[/caption]
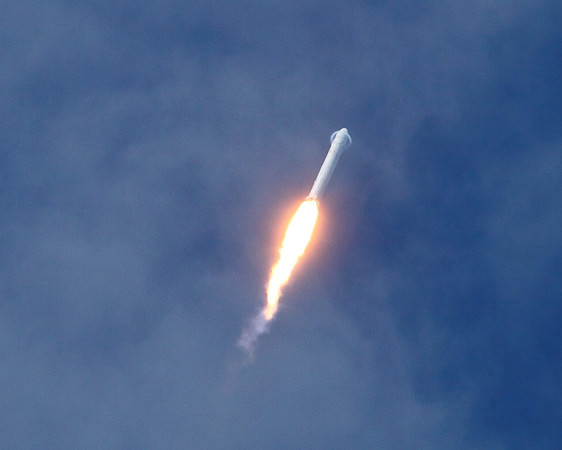
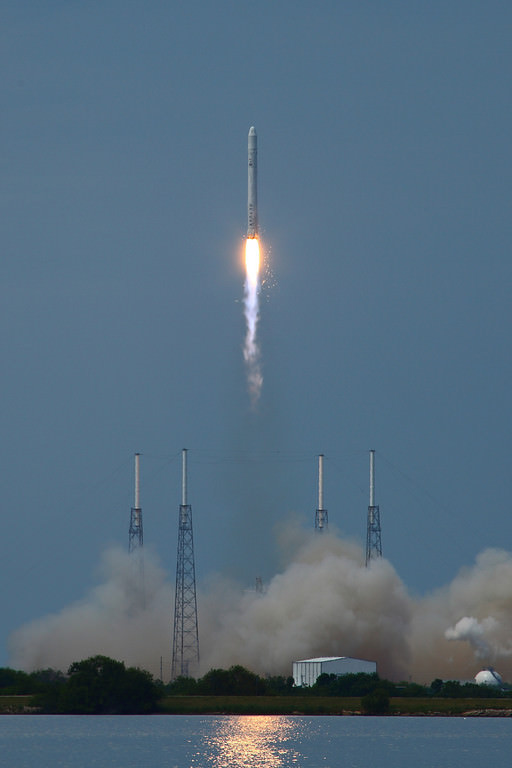
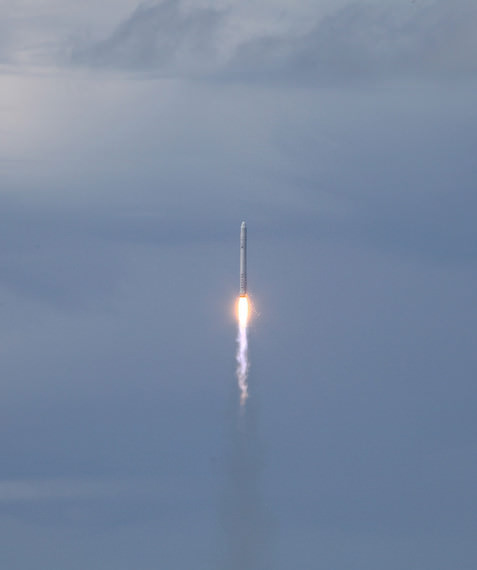
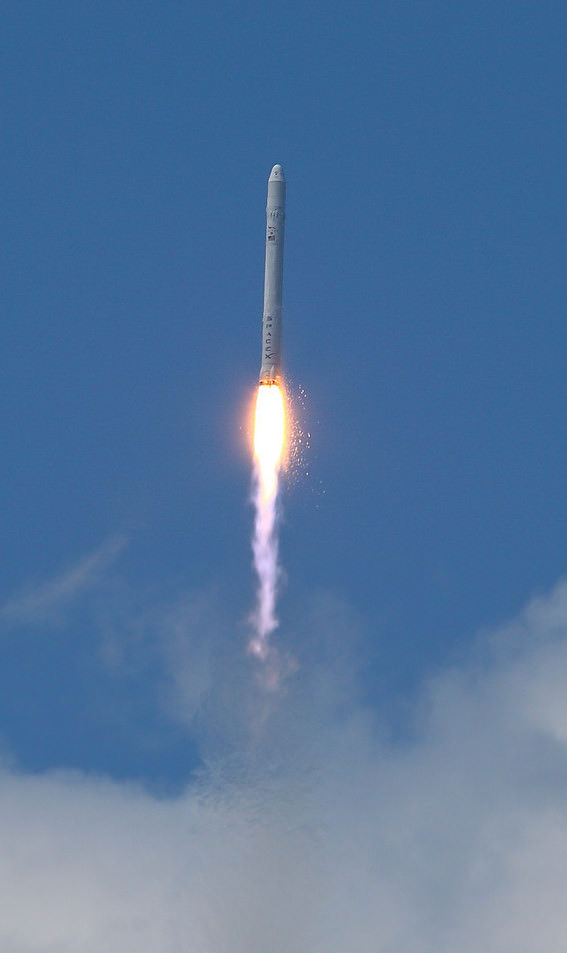
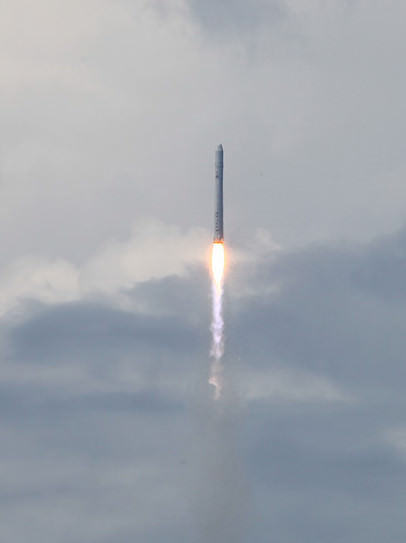
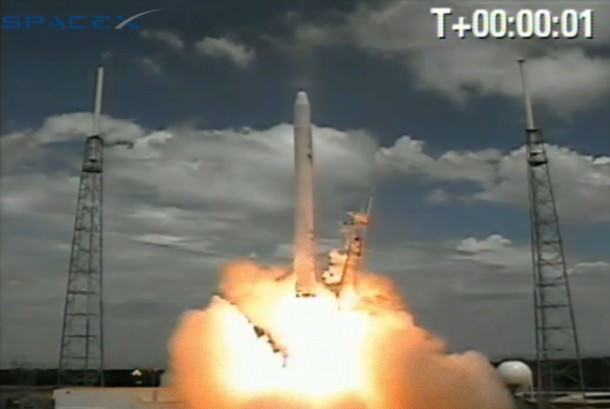
Hailed as a both a great day for commercial spaceflight as well as for NASA, SpaceX made history on Wednesday with a 100% successful test flight of its Dragon capsule and Falcon 9 rocket. “This is a new way of doing business,” said Alan Lindenmoyer manager of NASA’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Program Office, “and I would say today this is an indication that this public/private partnership is working and has proven to be successful. Thanks to SpaceX for the early Christmas present – this is a great way to start the holidays.”
At the press conference following the flight, SpaceX CEO Elon Musk at first appeared to be speechless: “Really, this has been better than I expected,” he said. “It all went right. I am sort of in semi shock—I wish I could be more articulate in moments like this, bit it’s hard to be articulate with a blown mind!”
But Musk soon found his words – and lots of them (with many great quotes, so keep reading…)

Lindenmoyer said SpaceX’s accomplishments are quite an achievement, since over the last 20 years, for new launch vehicles only about 50% of them are success are successful on their first or second flights, and only 1 out of 3 new vehicles have two successful flights in a row, which SpaceX has achieved.
Musk said the success really shouldn’t be a surprise since the Dragon spacecraft has so many redundancies: 18 thruster engines instead of 9, 3 parachutes when they really could land with one, extra thermal protection, and a very advanced heat shield. But in the end, SpaceX didn’t need to use any of the backup systems.
Preliminary data said the Dragon reentered the atmosphere spot on at a 12% angle of attack, with 2% dispersion. “This is a testament to the incredible work of the people at SpaceX,” he said. “Everyone did their jobs so well.”
Musk also emphasize that his company couldn’t have gotten to where they are without NASA, in not only monetary support ($278 million for the COTS program), but in leading the way in spaceflight.
“The core concepts of Falcon 9 and Dragon were demonstrated decades ago by NASA, and its an old saying, but we are only here because we stand on the shoulders of giants. So thank you,” he said.
Musk noted a few key things about the flight: The restart of Falcon 9’s second stage went perfectly; the second stage as restarted after the release of Dragon, and rose to an altitude of more than 11,000 km (6,800 miles), Musk said. Secondary satellite payloads of nanosatellites were released during the flight. And, Musk added, that altitude was with the trimmed, repaired nozzle. Reaching an altitude that high was not part of SpaceX’s primary objectives, but nice to have, Musk said.
Dragon went to an altitude of 300 km.
Musk also stressed that the difference between this Dragon capsule and one that could carry people isn’t that different.
“People sometimes think the different between cargo and crew required enormous amount of magical pixie dust,” he said “This is not the case. If there would have been people sitting in Dragon today, they would have had a nice ride, feeling about 4-5 G’s, which is about what an amusement park ride is like,” with an 8 meter per second descent speed which is quite comfortable from a landing perspective.

The only differences, Musk said, would be the addition of a launch escape system. And, he revealed, what SpaceX really hopes to do with future spacecraft is not a splashdown in the ocean but a propulsive landing on the ground.
“The architecture you saw today was similar to what was employed in Apollo era, but we are aiming for propulsive landing with gear, kind of like the Eagle landing on the moon, and being able to take off again” he said. “Full reusability of Dragon and Falcon 9 is important as well, and something we want to figure out over time.”
Musk also said this mission didn’t have many significant differences in one that would send the Dragon the ISS. “In our discussions with NASA they said if this flight went well they would strongly consider letting us go to the space station on next mission,” he said. “I hope that is what NASA will allow us to do, we need to still examine the data from this mission first, but I’m highly optimistic. There are additional elements to be added to Dragon such as solar panels and redundancy on flight computers and electronics, but feel highly confident we could make it to the ISS on our next flight by middle of next year.”
Today’s flight tested the fundamentals of a heat shield and precision landing. Musk said the performance of heat shield was spectacular, and projected that is could not only handle Earth reentry, but also lunar and Mars reentry.
SpaceX president Gwynne Shotwell noted some other technical details, of how Dragon was able to maintain attitude and thermal control, as well as maintain communications with ground stations and TEDRIS satellites, which requires specific directional pointing.
The entire launch and two orbit flight took 3 hours 19 min 52 seconds, and initial data said they landed within 10 km of their target, and a communiqué from the Air force said Dragon came within 800 meters.
Asked about the flame flare that came about 2 seconds after launch, Musk said the first look by engineers said it was a check valve on the second stage umbilical that came off and caught fire as the spacecraft engines passed by — not an explosion but a just little fire.
Musk said the point in the flight where he felt the most jubilation and great relief was when the parachutes deployed. “Drogue and main chute deploy were riskiest parts, so when that happened, it was done deal. Just mind-blowingly awesome.”
Asked if the success today would silence any of SpaceX’s critics, Musk said, “I think if there really are people who are going still find a way to cast aversions on what we’ve done today, I pity them. It just wouldn’t make any sense.”
He said politicians who initially wanted to cut commercial crew funds from NASA’s budget soon learned that such a move would not decrease but increase the deficit and also meant increased time with no American access to space. “I think some politicians were initially mislead, but then they realized the value of commercial crew, which is why it the cuts didn’t make it into the final report.”
Asked about the differences in Dragon and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Musk said that Space X would probably be the most rapid path to an American crew transport system. “If we would have had people on this flight we would have taken them to orbit and returned them safely,” he said. “Going to a crew system is just adding some additional safety systems for highly off nominal activities. Even for cargo missions we will be carrying plants and animals so I think we are in a very strong position to be one of the winners of the commercial crew contract.”
Musk added that competition is good, however, and NASA shouldn’t be too dependent on one company,” so hopefully there will be two or maybe three commercial crew providers and hopefully we are one of them.”
Musk agreed with Lindenmoyer on how this appears to vindicate the public/private model of space flight and shows that the commercial model works just as well in space flight as in air flight, or other arenas.
“The air mail program was a huge boost when the Post Office went commercial,” he said “and that resulted in explosion of innovation and improvement in technology. It really was the dawn of aviation in American where it went from joy rides that rich people could do, to today where aviation is accessible to almost everyone. I think historically COTS program will be seen in that light.”
On board Dragon was a few small satellites, and look for Musk to reveal tomorrow the nature of a humorous item that was on board. “I’m not going to reveal it today, as I don’t want some of the editors to use it in the first headlines,” he said. “It is kind of funny and if you like Monty Python you’ll like this one.”
Spam in a can?
Universe Today extends their congratulations to SpaceX. The future appears to be now.