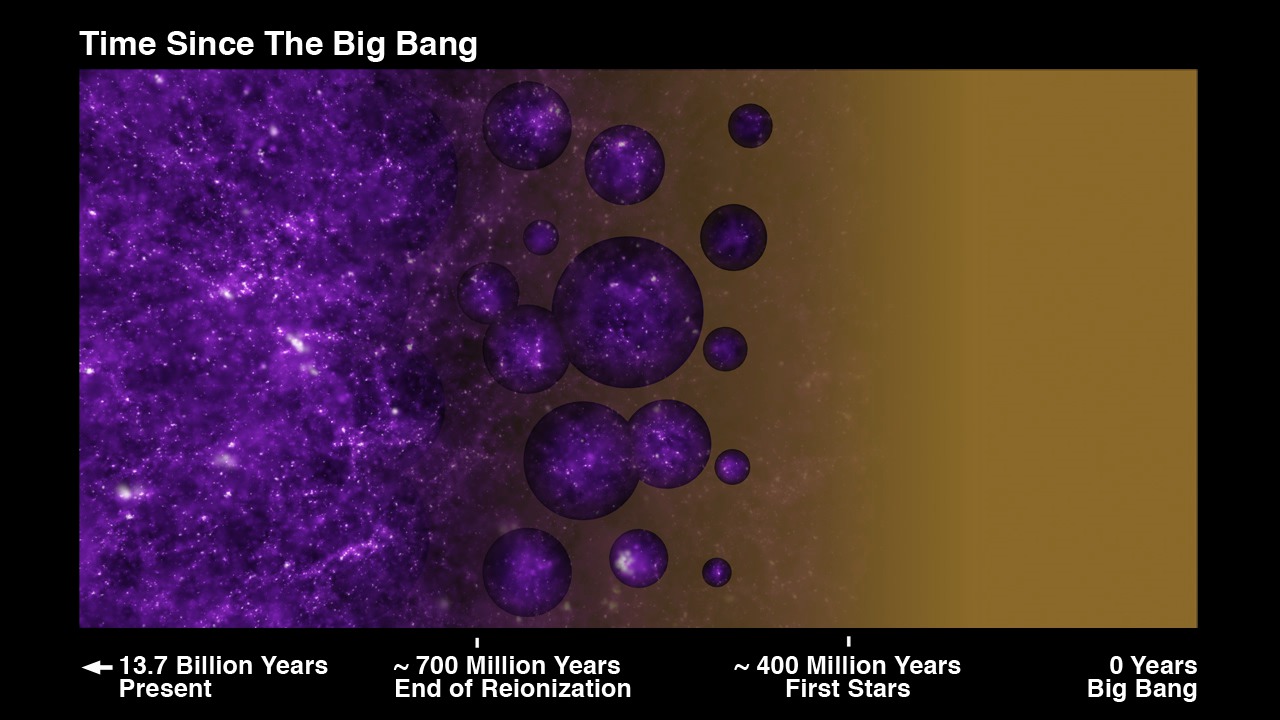
When the James Webb Space Telescope provided astronomers with a glimpse of the earliest galaxies in the Universe, there was some understandable confusion. Given that these galaxies existed during “Cosmic Dawn,” less than one billion years after the Big Bang, they seemed “impossibly large” for their age. According to the most widely accepted cosmological model—the Lambda Cold Dark Matter (LCDM) model—the first galaxies in the Universe did not have enough time to become so massive and should have been more modestly sized.
This presented astronomers with another “crisis in cosmology,” suggesting that the predominant model about the origins and evolution of the Universe was wrong. However, according to a new study by an international team of astronomers, these galaxies are not so “impossibly large” after all, and what we saw may have been the result of an optical illusion. In short, the presence of black holes in some of these early galaxies made them appear much brighter and larger than they actually were. This is good news for astronomers and cosmologists who like the LCDM the way it is!
Continue reading “Remember those Impossible Galaxies Found by JWST? It Turns Out They Were Possible After All”