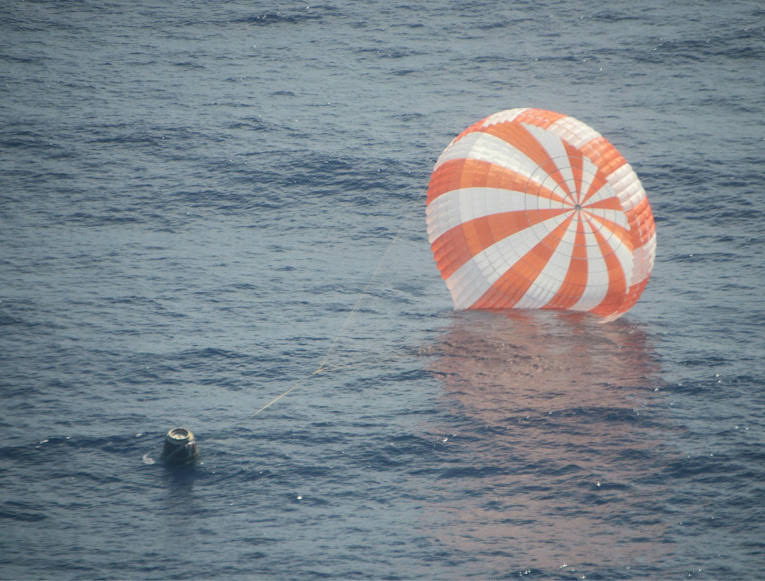
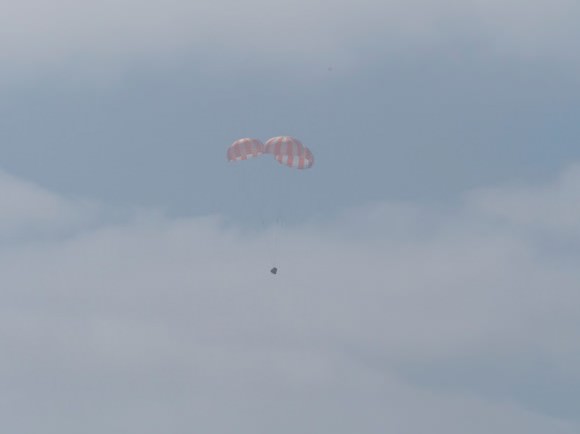
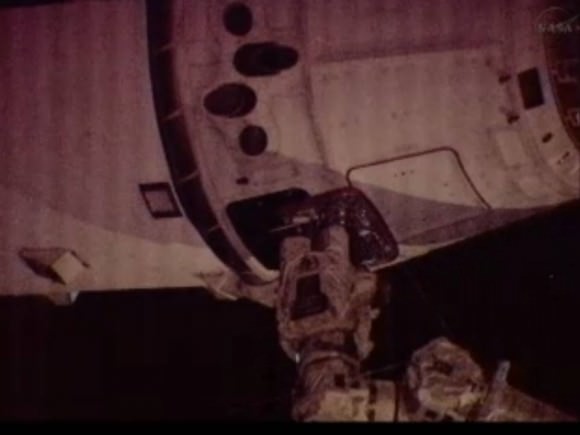
The Dragon capsule after splashing down successfully on October 28, 2012. Credit: SpaceX
After leaving the International Space Station earlier on Sunday, SpaceX’s Dragon capsule returned to Earth from the International Space Station, safely splashing down in the Pacific Ocean about 400 kilometers (250 miles) off the coast of southern California. Inside the capsule are 758 kg (1,673 pounds) of return cargo including hardware, supplies, and a GLACIER freezer packed with scientific samples, including blood and urine samples of the astronauts on the space station, being returned for medical analysis. Currently, Dragon is the only craft capable of returning a significant amount of supplies to Earth, and this mission marks the first time since the retirement of the space shuttle that NASA has been able to return research samples for analysis.
Both NASA and SpaceX were thrilled with the success of the mission.
“This historic mission signifies the restoration of America’s ability to deliver and return critical space station cargo,” said SpaceX CEO and Chief Technical Officer Elon Musk. “The reliability of SpaceX’s technology and the strength of our partnership with NASA provide a strong foundation for future missions and achievements to come.”
NASA Administrator Charles Bolden added his congratulations to SpaceX: “Just a little over one year after we retired the Space Shuttle, we have completed the first cargo resupply mission to the International Space Station. Not with a government owned and operated system, but rather with one built by a private firm — an American company that is creating jobs and helping keep the U.S. the world leader in space as we transition to the next exciting chapter in exploration. Congratulations to SpaceX and the NASA team that supported them and made this historic mission possible.”
Raw video footage of the Dragon splashing down:
The SpaceX recovery team is now transporting Dragon by boat to a port near Los Angeles, where early cargo will be delivered to NASA. Dragon then will be transported to SpaceX’s facility in McGregor, Texas for processing. There, the remaining cargo will be delivered to NASA.
After a successful test flight in May of this year, this was the first “official” resupply mission for SpaceX to the ISS. The Dragon was launched on October 7 and reached the ISS three days later.
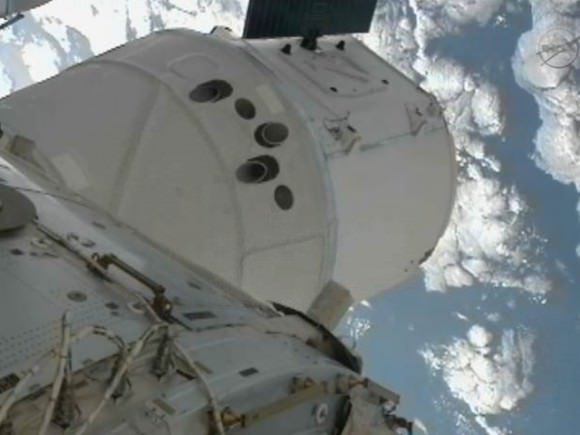
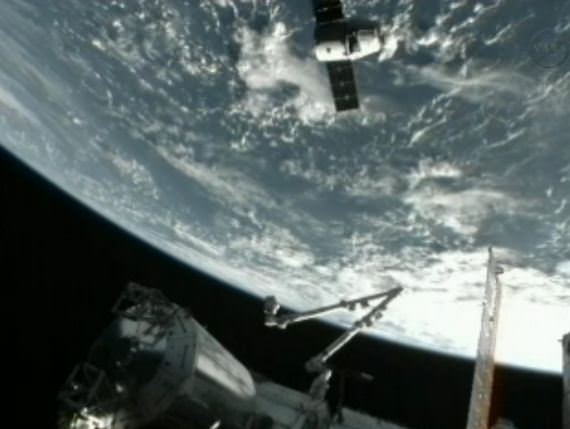
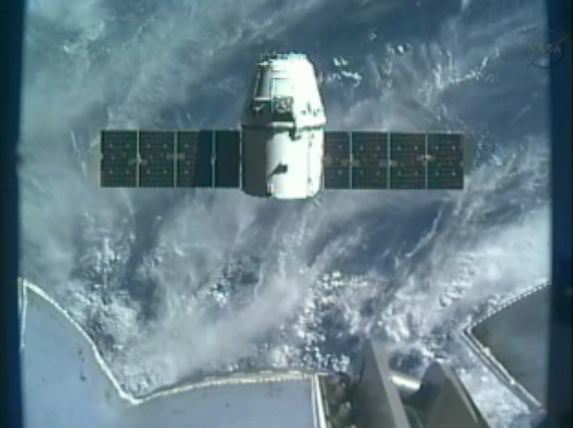
“It was nice while she was on board,” station commander Suni Williams radioed to back to Mission Control after the spacecraft was unberthed Sunday. “Literally and figuratively, there is a piece of us on that spacecraft going home to Earth.”
NASA Video of the Dragon capsule leaving the ISS:
The flight didn’t go with a hitch, however. An anomaly occurred with one of Falcon 9’s first-stage engines during the launch, and while it didn’t affect the mission to the ISS, a satellite that tagged along on the flight, the ORBCOMM OG2 prototype communications satellite, was delivered to the wrong orbit and ultimately fell back to Earth.
SpaceX and NASA are investigating the anomaly and analysis to date supports initial findings: the engine experienced a rapid loss of pressure and Falcon 9’s flight computer immediately commanded shutdown, as it is designed to do in such cases. SpaceX said they will continue to analyze all data in an effort to determine root cause and will apply those findings to future flights.
The next resupply mission for Dragon is tentatively scheduled for January 2013. Additionally, Orbital Sciences Corp, NASA’s second cargo hauler, plans to launch the first Cygnus capsule in February or March 2013.
Dragon floating down on parachutes. Credit: SpaceX












![A4IAv1HCQAEY5lM[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/A4IAv1HCQAEY5lM1-580x429.jpg)







