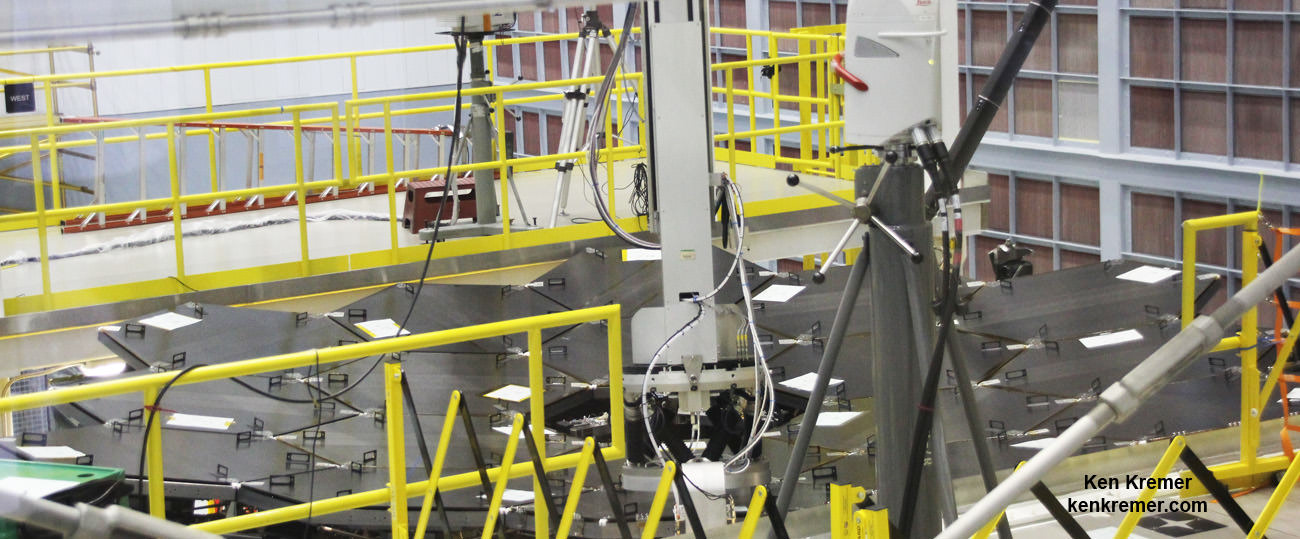

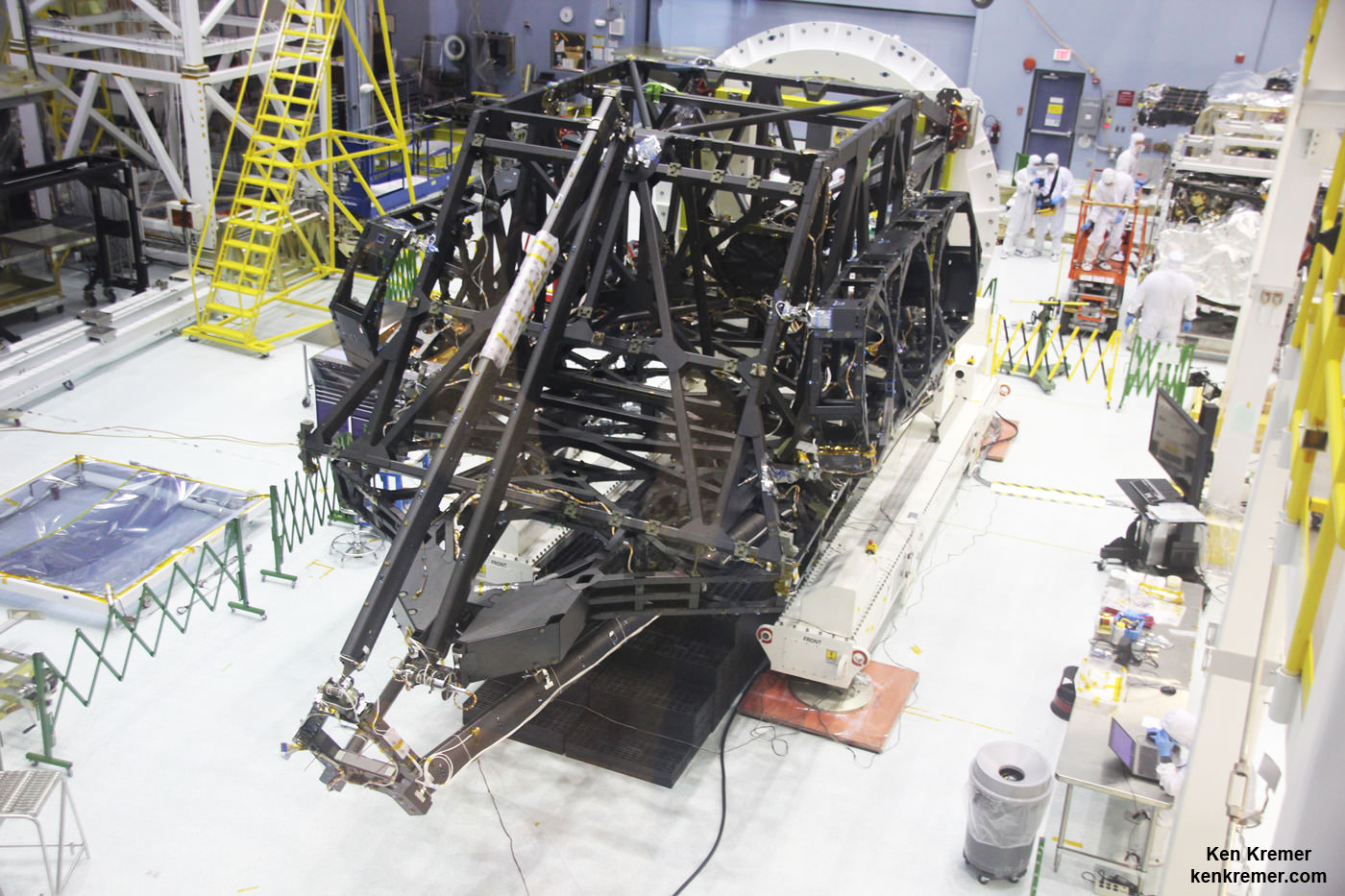
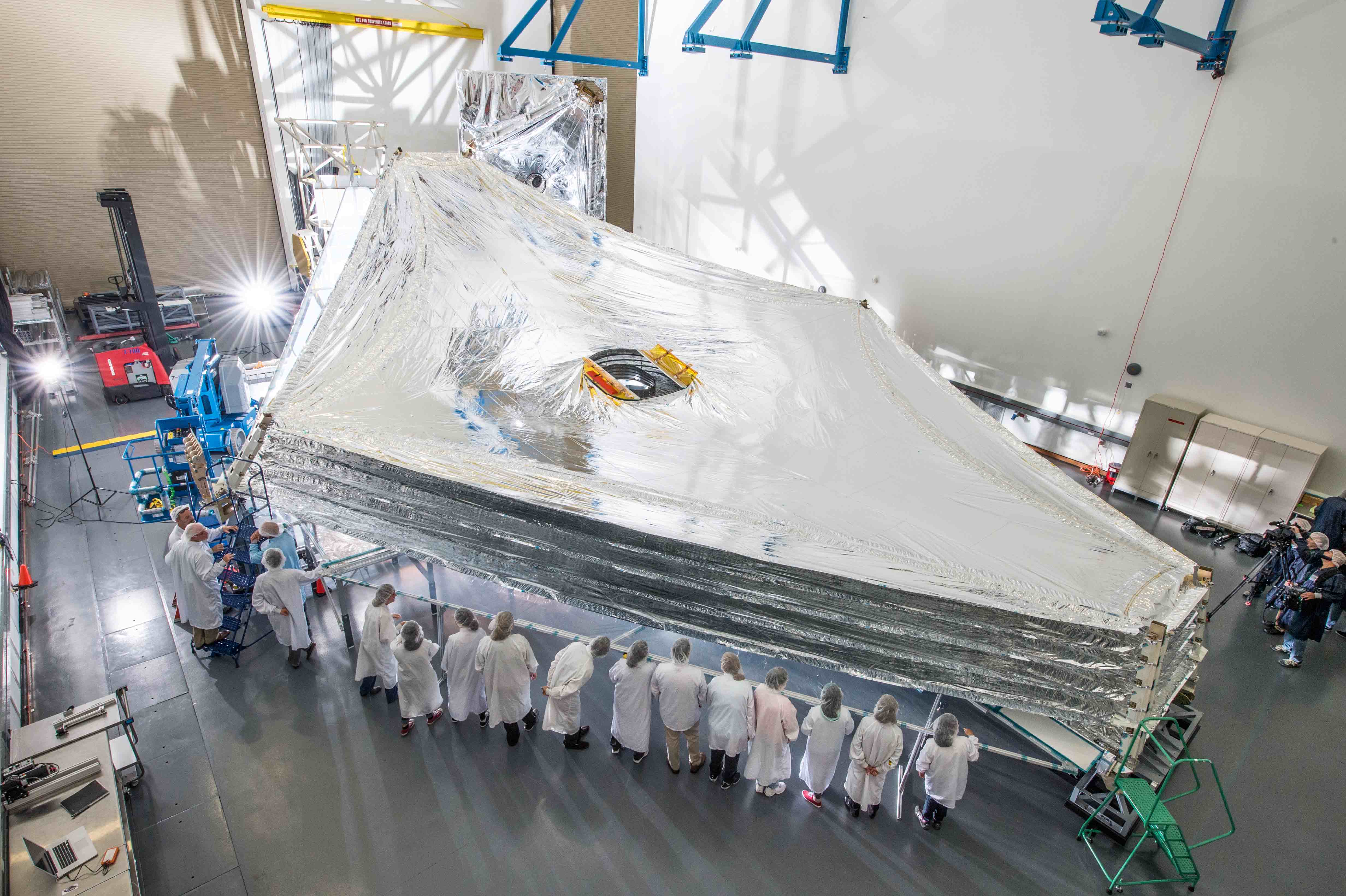
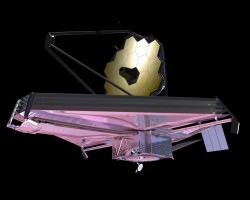
NASA GODDARD SPACE FLIGHT CENTER, MD – All 18 of the primary mirrors have been fully installed onto the flight structure of what will become the biggest and most powerful space telescope ever built by humankind – NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
Completion of the huge and complex primary mirror marks a historic milestone and a banner start to 2016 for JWST, commencing the final assembly phase of the colossal observatory that will revolutionize our understanding of the cosmos and our place it in.
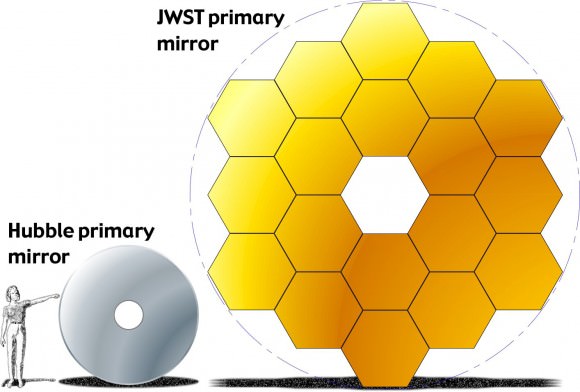
After JWST launches in slightly less than three years time, the gargantuan observatory will significantly exceed the light gathering power of the currently most powerful space telescope ever sent to space – NASA’s Hubble!
Indeed JWST is the scientific successor to NASA’s 25 year old Hubble Space Telescope.
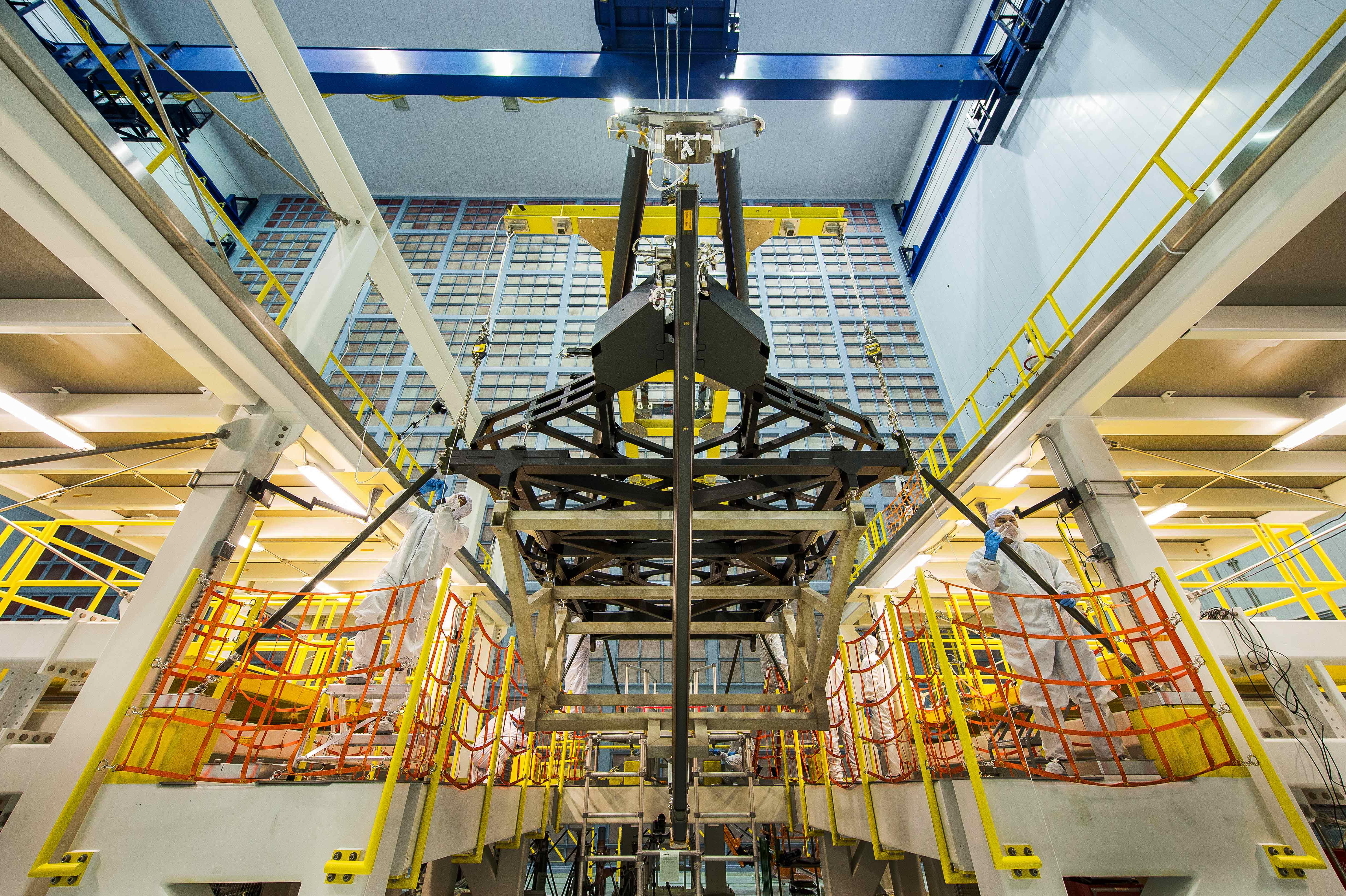
Technicians working inside the massive clean room at the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, have been toiling around the clock 24/7 to fully install all 18 primary mirror segments onto the mirror holding backplane structure. This author witnessed ongoing work in progress during installation of the last of the primary mirrors.
The engineers and scientists kept up the pace of their assembly work over the Christmas holidays and also during January’s record breaking monster Snowzilla storm, that dumped two feet or more of snow across the Eastern US from Washington DC to New York City and temporarily shut down virtually all travel.
The team used a specialized robotic arm functioning like a claw to meticulously latch on to, maneuver and attach each of the 18 primary mirrors onto the telescope structure.
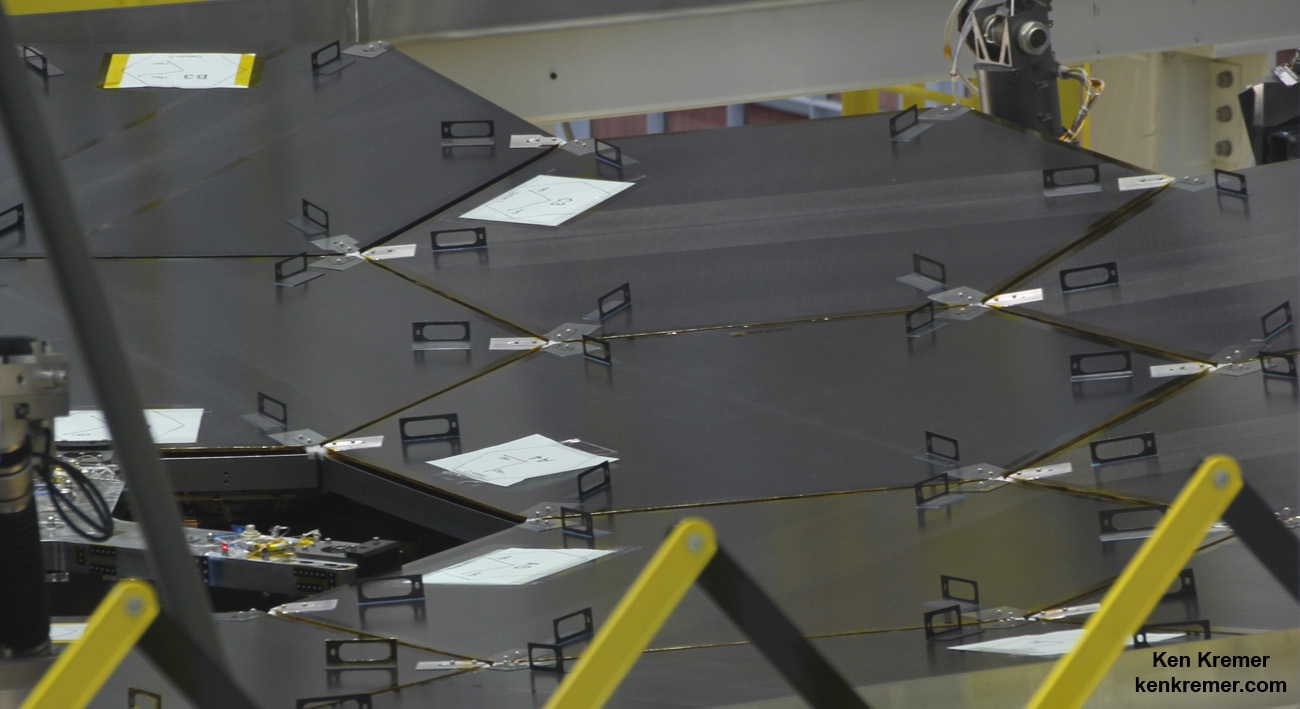
Each of the 18 hexagonal-shaped primary mirror segments measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). They are made of beryllium and about the size of a coffee table.
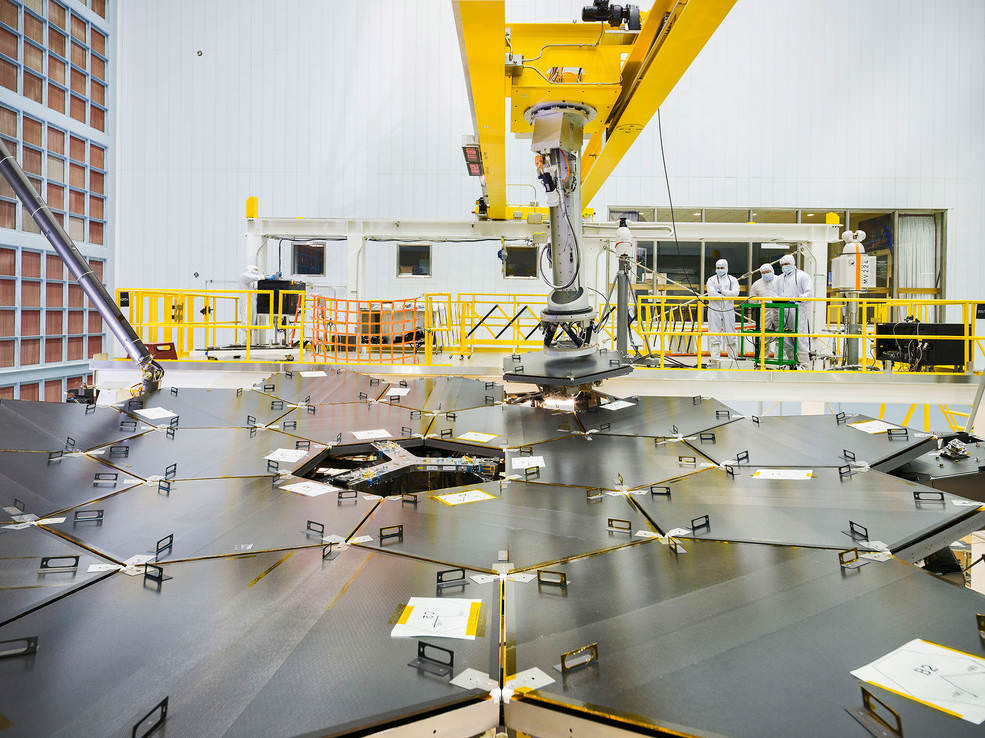

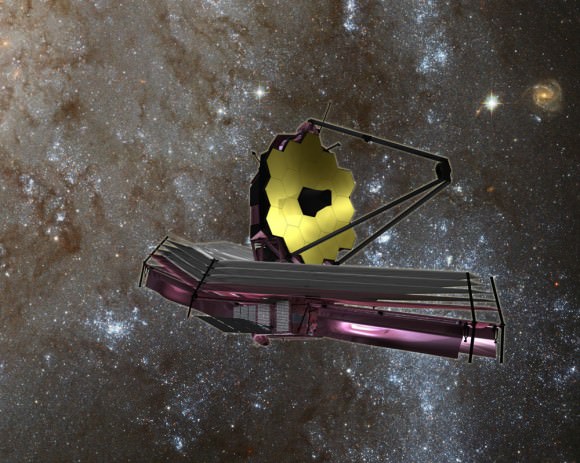
In space, the folded mirror structure will unfold into side by side sections and work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror, unprecedented in size and light gathering capability.
The telescopes mirror assembly is comprised of three segments – the main central segment holding 12 mirrors and a pair of foldable outer wing-like segments that hold three mirrors each.
The painstaking assembly work to piece the primary mirrors together began just before the Thanksgiving 2015 holiday, when the first unit was successfully installed onto the central segment of the mirror holding backplane assembly.
One by one the team populated the telescope structure with the primary mirrors at a pace of roughly two per week since the installations started some two and a half months ago.
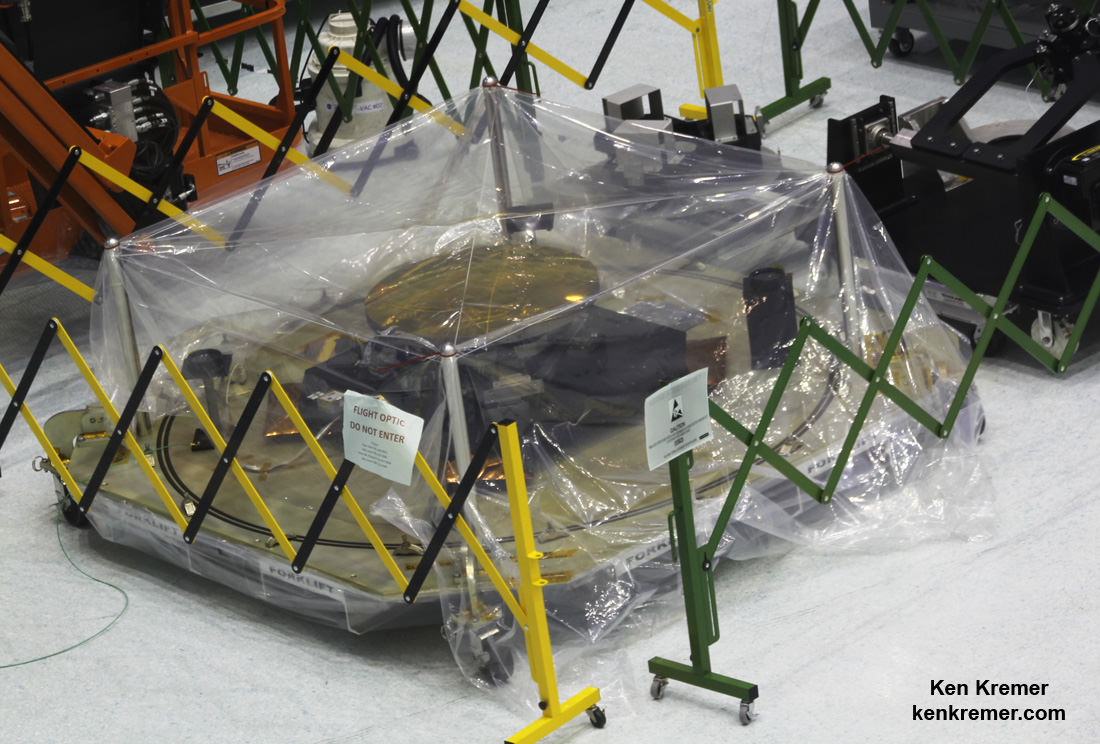
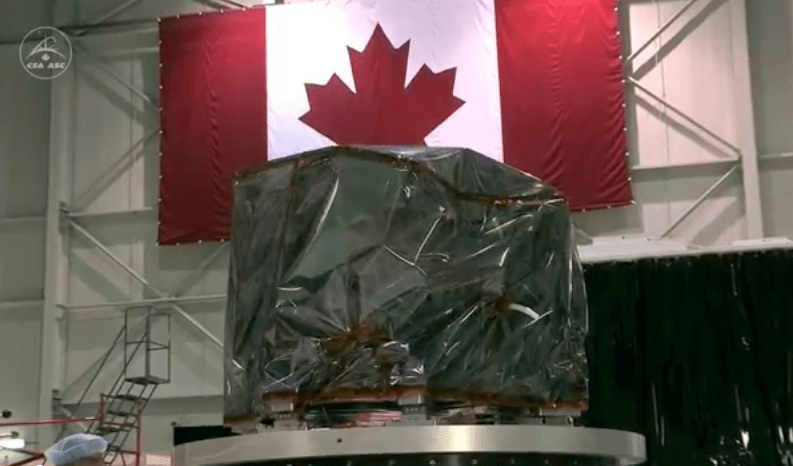
During the installation process each of the gold coated primary mirrors was covered with a black colored cover to protect them from optical contamination.
The mirror covers will be removed over the summer for testing purposes, said Lee Feinberg, optical telescope element manager at Goddard, told Universe Today.
The two wings were unfolded from their stowed-for-launch configuration to the “deployed” configuration to carry out the mirror installation. They will be folded back over into launch configuration for eventual placement inside the payload fairing of the Ariane V ECA booster rocket that will launch JWST three years from now.

“Scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install these incredible, nearly perfect mirrors that will focus light from previously hidden realms of planetary atmospheres, star forming regions and the very beginnings of the Universe,” said John Grunsfeld, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington, in a statement.
“With the mirrors finally complete, we are one step closer to the audacious observations that will unravel the mysteries of the Universe.”
The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope, according to NASA.
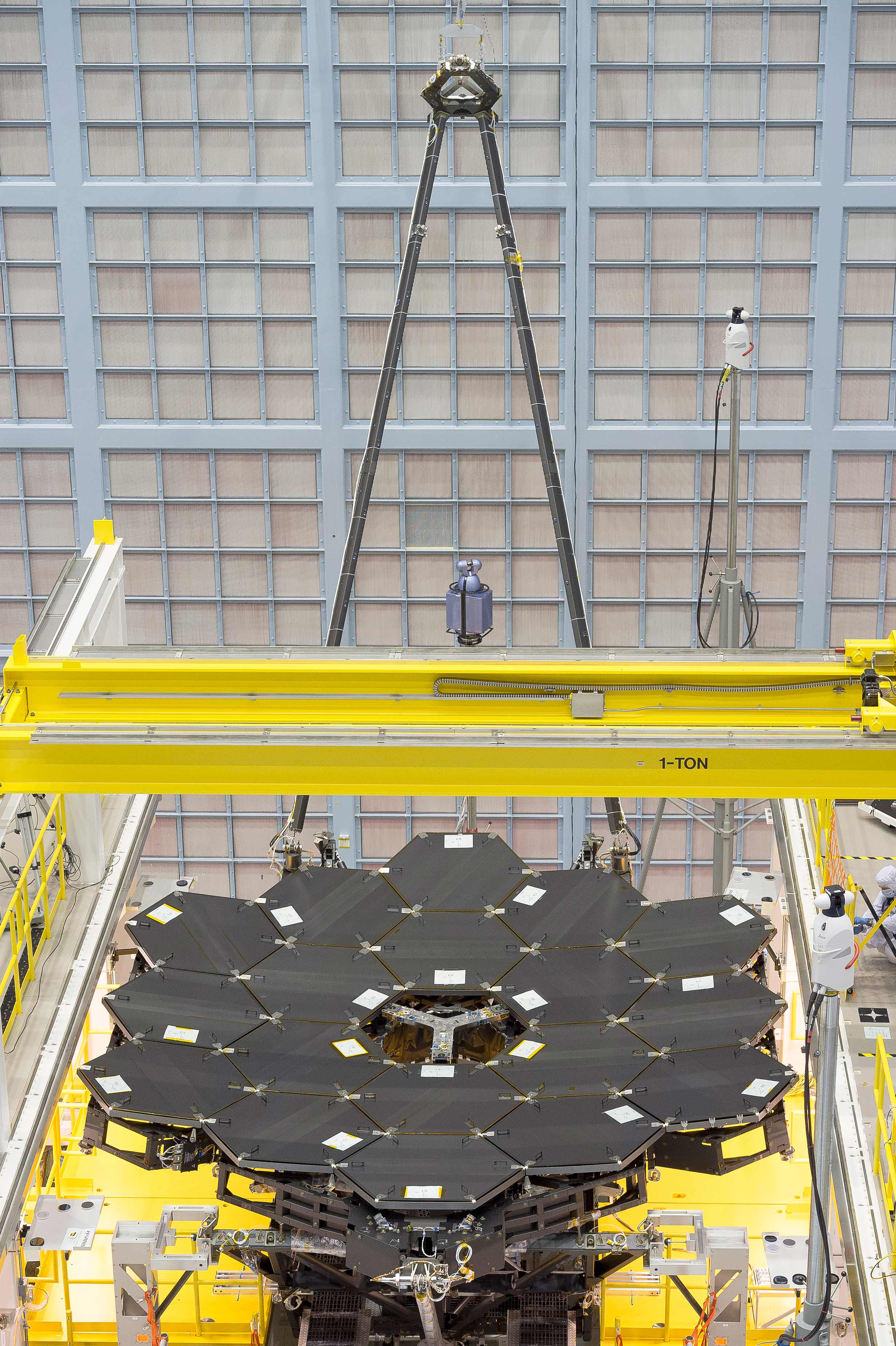

Among the next construction steps are installation of the aft optics assembly and the secondary mirror.
After that the team will install what’s known as the ‘heart of the telescope’ – the Integrated Science Instrument Module ISIM). Then comes acoustic and vibration tests throughout this year. Eventually the finished assembly will be shipped to Johnson Space Center in Houston “for an intensive cryogenic optical test to ensure everything is working properly,” say officials.

The flight structure and backplane assembly serve as the $8.6 Billion Webb telescopes backbone.
The telescope will launch on an Ariane V booster from the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana in 2018.
The Webb Telescope is a joint international collaborative project between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
Webb is designed to look at the first light of the Universe and will be able to peer back in time to when the first stars and first galaxies were forming. It will also study the history of our universe and the formation of our solar system as well as other solar systems and exoplanets, some of which may be capable of supporting life on planets similar to Earth.
“JWST has the capability to look back towards the very first objects that formed after the Big Bang,” said Dr. John Mather, NASA’s Nobel Prize Winning scientist, in a recent exclusive interview with Universe Today at NASA Goddard.

Watch this space for my ongoing reports on JWST mirrors, construction and testing.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
































 The FGS consists of two identical cameras that are critical to Webb’s ability to “see.” Their images will allow the telescope to determine its position, locate its celestial targets, and remain pointed to collect high-quality data. The FGS will guide the telescope with incredible precision, with an accuracy of one millionth of a degree.
The FGS consists of two identical cameras that are critical to Webb’s ability to “see.” Their images will allow the telescope to determine its position, locate its celestial targets, and remain pointed to collect high-quality data. The FGS will guide the telescope with incredible precision, with an accuracy of one millionth of a degree.