Cooling things down in space is trickier than it might sound. But that is exactly the process the James Webb telescope is going through right now. Getting down to cryogenic temperature is imperative for its infrared imaging systems to work correctly. While the telescope has already started, it will be another few weeks before the process is complete, and it’s ready to start capturing its first groundbreaking infrared images of the universe.
Continue reading “Webb is Cool, but it Still Needs to get Cooler”Could Astronauts Hibernate on Long Space Voyages?
A renewed era of space exploration is upon us, and many exciting missions will be headed to space in the coming years. These include crewed missions to the Moon and the creation of permanent bases there. Beyond the Earth-Moon system, there are multiple proposals for crewed missions to Mars and beyond. This presents significant challenges since a one-way transit to Mars can take six to nine months. Even with new propulsion technologies like nuclear rockets, it could still take more than three months to get to Mars.
In addition to the physical and mental stresses imposed on the astronauts by the duration and long-term exposure to microgravity and radiation, there are also the logistical challenges these types of missions will impose (i.e., massive spacecraft, lots of supplies, and significant expense). Looking for alternatives, the European Space Agency (ESA) is investigating hibernation technology that would allow their astronauts to sleep for much of the voyage and arrive at Mars ready to explore.
Continue reading “Could Astronauts Hibernate on Long Space Voyages?”NASA Announces 14 New “Tipping Point” Technologies for its Lunar Exploration
In four years, NASA plans to return astronauts to the Moon as part of Project Artemis. To ensure the success of this endeavor, as well as the creation of a program of sustainable lunar exploration by the end of the decade, NASA has partnered with multiple entities in the commercial space sector. Recently, they announced that contracts will be awarded to 14 additional companies to develop a range of proposed technologies.
These proposals are part of NASA’s fifth competitive Tipping Point solicitation, one of many private-public partnership programs overseen by NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD). For this latest solicitation, Tipping Point is awarding contracts with a combined value of over $370 million for technology demonstrations that will facilitate future lunar missions and commercial space capabilities.
Continue reading “NASA Announces 14 New “Tipping Point” Technologies for its Lunar Exploration”Pros and Cons of Various Methods of Interstellar Travel

It’s a staple of science fiction, and something many people have fantasized about at one time or another: the idea of sending out spaceships with colonists and transplanting the seed of humanity among the stars. Between discovering new worlds, becoming an interstellar species, and maybe even finding extra-terrestrial civilizations, the dream of spreading beyond the Solar System is one that can’t become reality soon enough!
For decades, scientists have contemplated how humanity might one-day reach achieve this lofty goal. And the range of concepts they have come up with present a whole lot of pros and cons. These pros and cons were raised in a recent study by Martin Braddock, a member of the Mansfield and Sutton Astronomical Society, a Fellow of the Royal Society of Biology, and a Fellow of the Royal Astronomical Society. Continue reading “Pros and Cons of Various Methods of Interstellar Travel”
Is Human Hibernation Possible? Going to Sleep for Long Duration Spaceflight
We’ve spent a few articles on Universe Today talking about just how difficult it’s going to be to travel to other stars. Sending tiny unmanned probes across the vast gulfs between stars is still mostly science fiction. But to send humans on that journey? That’s just a level of technology beyond comprehension.
For example, the nearest star is Proxima Centauri, located a mere 4.25 light years away. Just for comparison, the Voyager spacecraft, the most distant human objects ever built by humans, would need about 50,000 years to make that journey.
I don’t know about you, but I don’t anticipate living 50,000 years. No, we’re going to want to make the journey more quickly. But the problem, of course, is that going more quickly requires more energy, new forms of propulsion we’ve only starting to dream up. And if you go too quickly, mere grains of dust floating through space become incredibly dangerous.
Based on our current technology, it’s more likely that we’re going to have to take our time getting to another star.
And if you’re going to go the slower route, you’ve got a couple of options. Create a generational ship, so that successive generations of humans are born, live out their lives, and then die during the hundreds or even thousands of year long journey to another star.

Imagine you’re one of the people destined to live and die, never reaching your destination. Especially when you look out your window and watch a warp ship zip past with all those happy tourists headed to Proxima Centauri, who were start enough to wait for warp drives to be invented.
No, you want to sleep for the journey to the nearest star, so that when you get there, it’s like no time passed. And even if warp drive did get invented while you were asleep, you didn’t have to see their smug tourist faces as they zipped past.
Is human hibernation possible? Can we do it long enough to survive a long-duration spaceflight journey and wake up again on the other side?
Before I get into this, we’re just going to have to assume that we never merge with our robot overlords, upload ourselves into the singularity, and effortlessly travel through space with our cybernetic bodies.
For some reason, that whole singularity thing never worked out, or the robots went on strike and refused to do our space exploration for us any more. And so, the job of space travel fell to us, the fragile, 80-year lifespanned mammals. Exploring the worlds within the Solar System and out to other stars, spreading humanity into the cosmos.

Come on, we know it’ll totally be the robots. But that’s not what the science fiction tells us, so let’s dig into it.
We see animals, and especially mammals hibernating all the time in nature. In order to be able survive over a harsh winter, animals are capable of slowing their heart rate down to just a few beats a minute. They don’t need to eat or drink, surviving on their fat stores for months at a time until food returns.
It’s not just bears and rodents that can do it, by the way, there are actually a couple of primates, including the fat-tailed dwarf lemur from Madagascar. That’s not too far away on the old family tree, so there might be hope for human hibernation after all.
In fact, medicine is already playing around with human hibernation to improve people’s chances to survive heart attacks and strokes. The current state of this technology is really promising.
They use a technique called therapeutic hypothermia, which lowers the temperature of a person by a few degrees. They can use ice packs or coolers, and doctors have even tried pumping a cooled saline solution through the circulatory system. With the lowered temperature, a human’s metabolism decreases and they fall unconscious into a torpor.
But the trick is to not make them so unconscious that they die. It’s a fine line.
The results have been pretty amazing. People have been kept in this torpor state for up to 14 days, going through multiple cycles.
The therapeutic use of this torpor is still under research, and doctors are learning if it’s helpful for people with heart attacks, strokes or even the progression of diseases like cancer. They’re also trying to figure out if there are any downsides, but so far, there don’t seem to be any long-term problems with putting someone in this torpor state.
A few years ago, SpaceWorks Enterprises delivered a report to NASA on how they could use this therapeutic hypothermia for long duration spaceflight within the Solar System.
Currently, a trip to Mars takes about 6-9 months. And during that time, the human passengers are going to be using up precious air, water and food. But in this torpor state, SpaceWorks estimates that the crew will a reduction in their metabolic rate of 50 to 70%. Less metabolism, less resources needed. Less cargo that needs to be sent to Mars.

The astronauts wouldn’t need to move around, so you could keep them nice and snug in little pods for the journey. And they wouldn’t get into fights with each other, after 6-9 months of nothing but day after day of spaceflight.
We know that weightlessness has a negative effect on the body, like loss of bone mass and atrophy of muscles. Normally astronauts exercise for hours every day to counteract the negative effects of the reduced gravity. But SpaceWorks thinks it would be more effective to just put the astronauts into a rotating module and let artificial gravity do the work of maintaining their conditioning.
They envision a module that’s 4 metres high and 8 metres wide. If you spin the habitat at 20 revolutions per minute, you give the crew the equivalent of Earth gravity. Go at only 11.8 RPM and it’ll feel like Mars gravity. Down to 7.8 and it’s lunar gravity.
Normally spinning that fast in a habitat that small would be extremely uncomfortable as the crew would experience different forces at different parts of their body. But remember, they’ll be in a state of torpor, so they really won’t care.

Current plans for sending colonists to Mars would require 40 ton habitats to support 6 people on the trip. But according to SpaceWorks, you could reduce the weight down to 15 tons if you just let them sleep their way through the journey. And the savings get even better with more astronauts.
The crew probably wouldn’t all sleep for the entire journey. Instead, they’d sleep in shifts for a few weeks. Taking turns to wake up, check on the status of the spacecraft and crew before returning to their cryosleep caskets.
What’s the status of this now? NASA funded stage 1 of the SpaceWorks proposal, and in July, 2016 NASA moved forward with Phase 2 of the project, which will further investigate this technique for Mars missions, and how it could be used even farther out in the Solar System.
Elon Musk should be interested in seeing their designs for a 100-person module for sending colonists to Mars.

In addition, the European Space Agency has also been investigating human hibernation, and a possible way to enable long-duration spaceflight. They have plans to test out the technology on various non-hibernating mammals, like pigs. If their results are positive, we might see the Europeans pushing this technology forward.
Can we go further, putting people to sleep for decades and maybe even the centuries it would take to travel between the stars?
Right now, the answer is no. We don’t have any technology at our disposal that could do this. We know that microbial life can be frozen for hundreds of years. Right now there are parts of Siberia unfreezing after centuries of permafrost, awakening ancient microbes, viruses, plants and even animals. But nothing on the scale of human beings.
When humans freeze, ice crystals form in our cells, rupturing them permanently. There is one line of research that offers some hope: cryogenics. This process replaces the fluids of the human body with an antifreeze agent which doesn’t form the same destructive crystals.
Scientists have successfully frozen and then unfrozen 50-milliliters (almost a quarter cup) of tissue without any damage.
In the next few years, we’ll probably see this technology expanded to preserving organs for transplant, and eventually entire bodies, and maybe even humans. Then this science fiction idea might actually turn into reality. We’ll finally be able to sleep our way between the stars.
Who Discovered Helium?
Scientists have understood for some time that the most abundant elements in the Universe are simple gases like hydrogen and helium. These make up the vast majority of its observable mass, dwarfing all the heavier elements combined (and by a wide margin). And between the two, helium is the second lightest and second most abundant element, being present in about 24% of observable Universe’s elemental mass.
Whereas we tend to think of Helium as the hilarious gas that does strange things to your voice and allows balloons to float, it is actually a crucial part of our existence. In addition to being a key component of stars, helium is also a major constituent in gas giants. This is due in part to its very high nuclear binding energy, plus the fact that is produced by both nuclear fusion and radioactive decay. And yet, scientists have only been aware of its existence since the late 19th century.
NASA Investigating Deep-Space Hibernation Technology
Manned missions to deep space present numerous challenges. In addition to the sheer amount of food, water and air necessary to keep a crew alive for months (or years) at a time, there’s also the question of keeping them busy for the entirety of a long-duration flight. Exercise is certainly an option, but the necessary equipment will take up space and be a drain on power.
In addition, they’ll need room to move around, places to sleep, eat, work, and relax during their down time. Otherwise, they will be at risk of succumbing to feelings of claustrophobia, anxiety, insomnia, and depression – among other things.
Continue reading “NASA Investigating Deep-Space Hibernation Technology”
NASA Tanks: Not Just Heavy Metal Any More
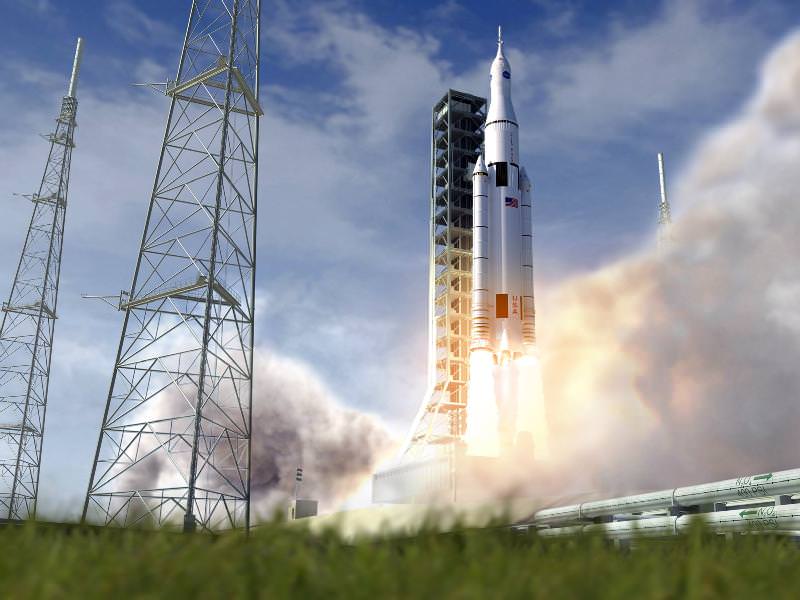

NASA’s future in fuels will see less heavy metal. Literally.
The agency just finished testing on a composite propellant tank that holds cryogenics, or super-chilled gases that are commonly used as rocket fuel (such as for the space shuttle). The agency brought the test tank down to -423 degrees Fahrenheit, put it through a few cycles and ramped up the internal pressure.
Composites are lighter material than the traditional metals that are used to hold these gases. NASA is excitedly throwing out descriptors such as “game-changing” when it talks about this, and has some reason to do so: composites are lighter than metals.
The light weight of composite tanks makes them lighter to lift off the ground. This reduces the costs of launch, which in turn reduces the overall cost of a mission. That will make penny-counters at the agency happier as the agency battles for funding dollars in fiscal 2014 and beyond.
The first of these tanks is likely to be used in the upper stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket, which is under development right now. That’s the rocket that’s supposed to send the Orion spacecraft (aiming for a 2014 test flight) into space in the latter years of this decade.
“The tank manufacturing process represents a number of industry breakthroughs, including automated fiber placement of oven-cured materials, fiber placement of an all-composite tank wall design that is leak-tight, and a tooling approach that eliminates heavy joints,” stated Dan Rivera, the Boeing cryogenic tank program manager at Marshall.
Boeing and NASA are now working on another composite tank that should be tested at Marshall later in 2013.
Source: NASA