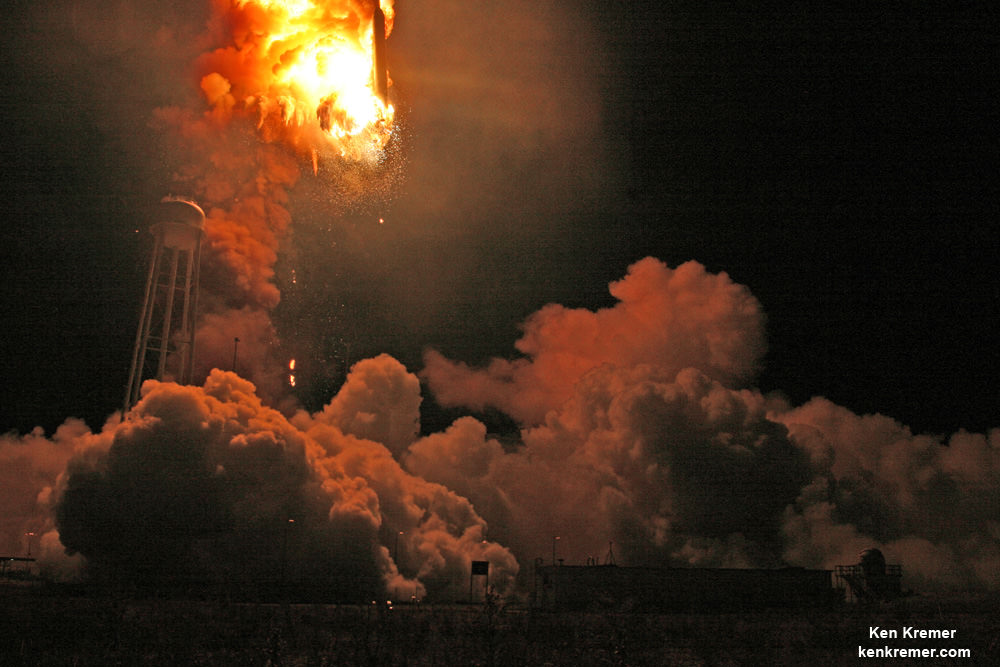
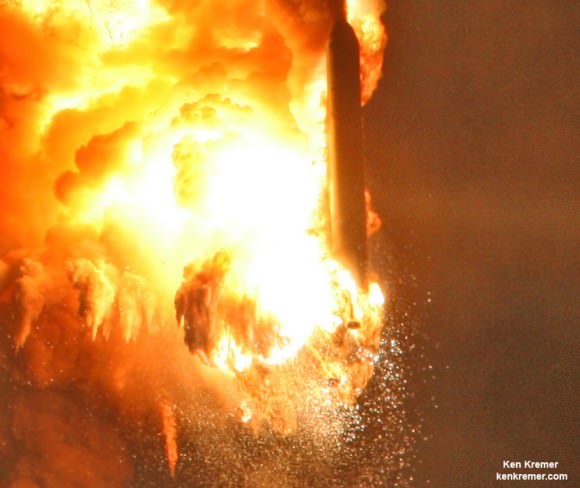
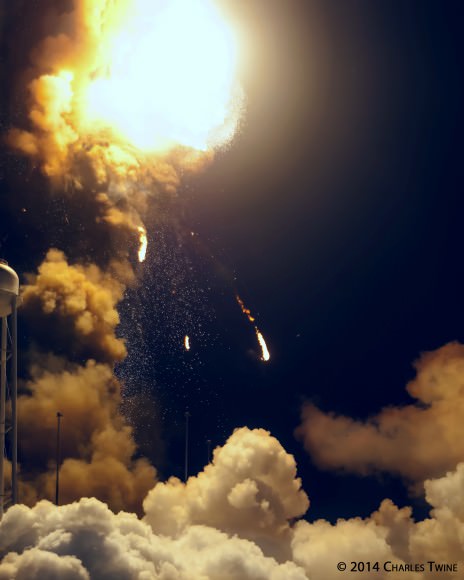
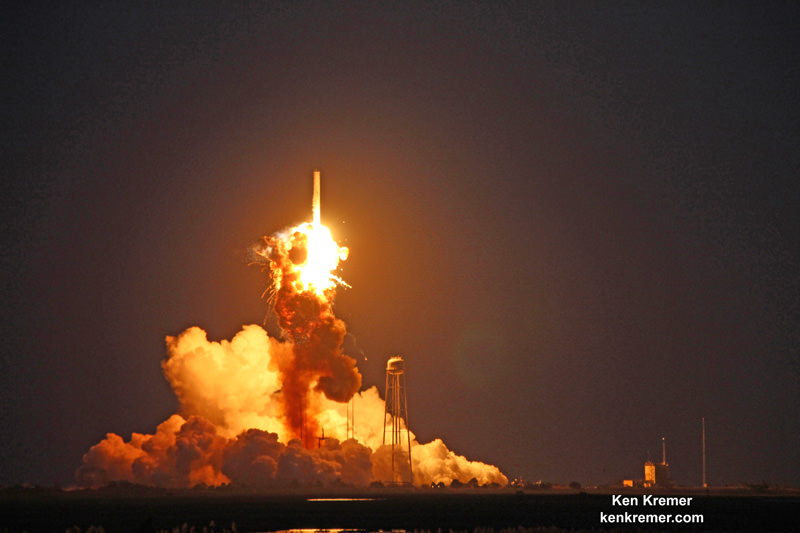
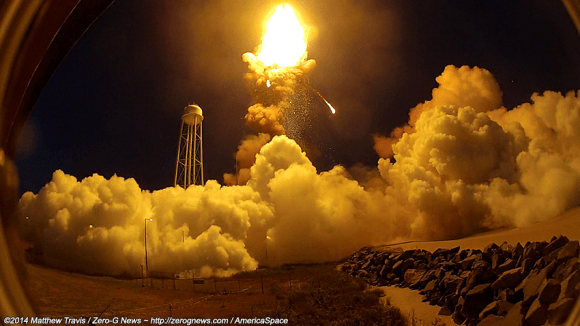
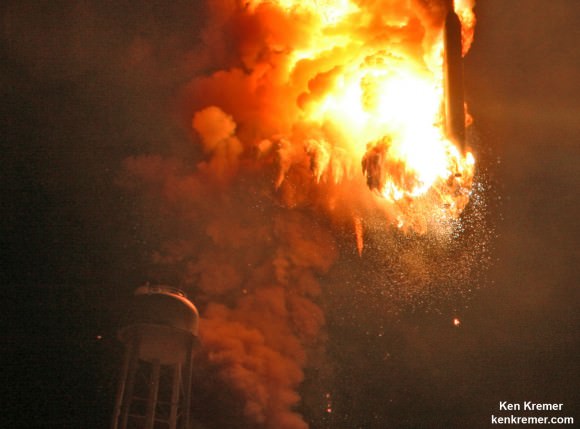
Video Caption: This up close launch pad camera view is a time lapse sequence of images showing the sudden catastrophic explosion of Orbital Sciences Antares Orb 3 rocket seconds after blastoff and destructive incineration as it plummets into a hellish inferno at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, VA, on Oct. 28, 2014, at 6:22 p.m. Credit: Ken Kremer – kenkremer.com/Universe Today/AmericaSpace/Zero-G News.
Story and images expanded
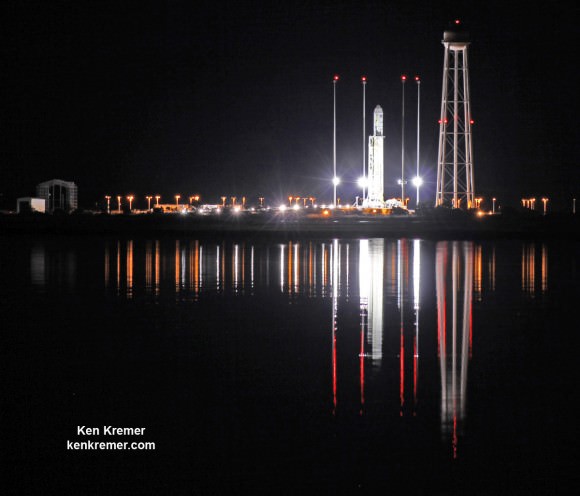
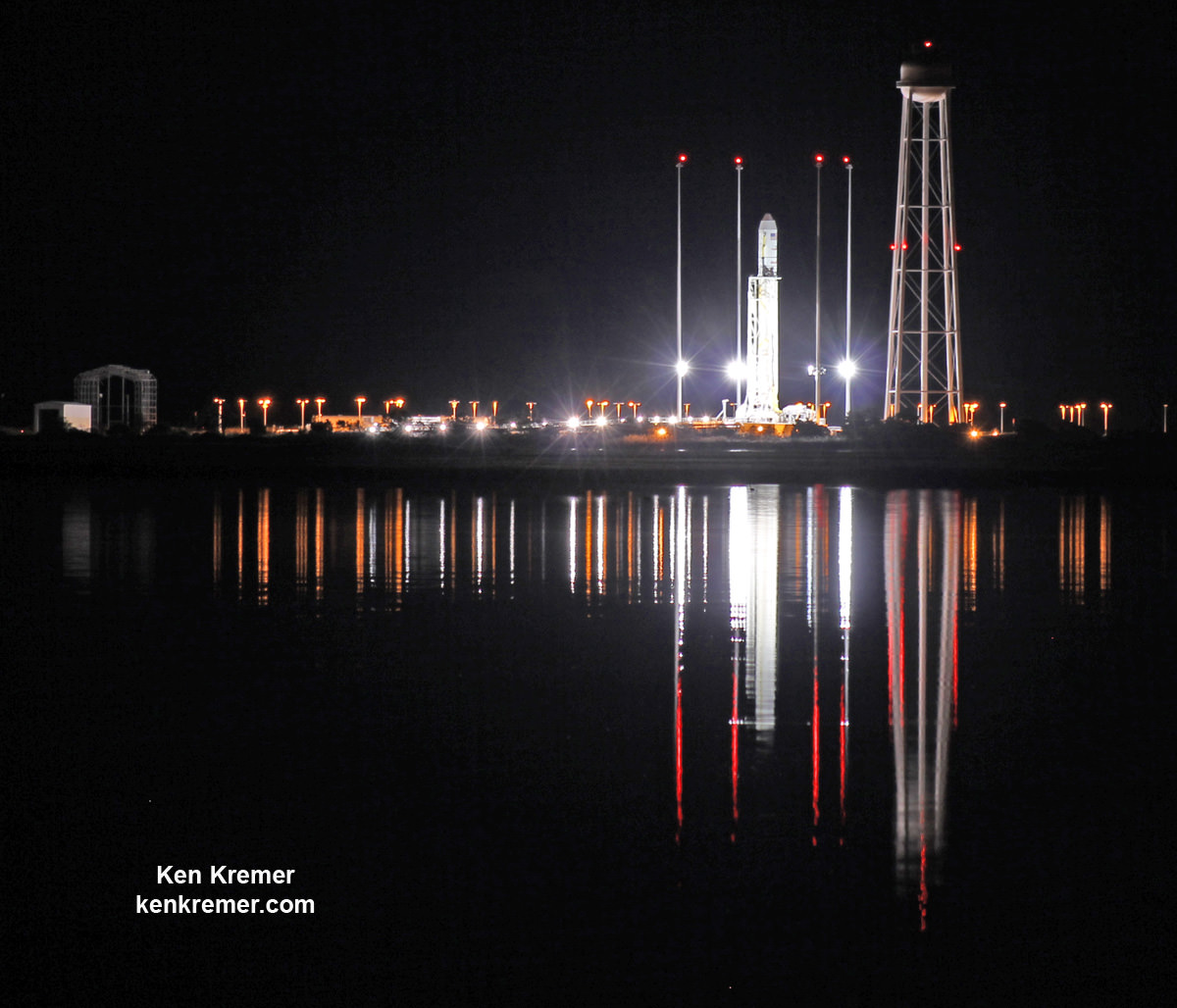
NASA WALLOPS FLIGHT FACILITY, VA – Moments after a seemingly glorious liftoff on Oct. 28, 2014, the Orbital Sciences Corp. commercial Antares rocket suffered a catastrophic failure as one of the Soviet-era first stage engines exploded and cascaded into a spectacular aerial fireball just above the launch pad at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility on the doomed Orb-3 mission to the International Space Station (ISS).
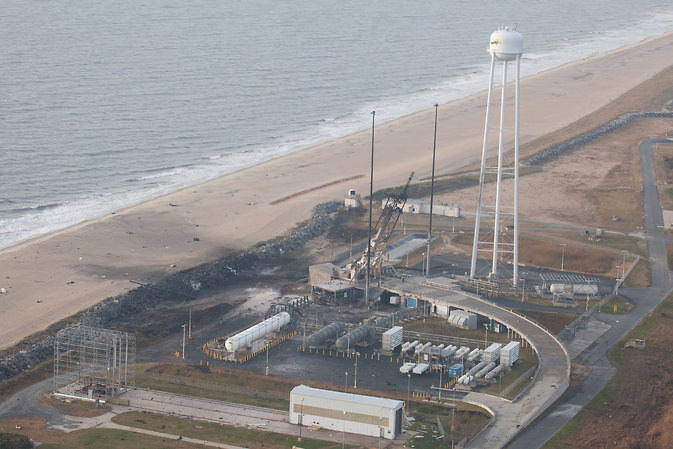
Although I witnessed and photographed the launch failure from the media viewing area on site at NASA Wallops from a distance of about 1.8 miles away, myself and a small group of space journalists working together from Universe Today, AmericaSpace, and Zero-G News had also placed sound activated cameras directly at the launch pad to capture the most spectacular up close views for what we all expected to be a “nominal” launch. Our imagery had been impounded by accident investigators – until being released to us now.
Now in part 2 of this exclusive series of video and photos our team can show you the terrible fate suffered by Antares after its destructive descent and frightening incineration as it was consumed by a hellish inferno.
My time lapse video above clearly shows the explosion and incendiary descent of Antares into a mammoth fireball.
As I reported in Part 1, all of our team’s cameras and image cards were impounded for nearly a month by Orbital’s official and independent Accident Investigation Board (AIB) that was assembled quickly in the aftermath of the Antares launch failure disaster and charged with determining the root cause of the launch failure.
The videos and photos captured on our image cards were used as evidence and scrutinized by the investigators searching for clues as to the cause and have only just been returned to us in the past few days.
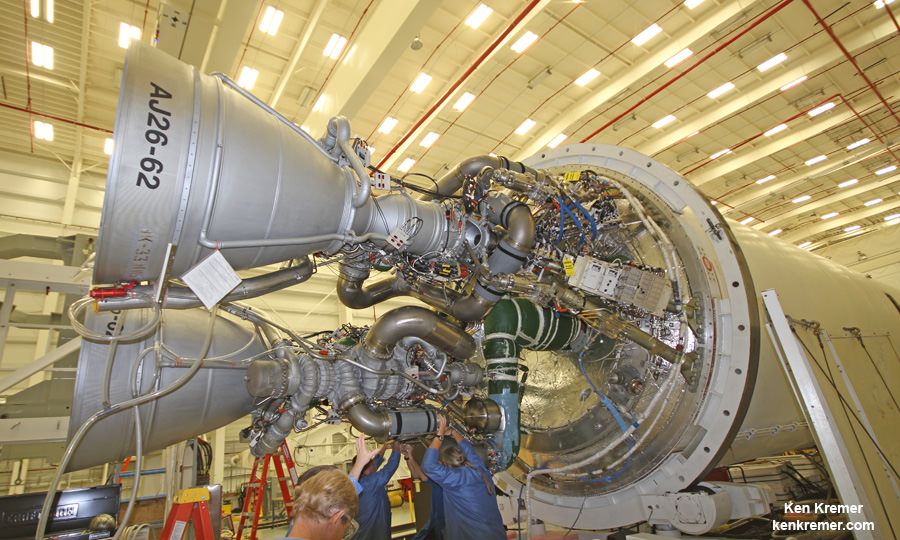
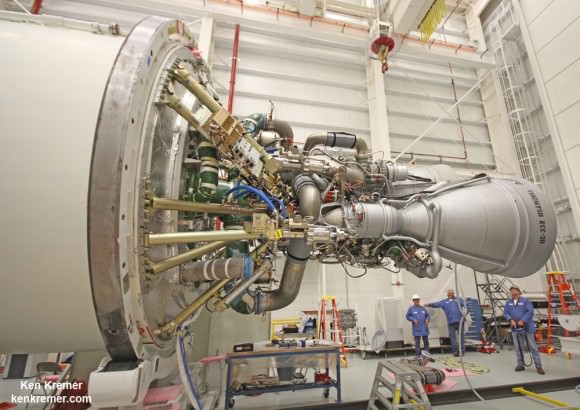
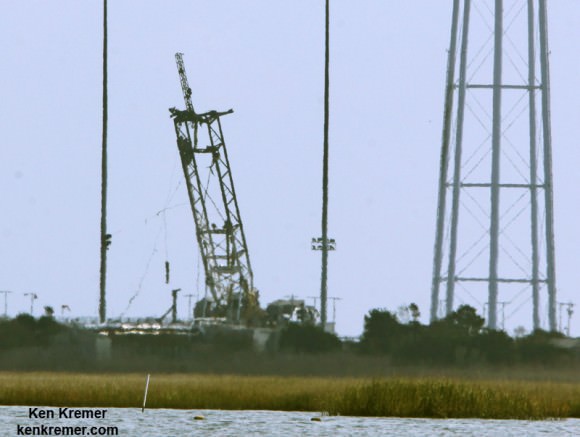
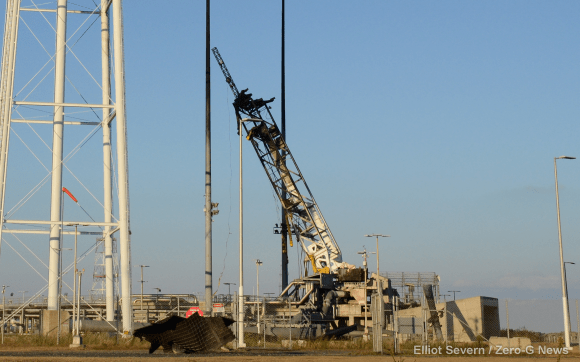
One image clearly shows that the south side engine nozzle of the AJ26 first stage engine was intact and had shut down after the initial explosion and during the plummet. Therefore it was the north side engine that blew up and led to the launch failure. See my up close AJ26 engine photo below.
Video Caption: AmericaSpace and Zero-G News video compilation of four cameras surrounding the launch pad to capture liftoff. The video runs through each at full speed before slowing down to give viewers a slow motion replay of the explosion. One of the cameras was right in the middle of the fireball, with chunks of broken rocket showering down around. CREDITS: Mike Barrett / Jeff Seibert / Matthew Travis / Elliot Severn / Peter Greenwood for www.ZeroGNews.com and www.AmericaSpace.com
Similar launch pad photos taken by NASA and Orbital Sciences cameras have not been publicly released and may not be released for some time to come.
The videos and images collected here are the work of my colleagues Matthew Travis, Elliot Severn, Alex Polimeni, Charles Twine, Jeff Seibert, Mike Barrett, and myself, and show exquisite, heretofore unreleased, views of the explosion, fireball, and wreckage from various positions all around the launch pad.
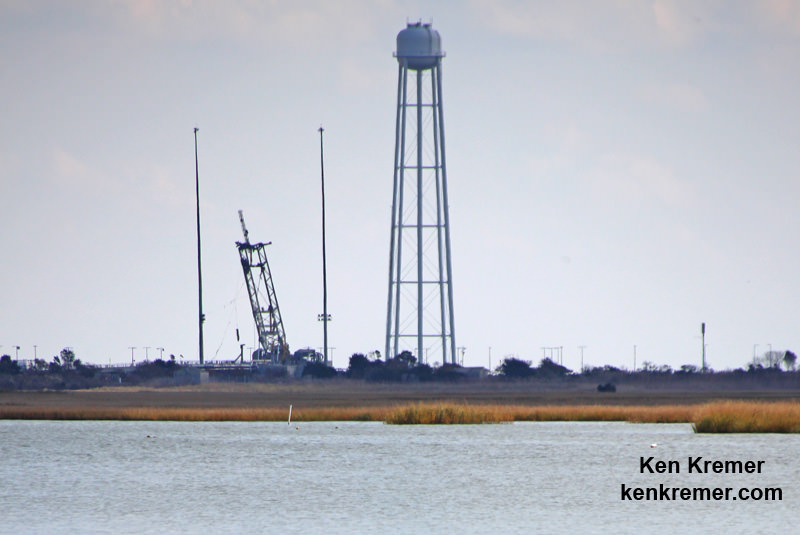
Our remote cameras were placed all around the Antares pad OA at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) on Wallops Island, VA, and somehow miraculously survived the rocket’s destruction as it plunged to the ground very near and just north of the seaside launch pad.
A turbopump failure in one of the rocket’s Soviet-era first stage engines has been identified as the most likely cause of the Antares’ destruction according to official statements from David Thompson, Orbital’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer.
The AJ26 engines were originally manufactured some 40 years ago in the then Soviet Union as the NK-33.
They were refurbished and “Americanized” by Aerojet Rocketdyne.
“While still preliminary and subject to change, current evidence strongly suggests that one of the two AJ26 main engines that powered Antares’ first stage failed about 15 seconds after ignition. At this time, we believe the failure likely originated in, or directly affected, the turbopump machinery of this engine, but I want to stress that more analysis will be required to confirm that this finding is correct,” said Thompson.


Overall this was the 5th Antares launch using the AJ26 engines.
Antares was carrying Orbital’s privately developed Cygnus pressurized cargo freighter loaded with nearly 5000 pounds (2200 kg) of science experiments, research instruments, crew provisions, spare parts, spacewalk and computer equipment and gear on a critical resupply mission dubbed Orb-3 bound for the International Space Station (ISS).

It was the heaviest cargo load yet lofted by a Cygnus. Some 800 pounds additional cargo was loaded on board compared to earlier flights. That was enabled by using the more powerful ATK CASTOR 30XL engine to power the second stage for the first time.
The astronauts and cosmonauts depend on a regular supply train from the ISS partners to kept it afloat and productive on a 24/7 basis.
The Orbital-3, or Orb-3, mission was to be the third of eight cargo resupply missions to the ISS through 2016 under the NASA Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract award valued at $1.9 Billion.
Orbital Sciences is under contract to deliver 20,000 kilograms of research experiments, crew provisions, spare parts, and hardware for the eight ISS flights.
Examine the video and photo gallery herein.

Watch here for Ken’s ongoing reporting about Antares and NASA Wallops.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.