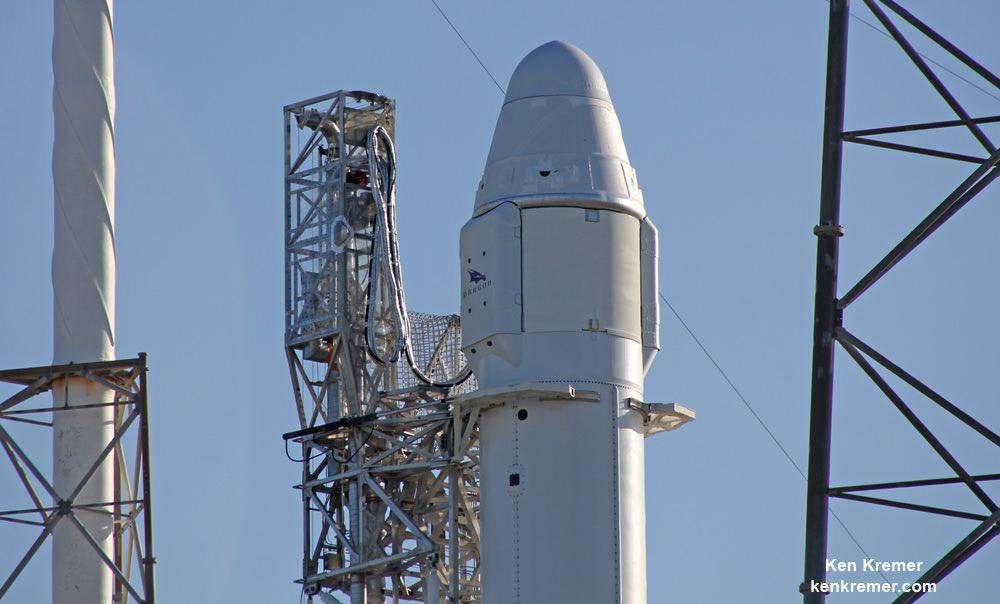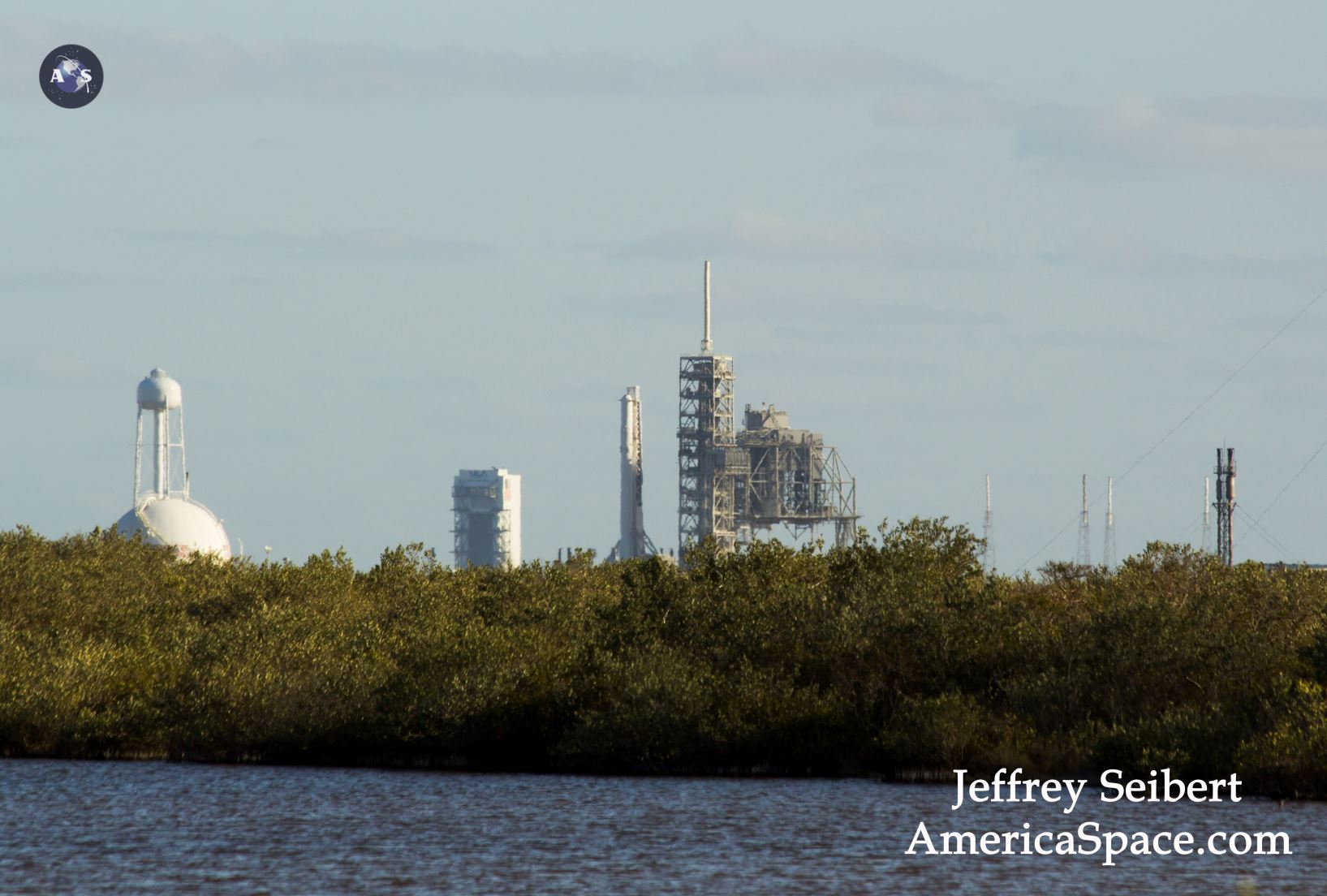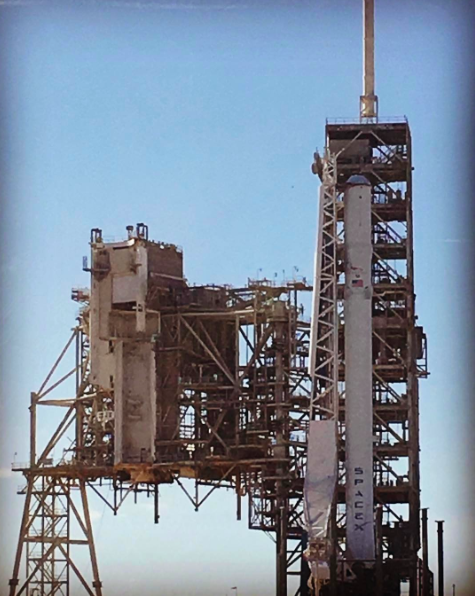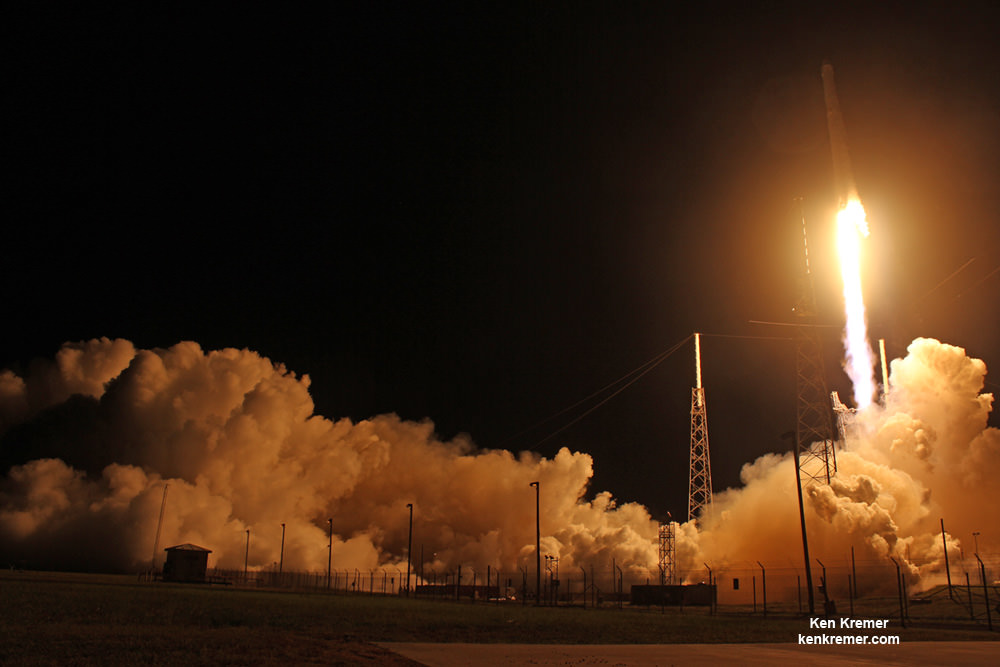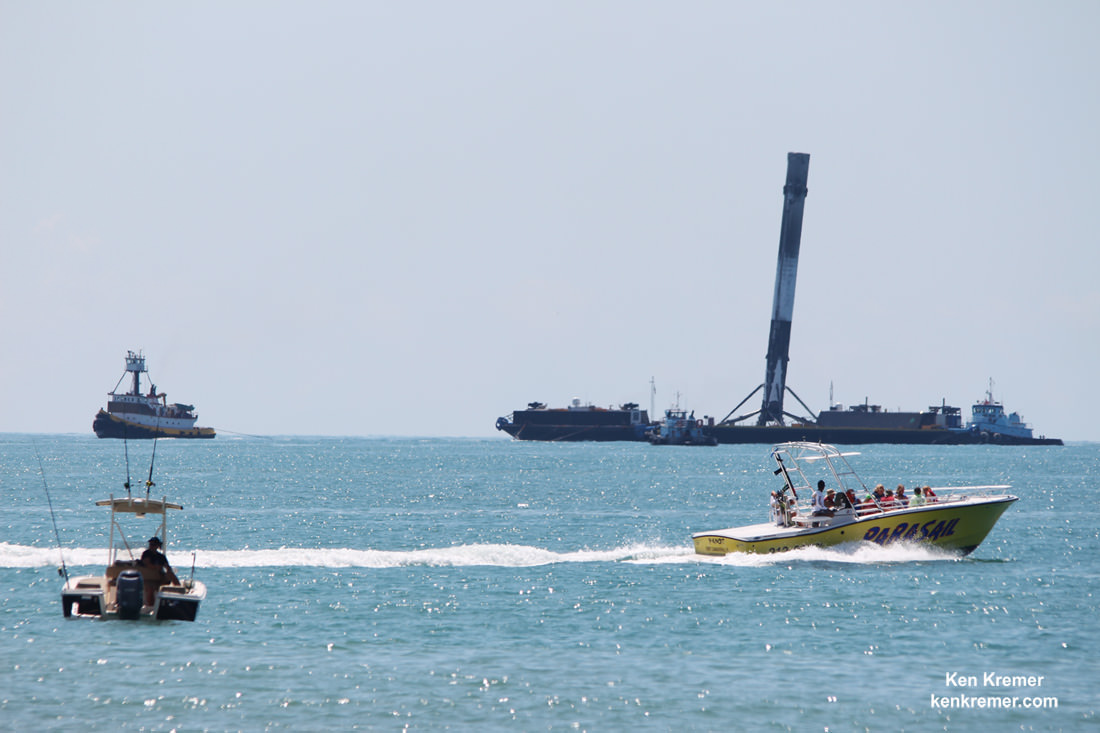
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – A SpaceX Dragon supply ship jam packed with more than 2.5 tons of critical science gear, crew supplies and 40 mice successfully arrived this morning at the International Space Station (ISS) – where six humans from the US, Russia and France are living and working aboard.
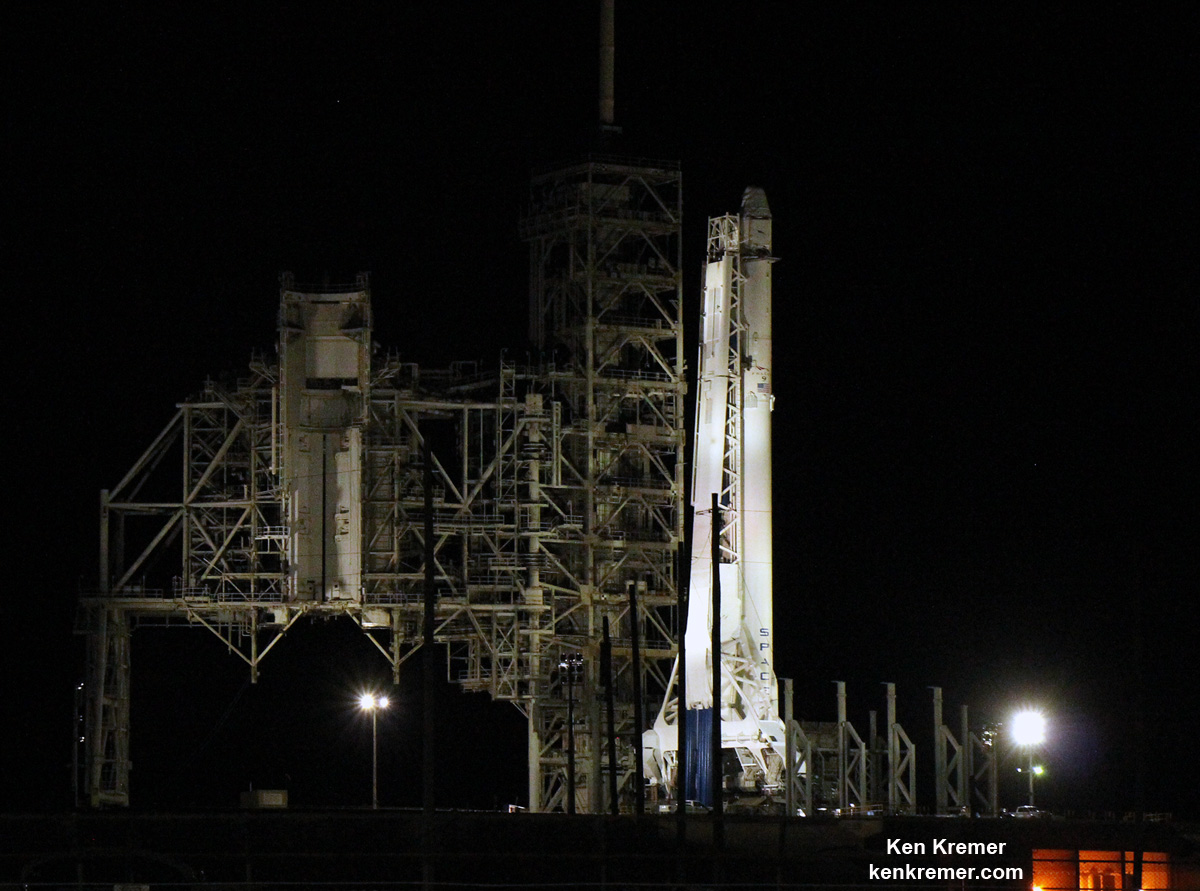
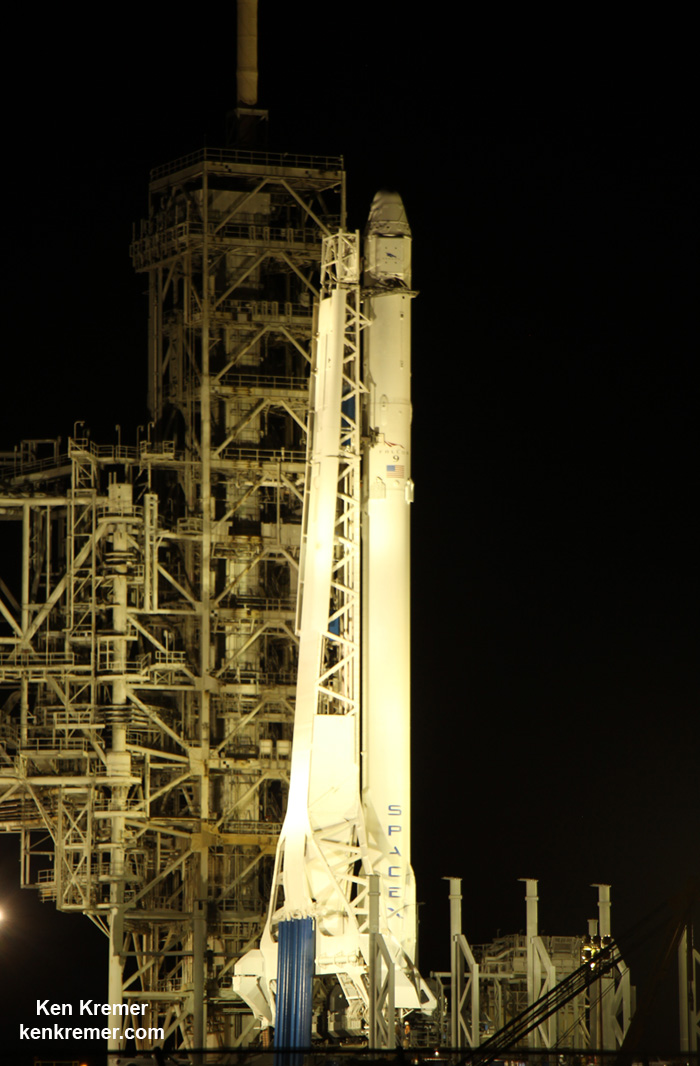
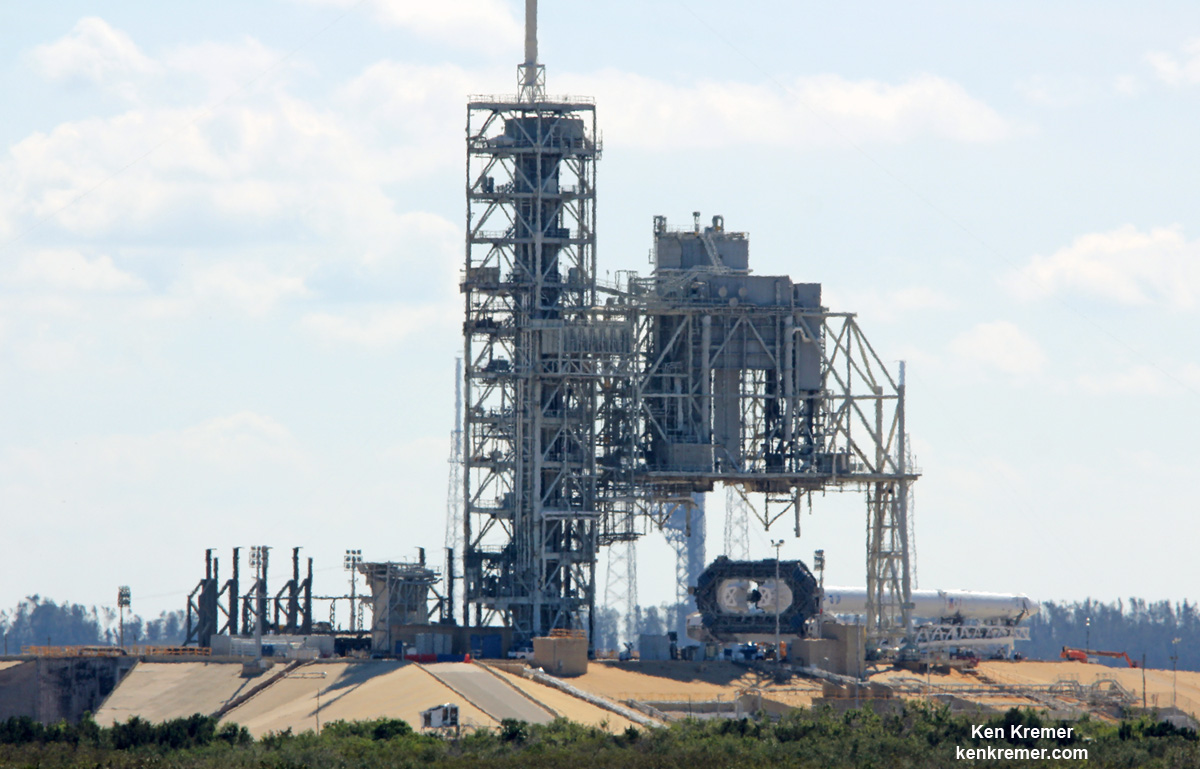
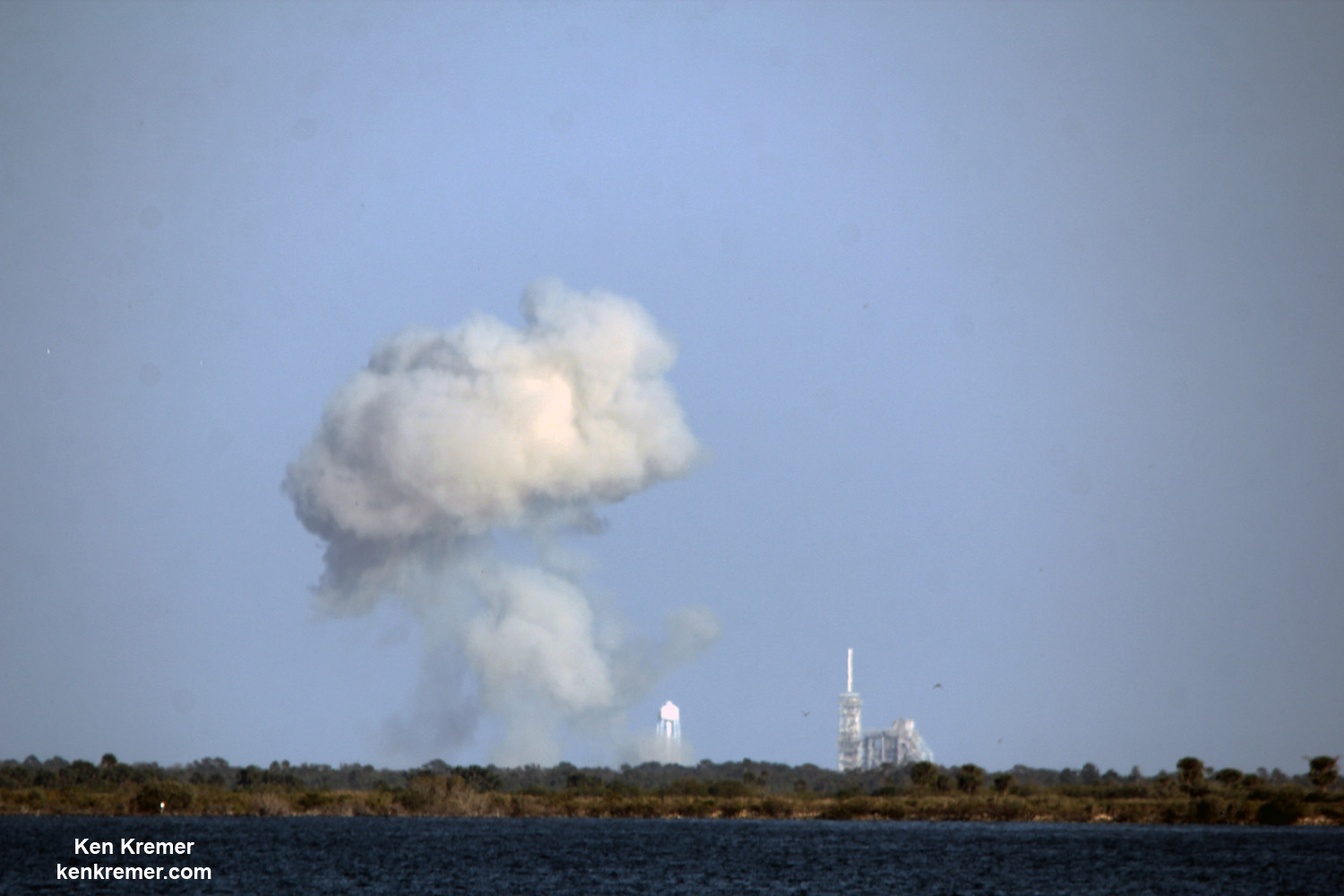
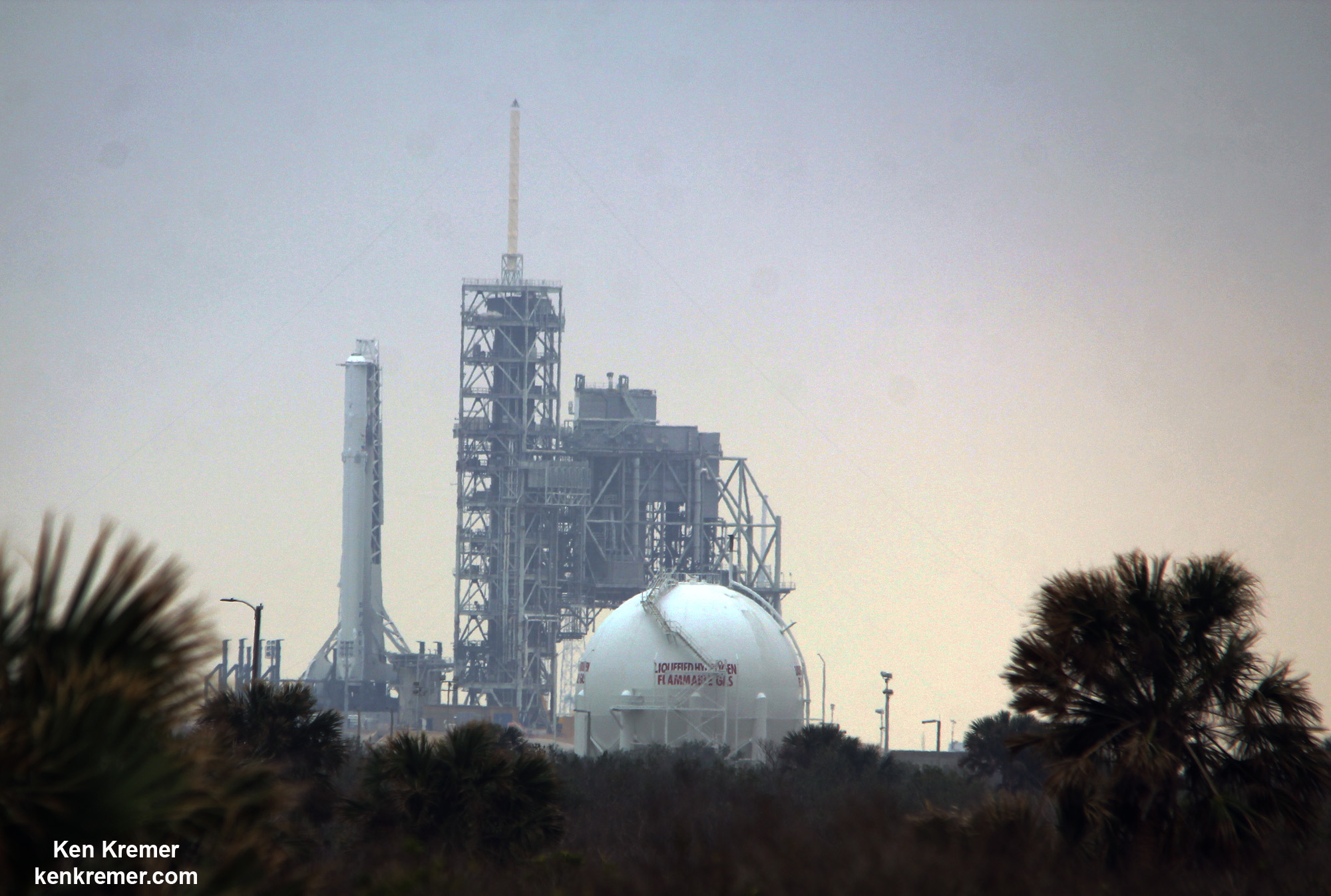
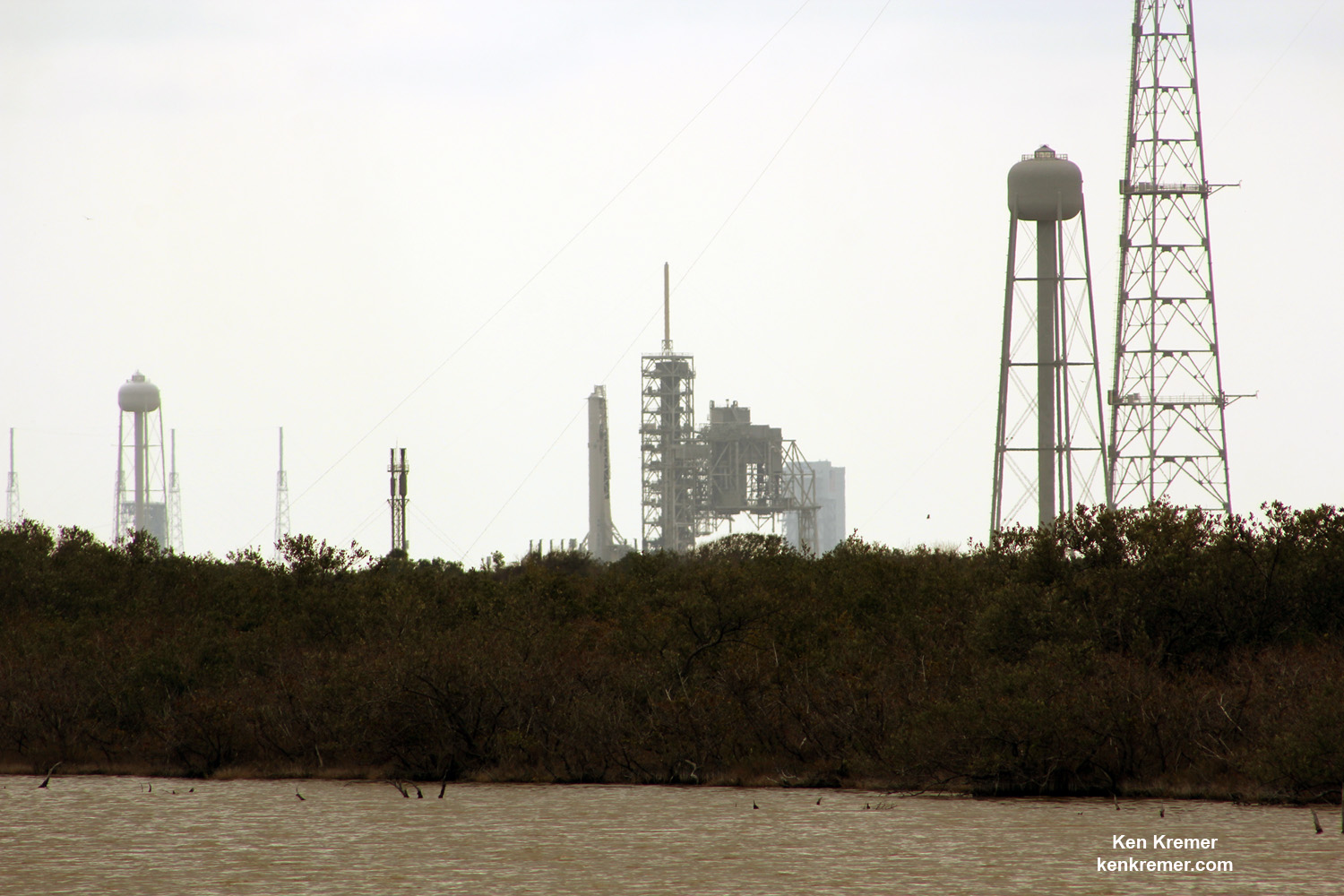
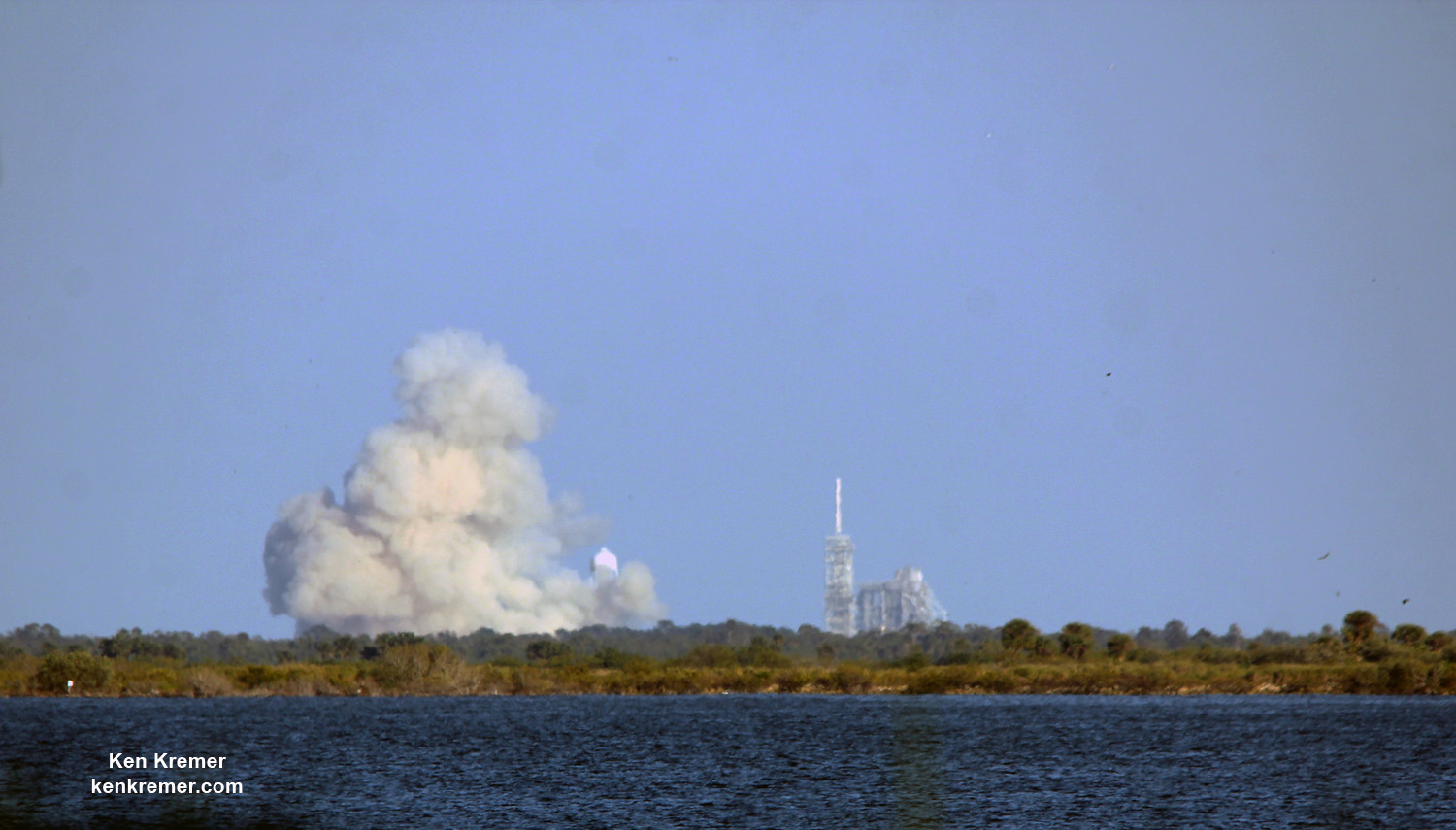
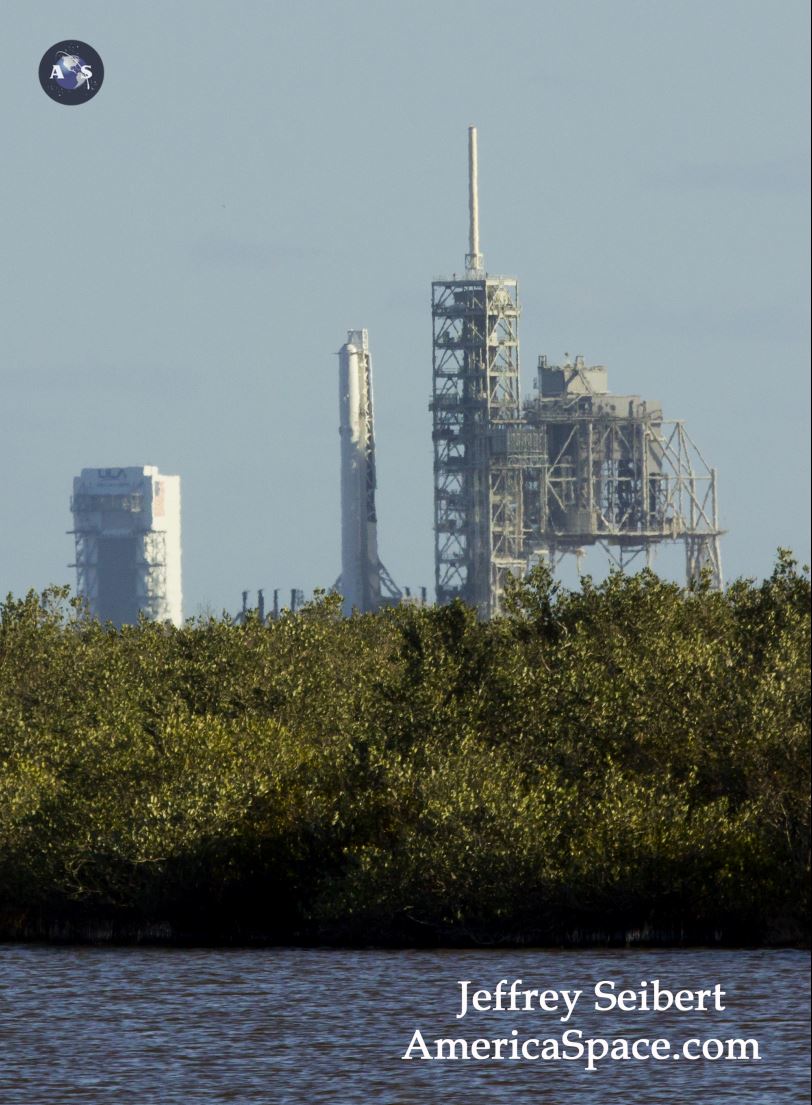
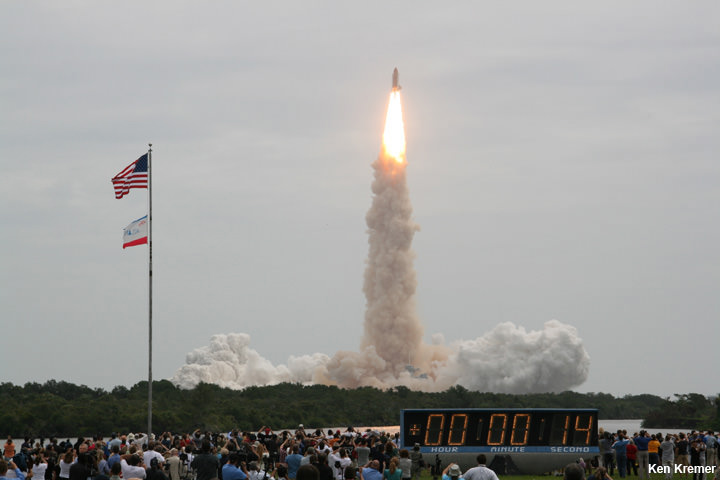
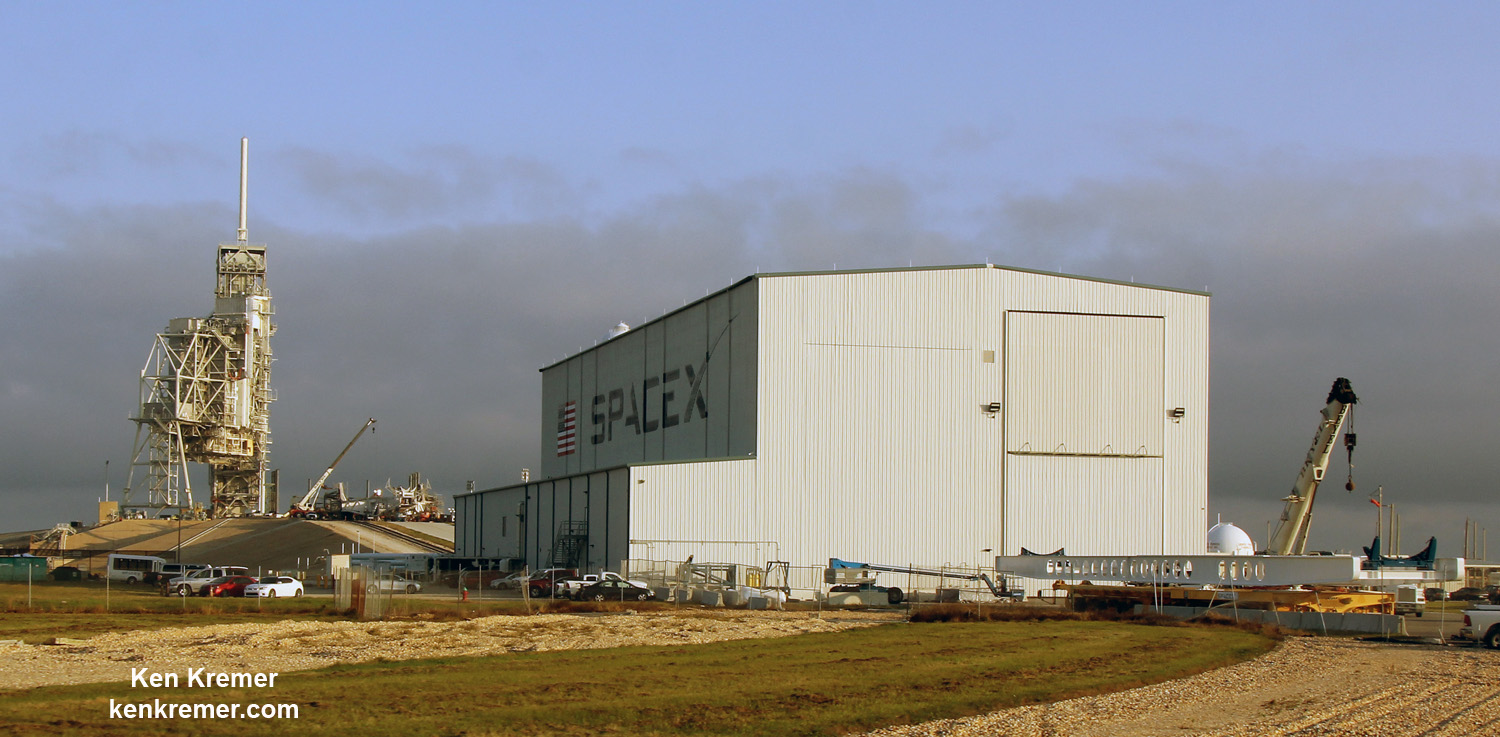
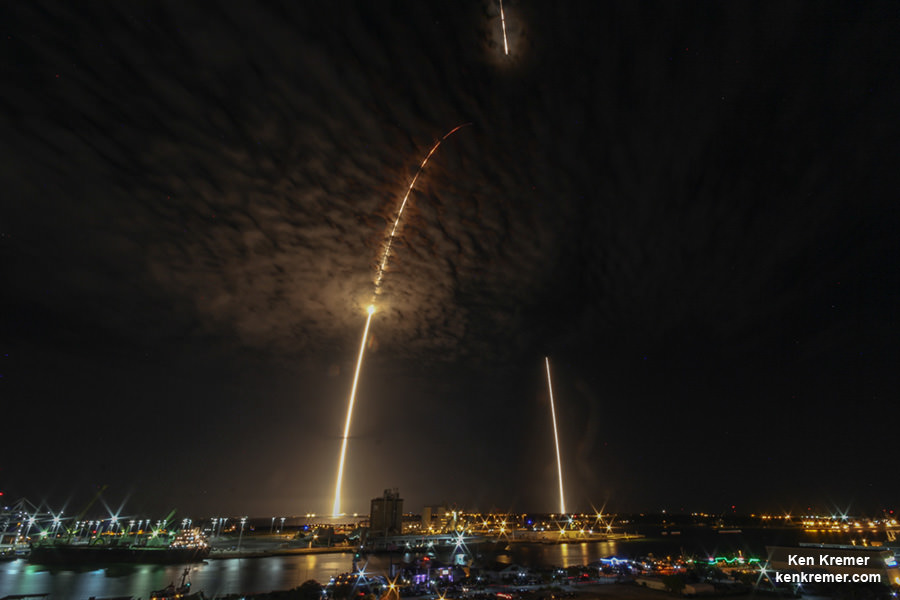
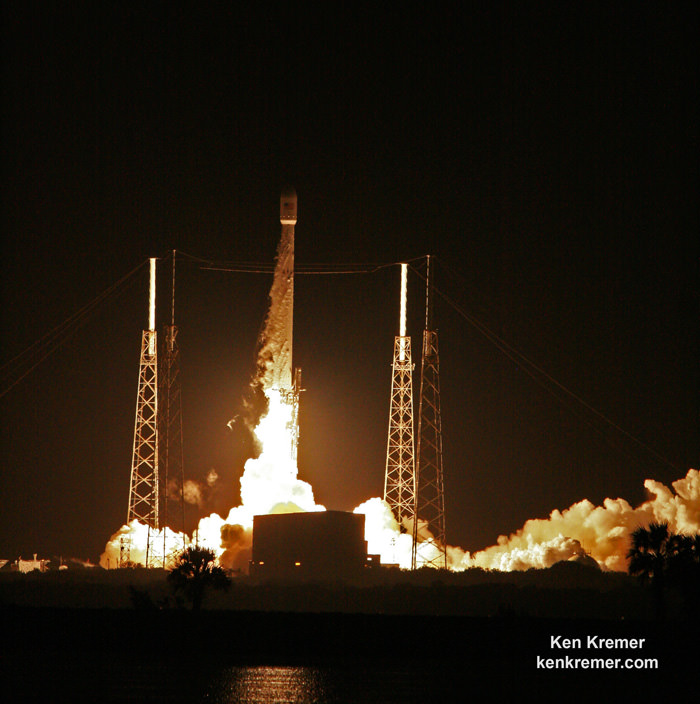
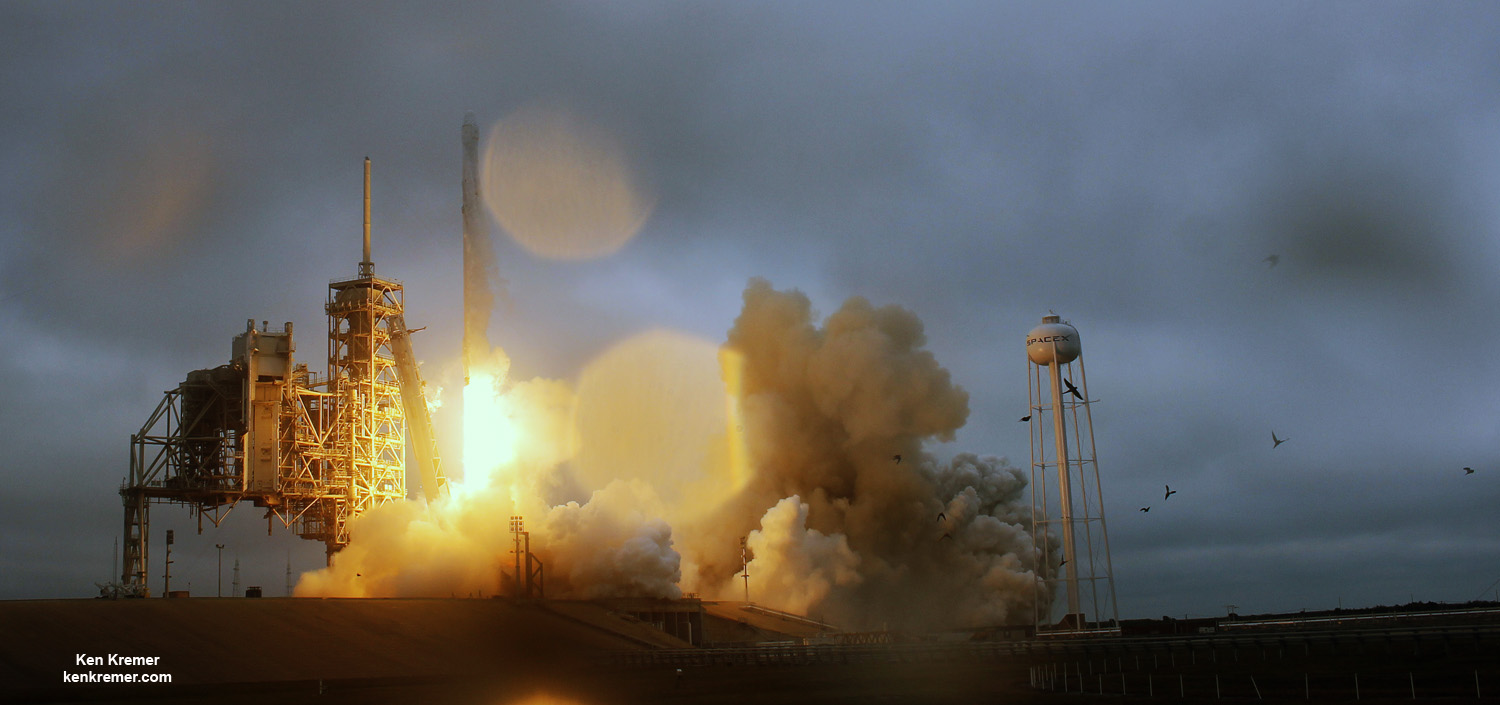
Dragon reached the station four days after it was launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) on Sunday, Feb. 19 on the first Falcon 9 rocket ever to blast off from historic launch pad 39A in a blaze of glory.
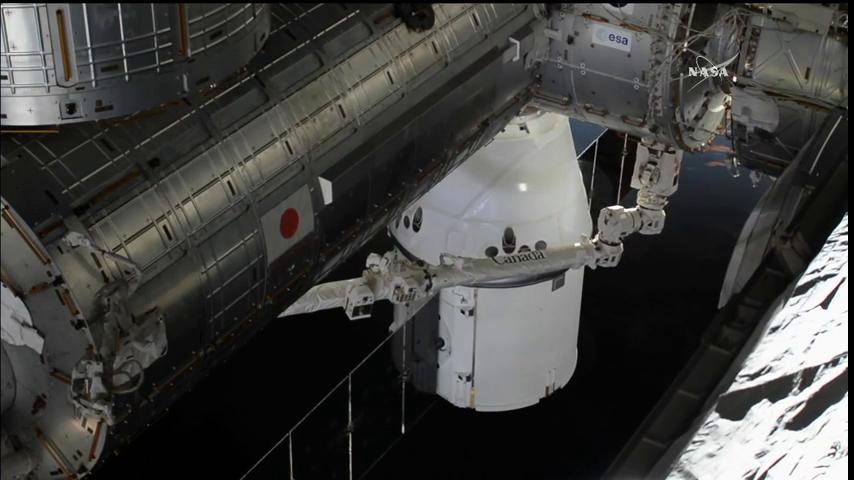
Astronauts Thomas Pesquet of ESA (European Space Agency) and station commander Shane Kimbrough of NASA deftly maneuvered the space station’s 57.7-foot (17.6-meter) Canadian-built Canadarm2 robotic arm to reach out and flawlessly capture the Dragon CRS-10 spacecraft at about 5:44 a.m. EST early Thursday, after it arrived at the station.

Pesquet and Kimbrough were working at the robotics work station inside the seven windowed Cupola module as they monitored Dragon’s approach for capture by the grappling snares on the terminus of the robotic arm this morning as the station was soaring over the northwest coast of Australia.
“Looks like we have a great Dragon capture,” said capcom astronaut Mike Hopkins.
“We want to congratulate all the teams working around the world for the successful arrival,” said Pesquet.
The million pound station is orbiting approximately 250 miles (400 km) above Earth.
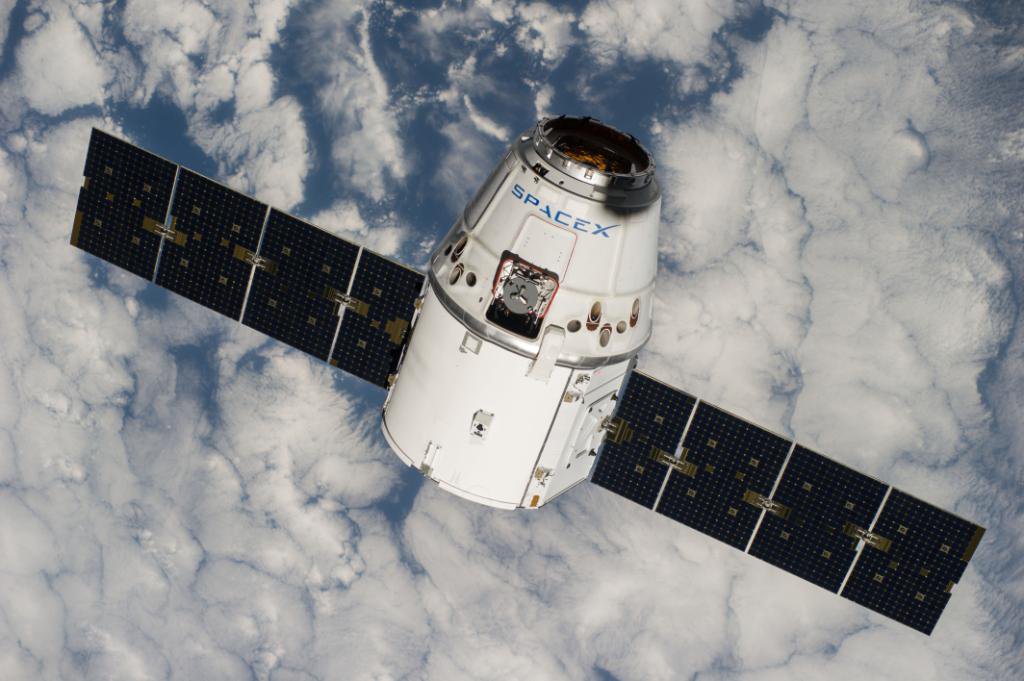

The commercial Dragon cargo freighter arrived about 16 minutes earlier than originally planned.
The duo were assisted by experienced NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson. The 57 year old Whitson will soon set a record for most time spent in space by an American on April 24.
The gumdrop shaped Dragon cargo freighter slowly and methodically approached the station and the capture point through the required approach corridor during the final stages of the orbital chase.
After hovering at the capture point in free drift at a distance of about 34 feet (11 m) from the orbiting outpost, the crew members extended the robotic arm and Dragon was successfully plucked from free space using Canardarm2 at the grapple fixture located on the side of the supply ship.
The entire thrilling approach and grappling sequence was broadcast live on NASA TV.

Robotics officers on the ground at the NASA’s Johnson Space Center then took over and berthed Dragon to the Earth facing port on the Harmony module at about 8 a.m. as the mated craft were soaring over central America.
16 latches and bolts on the stations Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) will hold Dragon firmly in place for a hard mate to the stations Harmony module.
4 gangs of 4 bolts were driven into place with ground commands from the robotics officer to firmly bolt Dragon to the nadir port on Harmony.
The second stage capture and Dragon installation was confrmed at 8:12 a.m. Feb 23 as the craft were flying over the US East Coast.
“Today’s’ re-rendezvous has gone by the book,” said NASA commentator Rob Navias.
“Dragon systems are in excellent shape.”
“There have been no issues and everything has gone as planned.”
“Today was smooth sailing as Dragon arrived below the space station and maneuvered its way through a carefully choreographed procedure to the grapple position for rendezvous and capture.”
“Dragon is now firmly attached to the International Space Station and the crew will begin unloading critical science payloads and supplies this afternoon.”
“Today’s’ re-rendezvous has gone by the book,” said NASA commentator Rob Navias.
“Dragon systems are in excellent shape.”
“There have been no issues and everything has gone as planned.”
Yesterday’s rendezvous was automatically aborted when a bad bit of navigational data was uplinked to Dragons relative GPS navigation system as it was about 0.7 miles below the station.
“The Dragon’s computers received an incorrect navigational update, triggering an automatic wave off. Dragon was sent on a “racetrack” trajectory in front of, above and behind the station for today’s second rendezvous attempt.”
There was never any danger to the crew, space station or Dragon. It merely arrived a day later than planned as it is fully equipped to do if needed.
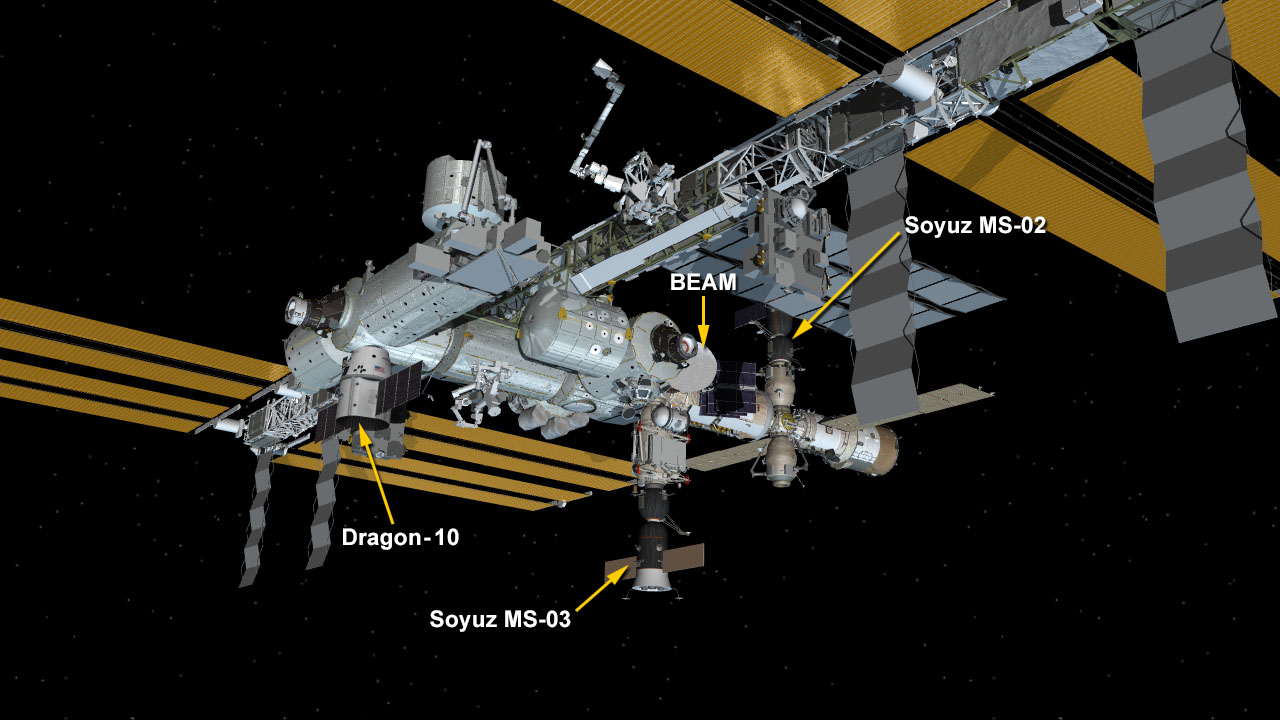
CRS-10 counts as the company’s tenth scheduled flight to deliver supplies, science experiments and technology demonstrations to the International Space Station (ISS).
The Dragon is the first of two cargo craft arriving at the station over two consecutive days.
The unpiloted Russian Progress 66 supply ship launched yesterday from Baikonur is slated to arrive early Friday morning with 2.9 tons of supplies. It will automatically dock at the Pirs docking module at about 3:45 a.m., with a trio of Russian cosmonauts monitoring all the action.
After conducting leak checks, the crew plans to open the hatch to Dragon later today.
They will quickly begin removing the highest priority science investigations and gear first.
Dragon will remain at the station for about 30 days.
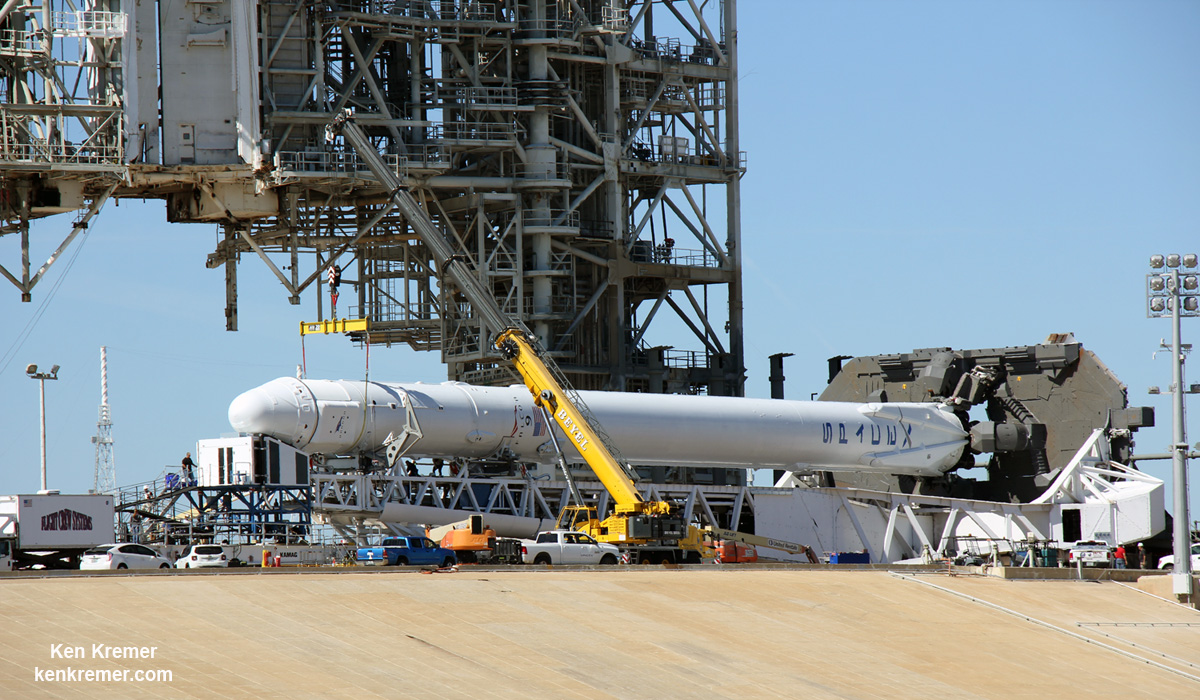

1000 pounds of ‘late stow’ experiments were loaded the day before the originally planned Feb. 18 liftoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
Dragon was successfully launched from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center atop the 213-foot-tall (65-meter) SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 9:38 a.m. EST on Feb. 19, 2017 from historic Launch Complex 39A to low Earth orbit.
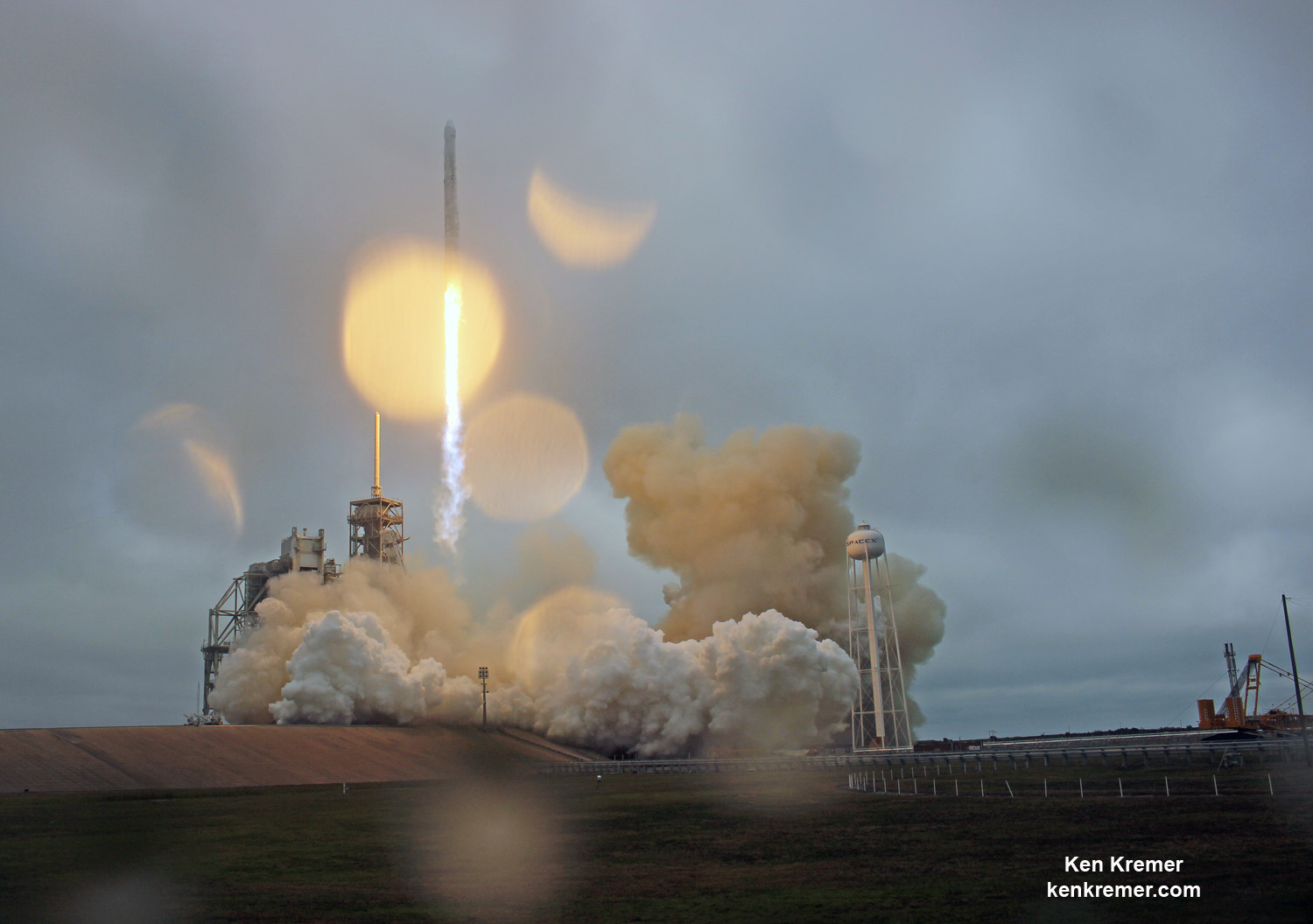

Dragon is carrying more than 5500 pounds of equipment, gear, food, crew supplies, hardware and NASA’s Stratospheric Aerosol Gas Experiment III (SAGE III) ozone mapping science payload in support of the Expedition 50 and 51 crew members.
SAGE III will measure stratospheric ozone, aerosols, and other trace gases by locking onto the sun or moon and scanning a thin profile of the atmosphere. It is one of NASA’s longest running earth science programs.
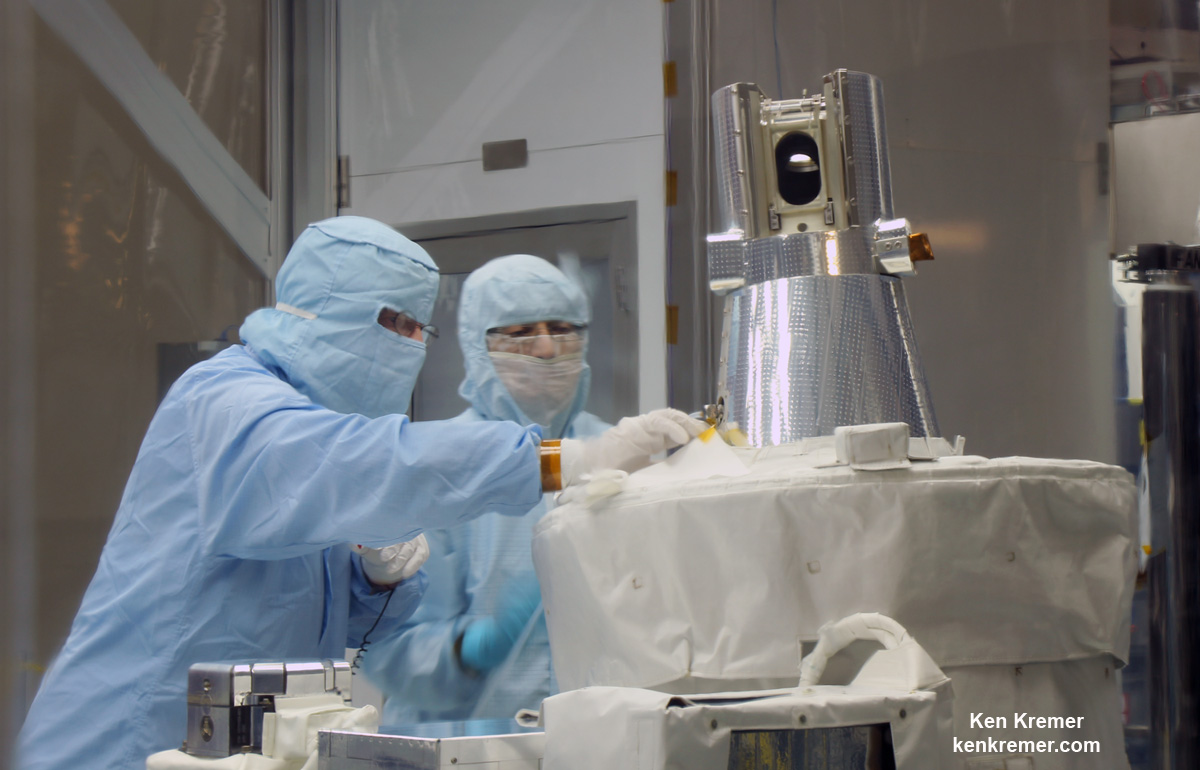

The LIS lightning mapper will measure the amount, rate and energy of lightning as it strikes around the world from the altitude of the ISS as it orbits Earth. Its data will complement that from the recently orbited GLM lighting mapper lofted to geosynchronous aboard the NASA/NOAA GOES-R spacecraft instrument.
NASA’s RAVEN experiment will test autonomous docking technologies for spacecraft.
SAGE III and RAVEN were stowed in the Dragon’s unpressurized truck.
The research supplies and equipment brought up by Dragon will support over 250 scientific investigations to advance knowledge about the medical, psychological and biomedical challenges astronauts face during long-duration spaceflight.
The 40 mice will be used in a wound healing experiment to test therapies in microgravity.
An advanced plant growth habitat will launch soon to test better technologies for growing crops in space that could contribute to astronauts nutrition on long duration spaceflights.
SpaceX Dragon CRS-10 Cargo manifest from NASA:
TOTAL CARGO: 5489.5 lbs. / 2490 kg
TOTAL PRESSURIZED CARGO WITH PACKAGING: 3373.1 lbs. / 1530 kg
• Science Investigations 1613.8 lbs. / 732 kg
• Crew Supplies 652.6 lbs. / 296 kg
• Vehicle Hardware 842.2 lbs. / 382 kg
• Spacewalk Equipment 22.0 lbs. / 10 kg
• Computer Resources 24.2 lbs. / 11 kg
• Russian Hardware 48.5 lbs. / 22 kg
UNPRESSURIZED
• SAGE-III & STP-H5 Lightning Imaging Sensor 2116.4 lbs. / 960 kg

Watch for Ken’s onsite CRS-10 mission reports direct from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.























